C/C++ string介绍(非常详细)
文章目录
- 介绍
- 一、使用方法
- 二、使用技巧
-
- 1.capacity
- 2.size与length
- 3.resize
- 4.c_str与data
- 5.at与[]
- 6.append,+=和push_back
- 7.assign和=
- 8.compare
- 9.clear
- 10.copy
- 11.empty
- 12.erase
- 13.find,find_first_of,find_last_of,find_first_not_of,find_last_not_of以及rfind
- 14.insert
- 15.front与back
- 16.replace
- 17.substr
- 18.pop_back
- 19.reserve
- 20.shrink_to_fit
- 21.swap
- 22.begin,end,rbegin和rend
介绍
string是官方提供的一个字符串操作类,相比于传统使用char*进行字符串操作,该类提供了相当多的字符串操作函数,使得该字符串类使用起来相当方便
一、使用方法
需要包含头文件:
#include需要使用命名空间:
using namespace std; //引用命名空间
string s; //创建string对象
或者
std::string s //创建string对象
二、使用技巧
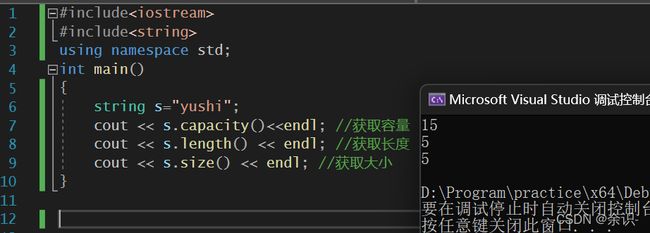
对于string类来说,首先需要了解的是容量和大小的概念
容量是指new或malloc了多少个内存,大小是指真正使用了多少内存
获得string的容量:
1.capacity
#include获取string的大小:
2.size与length
需要说明的是这两个函数没有任何区别
#include结果:
但这只是该类自动分配的内存,有时侯并不符合我们的实际需求
因为当字符串长度大于原有容量时,string类并不是在原有内存上扩展内存大小,而是重新开辟一块新内存,并将原内容复制到新内存上,这明显会降低效率
所以当我们知道自己所需要的内存大小时,可以直接从一开始就手动设置内存大小
3.resize
#include结果:
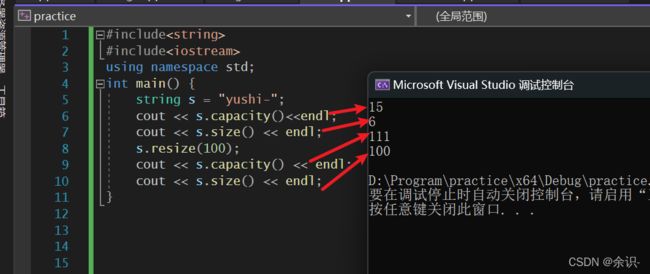
可以看到,该成员函数会直接让string大小设置到相应大小
除了容量和大小外,获取string的字符串指针也很常用
4.c_str与data
注意,这两个函数完全一样,就是返回字符串指针
#include5.at与[]
这两个是有区别的,虽然都是取出对应位置的字符,但at会进行越界检测,而[]不会
但在实际使用中,一般使用[],主要是因为方便,这个看自己习惯了
#include6.append,+=和push_back
这三个均为追加内存,主要区别是,append只能追加字符串,push_back只能追加单个字符.而+=都可以
#include
使用哪种方法,主要是看个人习惯,我比较习惯使用+=,毕竟非常方便
7.assign和=
这俩功能相同,就是给字符串赋值
#include8.compare
该函数用于比较和其它字符串的大小,按字典序比较,只有相等时返回0
#include9.clear
该函数作用如名,就是清空字符串
需要主要的是,该函数只是把字符串首个字符赋值为\0,达到清空效果
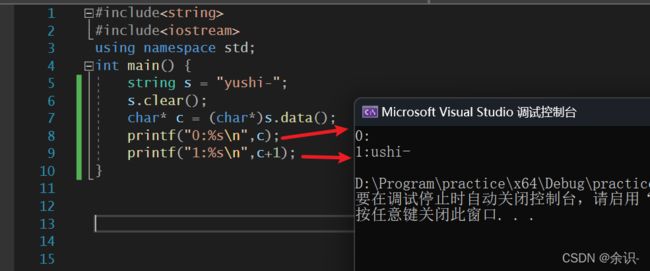
需要注意字符残留
10.copy
用于将本string中的内容复制到一个缓存区中
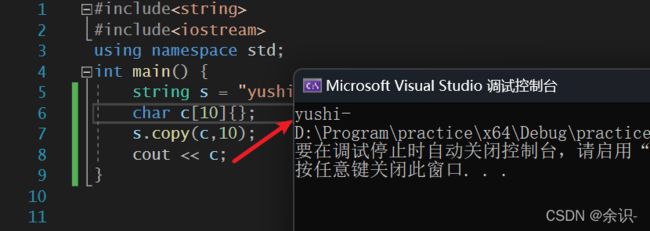
需要注意的是,该复制不会在复制后添加结束字符\0,可以事先对数组进行清零,比如我这里后面添加了{},表示清零
11.empty
该函数用来判断当前是否为空,如果为空,则返回1,否则返回0
#include12.erase
该函数用来删除字符串中的某一个字符,或某一段子字符串
注意,删除一个指定位置字符时,会截断后面的字符
#include#include13.find,find_first_of,find_last_of,find_first_not_of,find_last_not_of以及rfind
这一系列函数都是用来搜索字符或字符串用的
需要注意的是,如果搜索到结果,会返回搜到结果的第一个字符位置
如果没有搜索到结果,则返回string::npos
示例:
#include
不同搜索函数之间有细微差异,按自己需求选择函数,正常来说,一般只用得到find与rfind函数
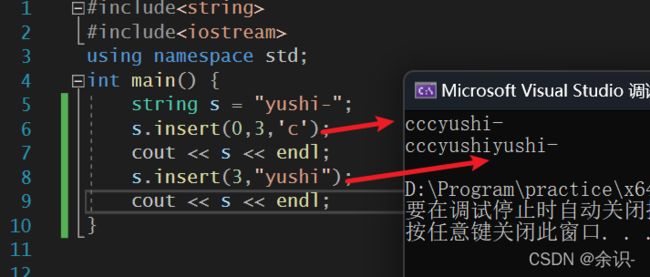
14.insert
该函数用于在字符内部指定位置插入指定字符或字符串
#include15.front与back
这两个函数用于取出第一个元素与最后一个元素
#include16.replace
替换指定范围内的字符串
#include17.substr
取出指定范围的子字符串
#include18.pop_back
去除最后一个字符
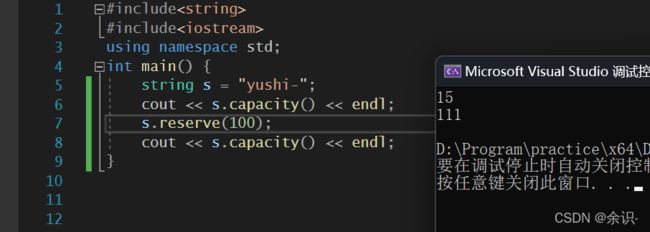
#include19.reserve
改变string的容量大小
#include20.shrink_to_fit
该函数的作用是,当实际长度比容量小太多时,会减少容量至合适的大小,避免空间浪费
#include21.swap
用于交换两个string的内容
#include22.begin,end,rbegin和rend
这四个函数用于获取迭代器,用于遍历或更改内容,所谓迭代器,可以理解为一种特殊的指针
以下代码为正反遍历一个string
#include