【java】Spring Cloud --OpenFeign源码解析学习
文章目录
- OpenFeign是什么?
- 实现原理
-
- 1. FeignClient的bean注册过程
- 2.OpenFeign调用过程
- 3. OpenFeign Configuration
- 总结
本文主要针对 spring-cloud-starter-openfeign 的 2.2.3.RELEASE 版本进行源码的解析。
OpenFeign是什么?
作为Spring Cloud的子项目之一,Spring Cloud OpenFeign以将OpenFeign集成到Spring Boot应用中的方式,为微服务架构下服务之间的调用提供了解决方案。
- 首先,利用了OpenFeign的声明式方式定义Web服务客户端;
- 其次还更进一步,通过集成Ribbon或Eureka实现负载均衡的HTTP客户端。
实现原理
讲清楚OpenFeign的实现原理,我们要从这两个步骤讲起:
- FeignClient的bean注册过程,以及动态代理过程;
- FeignClient的调用过程。
1. FeignClient的bean注册过程
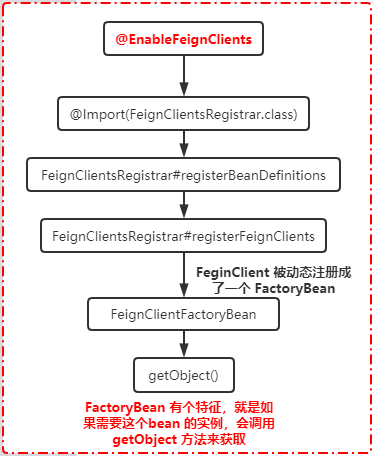
@EnableFeignClients
想要集成 Feign 客户端,需要我们通过注解 @EnableFeignClients 来开启。这个注解开启了FeignClient的解析过程。这个注解的声明如下,它用到了一个@Import注解,我们知道Import是用来导入一个配置类的,接下来去看一下FeignClientsRegistrar的定义:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableFeignClients {
}
FeignClientsRegistrar实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,它是一个动态注入bean的接口,Spring Boot启动的时候,会去调用这个类中的registerBeanDefinitions来实现动态Bean的装载。它的作用类似于ImportSelector。
然后就会进入 FeignClientsRegistrar# registerBeanDefinitions 。registerDefaultConfiguration 方法内部从 SpringBoot 启动类上检查是否有@EnableFeignClients, 有该注解的话, 则完成 Feign 框架相关的一些配置内容注册registerFeignClients 方法内部从 classpath 中, 扫描获得 @FeignClient修饰的类, 将类的内容解析为 BeanDefinition , 最终通过调用 Spring 框架中的BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.resgisterBeanDefinition 将解析处理过的 FeignClientBeanDeifinition 添加到 spring 容器中.
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//注册@EnableFeignClients中定义defaultConfiguration属性下的类,包装成FeignClientSpecification,注册到Spring容器。
//在@FeignClient中有一个属性:configuration,这个属性是表示各个FeignClient自定义的配置类,后面也会通过调用registerClientConfiguration方法来注册成FeignClientSpecification到容器。
//所以,这里可以完全理解在@EnableFeignClients中配置的是做为兜底的配置,在各个@FeignClient配置的就是自定义的情况。
registerDefaultConfiguration(metadata, registry);
registerFeignClients(metadata, registry);
}
这里面需要重点分析的就是 registerFeignClients 方法,这个方法主要是扫描类路径下所有的@FeignClient注解,然后进行动态Bean的注入。它最终会调用 registerFeignClient 方法。
public void registerFeignClients(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider scanner = getScanner();
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
Set<String> basePackages;
//获取注解
Map<String, Object> attrs = metadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableFeignClients.class.getName());
AnnotationTypeFilter annotationTypeFilter = new AnnotationTypeFilter(
FeignClient.class);
final Class<?>[] clients = attrs == null ? null
: (Class<?>[]) attrs.get("clients");
if (clients == null || clients.length == 0) {
scanner.addIncludeFilter(annotationTypeFilter);
basePackages = getBasePackages(metadata);
}
else {
final Set<String> clientClasses = new HashSet<>();
basePackages = new HashSet<>();
for (Class<?> clazz : clients) {
basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(clazz));
clientClasses.add(clazz.getCanonicalName());
}
AbstractClassTestingTypeFilter filter = new AbstractClassTestingTypeFilter() {
@Override
protected boolean match(ClassMetadata metadata) {
String cleaned = metadata.getClassName().replaceAll("\\$", ".");
return clientClasses.contains(cleaned);
}
};
scanner.addIncludeFilter(
new AllTypeFilter(Arrays.asList(filter, annotationTypeFilter)));
}
// 遍历配置的扫描包路径
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidateComponents = scanner
.findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidateComponent : candidateComponents) {
if (candidateComponent instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
// verify annotated class is an interface
AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition = (AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidateComponent;
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = beanDefinition.getMetadata();
Assert.isTrue(annotationMetadata.isInterface(),
"@FeignClient can only be specified on an interface");
Map<String, Object> attributes = annotationMetadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(
FeignClient.class.getCanonicalName());
String name = getClientName(attributes);
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,
attributes.get("configuration"));
// 注册Feign 客户端
registerFeignClient(registry, annotationMetadata, attributes);
}
}
}
}
registerFeignClient 在这个方法中,就是去组装BeanDefinition,也就是Bean的定义,然后注册到Spring IOC容器。
private void registerFeignClient(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, Map<String, Object> attributes) {
String className = annotationMetadata.getClassName();
BeanDefinitionBuilder definition = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(FeignClientFactoryBean.class);
// 省略代码.....
BeanDefinitionHolder holder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, className,
new String[] { alias });
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(holder, registry);
}
我们关注一下,BeanDefinitionBuilder是用来构建一个BeanDefinition的,它是通过 genericBeanDefinition 来构建的,并且传入了一个FeignClientFactoryBean的类,代码如下。
/**
* Create a new {@code BeanDefinitionBuilder} used to construct a {@link GenericBeanDefinition}.
* @param beanClass the {@code Class} of the bean that the definition is being created for
*/
public static BeanDefinitionBuilder genericBeanDefinition(Class<?> beanClass) {
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = new BeanDefinitionBuilder(new GenericBeanDefinition());
builder.beanDefinition.setBeanClass(beanClass);
return builder;
}
我们可以发现,FeignClient被动态注册成了一个FactoryBean.
Spring Cloud FengnClient实际上是利用Spring的代理工厂来生成代理类,所以在这里地方才会把所有的FeignClient的BeanDefinition设置为FeignClientFactoryBean类型,而FeignClientFactoryBean继承自FactoryBean,它是一个工厂Bean。在Spring中,FactoryBean是一个工厂Bean,用来创建代理Bean。工厂 Bean 是一种特殊的 Bean, 对于 Bean 的消费者来说, 他逻辑上是感知不到这个 Bean 是普通的 Bean 还是工厂 Bean, 只是按照正常的获取 Bean 方式去调用, 但工厂bean 最后返回的实例不是工厂Bean 本身, 而是执行工厂 Bean 的 getObject 逻辑返回的示例。
简单来说,FeignClient标注的这个接口,会通过FeignClientFactoryBean.getObject()这个方法获得一个代理对象。
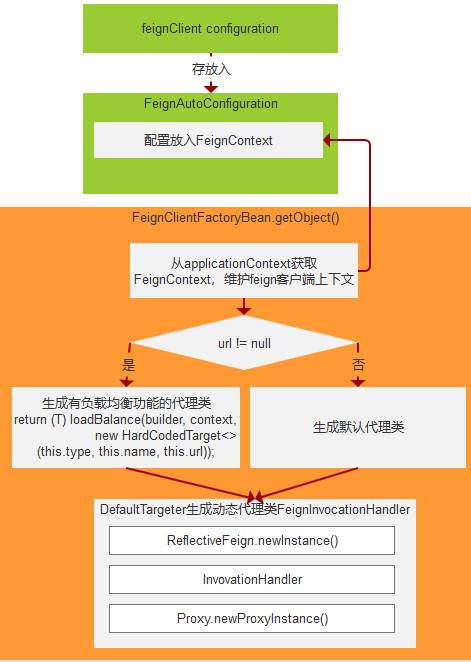
FeignClientFactoryBean.getObject:
getObject调用的是getTarget方法,它从applicationContext取出FeignContext,FeignContext继承了NamedContextFactory,它是用来统一维护feign中各个feign客户端相互隔离的上下文。
FeignContext注册到容器是在FeignAutoConfiguration上完成的。
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<FeignClientSpecification> configurations = new ArrayList<>();
@Bean
public FeignContext feignContext() {
FeignContext context = new FeignContext();
context.setConfigurations(this.configurations);
return context;
}
在初始化FeignContext时,会把configurations在容器中放入FeignContext中。configurations 的来源就是在前面registerFeignClients方法中将@FeignClient的配置 configuration。
接着,构建feign.builder,在构建时会向FeignContext获取配置的Encoder,Decoder等各种信息。FeignContext在上文中已经提到会为每个Feign客户端分配了一个容器,它们的父容器就是spring容器。
配置完Feign.Builder之后,再判断是否需要LoadBalance,如果需要,则通过LoadBalance的方法来设置。实际上他们最终调用的是Target.target()方法。
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return getTarget();
}
<T> T getTarget() {
//实例化Feign上下文对象FeignContext
FeignContext context = this.applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class);
Feign.Builder builder = feign(context);//构建Builder对象
//如果url为空,则走负载均衡,生成有负载均衡功能的代理类
if (!StringUtils.hasText(this.url)) {
if (!this.name.startsWith("http")) {
this.url = "http://" + this.name;
}
else {
this.url = this.name;
}
this.url += cleanPath();
return (T) loadBalance(builder, context,
new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type, this.name, this.url));
}
//如果指定了url,则生成默认的代理类
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.url) && !this.url.startsWith("http")) {
this.url = "http://" + this.url;
}
String url = this.url + cleanPath();
Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class);
if (client != null) {
if (client instanceof LoadBalancerFeignClient) {
// not load balancing because we have a url,
// but ribbon is on the classpath, so unwrap
client = ((LoadBalancerFeignClient) client).getDelegate();
}
if (client instanceof FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) {
// not load balancing because we have a url,
// but Spring Cloud LoadBalancer is on the classpath, so unwrap
client = ((FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) client).getDelegate();
}
builder.client(client);
}//生成默认代理类
Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class);
return (T) targeter.target(this, builder, context,
new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type, this.name, url));
}
loadBalance :生成具备负载均衡能力的feign客户端,为feign客户端构建起绑定负载均衡客户端。
protected <T> T loadBalance(Feign.Builder builder, FeignContext context,
HardCodedTarget<T> target) {
Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class);
if (client != null) {
builder.client(client);
Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class);
return targeter.target(this, builder, context, target);
}
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No Feign Client for loadBalancing defined. Did you forget to include spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon?");
}
Client client = (Client)this.getOptional(context, Client.class); 从上下文中获取一个 Client,默认是LoadBalancerFeignClient。它是在FeignRibbonClientAutoConfiguration这个自动装配类中,通过Import实现的
@Import({ HttpClientFeignLoadBalancedConfiguration.class,
OkHttpFeignLoadBalancedConfiguration.class,
DefaultFeignLoadBalancedConfiguration.class })
public class FeignRibbonClientAutoConfiguration {
.....
}
这里的通过 DefaultFeignLoadBalancedConfiguration 注入客户端 Client 的实现
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
class DefaultFeignLoadBalancedConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public Client feignClient(CachingSpringLoadBalancerFactory cachingFactory,
SpringClientFactory clientFactory) {
return new LoadBalancerFeignClient(new Client.Default(null, null), cachingFactory,
clientFactory);
}
}
接下去进入 targeter.target(this, builder, context, target) ,携带着构建好的这些对象去创建代理实例 ,这里有两个实现 HystrixTargeter 、DefaultTargeter 很显然,我们没有配置 Hystrix ,这里会走 DefaultTargeter
class DefaultTargeter implements Targeter {
@Override
public <T> T target(FeignClientFactoryBean factory, Feign.Builder feign,
FeignContext context, Target.HardCodedTarget<T> target) {
return feign.target(target);
}
}
然后会来到 feign.Feign.Builder#target(feign.Target)
public <T> T target(Target<T> target) {
return build().newInstance(target);
}
public Feign build() {
SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory synchronousMethodHandlerFactory =
new SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory(client, retryer, requestInterceptors, logger,
logLevel, decode404, closeAfterDecode, propagationPolicy);
ParseHandlersByName handlersByName =
new ParseHandlersByName(contract, options, encoder, decoder, queryMapEncoder,
errorDecoder, synchronousMethodHandlerFactory);
return new ReflectiveFeign(handlersByName, invocationHandlerFactory, queryMapEncoder);
}
最终会调用 ReflectiveFeign.newInstance
这个方法是用来创建一个动态代理的方法,在生成动态代理之前,会根据Contract协议(协议解析规则,解析接口类的注解信息,解析成内部的MethodHandler的处理方式。
从实现的代码中可以看到熟悉的Proxy.newProxyInstance方法产生代理类。而这里需要对每个定义的接口方法进行特定的处理实现,所以这里会出现一个MethodHandler的概念,就是对应方法级别的InvocationHandler。
public <T> T newInstance(Target<T> target) {
// 解析接口注解信息
//根据接口类和Contract协议解析方式,解析接口类上的方法和注解,转换成内部的MethodHandler处理方式
Map<String, MethodHandler> nameToHandler = targetToHandlersByName.apply(target);
Map<Method, MethodHandler> methodToHandler = new LinkedHashMap<Method, MethodHandler>();
List<DefaultMethodHandler> defaultMethodHandlers = new LinkedList<DefaultMethodHandler>();
// 根据方法类型
for (Method method : target.type().getMethods()) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
continue;
} else if (Util.isDefault(method)) {
DefaultMethodHandler handler = new DefaultMethodHandler(method);
defaultMethodHandlers.add(handler);
methodToHandler.put(method, handler);
} else {
methodToHandler.put(method, nameToHandler.get(Feign.configKey(target.type(), method)));
}
}
InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler);
// 基于Proxy.newProxyInstance 为接口类创建动态实现,将所有的请求转换给InvocationHandler 处理。
T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[] {target.type()}, handler);
for (DefaultMethodHandler defaultMethodHandler : defaultMethodHandlers) {
defaultMethodHandler.bindTo(proxy);
}
return proxy;
}
targetToHandlersByName.apply(target) :根据Contract协议规则,解析接口类的注解信息,解析成内部表现:targetToHandlersByName.apply(target);会解析接口方法上的注解,从而解析出方法粒度的特定的配置信息,然后生产一个SynchronousMethodHandler 然后需要维护一个
public Map<String, MethodHandler> apply(Target target) {
List<MethodMetadata> metadata = contract.parseAndValidateMetadata(target.type());
Map<String, MethodHandler> result = new LinkedHashMap<String, MethodHandler>();
for (MethodMetadata md : metadata) {
BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs buildTemplate;
if (!md.formParams().isEmpty() && md.template().bodyTemplate() == null) {
buildTemplate =
new BuildFormEncodedTemplateFromArgs(md, encoder, queryMapEncoder, target);
} else if (md.bodyIndex() != null) {
buildTemplate = new BuildEncodedTemplateFromArgs(md, encoder, queryMapEncoder, target);
} else {
buildTemplate = new BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs(md, queryMapEncoder, target);
}
if (md.isIgnored()) {
result.put(md.configKey(), args -> {
throw new IllegalStateException(md.configKey() + " is not a method handled by feign");
});
} else {
result.put(md.configKey(),
factory.create(target, md, buildTemplate, options, decoder, errorDecoder));
}
}
return result;
}
SpringMvcContract
当前Spring Cloud 微服务解决方案中,为了降低学习成本,采用了Spring MVC的部分注解来完成 请求协议解析,也就是说 ,写客户端请求接口和像写服务端代码一样:客户端和服务端可以通过SDK的方式进行约定,客户端只需要引入服务端发布的SDK API,就可以使用面向接口的编码方式对接服务。
2.OpenFeign调用过程
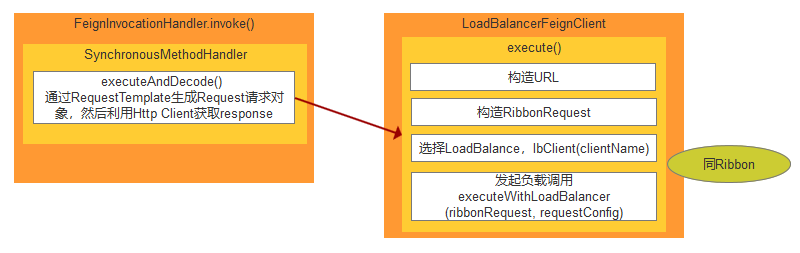
在前面的分析中,我们知道OpenFeign最终返回的是一个 ReflectiveFeign.FeignInvocationHandler 的对象。那么当客户端发起请求时,会进入到 FeignInvocationHandler.invoke 方法中,这个大家都知道,它是一个动态代理的实现。
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if ("equals".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
Object otherHandler =
args.length > 0 && args[0] != null ? Proxy.getInvocationHandler(args[0]) : null;
return equals(otherHandler);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
return false;
}
} else if ("hashCode".equals(method.getName())) {
return hashCode();
} else if ("toString".equals(method.getName())) {
return toString();
}
// 利用分发器筛选方法,找到对应的handler 进行处理
return dispatch.get(method).invoke(args);
}
而接着,在invoke方法中,会调用 this.dispatch.get(method)).invoke(args) 。this.dispatch.get(method) 会返回一个SynchronousMethodHandler,进行拦截处理。这个方法会根据参数生成完成的RequestTemplate对象,这个对象是Http请求的模版,代码如下。
@Override
public Object invoke(Object[] argv) throws Throwable {
RequestTemplate template = buildTemplateFromArgs.create(argv);
Options options = findOptions(argv);
Retryer retryer = this.retryer.clone();
while (true) {
try {
return executeAndDecode(template, options);
} catch (RetryableException e) {
try {
retryer.continueOrPropagate(e);
} catch (RetryableException th) {
Throwable cause = th.getCause();
if (propagationPolicy == UNWRAP && cause != null) {
throw cause;
} else {
throw th;
}
}
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logRetry(metadata.configKey(), logLevel);
}
continue;
}
}
}
经过上述的代码,我们已经将restTemplate拼装完成,上面的代码中有一个 executeAndDecode() 方法,该方法通过RequestTemplate生成Request请求对象,然后利用Http Client获取response,来获取响应信息。
Object executeAndDecode(RequestTemplate template, Options options) throws Throwable {
//转化为Http请求报文
Request request = targetRequest(template);
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logRequest(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, request);
}
Response response;
long start = System.nanoTime();
try {
//发起远程通信
response = client.execute(request, options);
// ensure the request is set. TODO: remove in Feign 12
//获取返回结果
response = response.toBuilder()
.request(request)
.requestTemplate(template)
.build();
} catch (IOException e) {
// .......
}
经过上面的分析,这里的 client.execute 的 client 的类型是LoadBalancerFeignClient,这里就很自然的进入 LoadBalancerFeignClient#execute。
public Response execute(Request request, Request.Options options) throws IOException {
try {
URI asUri = URI.create(request.url());
String clientName = asUri.getHost();
URI uriWithoutHost = cleanUrl(request.url(), clientName);
FeignLoadBalancer.RibbonRequest ribbonRequest = new FeignLoadBalancer.RibbonRequest(
this.delegate, request, uriWithoutHost);
IClientConfig requestConfig = getClientConfig(options, clientName);
return lbClient(clientName)
.executeWithLoadBalancer(ribbonRequest, requestConfig).toResponse();
}
catch (ClientException e) {
IOException io = findIOException(e);
if (io != null) {
throw io;
}
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
其实这个execute里面得流程就是 Ribbon 的那一套。我们可以简单的看一下。首先是构造URI,构造RibbonRequest,选择 LoadBalance,发起调用。
来看一下lbClient 选择负载均衡器的时候做了什么
public FeignLoadBalancer create(String clientName) {
FeignLoadBalancer client = this.cache.get(clientName);
if (client != null) {
return client;
}
IClientConfig config = this.factory.getClientConfig(clientName);
ILoadBalancer lb = this.factory.getLoadBalancer(clientName);
ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector = this.factory.getInstance(clientName,
ServerIntrospector.class);
client = this.loadBalancedRetryFactory != null
? new RetryableFeignLoadBalancer(lb, config, serverIntrospector,
this.loadBalancedRetryFactory)
: new FeignLoadBalancer(lb, config, serverIntrospector);
this.cache.put(clientName, client);
return client;
}
可以得出的结论就是 this.factory.getLoadBalancer(clientName) 跟Ribbon 源码里的获取方式一样,无疑这里获取的就是默认的 ZoneAwareLoadBalancer。然后包装成一个 FeignLoadBalancer 进行返回
既然负载均衡器选择完了,那么一定还有个地方通过该负载去选择一个服务,接着往下看:
public T executeWithLoadBalancer(final S request, final IClientConfig requestConfig) throws ClientException {
LoadBalancerCommand<T> command = buildLoadBalancerCommand(request, requestConfig);
try {
return command.submit(
new ServerOperation<T>() {
@Override
public Observable<T> call(Server server) {
URI finalUri = reconstructURIWithServer(server, request.getUri());
S requestForServer = (S) request.replaceUri(finalUri);
try {
return Observable.just(AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient.this.execute(requestForServer, requestConfig));
}
catch (Exception e) {
return Observable.error(e);
}
}
})
.toBlocking()
.single();
} catch (Exception e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof ClientException) {
throw (ClientException) t;
} else {
throw new ClientException(e);
}
}
}
上面这段代码就是通过获取到的负载进行执行请求,但是这个时候 服务还没有选择,我们跟进去 submit 请求看一看究竟:
public Observable<T> submit(final ServerOperation<T> operation) {
final ExecutionInfoContext context = new ExecutionInfoContext();
// .........
Observable<T> o =
(server == null ? selectServer() : Observable.just(server))
.concatMap(new Func1<Server, Observable<T>>() {
//........
});
// .......
}
可以看到这里有个 selectServer的方法 ,跟进去:
public Server getServerFromLoadBalancer(@Nullable URI original, @Nullable Object loadBalancerKey) throws ClientException {
String host = null;
int port = -1;
if (original != null) {
host = original.getHost();
}
if (original != null) {
Pair<String, Integer> schemeAndPort = deriveSchemeAndPortFromPartialUri(original);
port = schemeAndPort.second();
}
// Various Supported Cases
// The loadbalancer to use and the instances it has is based on how it was registered
// In each of these cases, the client might come in using Full Url or Partial URL
ILoadBalancer lb = getLoadBalancer();
if (host == null) {
// ............
} else {
// ...........if (shouldInterpretAsVip) {
Server svc = lb.chooseServer(loadBalancerKey);
if (svc != null){
host = svc.getHost();
if (host == null){
throw new ClientException(ClientException.ErrorType.GENERAL,
"Invalid Server for :" + svc);
}
logger.debug("using LB returned Server: {} for request: {}", svc, original);
return svc;
} else {
// just fall back as real DNS
logger.debug("{}:{} assumed to be a valid VIP address or exists in the DNS", host, port);
}
} else {
// consult LB to obtain vipAddress backed instance given full URL
//Full URL execute request - where url!=vipAddress
logger.debug("Using full URL passed in by caller (not using load balancer): {}", original);
}
}
// ..........
return new Server(host, port);
}
可以看到的是这里获取到了之前构造好的 ZoneAwareLoadBalancer 然后调用 chooseServer 方法获取server ,这个是跟Ribbon 中是一样的流程,这里就不赘述了。
获取到了server 后,会回调先前 executeWithLoadBalancer 方法里构造的 ServerOperation 的 call 方法:
return command.submit(
new ServerOperation<T>() {
@Override
public Observable<T> call(Server server) {
URI finalUri = reconstructURIWithServer(server, request.getUri());
S requestForServer = (S) request.replaceUri(finalUri);
try {
return Observable.just(AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient.this.execute(requestForServer, requestConfig));
}
catch (Exception e) {
return Observable.error(e);
}
}
})
.toBlocking()
.single();
然后会执行 AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient.this.execute(requestForServer, requestConfig) 进行最后的调用,实际上这里走的是 FeignLoadBalancer#execute
@Override
public RibbonResponse execute(RibbonRequest request, IClientConfig configOverride)
throws IOException {
Request.Options options;
if (configOverride != null) {
RibbonProperties override = RibbonProperties.from(configOverride);
options = new Request.Options(override.connectTimeout(this.connectTimeout),
override.readTimeout(this.readTimeout));
}
else {
options = new Request.Options(this.connectTimeout, this.readTimeout);
}
Response response = request.client().execute(request.toRequest(), options);
return new RibbonResponse(request.getUri(), response);
}
而这里调用的 request.client().execute(request.toRequest(), options) 则是 DefaultFeignLoadBalancedConfiguration 注入的 LoadBalancerFeignClient ,在构造 LoadBalancerFeignClient 的时候 ,传递了个 feign.Client.Default ,然后利用 feign.Client.Default 构造了一个 RibbonRequest。
所以这里走 feign.Client.Default#execute :
@Override
public Response execute(Request request, Options options) throws IOException {
HttpURLConnection connection = convertAndSend(request, options);
return convertResponse(connection, request);
}
利用 JDK 提供的 HttpURLConnection 发起远程的 HTTP通讯。至此发起请求的流程就完成了。下面附上一张这个过程的流程图,对于Ribbon的调用过程请参考 :Ribbon 源码分析。
3. OpenFeign Configuration
针对 feign 的 Configuration ,官方给我们提供了很多的个性化配置,具体可以参考 org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClientProperties.FeignClientConfiguration
public static class FeignClientConfiguration {
// 日志
private Logger.Level loggerLevel;
// 连接超时
private Integer connectTimeout;
private Integer readTimeout;
//重试
private Class<Retryer> retryer;
//解码
private Class<ErrorDecoder> errorDecoder;
private List<Class<RequestInterceptor>> requestInterceptors;
// 编码
private Boolean decode404;
private Class<Decoder> decoder;
private Class<Encoder> encoder;
// 解析
private Class<Contract> contract;
private ExceptionPropagationPolicy exceptionPropagationPolicy;
}
这里举个简单的例子,以Logger 为例。我们想为每个不同的 FeignClient 设置日志级别。
- 添加配置类:
@Configuration
public class FooConfiguration {
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel() {
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}
- 配置日志级别 ,logging.level + FeignClient 包的全路径。
logging.level.com.xxx.xxxService: DEBUG
就这样就配置完成了。重启服务就可以看到效果。
更多配置请参考官网。
总结
Spring Cloud OpenFeign 的核心工作原理经上文探究可以非常简单的总结为:
-
通过 @EnableFeignCleints 触发 Spring 应用程序对 classpath 中 @FeignClient 修饰类的扫描
解析到 @FeignClient 修饰类后, Feign 框架通过扩展 Spring Bean Deifinition 的注册逻辑, 最终注册一个 FeignClientFacotoryBean 进入 Spring 容器Spring 容器在初始化其他用到 @FeignClient 接口的类时, 获得的是 FeignClientFacotryBean 产生的一个代理对象 Proxy。 -
基于 java 原生的动态代理机制, 针对 Proxy 的调用, 都会被统一转发给 Feign 框架所定义的一个 InvocationHandler , 由该 Handler 完成后续的 HTTP 转换, 发送, 接收, 翻译HTTP响应的工作。