Java相关网络编程。文字不多,代码为主,自学用,谨慎借鉴,有错误请指正
目录
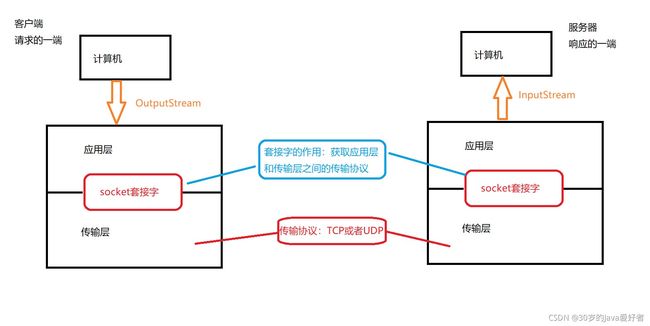
Socket套接字
基于TCP的网络编程:可靠的
三次握手和四次挥手
建立连接:三次握手
释放资源:四次挥手
InetAddress:封装ip
InetSocketAddress:封装ip和端口号
TCP单向通信
客户端
服务器
TCP双向通信
客户端
服务器
解决客户端完成登录后,服务器也会关闭的问题。
user类
客户端
服务器
服务器线程
UDP:不可靠
单向通信
发送方
接收方
双向通信
发送方
接收方
发现问题
发送方
接收方
TCP和UDP的区别
TCP
UDP
Socket套接字
基于TCP的网络编程:可靠的
三次握手和四次挥手
建立连接:三次握手
释放资源:四次挥手
InetAddress:封装ip
public class InetAddressTest {
@Test
public void test1() throws UnknownHostException {
// 封装ip地址
InetAddress ia = InetAddress.getByName("192.168.166.***");
System.out.println(ia);// /192.168.166.***
InetAddress localhost = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
System.out.println(localhost); // localhost/127.0.0.1
InetAddress byName = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
System.out.println(byName); // /127.0.0.1
InetAddress byName1 = InetAddress.getByName("LAPTOP-S9L7***");// 封装计算机名
System.out.println(byName1); // LAPTOP-S9L7J***/192.168.166.***
InetAddress byName2 = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");// 封装域名
System.out.println(byName2); // www.baidu.com/110.242.68.3
System.out.println(byName2.getHostName()); // 获取域名:www.baidu.com
System.out.println(byName2.getHostAddress()); // 获取ip地址:110.242.68.3
}
}InetSocketAddress:封装ip和端口号
@Test
public void testInetSocketAddress(){
InetSocketAddress isa = new InetSocketAddress("192.168.166.***",8080);
System.out.println(isa.getHostName());// LAPTOP-S9L7JLAE
System.out.println(isa.getPort());// 8080
InetAddress address = isa.getAddress();
System.out.println(address.getHostAddress());// 192.168.166.***
System.out.println(address.getHostName());// LAPTOP-S9L7***
}TCP单向通信
客户端
public class TestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建套接字:指定服务器的ip地址和端口号
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.166.132",8888);
// 获取输出流用于向外发送数据
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
// OutputStream的方法中没有write出String的方法
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
// 将字符串内容输出
dos.writeUTF("你好,我是yzc");
// 关闭流
dos.close();
os.close();
s.close();
}服务器
accept():这是个阻塞方法,等待接受客户端的数据,只有接收到客户端的数据之后才能继续执行。返回值是个Socket,就是客户端的那个socket,接到了这个socket之后,客户端和服务器才真正产生了连接,才能真正通信
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 指定服务器端口号
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
Socket s = ss.accept();// 阻塞方法
//获取到输入流
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
// 读取对方客户端发来的数据
String str = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(str);
dis.close();
is.close();
s.close();
ss.close();
}测试的话:先开启服务器在开启客户端
TCP双向通信
客户端
public class TestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建套接字:指定服务器的ip地址和端口号
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.166.132",8888);
// 获取输出流用于向外发送数据
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
// OutputStream的方法中没有write出String的方法
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
// 将字符串内容输出
dos.writeUTF("你好,我是yzc");
// 接受服务器的返回信息
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
System.out.println("服务器的返回信息:" + dis.readUTF());
// 关闭流
dos.close();
os.close();
s.close();
}
}
服务器
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 指定服务器端口号
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
Socket s = ss.accept();// 阻塞方法
//获取到输入流
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
// 读取对方客户端发来的数据
String str = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("客户端发来的消息" + str);
// 告知客户端,他发来的信息我已经收到
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
dos.writeUTF("你的消息服务器已经收到了");
dos.close();
os.close();
dis.close();
is.close();
s.close();
ss.close();
}
}
解决客户端完成登录后,服务器也会关闭的问题。
解决:写一个线程,将客户端处理的过程写到线程中去,然后再服务器处理客户端的方法处加上一个死循环,用来监听客户端的访问即可。
user类
public class User implements Serializable {
private String name;
private String password;
public User(String name, String password) {
this.name = name;
this.password = password;
}
}客户端
public class TestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建套接字:指定服务器的ip地址和端口号
Socket s = null;
OutputStream os = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
InputStream is = null;
DataInputStream dis = null;
try {
s = new Socket("192.168.166.132", 8888);
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String name = input.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String pwd = input.next();
User user = new User(name, pwd);
// 获取输出流用于向外发送数据
os = s.getOutputStream();
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
oos.writeObject(user);
is = s.getInputStream();
dis = new DataInputStream(is);
if (dis.readBoolean()) {
System.out.println("登陆成功");
} else {
System.out.println("登陆失败");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭流
try {
if (dis != null) {
dis.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (is != null) {
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// dos.close();
try {
if (oos != null) {
oos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (os != null) {
os.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (s != null) {
s.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
服务器
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 指定服务器端口号
ServerSocket ss = null;
Socket s = null;
int count = 0;
try {
ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
while (true) {
s = ss.accept();// 阻塞方法
new ServerThread(s).start();
count++;
System.out.println("您是第" + count + "个访问的,您的ip地址是:" + s.getInetAddress());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
服务器线程
public class ServerThread extends Thread {
Socket s = null;
public ServerThread(Socket s) {
this.s = s;
}
InputStream is = null;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
OutputStream os = null;
DataOutputStream dos = null;
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//获取到输入流
is = s.getInputStream();
ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
User user = (User) (ois.readObject());
// 对对象进行验证
boolean flag = false;
if ("yzc".equals(user.getName()) && "123456".equals(user.getPassword())) {
flag = true;
}
os = s.getOutputStream();
dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
dos.writeBoolean(flag);
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (dos != null) {
dos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (os != null) {
os.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (ois != null) {
ois.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (is != null) {
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
UDP:不可靠
以网络聊天位案例:
单向通信
发送方
public class TestSend {// 发送方
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("学生上线");
// 获取套接字:指定发送方的端口号
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(8888);
// 准备数据包
String str = "你好啊";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"),9999);
// 发送
ds.send(dp);
// 关闭资源
ds.close();
}
}接收方
public class TestReceive { // 接收方
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("老师上线了");
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(9999);
// 创建空数据包,打算用来接受对方传过来的数据包
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(b, b.length);
// 接受对方的数据包,然后放入dp数据包中填充
ds.receive(dp);
// 取出数据包中的有效数据
byte[] date = dp.getData();
System.out.println("学生对我说:" + new String(date,0, dp.getLength()));
}
}双向通信
发送方
public class TestSend {// 发送方
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("学生上线");
// 获取套接字:指定发送方的端口号
DatagramSocket ds = null;
try {
ds = new DatagramSocket(8888);
// 准备数据包
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("学生:");
String str = input.next();
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 9999);
// 发送
ds.send(dp);
// 老师回复信息
// 创建空数据包,打算用来接受对方传过来的数据包
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp2 = new DatagramPacket(b, b.length);
// 接受对方的数据包,然后放入dp数据包中填充
ds.receive(dp2);
// 取出数据包中的有效数据
byte[] date = dp2.getData();
String s = new String(date, 0, dp2.getLength());
System.out.println("老师对我说:" + s);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 关闭资源
ds.close();
}
}
}
接收方
public class TestReceive { // 接收方
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("老师上线了");
DatagramSocket ds = null;
try {
ds = new DatagramSocket(9999);
// 创建空数据包,打算用来接受对方传过来的数据包
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(b, b.length);
// 接受对方的数据包,然后放入dp数据包中填充
ds.receive(dp);
// 取出数据包中的有效数据
byte[] date = dp.getData();
String s = new String(date, 0, dp.getLength());
System.out.println("学生对我说:" + s);
// 老师进行回复
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("老师:");
String str = input.next();
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
DatagramPacket dp2 = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 8888);
// 发送
ds.send(dp2);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
ds.close();
}
}
}发现问题
上述通信需要你来我往,不能互相说一次就结束,应该以学生说拜拜为止,双方都下线
发送方
public class TestSend {// 发送方
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("学生上线");
// 获取套接字
DatagramSocket ds = null;
try {
// 指定发送方的端口号
ds = new DatagramSocket(8888);
while (true) {
// 学生说话
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("学生:");
String str = input.next();
// 准备数据包,将学生输入的话封装在数据包内
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 9999);
// 发送
ds.send(dp);
// 如果学生说拜拜,则双方停止交流
if ("拜拜".equals(str)) {
System.out.println("学生已下线");
break;
}
// 老师回复信息
// 创建空数据包,打算用来接受对方传过来的数据包
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp2 = new DatagramPacket(b, b.length);
// 接受对方的数据包,然后放入dp2数据包中填充
ds.receive(dp2);
// 取出数据包中的有效数据
byte[] date = dp2.getData();
String s = new String(date, 0, dp2.getLength());
System.out.println("老师对我说:" + s);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭资源
if (ds != null) {
ds.close();
}
}
}
}
接收方
public class TestReceive { // 接收方
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("老师上线了");
// 准备套接字
DatagramSocket ds = null;
try {
// 确定本机端口号
ds = new DatagramSocket(9999);
while (true) {
// 创建空数据包,打算用来接受对方传过来的数据包
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(b, b.length);
// 接受对方的数据包,然后放入dp数据包中填充
ds.receive(dp);
// 取出数据包中的有效数据
byte[] date = dp.getData();
String s = new String(date, 0, dp.getLength());
System.out.println("学生对我说:" + s);
// 如果学生说拜拜,则双方停止交流
if ("拜拜".equals(s)) {
System.out.println("学生已下线,老师可以下线了");
break;
}
// 老师进行回复
// 获取老师说的话
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("老师:");
String str = input.next();
// 准备数据包,将老师的话封装进数据包中
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
DatagramPacket dp2 = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 8888);
// 发送
ds.send(dp2);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (ds != null) {
ds.close();
}
}
}
}解决
TCP和UDP的区别
TCP
客户端:socket 程序感受到的 使用输出流
服务器:serversocket 程序感受到的 使用输入流
客户端和服务端的地位不平等
UDP
发送方:DatagramSocket 发送:数据包DatagramPacket
接收方:DatagramSocket 接收:数据包DatagramPacket
发送方和接收方的地位是平等的