Netty知识点梳理
概述
简介
应用场景
互联网行业
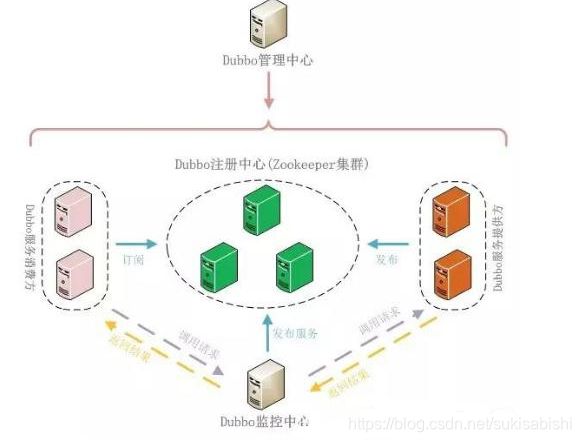
1.互联网行业:在分布式系统中,各个 节点之间需要远程服务调用,高性能 的 RPC 框架必不可少,Netty 作为异步 高性能的通信框架,往往作为基础通 信组件被这些 RPC 框架使用。
2.典型的应用有:阿里分布式服务框架 Dubbo 的 RPC 框架使用 Dubbo 协议进 行节点间通信,Dubbo 协议默认使用 Netty 作为基础通信组件,用于实现各 进程节点之间的内部通信
游戏行业
1.无论是手游服务端还是大型的网络游戏, Java 语言得到了越来越广泛的应用
2.Netty 作为高性能的基础通信组件,提 供了 TCP/UDP 和 HTTP 协议栈,方便定 制和开发私有协议栈,账号登录服务器
3.地图服务器之间可以方便的通过 Netty 进行高性能的通信
大数据领域
1.经典的 Hadoop 的高性能通信和 序列化组件 Avro(实现数据文件共享) 的 RPC 框架, 默认采用 Netty 进行跨界点通信
2.它的 Netty Service 基于 Netty 框 架二次封装实现。

其它开源项目使用到Netty
网址:https://netty.io/wiki/related-projects.html
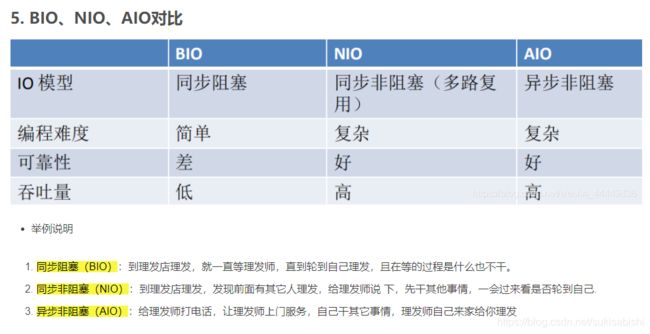
BIO、NIO和AIO
IO 模型
I/O 模型基本说明
BIO、NIO、AIO适用场景分析
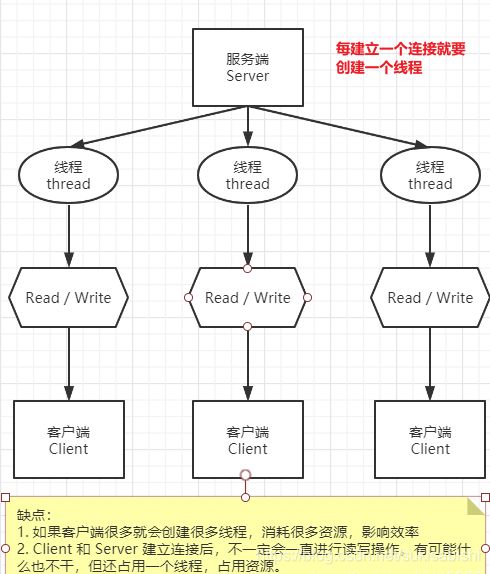
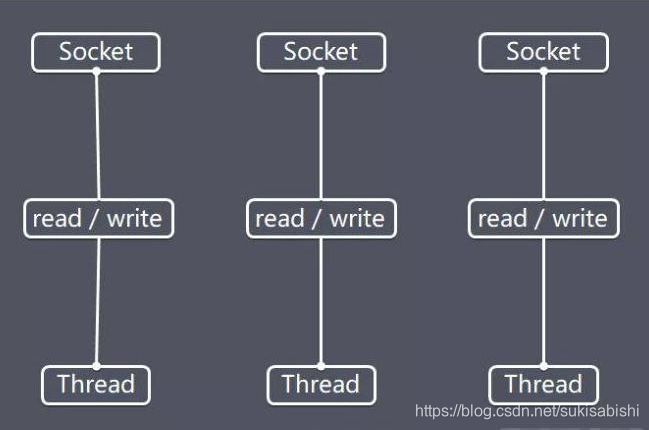
BIO
基本介绍
工作机制
应用实例
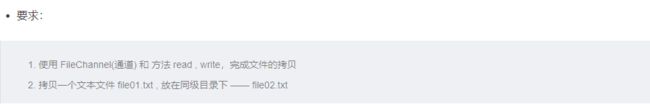
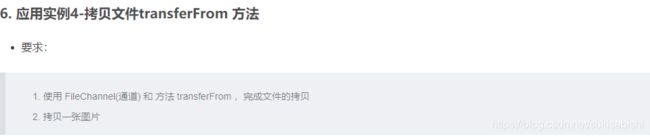
要求:
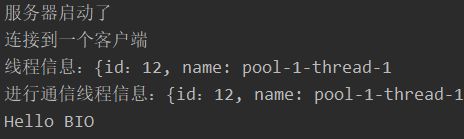
1.使用BIO模型编写一个服务器端,监听6666端口,当有客户端连接时,就启 动一个线程与之通讯。
2.要求使用线程池机制改善,可以连接多个客户端.
3.服务器端可以接收客户端发送的数据(telnet 方式即可)。
public class BIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 创建一个线程池
ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
// 监听“6666” 端口,接收客户连接请求,并生成与客户端连接的Socket
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(6666);
System.out.println("服务器启动了");
while (true){
// 监听,等待客户端连接
final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("连接到一个客户端");
// 2. 如果有客户端连接,就创建一个线程,与之通信
threadPool.execute(()->{
handler(socket);
});
}
}
/**
* 和客户端通信的方法
* 循环的读取客户端的数据,然后输出
*/
public static void handler(Socket socket){
// 打印线程信息
System.out.println("线程信息:{id:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+", " +
"name: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 用于接收数据
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
// 通过 socket 获取输入流
try {
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
// 循环的读取客户端发送的数据
while (true){
System.out.println("进行通信线程信息:{id:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+", " +
"name: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
int read = inputStream.read(bytes);
if (read != -1){
// 说明还可以读
// 输出客户端发送的数据
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0, read));
}else {
// 读取完毕
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("关闭连接");
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
连接服务,测试
打开 CMD,连接 6666 端口
![]()
输入 Ctrl + ],传递数据

查看控制台
小结
- 从上面的结果可以发现,处理请求的线程 和 服务端客户端之间连接的线程是同一个
- 通过 Debug 方式运行可以发现,当连接上服务端之后,不进行任何操作,改线程只会阻塞在 int read = inputStream.read(bytes);
问题分析
NIO
基本介绍
NIO 和 BIO 的比较
NIO 三大核心
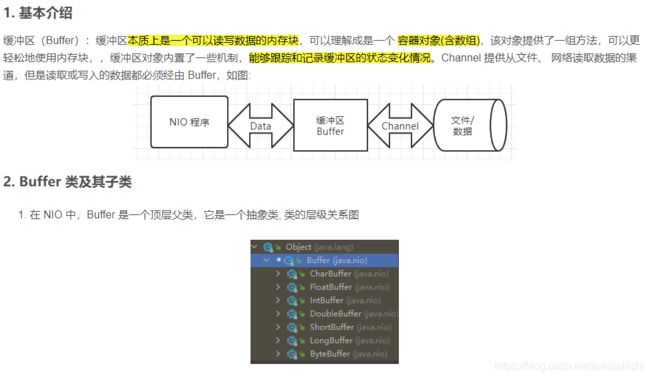
Selector 、 Channel 和 Buffer 的简单关系图
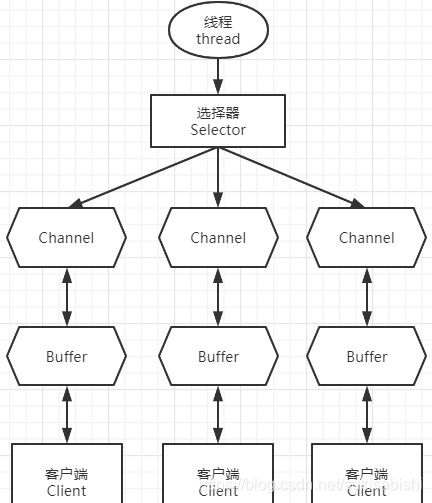
关系图的说明:
1.每个 Channel 都会对应一个 Buffer
2.Selector 对应一个线程, 一个 Selector 对应多个 Channel(连接)
3.该图反应了有三个 Channel 注册到该 selector
4.程序切换到哪个 Channel 是由事件决定的, Event 就是一个重要的概念
5.Selector 会根据不同的事件,在各个 Channel(通道)上切换
6.Buffer 就是一个内存块 , 底层是有一个数组
7.数据的读取写入是通过 Buffer, 这个和BIO , BIO 中要么是输入流,或者是 输出流, 不能双向,但是NIO的 Buffer 是可以读也可以写, 需要 flip 方法切换
8.Channel 是双向的, 可以返回底层操作系统的情况, 比如 Linux , 底层的操作系统 通道就是双向的
缓冲区(Buffer)
public class BasicBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个 Buffer, 一个可以存放 5 个整数的 Buffer
IntBuffer intBuffer = IntBuffer.allocate(5);
// 向 Buffer 中存放数据
for (int i = 0; i < intBuffer.capacity(); i++) {
intBuffer.put(i);
}
// 从 Buffer 读取数据
// 对 Buffer 进行读写切换
intBuffer.flip();
while (intBuffer.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(intBuffer.get());
}
}
}

![]()
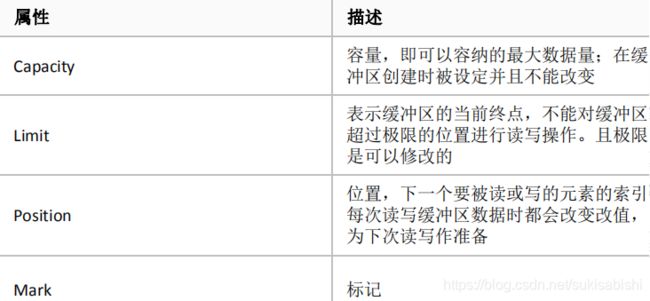
这几个属性的大小关系 :mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
![]()
标 ★ 为常用
public abstract class Buffer {
//JDK1.4时,引入的api
public final int capacity( )// ★ 返回此缓冲区的容量
public final int position( )// ★ 返回此缓冲区的位置
public final Buffer position (int newPositio)// ★ 设置此缓冲区的位置
public final int limit( )// ★ 返回此缓冲区的限制
public final Buffer limit (int newLimit)// ★ 设置此缓冲区的限制
public final Buffer mark( )//在此缓冲区的位置设置标记
public final Buffer reset( )//将此缓冲区的位置重置为以前标记的位置
public final Buffer clear( )// ★ 清除此缓冲区, 即将各个标记恢复到初始状态,但是数据并没有真正擦除, 后面操作会覆盖
public final Buffer flip( )// ★ 反转此缓冲区
public final Buffer rewind( )//重绕此缓冲区
public final int remaining( )//返回当前位置与限制之间的元素数
public final boolean hasRemaining( )// ★ 告知在当前位置和限制之间是否有元素
public abstract boolean isReadOnly( );// ★ 告知此缓冲区是否为只读缓冲区
//JDK1.6时引入的api
public abstract boolean hasArray();// ★ 告知此缓冲区是否具有可访问的底层实现数组
public abstract Object array();// ★ 返回此缓冲区的底层实现数组
public abstract int arrayOffset();//返回此缓冲区的底层实现数组中第一个缓冲区元素的偏移量
public abstract boolean isDirect();//告知此缓冲区是否为直接缓冲区
}
public abstract class ByteBuffer {
//缓冲区创建相关api
public static ByteBuffer allocateDirect(int capacity)// ★ 创建直接缓冲区
public static ByteBuffer allocate(int capacity)// ★ 设置缓冲区的初始容量
public static ByteBuffer wrap(byte[] array)//把一个数组放到缓冲区中使用
//构造初始化位置offset和上界length的缓冲区
public static ByteBuffer wrap(byte[] array,int offset, int length)
//缓存区存取相关API
public abstract byte get( );// ★ 从当前位置position上get,get之后,position会自动+1
public abstract byte get (int index);// ★ 从绝对位置get ,position 不会变化
public abstract ByteBuffer put (byte b);// ★ 从当前位置上添加,put之后,position会自动+1
public abstract ByteBuffer put (int index, byte b);// ★ 从绝对位置上put ,position 不会变化
}
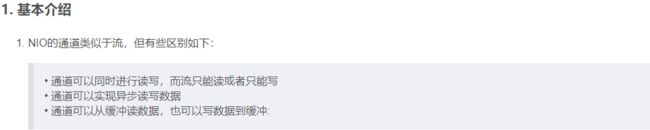
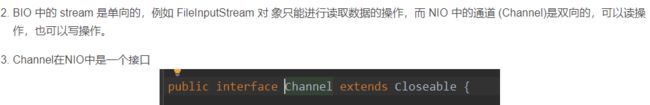
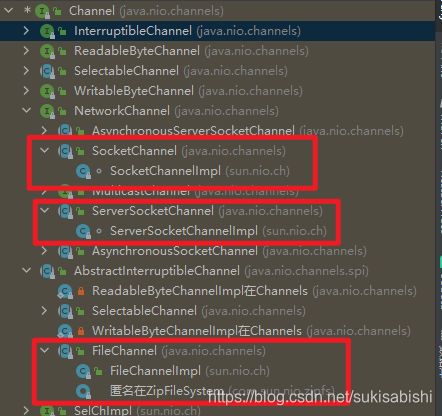
通道(Channel)
public class FileChannel01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 得到数据
String str = "Hello";
// 2. 把数据写入 Buffer
// 创建一个输出流 , channel
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\file01.txt");
// 通过输出流,获取对应的 FileChannel
// fileChannel 真实类型是 fileChannelImpl
FileChannel fileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
// 创建一个缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 把数据放入到 byteBuffer
byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes());
// 3. 把 Buffer 的数据传入输出流
// 4. 通过 输出流 中的 fileChannel 对象把数据写入
// 反转 Buffer
byteBuffer.flip();
// 把 Buffer 的数据写入 fileChannel
fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
// 关闭流
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
public class FileChannel02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 通过 输入流 中的 fileChannel 对象把数据读出
// 创建输入流
File file = new File("D:\\file01.txt");
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
// 通过 输入流 获得对应的 FileChannel
FileChannel fileChannel = inputStream.getChannel();
// 2. 把 输入流 的数据传入 Buffer
// 创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) file.length());
// 把数据从 fileChannel 读入到缓冲区
fileChannel.read(buffer);
// 3. 把数据从 Buffer 中取出
// 将缓冲区的字节转换成字符串
String s = new String(buffer.array());
// 4. 显示数据
System.out.println(s);
}
}
public class FileChannel03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建输入流对象,并获取对应的 Channel
File file = new File("D:\\file01.txt");
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
FileChannel inputStreamChannel = inputStream.getChannel();
// 创建输出流对象,并获取对应的 Channel
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\file02.txt");
FileChannel outputStreamChannel = outputStream.getChannel();
// 创建 Buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
int read = 0;
while (read != -1){
// 重置 Buffer 中的标志位,以免上一轮循环中 Buffer 中的信息,影响本轮操作
buffer.clear();
// 循环的 从 输入流 读取数据并写入到 输出流
read = inputStreamChannel.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
outputStreamChannel.write(buffer);
}
// 关闭输入、输出流
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
}
}
public class FileChannel04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建输入流对象,并获取对应的 Channel
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\Demo.png");
FileChannel inputStreamChannel = inputStream.getChannel();
// 创建输出流对象,并获取对应的 Channel
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\Demo-2.png");
FileChannel outputStreamChannel = outputStream.getChannel();
// 使用 transferForm 完成拷贝
// 参数 : 被复制的流的Channel ; 起始位置 ; 结束位置
outputStreamChannel.transferFrom(inputStreamChannel,0,inputStreamChannel.size());
// 关闭输入、输出流
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
}
}
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = buffer.asReadOnlyBuffer();
System.out.println(buffer);
System.out.println(byteBuffer);
![]()
![]()
/* 说明
1. MappedByteBuffer 可以让文件直接在内存中修改,这样操作系统并不需要拷贝一次
2. MappedByteBuffer 实际类型是 DirectByteBuffer
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile("D:\\file01.txt", "rw");
// 获取对应的文件通道
FileChannel channel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
// 参数 :使用 只读/只写/读写 模式 ; 可以修改的起始位置 ; 映射到内存的大小,即可以将文件的多少个字节映射到内存
// 这里就表示,可以对 file01.txt 文件中 [0,5) 的字节进行 读写操作
MappedByteBuffer map = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 5);
// 进行修改操作
map.put(0, (byte) 'A');
map.put(3, (byte) '3');
// 关闭通道
channel.close();
}
public class ScatteringAndGatheringTest {
/*
Scattering : 将数据写入到 Buffer 时,可以采用 Buffer 数组,依次写入【分散】
Gathering : 从 Buffer 读取数据,可以采用 Buffer 数组,依次读取
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 使用 ServerSocketChannel 和 InetSocketAddress 网络
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(6666);
// 绑定端口到 socket,并启动
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress);
// 创建 Buffer 数组
ByteBuffer[] byteBuffers = new ByteBuffer[2];
byteBuffers[0] = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
byteBuffers[1] = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
// 等待客户端连接(telnet)
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
// 循环的读取数据
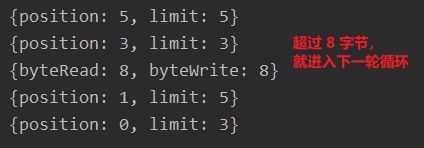
while (true){
// 表示累计读取的字节数
int byteRead = 0;
// 假设从客户端最多接收 8 个字节
while (byteRead < 8){
// 自动把数据分配到 byteBuffers-0、byteBuffers-1
long read = socketChannel.read(byteBuffers);
byteRead += read;
// 使用流打印,查看当前 Buffer 的 Position 和 Limit
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).stream().
map(byteBuffer -> "{position: "+byteBuffer.position()+", limit: "+byteBuffer.limit()+"}")
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
// 将所有的 Buffer 进行反转,为后面的其他操作做准备
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(Buffer::flip);
// 将数据读出,显示到客户端
int byteWrite = 0;
while (byteWrite < 8){
long write = socketChannel.write(byteBuffers);
byteWrite += write;
}
// 将所有的 Buffer 进行清空,为后面的其他操作做准备
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(Buffer::clear);
// 打印处理的字节数
System.out.println("{byteRead: "+byteRead+", byteWrite: "+byteWrite+"}");
}
}
Selector(选择器)
public abstract class Selector implements Closeable {
public static Selector open();//得到一个选择器对象
public int select(long timeout);//监控所有注册的通道,当其 中有 IO 操作可以进行时,将 对应的 SelectionKey 加入到内部集合中并返回,参数用来 设置超时时间
public Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys();//从内部集合中得 到所有的 SelectionKey
}
selector.select()//阻塞
selector.select(1000);//阻塞1000毫秒,在1000毫秒后返回
selector.wakeup();//唤醒
selector selector.selectNow();//不阻塞,立马返还
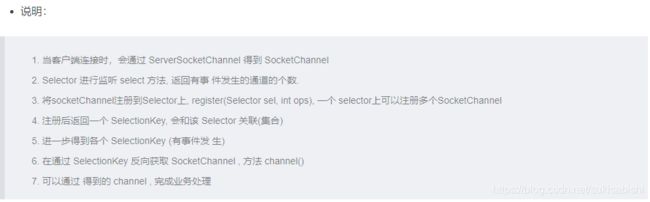
NIO 非阻塞 网络编程原理分析
NIO 非阻塞 网络编程快速入门
public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// 创建 ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 得到一个 Selector 实例
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 绑定端口,在服务端进行监听
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(6666));
// 设置为非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 把 ServerSocketChannel 注册到 Selector 关心事件为 OP_ACCEPT(连接)
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// 循环等待客户端连接
while (true){
// 等待一秒,如果没有事件发生,就继续
if (selector.select(1000) == 0){
System.out.println("服务器等待了 1 s,无连接");
continue;
}
// 如果有事件发生,获取到发生事件的 SelectionKey 集合
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
// 通过 SelectionKey 反向获取对应通道
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()){
// 获取 keyIterator
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
// 根据 key 发生的事件,做相应的处理
// 如果是连接的事件
if (key.isAcceptable()){
// 通过 serverSocketChannel 给该客户端生成一个 SocketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
// 设置为非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 将当前的 socketChannel 注册到 Selector,关心事件为 OP_READ(读),
// 同时给 socketChannel 关联一个 Buffer
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
}
// 如果是读事件
if (key.isReadable()){
// 通过 key 反向获取对应的 Channel
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
// 获取该 SocketChannel 关联的 Buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
// 把 Channel 中的数据读入到 Buffer 中
channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println("from 客户端——"+new String(buffer.array()));
}
// 处理完毕后要手动删除当前的 SelectionKey,避免多线程重复操作
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
![]()
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 得到一个网络通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
// 设置非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 提供服务端的 ip、 端口
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 6666);
// 连接服务端
if (!socketChannel.connect(inetSocketAddress)){
// 如果没有完成
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()){
System.out.println("连接中……因为连接需要时间,客户端不会阻塞,可以做其他工作");
}
}
// 如果连接成功就发送数据
String str = "Hello,NIO";
// wrap 通过参数中的字节数组的大小,直接生成对应大小的 Buffer,并把字节数组存入
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());
// 发送数据, 把 Buffer 中的数据写入 Channel
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
}
}
SelectionKey
![]()
int OP_ACCEPT:有新的网络连接可以 accept,值为 16
int OP_CONNECT:代表连接已经建立,值为 8
int OP_READ:代表读操作,值为 1
int OP_WRITE:代表写操作,值为 4
![]()
public static final int OP_READ = 1 << 0;
public static final int OP_WRITE = 1 << 2;
public static final int OP_CONNECT = 1 << 3;
public static final int OP_ACCEPT = 1 << 4;
public abstract class SelectionKey {
public abstract Selector selector();//得到与之关联的 Selector 对象
public abstract SelectableChannel channel();//得到与之关 联的通道
public final Object attachment();//得到与之关联的共享数 据
public abstract SelectionKey interestOps(int ops);//设置或改 变监听事件
public final boolean isAcceptable();//是否可以 accept
public final boolean isReadable();//是否可以读
public final boolean isWritable();//是否可以写
}
ServerSocketChannel
public abstract class ServerSocketChannel extends AbstractSelectableChannel implements NetworkChannel{
public static ServerSocketChannel open()//得到一个 ServerSocketChannel 通道
public final ServerSocketChannel bind(SocketAddress local)//设置服务器端端口 号
public final SelectableChannel configureBlocking(boolean block)//设置阻塞或非 阻塞模式,取值 false 表示采用非阻塞模式
public SocketChannel accept()//接受一个连接,返回代表这个连接的通道对象
public final SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops)//注册一个选择器并设置 监听事件
}
SocketChannel
public abstract class SocketChannel extends AbstractSelectableChannel implements ByteChannel, ScatteringByteChannel, GatheringByteChannel, NetworkChannel{
public static SocketChannel open();//得到一个 SocketChannel 通道
public final SelectableChannel configureBlocking(boolean block);//设置阻塞或非阻塞 模式,取值 false 表示采用非阻塞模式
public boolean connect(SocketAddress remote);//连接服务器
public boolean finishConnect();//如果上面的方法连接失败,接下来就要通过该方法 完成连接操作
public int write(ByteBuffer src);//往通道里写数据
public int read(ByteBuffer dst);//从通道里读数据
public final SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops, Object att);//注册一个选择器并 设置监听事件,最后一个参数可以设置共享数据
public final void close();//关闭通道
}
NIO 网络编程应用实例-群聊系统
public class Server {
// 定义属性
private Selector selector;
private ServerSocketChannel listenerChannell;
private static final int PORT = 6666;
// 构造器
public Server(){
try {
// 得到选择器
selector = Selector.open();
// 得到 ServerSocketChannel
listenerChannell = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 绑定端口
listenerChannell.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
// 设置非阻塞
listenerChannell.configureBlocking(false);
// 把 listenerChannell 注册到 Selector 中,关注连接事件
listenerChannell.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
}
}
// 监听,处理客户端的连接事件
public void listen(){
try {
// 循环处理
while (true){
int select = selector.select();
if (select > 0){ // 表示有事件要处理
// 遍历得到 SelectionKey 集合
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
// 取出 SelectionKey
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
//处理连接事件
if (key.isAcceptable()){
// 通过 ServerSocketChannel 获得 socketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = listenerChannell.accept();
// 设置非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 将 socketChannel 注册到 Selector
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
// 给出提示
System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress() + "上线了~");
}
// 处理读事件
if (key.isReadable()){
// 处理读的方法
read(key);
}
iterator.remove();
}
}else {
System.out.println("等待中……");
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
}
}
// 读取客户端消息
public void read(SelectionKey key){
// 定义一个 SocketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = null;
try {
// 得到关联的 Channel
socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
// 创建 ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 将 socketChannel 的数据读到 Buffer
int read = socketChannel.read(buffer);
// 根据 read 的值,做出对应的处理
if (read > 0){
// 读取到了数据
String s = new String(buffer.array());
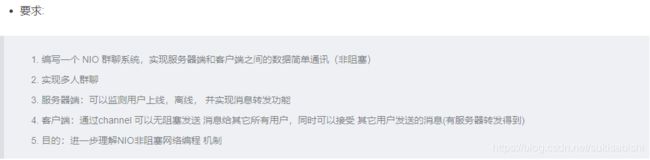
System.out.println("【服务端】收到客户端消息:"+ s);
// 向其他客户端转发消息,需要排除自己
sendMessageToOther(s,socketChannel);
}
}catch (IOException e){
// 如果在读取数据时, 发生异常,则表示离线了
try {
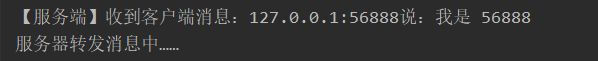
System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress() + "离线了~");
// 取消注册
key.channel();
// 关闭通道
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException ioException) {
ioException.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 转发消息给其他客户端
public void sendMessageToOther(String message, SocketChannel selfChannel) throws IOException {
System.out.println("服务器转发消息中……");
// 遍历所有注册到 Selector 上的 socketChannel ,并排除自己
for (SelectionKey key : selector.keys()) {
// 通过 key 取出对应的 SocketChannel
Channel channel = key.channel();
// 排除自己, channel 必须是一个 SocketChannel 类型的 并且 channel 不等于自己
if (channel instanceof SocketChannel && channel != selfChannel){
// 转换 Channel 类型
SocketChannel dest = (SocketChannel) channel;
// 将 message 存储到 Buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(message.getBytes());
// 将 Buffer 的数据写入通道
dest.write(buffer);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个服务器对象
Server server = new Server();
server.listen();
}
}
public class Client {
// 定义相关属性
// 服务器的IP
private final String HOST = "127.0.0.1";
// 服务器的端口
private final int PORT = 6666;
private Selector selector;
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private String username;
// 构造器
public Client() throws IOException {
// 完成初始化
selector = Selector.open();
// 连接服务器
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress(HOST, PORT));
// 设置 非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 将 socketChannel 注册到 Selector
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
// 得到 username
username = socketChannel.getLocalAddress().toString().substring(1);
System.out.println(username + "is OK!");
}
// 向服务器发送消息
public void sendMessage(String message){
message = username + "说:"+ message;
try {
// 把 message 写入 buffer
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(message.getBytes()));
// 读取从服务器端回复的消息
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
}
}
public void readmessage(){
try {
int select = selector.select();
if (select > 0){
// 有事件发生的通道
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
if (key.isReadable()){
// 得到相关的通道
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
channel.read(buffer);
String msg = new String(buffer.array());
System.out.println(msg.trim());
}
}
}else {
System.out.println("没有可用的通道");
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 启动客户端
Client client = new Client();
// 启动一个线程,每个三秒读取从服务器端读取数据
new Thread(()->{
while (true){
client.readmessage();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
// 发送数据给服务端
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()){
String line = scanner.nextLine();
client.sendMessage(line);
}
}
}
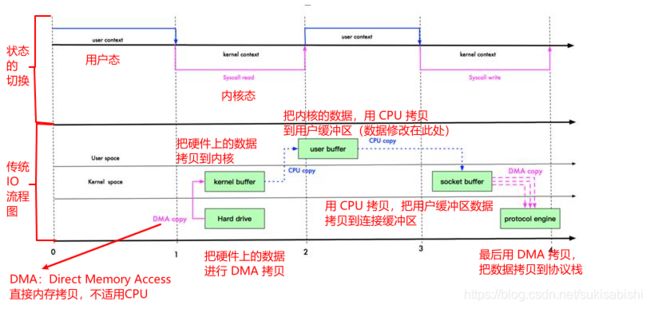
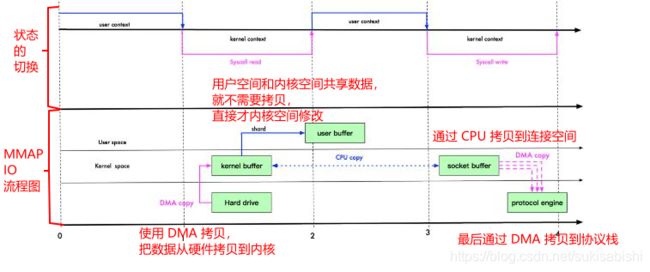
NIO与零拷贝
File file = new File("test.txt");
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
byte[] arr = new byte[(int) file.length()];
raf.read(arr);
Socket socket = new ServerSocket(8080).accept();
socket.getOutputStream().write(arr);
public class OldIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 监听 7001,端口
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(7001);
while (true) {
// 监视连接
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
// 通过 serversocket 获得输入流
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
try {
byte[] byteArray = new byte[4096];
// 循环的读取数据
while (true) {
int readCount = dataInputStream.read(byteArray, 0, byteArray.length);
if (-1 == readCount) {
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
![]()
public class OldIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 7001);
// 需要拷贝的大文件
String fileName = "protoc-3.6.1-win32.zip";
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(fileName);
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
long readCount;
long total = 0;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while ((readCount = inputStream.read(buffer)) >= 0) {
total += readCount;
dataOutputStream.write(buffer);
}
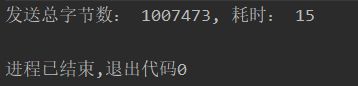
System.out.println("发送总字节数: " + total + ", 耗时: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));
dataOutputStream.close();
socket.close();
inputStream.close();
}
}
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(7001));
// 创建 Buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4096);
while (true){
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
int readBytes = 0;
while (readBytes != -1){
try {
readBytes = socketChannel.read(buffer);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 倒带 : Position = 0,Mark 作废
buffer.rewind();
}
}
}
}
![]()
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost",7001));
String fileName = "protoc-3.6.1-win32.zip";
FileChannel channel = new FileInputStream(fileName).getChannel();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 开始传输
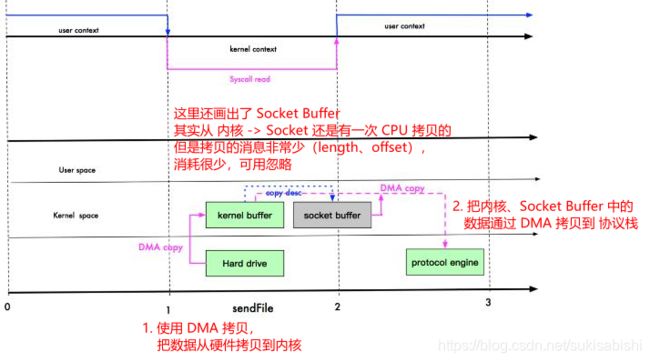
// transferTo 方法底层使用 零拷贝
//在 Linux 下,一个 transferTo 方法,就可以完成传输
//在 Windows 下,transferTo 一次调用只能发送 8M 文件,所以就需要分段传输,而且要注意传输时的位置
long transfer = channel.transferTo(0, channel.size(), socketChannel);
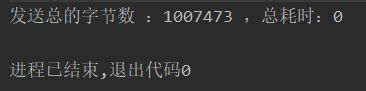
System.out.println("发送总的字节数 :"+ transfer + " ,总耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));
}
}
Netty 概述
线程模型基本介绍
概述
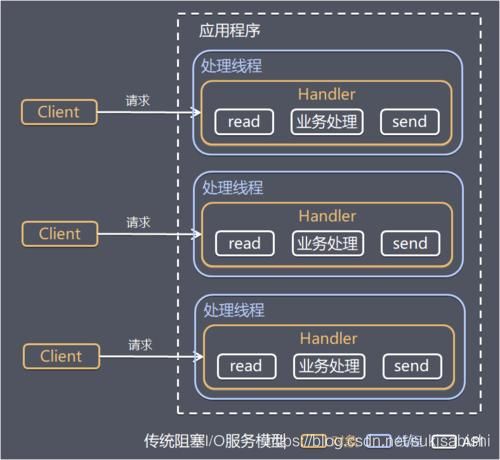
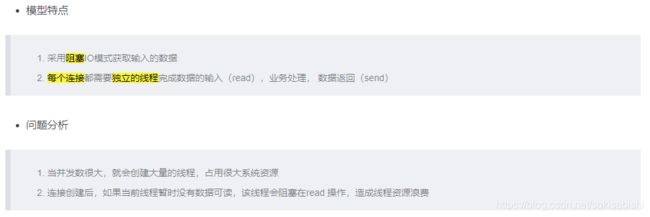
传统阻塞 I/O 服务模型
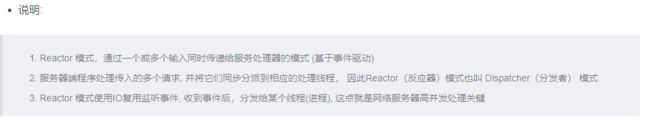
Reactor 模式
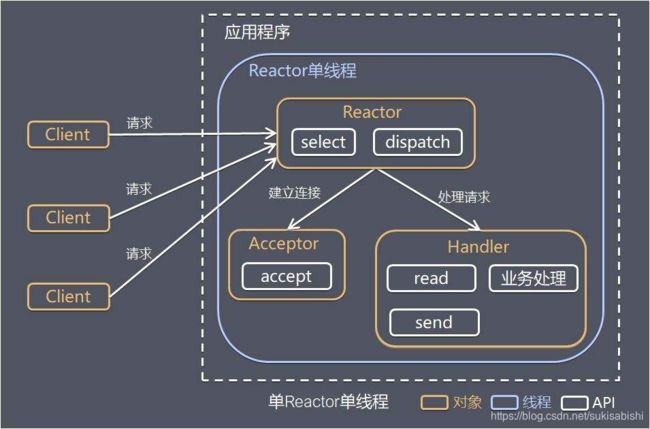
单 Reactor 单线程
单Reactor多线程
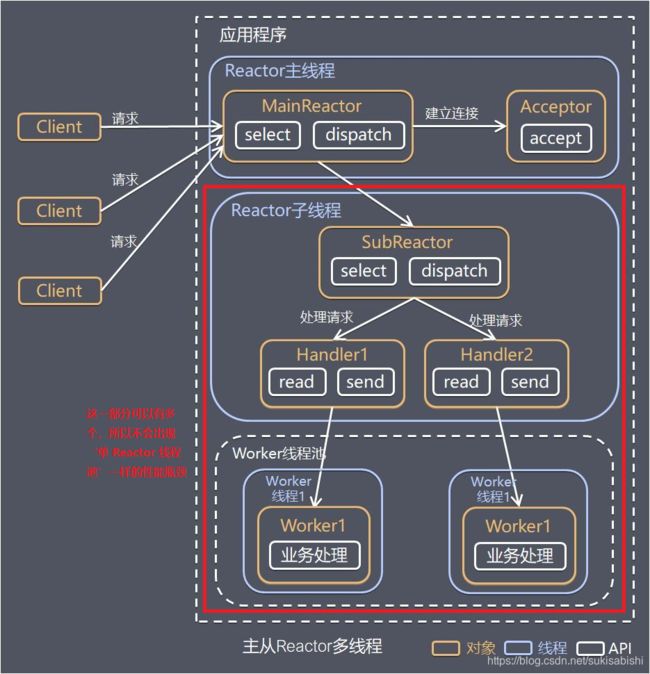
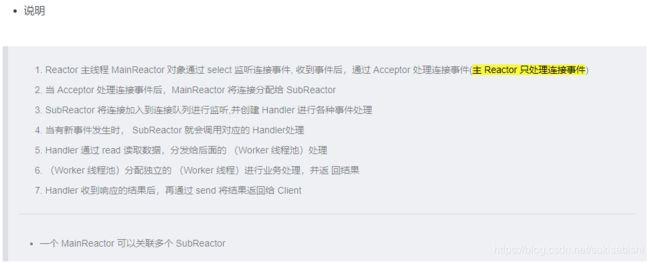
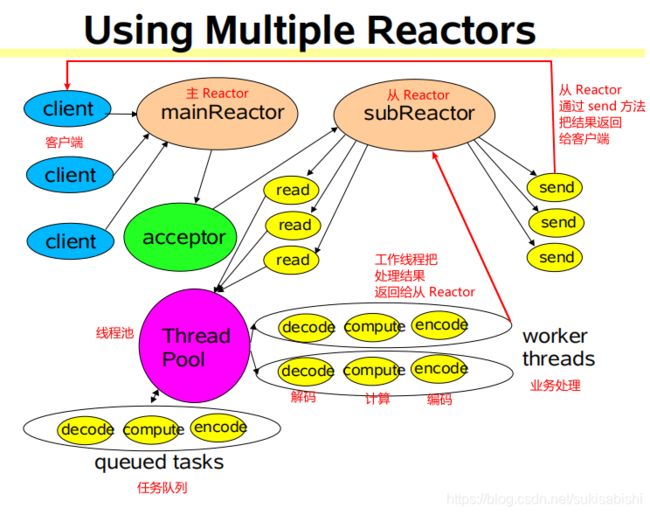
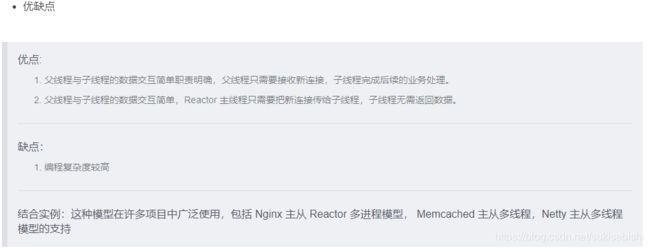
主从 Reactor 多线程
Reactor 模式小结
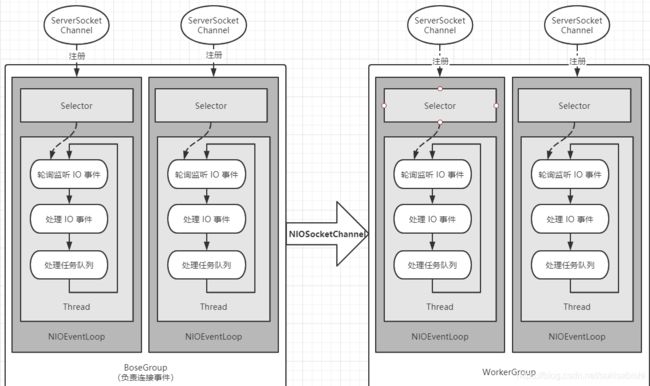
Netty模型
Netty 工作原理示意图
![]()
简单版
进阶版
详细版
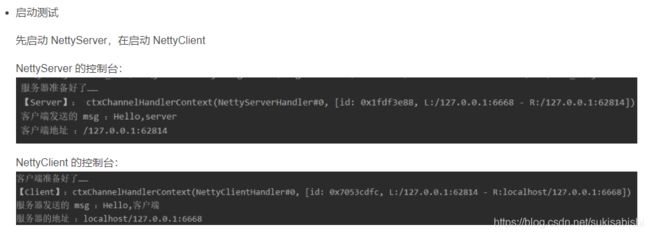
Netty快速入门实例-TCP服务
<!--netty依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.52.Final</version>
</dependency>
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 创建 BossGroup 和 WorkerGroup
/*
说明
1. 创建两个线程组 BossGroup 和 WorkerGroup
2. BossGroup 只处理连接请求
3. WorkerGroup 处理真正客户端的业务
4. 运行时,这两个都是无限循环
*/
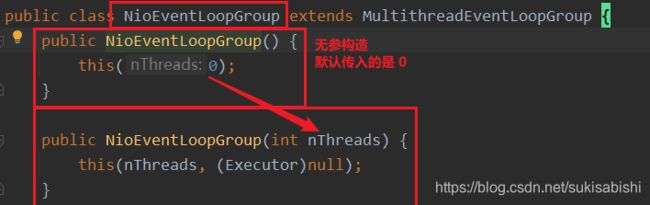
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
// 进行异常处理,try - catch
try {
// 创建 服务端 启动对象,并配置参数
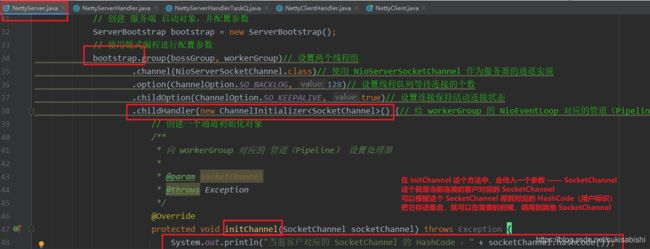
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
// 使用链式编程进行配置参数
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)// 设置两个线程组
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)// 使用 NioServerSocketChannel 作为服务器的通道实现
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)// 设置线程队列等待连接的个数
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)// 设置连接保持活动连接状态
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {// 给 workerGroup 的 NioEventLoop 对应的管道(Pipeline)设置处理器
// 创建一个通道初始化对象
/**
* 向 workerGroup 对应的 管道(Pipeline) 设置处理器
*
* @param socketChannel
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
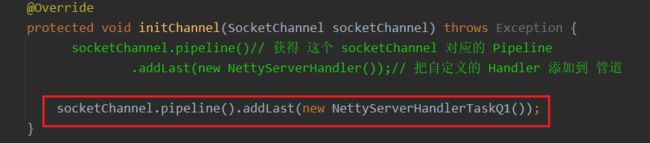
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline()// 获得 这个 socketChannel 对应的 Pipeline
.addLast(new NettyServerHandler());// 把自定义的 Handler 添加到 管道
}
});
System.out.println("服务器准备好了……");
// 绑定一个端口,并且同步。生成了一个 ChannelFuture 对象
// 这里就已经启动了服务器
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(6668).sync();
// 对 关闭通道 进行监听
// 这里只是监听,只有关闭通道时才进行处理,这句话不是直接关闭了通道
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
/**
* 1. 自定义一个 Handler 需要继承 Netty 规定好的某个 处理器适配器
* 2. 这时自定义的 Handler ,才能称为一个 Handler
*/
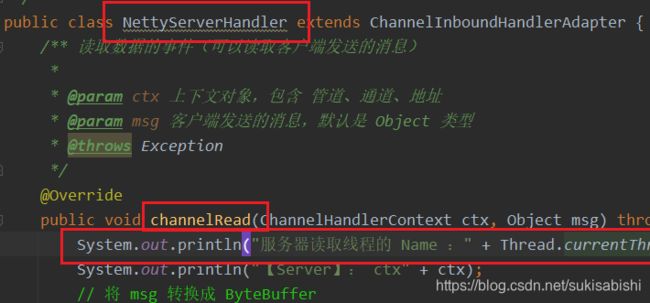
public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/** 读取数据的事件(可以读取客户端发送的消息)
*
* @param ctx 上下文对象,包含 管道、通道、地址
* @param msg 客户端发送的消息,默认是 Object 类型
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("【Server】: ctx" + ctx);
// 将 msg 转换成 ByteBuffer
/*
说明 :
1. 注意这个是 ByteBuf ,是 io.netty.buffer 包下的,不是 NIO 下的 Buffer
2. ByteBuf 比 Buffer 的性能更高一点
*/
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
// 把 buf 转成 UTF8 格式的字符串
System.out.println("客户端发送的 msg :" + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("客户端地址 :" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
}
/**
* 数据读取完毕后,返回消息给客户端
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 把数据写入缓冲区,并刷新缓冲区
// 一般来说,需要对这个发送的消息进行编码
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello,客户端",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
/**
* 处理异常
* @param ctx
* @param cause
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
// 关闭通道
ctx.channel().close();
}
}
public class NettyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 客户端需要一个事件循环组
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 客户端启动对象 —— Bootstrap ,不是 服务端的 ServerBootstrap
// 并且是 io.netty.bootstrap 包下的
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
// 设置相关参数
bootstrap.group(group)// 设置线程组
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)// 设置客户端通道的实现类
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {// 设置处理器
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new NettyClientHandler());// 加入自己的处理器
}
});
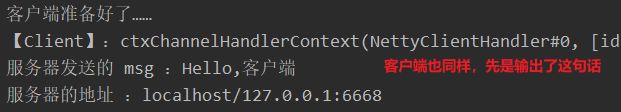
System.out.println("客户端准备好了……");
// 启动客户端连接服务器端
// 这里涉及到一个 Netty 的异步模型,后面详述
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 6668).sync();
// 对关闭通道进行监听
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
* 当通道就绪时,就会触发该方法,就可以发信息了
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("【Client】:ctx" + ctx);
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello,server", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
/**
* 当通道有读取事件时 ,会触发
* @param ctx
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("服务器发送的 msg :" + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("服务器的地址 :"+ ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
}
/**
* 异常处理
* @param ctx
* @param cause
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.channel().close();
}
}
对‘Netty快速入门实例’的分析
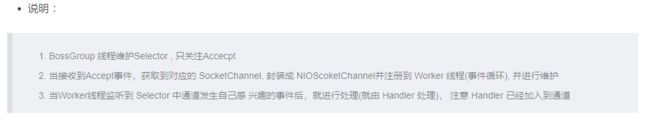
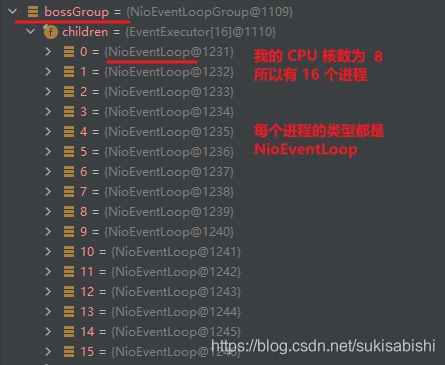
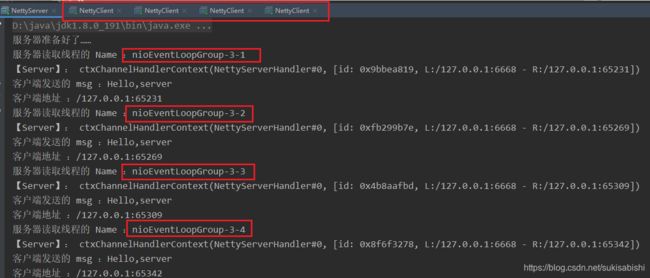
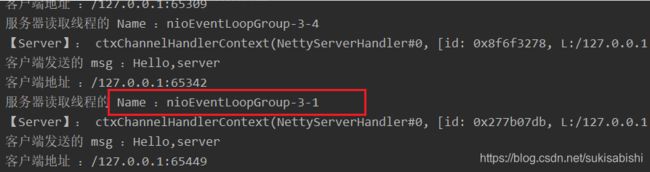
BossGroup 和 WorkGroup 怎么确定自己有多少个 NIOEventLoop
WorkerGroup 是如何分配这些进程的
BossGroup 和 WorkerGroup 中的 Selector 和 TaskQueue
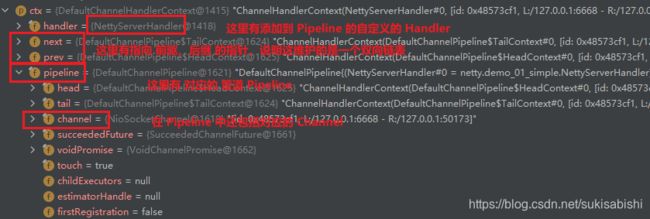
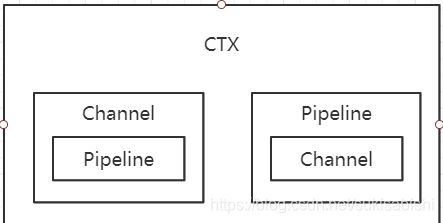
CTX 上下文、Channel、Pipeline 之间关系
TaskQueue 任务队列
概述
体验任务的阻塞
public class NettyServerHandlerTaskQ extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/** 读取数据的事件(可以读取客户端发送的消息)
*
* @param ctx 上下文对象,包含 管道、通道、地址
* @param msg 客户端发送的消息,默认是 Object 类型
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
// 比如这里有一个非常耗时的任务,希望可以异步执行
// 把该任务提交到 Channel 对应的 NIOEventLoop 的 TaskQueue 中
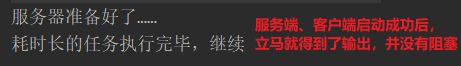
Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello,客户端,这是一个执行耗时长的任务",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("耗时长的任务执行完毕,继续");
}
/**
* 数据读取完毕后,返回消息给客户端
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello,客户端",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
// 关闭通道
ctx.channel().close();
}
}
TaskQueue 使用场景-1
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
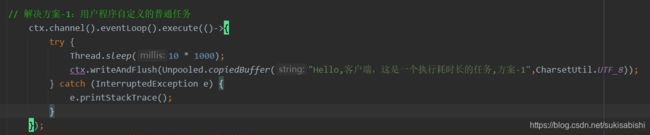
// 解决方案-1:用户程序自定义的普通任务
ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello,客户端,这是一个执行耗时长的任务,方案-1",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
System.out.println("耗时长的任务执行完毕,继续");
}
TaskQueue 使用场景-2
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
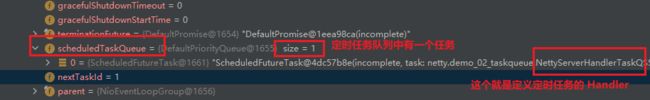
// 解决方案-2:用户自定义定时任务
// 把任务提交到 scheduledTaskQueue
// 在和服务端连接成功后 5s 开始异步执行 run 方法
ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(5 * 1000);
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello,客户端,这是一个执行耗时长的任务,方案-2",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("耗时长的任务执行完毕,继续");
}
TaskQueue 使用场景-3
总结
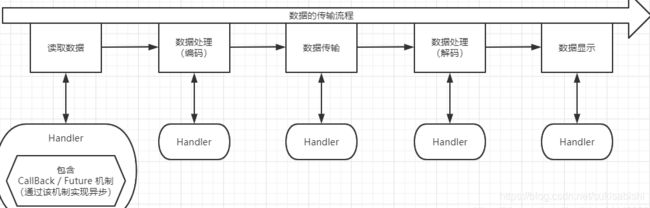
异步模型和HTTP示例
基本介绍
Future 说明
工作原理示意图
Future-Listener 机制
channelFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception {
if (channelFuture.isSuccess()){
System.out.println("监听端口 6668 成功");
}else {
System.out.println("监听端口 6668 失败");
}
}
});
小结
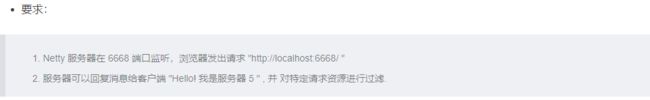
快速入门实例-HTTP服务
public class HttpServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8);
try {
// 创建 服务端 启动对象,并配置参数
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
// 使用自己写的 ServerInitializer 完成初始化
.childHandler(new HttpServerInitializer());
System.out.println("服务器准备好了……");
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(6660).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
![]()
public class HttpServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
// 向管道加入处理器
// 得到管道
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
// 加入一个 Netty 提供的 httpServerCodec (CoDec => Coder + Decoder => 编解码器)
pipeline.addLast("MyHttpServerCodec",new HttpServerCodec());
// 增加一个自己的 Handler
pipeline.addLast("MyServerHandler", new HttpServerHandler());
}
}
/*
1. SimpleChannelInboundHandler 是之前使用的 ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter 的子类
2. HttpObject 这个类型表示, 客户端、服务端 相互通信的数据需要被封装成什么类型
*/
public class HttpServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpObject> {
/**
* 读取客户端数据
* @param channelHandlerContext 上下文
* @param httpObject 传递过来的消息
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
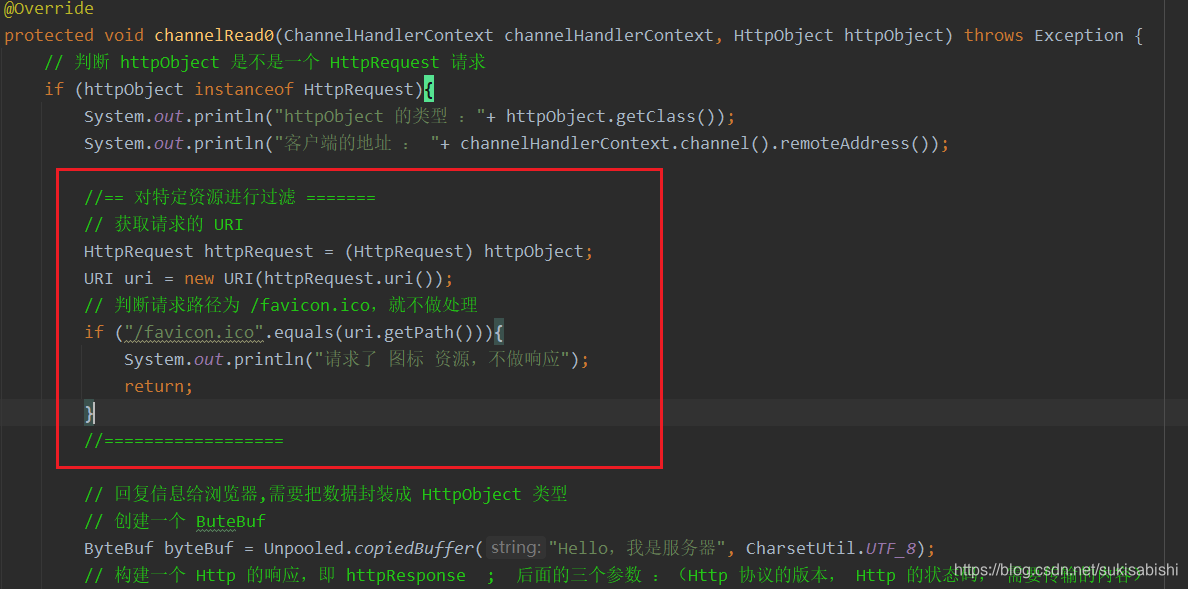
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, HttpObject httpObject) throws Exception {
// 判断 httpObject 是不是一个 HttpRequest 请求
if (httpObject instanceof HttpRequest){
System.out.println("httpObject 的类型 :"+ httpObject.getClass());
System.out.println("客户端的地址 : "+ channelHandlerContext.channel().remoteAddress());
// 回复信息给浏览器,需要把数据封装成 HttpObject 类型
// 创建一个 ButeBuf
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello,我是服务器", CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
// 构建一个 Http 的响应,即 httpResponse ; 后面的三个参数 :(Http 协议的版本, Http 的状态码, 需要传输的内容)
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK, byteBuf);
// 设置文本的类型,及字符编码
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain;charset=utf-8");
// 文本的长度
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH, byteBuf.readableBytes());
// 将构建好的 response 返回
channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}
}
```java
// 获取请求的 URI
HttpRequest httpRequest = (HttpRequest) httpObject;
URI uri = new URI(httpRequest.uri());
// 判断请求路径为 /favicon.ico,就不做处理
if ("/favicon.ico".equals(uri.getPath())){
System.out.println("请求了 图标 资源,不做响应");
return;
}
# Netty 核心模块
## Bootstrap 和 ServerBootstrap


## Future 和 ChannelFuture


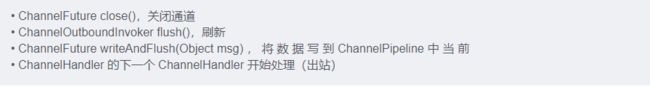
## Channel

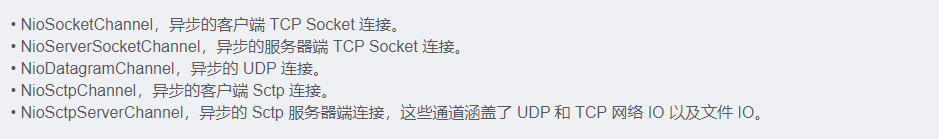
## Selector

## ChannelHandler 及其实现类

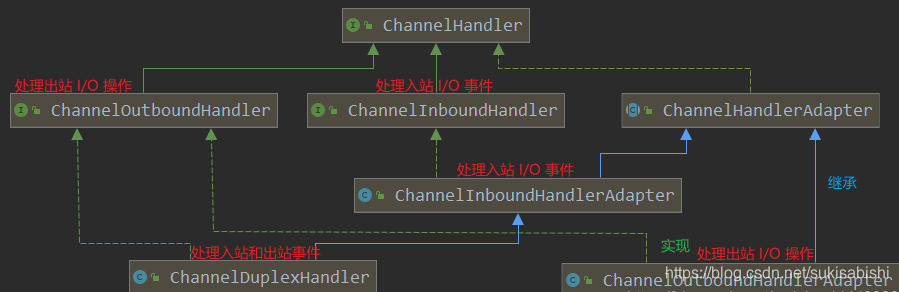
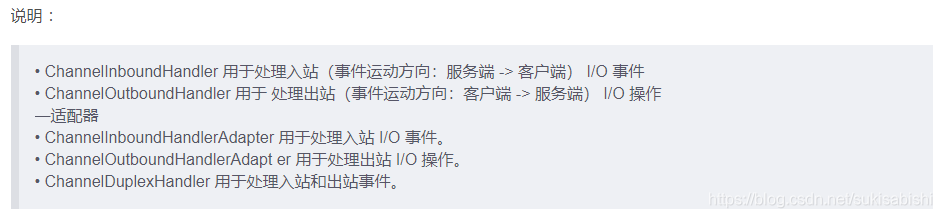

```java
public class ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter extends ChannelHandlerAdapter implements ChannelInboundHandler {
// 通道注册事件
public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelRegistered();
}
// 通道注销事件
public void channelUnregistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelUnregistered();
}
// 通道就绪事件
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelActive();
}
// 通道读取数据事件
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
// 通道读取数据完毕事件
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelReadComplete();
}
// 通道发生异常事件
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause);
}
}
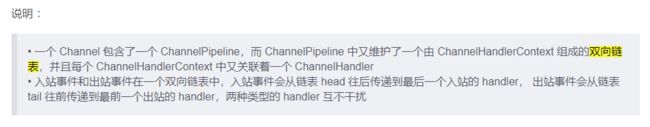
Pipeline 和 ChannelPipeline
ChannelHandlerContext
ChannelOption
EventLoopGroup 和其实现类 NioEventLoopGroup
Unpooled 类
public class ByteBuf01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个 byteBuf
/*
说明
1. 创建一个对象,该对象包含一个数组,是一个 byte[10]
2. Netty 的 Buf 存取数据,不需要像 NIO 一样使用 Filp 切换
Netty 底层维护了一个 ReaderIndex(下一个读的位置) 和 WriterIndex(下一个写的位置)
*/
ByteBuf buffer = Unpooled.buffer(10);
// 向 buf 存数据
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
buffer.writeByte(i);
}
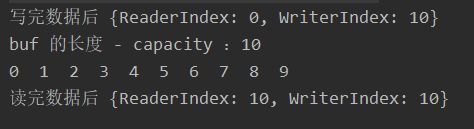
System.out.println("写完数据后 {ReaderIndex: "+buffer.readerIndex()+", WriterIndex: "+buffer.writerIndex()+"}");
System.out.println("buf 的长度 - capacity :"+ buffer.capacity());
// 输出
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.capacity(); i++) {
// 读数据的方式-1 :直接 get 第几个 byte
//System.out.println(buffer.getByte(i));
// 读数据的方式-2 :通过移动 ReaderIndex 遍历
System.out.print(buffer.readByte() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("读完数据后 {ReaderIndex: "+buffer.readerIndex()+", WriterIndex: "+buffer.writerIndex()+"}");
}
}
public class ByteBuf02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 用其他方式创建 Buf ,参数 :(存入 Buf 的文本 , 字符编码)
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("【呵呵】:Hello,Buf", CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
// 使用相关的 API
if (byteBuf.hasArray()){ // 如果有内容
// 获得 buf 中的数据
byte[] bytes = byteBuf.array();
// 转成 String 输出
System.out.println(new String(bytes, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
// 查看 ByteBuf 中真正存的是什么
System.out.println("ByteBuf : "+ byteBuf);
// 数组的偏移量
System.out.println("偏移量 :"+ byteBuf.arrayOffset());
System.out.println("WriterIndex: "+byteBuf.writerIndex());
byteBuf.getByte(0);
System.out.println("getByte 后 :ReaderIndex: "+byteBuf.readerIndex()+",可读取的字节数 :" + byteBuf.readableBytes());
byteBuf.readByte();
System.out.println("readByte 后 :ReaderIndex: "+byteBuf.readerIndex()+",可读取的字节数 :" + byteBuf.readableBytes());
// 读取某一段,参数:(起点,终点,字符集编码)
System.out.println(byteBuf.getCharSequence(9, 24, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
}
}
Netty应用实例-群聊系统
public class ChatServer {
// 端口
private int port;
/**
* 构造器
*/
public ChatServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
/**
* 处理客户端的请求
*/
public void run() throws InterruptedException {
// 创建两个线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8);
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
// 获取 Pipeline
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
// 通过 Pipeline 添加编、解码器(Netty 自带)
pipeline.addLast("decoder",new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder",new StringEncoder());
// 加入自己的 Handler
pipeline.addLast(new ChatServerHandler());
}
});
System.out.println("服务端准备完毕");
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new ChatServer(8000).run();
}
}
public class ChatServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
/**
* 定义一个 Channel 线程组,管理所有的 Channel, 参数 执行器
* GlobalEventExecutor => 全局事件执行器
* INSTANCE => 表示是单例的
*/
private static ChannelGroup channelGroup = new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
//定义一个时间的输出格式
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
/**
* 当连接建立之后,第一个被执行
* 一连接成功,就把当前的 Channel 加入到 ChannelGroup,并将上线消息推送给其他客户
*/
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 获取当前 Channel
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
// 将该客户上线的信息,推送给其他在线的 客户端
// 该方法,会将 ChannelGroup 中所有的 Channel 遍历,并发送消息
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
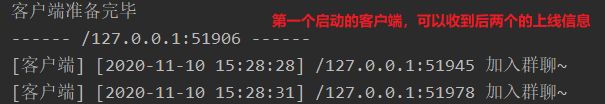
channelGroup.writeAndFlush("[客户端] ["+dateFormat.format(date)+"] "+channel.remoteAddress()+" 加入群聊~\n");
// 将当前 Channel 加入 ChannelGroup
channelGroup.add(channel);
}
/**
* 当断开连接激活,将 XXX 退出群聊消息推送给当前在线的客户
* 当某个 Channel 执行到这个方法,会自动从 ChannelGroup 中移除
*/
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
channelGroup.writeAndFlush("[客户端] ["+dateFormat.format(date)+"] "+ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + " 退出群聊~\n");
// 输出 ChannelGroup 的大小
System.out.println("==== ChannelGroup-Size : " + channelGroup.size());
}
/**
* 当 Channel 处于一个活动的状态激活,可以提示 XXX 上线
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("["+dateFormat.format(date)+"] "+ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + " 已上线~\n");
}
/**
* 当 Channel 处于不活动的状态激活,提示 XXX 离线
*/
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("["+dateFormat.format(date)+"] "+ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + " 已下线~\n");
}
/**
* 读取数据,并把读取到的数据转发给所有 客户
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, String s) throws Exception {
// 获取到 当前 Channel
Channel channel = channelHandlerContext.channel();
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
//遍历 ChannelGroup 根据不同的情况,推送不同的消息
channelGroup.forEach(ch -> {
if (ch != channel){//遍历到的当前的 ch 不是发消息的 Channel
ch.writeAndFlush("[客户端] ["+dateFormat.format(date)+"] "+channel.remoteAddress()+" 发送了消息 :"+s+"\n");
}else {// 当前 ch 就是发消息的那个客户
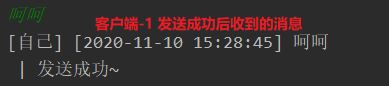
ch.writeAndFlush("[自己] ["+dateFormat.format(date)+"] "+s+" | 发送成功~\n");
}
});
}
/**
* 异常处理
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
// 关闭该通道
ctx.close();
}
}
public class ChatClient {
// 主机地址
private final String HOST;
// 端口号
private final int PORT;
public ChatClient(String HOST, int PORT) {
this.HOST = HOST;
this.PORT = PORT;
}
public void run() throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
pipeline.addLast(new ChatClientHandler());
}
});
System.out.println("客户端准备完毕");
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect(HOST, PORT).sync();
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
System.out.println("------ "+ channel.localAddress()+" ------");
// 因为客户端需要输入信息,所以需要扫描器
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()){
String s = scanner.nextLine();
// 通过 Channel 发送到 服务端
channel.writeAndFlush(s+"\r\n");
}
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new ChatClient("localhost",8000).run();
}
}
public class ChatClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, String msg) throws Exception {
// 直接输出从服务端获得的信息
System.out.println(msg.trim());
}
}
Netty心跳检测机制案例
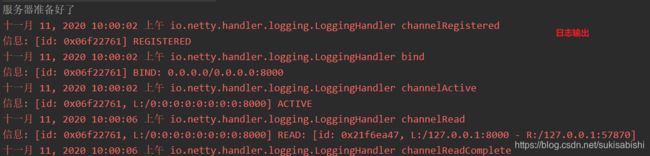
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8);
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))// 在 bossGroup 增加 日志处理器
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
/*
说明:
1. IdleStateHandler 是 Netty 提供的 空闲状态处理器
2. 四个参数:
readerIdleTime : 表示多久没有 读 事件后,就会发送一个心跳检测包,检测是否还是连接状态
writerIdleTime : 表示多久没有 写 事件后,……
allIdleTime : 表示多久 既没读也没写 后,……
TimeUnit : 时间单位
3. 当 Channel 一段时间内没有执行 读 / 写 / 读写 事件后,就会触发一个 IdleStateEvent 空闲状态事件
4. 当 IdleStateEvent 触发后,就会传递给 Pipeline 中的下一个 Handler 去处理,
通过回调下一个 Handler 的 userEventTriggered 方法,在该方法中处理 IdleStateEvent
*/
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(3, 5, 7, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
// 对 空闲检测 进一步处理的 自定义的 Handler
pipeline.addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
});
System.out.println("服务器准备好了");
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(8000).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
public class ServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
* 对 空闲事件 的处理
* @param ctx 上下文
* @param evt 传递过来的事件
* @throws Exception
*/
private int list[] = new int[3];
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
// 判断这个事件是否是 IdleStateEvent 空闲事件
if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent){
// 将 event 向下转型 => IdleStateEvent
IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
String eventType = null;
int index = -1;
// 判断具体是哪一个空闲事件
switch (event.state()){
// 读空闲
case READER_IDLE:
eventType = "读空闲";
index = 0;
break;
case WRITER_IDLE:
eventType = "写空闲";
index = 1;
break;
case ALL_IDLE:
eventType = "读写空闲";
index = 2;
break;
}
list[index] ++;
System.out.println("[超时事件] "+ctx.channel().remoteAddress()+" 发生了 "+eventType+"---第"+list[index]+"次");
System.out.println("服务器进行相应处理");
if (list[index] >= 3){
ctx.channel().close();
System.out.println("关闭该通道");
}
}
}
}
Netty 通过WebSocket编程实现服务器和客户端长连接
public class WebServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8);
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
// 因为基于 HTTP 协议,所以需要使用 HTTP 的编解码器
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
// 添加块处理器
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
/*
说明:
1. 因为 HTTP 数据传输时是分段的,HttpObjectAggregator 可以将多个端聚合
2. 这就是为什么浏览器发送大量数据时,就会发出多次 HTTP 请求
*/
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(8192));
/*
说明:
1. 对于 WebSocket 是以 帧 的形式传递的
2. 后面的参数表示 :请求的 URL
3. WebSocketServerProtocolHandler 将 HTTP 协议升级为 WebSocket 协议,即保持长连接
*/
pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/hello"));
// 自定义的 Handler
pipeline.addLast(new WebServerHandler());
}
});
System.out.println("服务器准备好了");
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(8000).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
public class WebServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> {
// TextWebSocketFrame 类型是 WebSocket 的一个子类,表示一个文本帧
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("服务器端收到消息:" + msg.text());
// 回复浏览器
channelHandlerContext.channel().writeAndFlush(
new TextWebSocketFrame("【服务器】"+ LocalDateTime.now()+" | "+msg.text()));
}
// web 连接后触发
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// id 表示标识,asLongText 输出的是唯一的,asShortText 不一定是唯一的
System.out.println("handlerAdded 被调用-- "+ctx.channel().id().asLongText()+" (LongText)");
System.out.println("handlerAdded 被调用-- "+ctx.channel().id().asShortText()+" (ShortText)");
}
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// id 表示标识,asLongText 输出的是唯一的,asShortText 不一定是唯一的
System.out.println("handlerRemoved 被调用-- "+ctx.channel().id().asLongText()+" (LongText)");
System.out.println("handlerRemoved 被调用-- "+ctx.channel().id().asShortText()+" (ShortText)");
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
System.out.println("【异常】 " + cause.getMessage());
ctx.close();
}
}
![]()
<body>
<form onsubmit="return false">
<p>输入文本</p>
<textarea id="message" name="message" style="height: 300px; width: 300px"></textarea>
<input type="button" value="发送消息" onclick="send(this.form.message.value)">
<p>回复文本</p>
<textarea id="responseText" style="height: 300px; width: 300px"></textarea>
<input type="button" value="清空内容" onclick="document.getElementById('responseText').value=''">
</form>
</body>
<script>
var socket;
// 判断当前浏览器是否支持 WebSocket
if (window.WebSocket){
socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8000/hello");
// 相当于 channelRead0 方法,ev 收到服务器端回送的消息
socket.onmessage = function (ev){
var rt = document.getElementById("responseText");
rt.value = rt.value + "\n" + ev.data;
}
// 相当于连接开启,感知到连接开启
socket.onopen = function (){
var rt = document.getElementById("responseText");
rt.value = rt.value + "\n" + "连接开启……";
}
// 感知连接关闭
socket.onclose = function (){
var rt = document.getElementById("responseText");
rt.value = rt.value + "\n" + "连接关闭……";
}
}else {
alert("不支持 WebSocket");
}
// 发送消息到服务器
function send(message){
// 判断 WebSocket 是否创建好了
if (!window.socket){
return ;
}
// 判断 WebSocket 是否开启
if (socket.readyState == WebSocket.OPEN){
// 通过 Socket 发送消息
socket.send(message);
}else {
alert("连接未开启");
}
}
</script>