Python pandas 操作 excel 详解
文章目录
- 1 概述
-
- 1.1 pandas 和 openpyxl 区别
- 1.2 Series 和 DataFrame
- 2 常用操作
-
- 2.1 创建 Excel:to_excel()
- 2.2 读取 Excel:read_excel()
-
- 2.2.1 header:标题的行索引
- 2.2.2 index_col:索引列
- 2.2.3 dtype:数据类型
- 2.2.4 skiprows:跳过的行数
- 2.2.5 usercols:指定列数
- 2.2.6 head(n)、tail(n):读取前、后 n 行数据
- 2.3 读写数据
-
- 2.3.1 at():获取单元格
- 2.3.2 loc[]:数据筛选
- 2.3.3 sort_values():数据排序
- 3 实战
-
- 3.1 遍历 Excel
1 概述
1.1 pandas 和 openpyxl 区别
- Python 中的 pandas 和 openpyxl 库,均可以处理 excel 文件,其中主要区别:
- pandas:① 数据操作和分析方面表现优异。它提供了各种文件格式(包括 Excel)中读取数据的函数,在过滤数据、汇总数据、处理缺失值和执行其它数据转换任务方便,特别有用。② 使用方便。DataFrame 对象,使用快速方便,且功能十分强大。
- openpyxl:侧重单元格格式设置。这个库也允许我们直接处理 Excel 文件。pandas 快,但 pandas 做不了的事情,可以让 openpyxl 来做,例如:单元格注释、填充背景色 等等
1.2 Series 和 DataFrame
- Series:连续。可理解为 “一维数组”,由一行 或 一列 组成,具体是行,还是列,由 DataFrame 指定
- DataFrame:数据框。可理解为 “二维数组”,由行和列组成
import pandas as pd
# Series 示例
s = pd.Series(['a', 'b', 'c'], index=[1, 2, 3], name='A')
print(s)
# 1 a
# 2 b
# 3 c
# Name: A, dtype: object
# DataFrame 示例
s1 = pd.Series(['a', 'b', 'c'], index=[1, 2, 3], name='A')
s2 = pd.Series(['aa', 'bb', 'cc'], index=[1, 2, 3], name='B')
s3 = pd.Series(['aaa', 'bbb', 'ccc'], index=[1, 2, 3], name='C')
# 方式1:指定 Series 为行
df = pd.DataFrame([s1, s2, s3])
print(df)
# 1 2 3
# A a b c
# B aa bb cc
# C aaa bbb ccc
# 方式2:指定 Series 为列
df = pd.DataFrame({s1.name: s1, s2.name: s2, s3.name: s3})
print(df)
# A B C
# 1 a aa aaa
# 2 b bb bbb
# 3 c cc ccc
2 常用操作
2.1 创建 Excel:to_excel()
import pandas as pd
# 测试数据
data = {'ID': [1, 2, 3], 'Name': ['张三', '李四', '王五']}
# 1.创建 DataFrame 对象
df = pd.DataFrame(data=data)
# 可选操作。将 ID 设为索引,若不设置,会使用默认索引 narray(n)
df = df.set_index('ID') # 写法1
# df.set_index('ID', inplace=True) # 写法2
# 2.写入 excel 至指定位置(若文件已存在,则覆盖)
df.to_excel(r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx')
2.2 读取 Excel:read_excel()
import pandas as pd
# 1.读取 excel。默认读取第一个 sheet
student = pd.read_excel(r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx')
# 2.读取常用属性
print(student.shape) # 形状(行,列)
print(student.columns) # 列名
import pandas as pd
# 1.读取指定 sheet 的 excel,以下两种方式等同
student = pd.read_excel(r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx', sheet_name=1)
# student = pd.read_excel(r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet2')
# 2.读取常用属性
print(student.shape) # 形状(行,列)
print(student.columns) # 列名
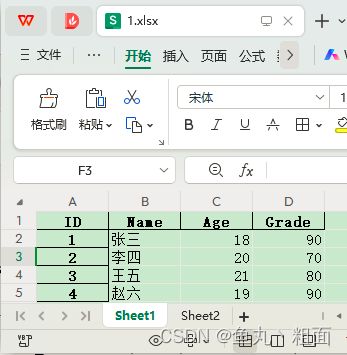
2.2.1 header:标题的行索引
场景1:默认。第一行为标题(行索引为 0,即:header=0)
import pandas as pd
# 文件路径
filePath = r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx'
# 1.读取 excel(默认第 1 行为标题,行索引为 0,即:header=0)
student = pd.read_excel(filePath)
print(student.columns)
# Index(['ID', 'Name', 'Age', 'Grade'], dtype='object')
import pandas as pd
# 文件路径
filePath = r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx'
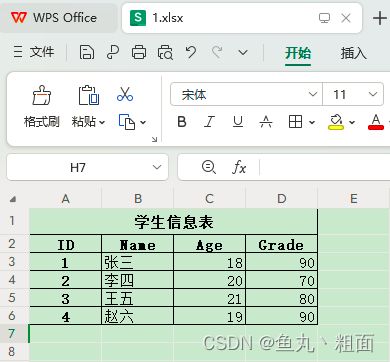
# 场景2:excel 中第 2 行才是我们想要的标题(即:header=1)
student = pd.read_excel(filePath, header=1)
print(student.columns)
# Index(['ID', 'Name', 'Age', 'Grade'], dtype='object')
import pandas as pd
# 文件路径
filePath = r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx'
# 场景3:excel 中没有标题,需要人为设定
student = pd.read_excel(filePath, header=None)
student.columns = ['ID', 'Name', 'Age', 'Grade']
student.set_index('ID', inplace=True) # 指定索引列,并替换原数据
student.to_excel(filePath) # 写入至 Excel
print(student)
# Name Age Grade
# ID
# 1 张三 18 90
# 2 李四 20 70
# 3 王五 21 80
# 4 赵六 19 90
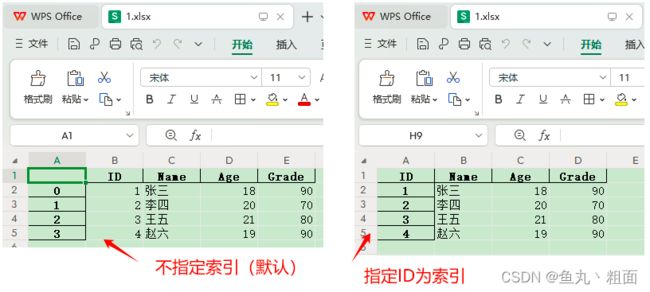
2.2.2 index_col:索引列
import pandas as pd
# 文件路径
filePath = r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx'
# 读取 Excel,不指定索引列(会默认新增一个索引列,从 0 开始)
student = pd.read_excel(filePath)
print(student)
# ID Name Age Grade
# 0 1 张三 18 90
# 1 2 李四 20 70
# 2 3 王五 21 80
# 3 4 赵六 19 90
# 读取 Excel,指定索引列
student = pd.read_excel(filePath, index_col='ID')
print(student)
# Name Age Grade
# ID
# 1 张三 18 90
# 2 李四 20 70
# 3 王五 21 80
# 4 赵六 19 90
索引相关:
import pandas as pd
# 文件路径
filePath = r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx'
# 1.读取 excel,并指定索引列
student = pd.read_excel(filePath, index_col='ID')
2.2.3 dtype:数据类型
import pandas as pd
# 文件路径
filePath = r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx'
# 1.读取 excel 并指定 数据类型
student = pd.read_excel(filePath, dtype={'ID': str, 'Name': str, 'Age': int, 'Grade': float})
print(student)
# ID Name Age Grade
# 0 1 张三 18 90.0
# 1 2 李四 20 70.0
# 2 3 王五 21 80.0
# 3 4 赵六 19 90.0
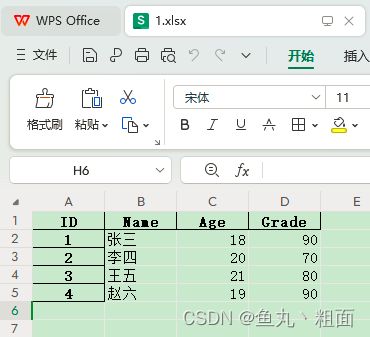
2.2.4 skiprows:跳过的行数
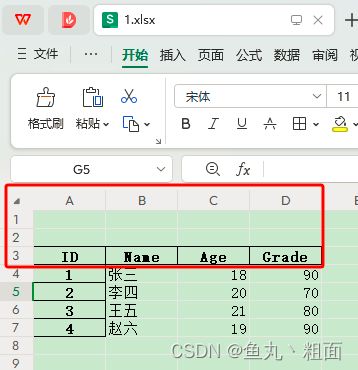
- 比如:Excel 中有空行,如下图
- 实际的数据是在第 3 行,所以要跳过前 2 行
import pandas as pd
# 文件路径
filePath = r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx'
student = pd.read_excel(filePath, skiprows=2)
print(student)
# ID Name Age Grade
# 0 1 张三 18 90
# 1 2 李四 20 70
# 2 3 王五 21 80
# 3 4 赵六 19 90
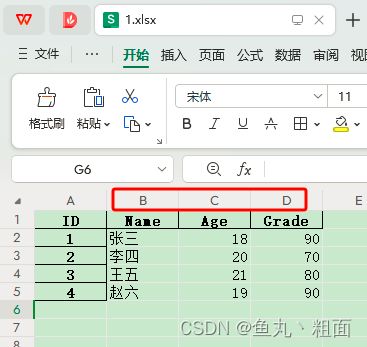
2.2.5 usercols:指定列数
import pandas as pd
# 文件路径
filePath = r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx'
# 读取 Excel B - D 列(均包含)
student = pd.read_excel(filePath, usecols='B:D')
print(student)
# Name Age Grade
# 0 张三 18 90
# 1 李四 20 70
# 2 王五 21 80
# 3 赵六 19 90
2.2.6 head(n)、tail(n):读取前、后 n 行数据
- 有时候,excel 数据量很大,读取全部会很耗时,也没必要
- 咱测试时,仅读取部分行即可
import pandas as pd
# 1.读取 excel
student = pd.read_excel(r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx')
# 读取前 3 行数据(默认 5 行)
print(student.head(3))
# 读取后 3 行数据(默认 5 行)
print(student.tail(3))
2.3 读写数据
2.3.1 at():获取单元格
import pandas as pd
# 文件路径
filePath = r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx'
# 1.读取 excel 并指定 索引
student = pd.read_excel(filePath, index_col=None)
for i in person.index:
# 读写单元格:ID列,i行 的数据
student['ID'].at[i] = i + 2
print(student)
2.3.2 loc[]:数据筛选
import pandas as pd
def age_18_to_20(age):
return 18 <= age <= 20
def grade_good(grade):
return 90 <= grade <= 100
# 文件路径
filePath = r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx'
# 1.读取 excel 并指定 索引
student = pd.read_excel(filePath, index_col='ID')
student = student.loc[student['Age'].apply(age_18_to_20)].loc[student['Grade'].apply(grade_good)]
print(student)
2.3.3 sort_values():数据排序
import pandas as pd
# 文件路径
filePath = r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx'
# 1.读取 excel 并指定 索引
student = pd.read_excel(filePath, index_col='ID')
# 功能:排序
# by:待排序的字段
# ascending:顺序(True) 还是 逆序(False)
# inplace:是否替换当前对象
# 方式1:排序单个字段
student.sort_values(by='Grade', ascending=False, inplace=True)
print(student)
# Name Grade
# ID
# 1 张三 90
# 4 赵六 90
# 3 王五 80
# 2 李四 70
# 方式2:排序多个字段,如:先顺序排列 Grade, 后逆序排列 ID
student.sort_values(by=['Grade', 'ID'], ascending=[True, False], inplace=True)
print(student)
# Name Grade
# ID
# 2 李四 70
# 3 王五 80
# 4 赵六 90
# 1 张三 90
3 实战
3.1 遍历 Excel
import pandas as pd
def read_excel(excel_name):
data = pd.read_excel(excel_name)
for row in data.itertuples():
# Index:索引, Name:字段名
print(row.Index, row.Name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
filePath = r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Temp\1.xlsx'
read_excel(filePath)