Android Ams对于Activity生命周期的管理
分析Activity的生命周期管理,我觉得应该先看下面两篇关于Activity的官方文档:
了解 Activity 生命周期
处理 Activity 状态更改
里面有下面一段话,比较简洁的说出了Activity生命周期。

常见的触发Activity生命周期变更的方式有几种
1 上面的Activity finish露出下面的Activity。
2 一个Activity启动另外一个Activity,然后调用者finish。
3 一个Activity启动另外一个Activity,然后调用者不finish。
4 onNewIntent。
5 通过最近任务恢复Activity。
这里面最为复杂的就是2和3这两种情况,在我们实际使用Android手机过程中,大多数情况是先调用启动Activiy再调用finish,所以很多时候3流程是流程2的一部分,也就是图1 Activity协调这段话中描述的生命周期,假设ActivityA 启动ActivityB。 整个生命周期流程是这样的。
ActivityB.onPause() -> ActivityA.onCreate() -> ActivityA.onStart()-> ActivityA.onResume()->ActivityB.onStop()

文档中还说要把执行cpu相对密集的操作放在onStop()里面。为什么这么做呢,在ActivityA刚刚启动的过程中,应该是应用最繁忙的时候,将cpu密集的操作放在ActivityB的onStop操作中会不会影响ActivityA的启动速度(ActivityA和ActivityB通常在一个进程里面,共用一个主线程)?这里Android是有考量的,ActivityB的onStop操作并不会在ActivityA.onResume执行后马上执行,要等到ActivityA所在进程的主进程进入Idle状态才会触发ActivityB的stop函数。
为了实现上述生命周期管理,ActivityManagerService的实现大概如下图:
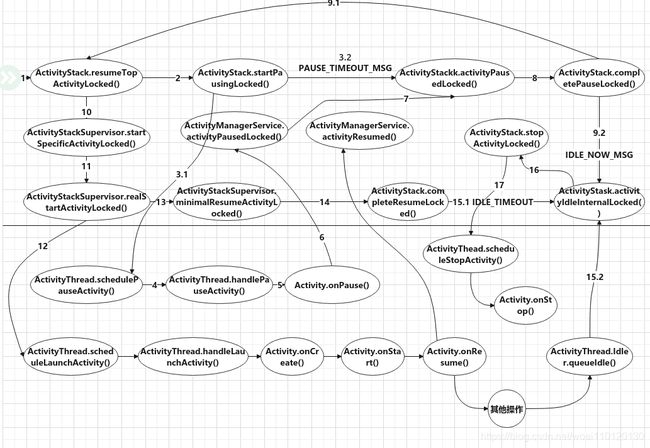
这个图看起来比较复杂,图中删除了一些中间函数,只保留了关键函数。这里我来说明下,首先在启动Activity时,在准备好stask和task后,调用ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityLocked() 函数来显示栈顶的Activity,ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityLocked() 函数可能是处理Activity的关闭,也可能处理新Activity的启动,从函数名字可以看出来,函数只是用户resume栈顶Activity。 在启动新Activity过程中,发现栈上存在resumed状态的Activity,就会先调用ActivityStack.startPausingLocked()函数来pause当前栈上resumed的Activity。 这个过程会通过ActivityThread的binder对象调用到App进程中ActivityThread.schedulePauseActivity()函数。ActivityThread.schedulePauseActivity()函数发送一个系统Message给app主线程,App主线程收到消息调用ActivityThread.handlePauseActivity()函数,ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityLocked() 返回。 App端ActivityThread.handlePauseActivity()函数会调用Activity.onPause()方法,执行完Activity.onPause() 函数后ActivityThread.handlePauseActivity()函数调用ActivityManagerService.activityPauseLock()函数通知AMS应用的Activity pause完成,这时候就可以去resume 栈上的activity了。对于ActivityStack.startPausingLocked()调用App进程来进行pause, 由于用户进程不一定可靠,有可能超时, ActivityStack.startPausingLocked()函数还留了一手,就是发送一个延时500ms的PAUSE_TIMEOUT_MSG消息出去,如果App端500ms内没有处理完Ams的pause请求,该消息就会被处理。对于PAUSE_TIME_MSG超时消息的处理(3.2),和App端调用ActivityManagerService.activityPauseLock()的情况(分支7),最终都会调用到ActivityStack.activityPauseLocked()函数。该函数调用ActivityStack.completePaused()函数来处理pause完成。 这个函数会调用ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityLocked() 函数(注意又调用了ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityLocked(),这时stack上的resume activity已经不存在了,所以不需要再pauseActivity, 直接进入启动新Activity流程, 启动新Activity是通过ActivityStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked()函数完成的,该函数调用了ActivityStackSupervisor.relStartActivityLocked()函数,最终调用到App端的ActivityThread.scheduleLaunchActivity(). 对于客户端的调用也是异步的, 客户端会依次调用Activity.onCreate(), Activity.onStart()以及Activity.onResume()。同时
ActivityStackSupervisor.relStartActivityLocked()函数会调用ActivityStackSupervisor.minimalResumeActivityLocked()函数,ActivityStackSupervisor.minimalResumeActivityLocked()函数调用ActivityStack.completeResumeLocked() 处理Activity启动完成消息(注意这里并没有等待客户端Activity.onResume()完成)。ActivityStack.completeResumeLocked() 函数会发送一个延迟10s的IDLE_TIMEOUT消息等待App端idle超时,如15.1。 同时客户端这边,当主线程MessageQueue中没有马上要处理的消息的时候会调用ActivityThread.Idler.queueIdle()函数,该函最终会调用到ActivityStack.activityIdleInternalLocked()函数处通知客户端进入idle状态(也就是不那么忙了)。这时候ActivityStack.activityIdleInternalLocked()函数就会处理之前被pause的activity的其他生命周期,如Activity.onStop(),Activity.onDestory()。 当然客户端这边也许很久才会进入idle状态(一定是一个比较差劲的开发者写了糟糕的代码),这时候就会触发IDLE_TIMEOUT消息, DLE_TIMEOUT消息的处理函数同样会调用ActivityStack.activityIdleInternalLocked()函数来执行被pause的activity后续生命周期方法。 还有一种情况需要马上执行Activity的onStop(),onDestory()等生命周期函数, 这时候发送一条IDLE_NOW消息,IDLE_NOW消息的处理函数同样会调用ActivityStack.activityIdleInternalLocked()函数来执行被pause的activity后续生命周期方法。
其实Activity生命周期相互作用的函数就onResume和onPause,这两个函数要保证时序,其他的都没有影响。
下面我们从代码来详细分析.
从ActivityManagerService对于Task的管理这篇文章我们知道Ams使用ActivityStack类管理返回栈。 使用ActivityStackSupervisor 管理多个ActivityStack,所以Activity的启动也是先经过ActivityStackSupervisor来确定启动在哪个栈上的。主要的函数就是startActivityUncheckedLocked函数。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStackSupervisor.java
final int startActivityUncheckedLocked(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor, int startFlags,
boolean doResume, Bundle options, TaskRecord inTask) {
........
ActivityStack.logStartActivity(EventLogTags.AM_CREATE_ACTIVITY, r, r.task);
targetStack.mLastPausedActivity = null;
targetStack.startActivityLocked(r, newTask, doResume, keepCurTransition, options);
......
}
startActivityUncheckedLocked 函数的逻辑其实我在ActivityManagerService->Activity启动->任务选择和Activity复用(Android 6.0) 一文中基本说明过。到了调用targetStack.startActivityLocked这一步已经代要启动一个新的Activity了。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java
2074 final void startActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, boolean newTask,
2075 boolean doResume, boolean keepCurTransition, Bundle options) {
2076 TaskRecord rTask = r.task;
2077 final int taskId = rTask.taskId;
2078 // mLaunchTaskBehind tasks get placed at the back of the task stack.
2079 if (!r.mLaunchTaskBehind && (taskForIdLocked(taskId) == null || newTask)) {
// 需要的情况把要启动的Activity对应的Task放到stack的顶部,对应把Wms侧的Task也放到栈顶
2080 // Last activity in task had been removed or ActivityManagerService is reusing task.
2081 // Insert or replace.
2082 // Might not even be in.
2083 insertTaskAtTop(rTask, r);
2084 mWindowManager.moveTaskToTop(taskId);
2085 }
2086 TaskRecord task = null;
2087 if (!newTask) {
// 对于不是新创建的Task,判断要启动的Activity对应的Task上面是否还有其他的Task有全屏的Activity。
// 如果有的话代表要启动的Activity对应的Task会被遮挡,也就不需要启动了,
// 这里把ActivityRecord移动的Task顶即可,当需要显示它的时候再启动。 同样也把AppToken添加到Wms侧的
// task上。
2088 // If starting in an existing task, find where that is...
2089 boolean startIt = true;
2090 for (int taskNdx = mTaskHistory.size() - 1; taskNdx >= 0; --taskNdx) {
2091 task = mTaskHistory.get(taskNdx);
2092 if (task.getTopActivity() == null) {
2093 // All activities in task are finishing.
2094 continue;
2095 }
2096 if (task == r.task) {
2097 // Here it is! Now, if this is not yet visible to the
2098 // user, then just add it without starting; it will
2099 // get started when the user navigates back to it.
2100 if (!startIt) {
2101 if (DEBUG_ADD_REMOVE) Slog.i(TAG, "Adding activity " + r + " to task "
2102 + task, new RuntimeException("here").fillInStackTrace());
2103 task.addActivityToTop(r);
2104 r.putInHistory();
2105 mWindowManager.addAppToken(task.mActivities.indexOf(r), r.appToken,
2106 r.task.taskId, mStackId, r.info.screenOrientation, r.fullscreen,
2107 (r.info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_SHOW_FOR_ALL_USERS) != 0,
2108 r.userId, r.info.configChanges, task.voiceSession != null,
2109 r.mLaunchTaskBehind);
2110 if (VALIDATE_TOKENS) {
2111 validateAppTokensLocked();
2112 }
2113 ActivityOptions.abort(options);
2114 return;
2115 }
2116 break;
2117 } else if (task.numFullscreen > 0) {
2118 startIt = false;
2119 }
2120 }
2121 }
2122
2123 // Place a new activity at top of stack, so it is next to interact
2124 // with the user.
2125
2126 // If we are not placing the new activity frontmost, we do not want
2127 // to deliver the onUserLeaving callback to the actual frontmost
2128 // activity
2129 if (task == r.task && mTaskHistory.indexOf(task) != (mTaskHistory.size() - 1)) {
2130 mStackSupervisor.mUserLeaving = false;
2131 if (DEBUG_USER_LEAVING) Slog.v(TAG_USER_LEAVING,
2132 "startActivity() behind front, mUserLeaving=false");
2133 }
2134
2135 task = r.task;
2136
2137 // Slot the activity into the history stack and proceed
2138 if (DEBUG_ADD_REMOVE) Slog.i(TAG, "Adding activity " + r + " to stack to task " + task,
2139 new RuntimeException("here").fillInStackTrace());
2140 task.addActivityToTop(r);
2141 task.setFrontOfTask();
2142
2143 r.putInHistory();
2144 if (!isHomeStack() || numActivities() > 0) { // 非HomeStack的清空(非桌面Activity和最近任务Activit)
......
// 设置切换动画类型
......
2173 boolean doShow = true;
2174 if (newTask) {
2175 // Even though this activity is starting fresh, we still need
2176 // to reset it to make sure we apply affinities to move any
2177 // existing activities from other tasks in to it.
2178 // If the caller has requested that the target task be
2179 // reset, then do so.
2180 if ((r.intent.getFlags() & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
// 如果reset task把要启动的Activity清掉或者从Task顶部移除则不需要显示该要启动的Activity
2181 resetTaskIfNeededLocked(r, r);
2182 doShow = topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked(null) == r;
2183 }
2184 } else if (options != null && new ActivityOptions(options).getAnimationType()
2185 == ActivityOptions.ANIM_SCENE_TRANSITION) {
// ANIM_SCENE_TRANSITION类型的切换动画不需要马上显示要启动的Activity
2186 doShow = false;
2187 }
......
// 设置startingwindow相关
......
2218 } else {
2219 // If this is the first activity, don't do any fancy animations,
2220 // because there is nothing for it to animate on top of.
// 桌面或者最近任务Activity,不需要设置动画
2221 mWindowManager.addAppToken(task.mActivities.indexOf(r), r.appToken,
2222 r.task.taskId, mStackId, r.info.screenOrientation, r.fullscreen,
2223 (r.info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_SHOW_FOR_ALL_USERS) != 0, r.userId,
2224 r.info.configChanges, task.voiceSession != null, r.mLaunchTaskBehind);
2225 ActivityOptions.abort(options);
2226 options = null;
2227 }
2228 if (VALIDATE_TOKENS) {
2229 validateAppTokensLocked();
2230 }
2231
2232 if (doResume) {
// 需要显示的Activity的情况调用resumeTopActivitiesLocked来恢复焦点栈Activity
2233 mStackSupervisor.resumeTopActivitiesLocked(this, r, options);
2234 }
2235 }
startActivityLocked函数主要判断是否要启动,对于要启动的Activity设置切换动画,设置starting window。最后对真的要显示的Activity执行mStackSupervisor.resumeTopActivitiesLocked(this, r, options)来将Activity设置成resumeActivity状态。注意resumeTopActivitiesLocked函数的名字是remumeTopActivitiesLocked,并不是start某Activity,而是要显示某个Activity,这也说明该函数的调用路径是有新的Activity启动,需要设置为栈顶的Activity为resumed状态,也可能是某个Activity关闭需要设置下面的Activity为resumed状态。所以分析该函数的时候要分这两种情况去分析。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStackSupervisor.java
2727 boolean resumeTopActivitiesLocked(ActivityStack targetStack, ActivityRecord target,
2728 Bundle targetOptions) {
2729 if (targetStack == null) {
2730 targetStack = mFocusedStack;
2731 }
2732 // Do targetStack first.
2733 boolean result = false;
2734 if (isFrontStack(targetStack)) {
2735 result = targetStack.resumeTopActivityLocked(target, targetOptions);
2736 }
2737
2738 for (int displayNdx = mActivityDisplays.size() - 1; displayNdx >= 0; --displayNdx) {
2739 final ArrayList<ActivityStack> stacks = mActivityDisplays.valueAt(displayNdx).mStacks;
2740 for (int stackNdx = stacks.size() - 1; stackNdx >= 0; --stackNdx) {
2741 final ActivityStack stack = stacks.get(stackNdx);
2742 if (stack == targetStack) {
2743 // Already started above.
2744 continue;
2745 }
2746 if (isFrontStack(stack)) {
2747 stack.resumeTopActivityLocked(null);
2748 }
2749 }
2750 }
2751 return result;
2752 }
resumeTopActivitiesLocked函数如果参数中没指定目标stack则使用焦点stack来作为候选stack,否则使用参数的stack作为候选stack。 2735如果候选stack 是焦点stack则调用stack的resumeTopActivityLocked来设置栈顶Activity状态到resumed。这里有可能候选stack不是焦点stack,则2738-2750行遍历所有屏幕上的stack,找到焦点stack来恢复焦点stack的栈顶activity到remued状态。这个遍历感觉有点多此一举。 这里我们可以知道焦点stack只有一个,就像我们的pc机桌面,同时只能操作一个窗口,某人的键盘事件会发给该窗口。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java
final boolean resumeTopActivityLocked(ActivityRecord prev, Bundle options) {
if (mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity) {
// Don't even start recursing.
return false;
}
boolean result = false;
try {
// Protect against recursion.
mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity = true;
if (mService.mLockScreenShown == ActivityManagerService.LOCK_SCREEN_LEAVING) {
mService.mLockScreenShown = ActivityManagerService.LOCK_SCREEN_HIDDEN;
mService.updateSleepIfNeededLocked();
}
result = resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(prev, options);
} finally {
mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity = false;
}
return result;
}
这里通过mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity 参数,防止两个参数的resumeTopActivityInnerLocked函数嵌套调用。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java
1561 private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, Bundle options) {
// prev可能是要关闭的Activity,也可能是要启动的Activity。
......
1576 // 删除栈顶要恢复的Activity下面所有不需要的staring window
1577 cancelInitializingActivities();
1578
// 获取要resume的activity,记住next为要设置状态为resmued的Activity。
1579 // Find the first activity that is not finishing.
1580 final ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(null);
1581
1582 // Remember how we'll process this pause/resume situation, and ensure
1583 // that the state is reset however we wind up proceeding.
1584 final boolean userLeaving = mStackSupervisor.mUserLeaving;
1585 mStackSupervisor.mUserLeaving = false;
1586
1587 final TaskRecord prevTask = prev != null ? prev.task : null;
1588 if (next == null) { // stack上已经没有可以设置为resmued的Activity
1589 // There are no more activities!
1590 final String reason = "noMoreActivities";
1591 if (!mFullscreen) {
1592 // Try to move focus to the next visible stack with a running activity if this
1593 // stack is not covering the entire screen.
// 分屏的情况这个stack上没有可显示的Activity,找到其他可见的stack设置为焦点Stack来显示上面的
//Activity(设置为resumed状态)。
1594 final ActivityStack stack = getNextVisibleStackLocked();
1595 if (adjustFocusToNextVisibleStackLocked(stack, reason)) {
1596 return mStackSupervisor.resumeTopActivitiesLocked(stack, prev, null);
1597 }
1598 }
1599 // Let's just start up the Launcher...
1600 ActivityOptions.abort(options);
1601 if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
1602 "resumeTopActivityLocked: No more activities go home");
1603 if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
1604 // Only resume home if on home display
1605 final int returnTaskType = prevTask == null || !prevTask.isOverHomeStack() ?
1606 HOME_ACTIVITY_TYPE : prevTask.getTaskToReturnTo();
// 全屏焦点stack上没有可设置为resumed状态的Activity, 如果是Home display上可以启动桌面,设置
// HomeStack为焦点stack,设置HomeStack栈顶的Activity为resmued状态。
// 否则返回false,表示没有真正执行resume activity
1607 return isOnHomeDisplay() &&
1608 mStackSupervisor.resumeHomeStackTask(returnTaskType, prev, reason);
1609 }
1610
1611 next.delayedResume = false;
1612
1613 // If the top activity is the resumed one, nothing to do.
1614 if (mResumedActivity == next && next.state == ActivityState.RESUMED &&
1615 mStackSupervisor.allResumedActivitiesComplete()) {
// 要resume的Activity已经是RESUMED状态则不需要做什么了,返回false,
// 表示没有真正执行resume activity
1616 // Make sure we have executed any pending transitions, since there
1617 // should be nothing left to do at this point.
1618 mWindowManager.executeAppTransition();
1619 mNoAnimActivities.clear();
1620 ActivityOptions.abort(options);
1621 if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
1622 "resumeTopActivityLocked: Top activity resumed " + next);
1623 if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
1624 return false;
1625 }
1626
1627 final TaskRecord nextTask = next.task;
1628 if (prevTask != null && prevTask.stack == this &&
1629 prevTask.isOverHomeStack() && prev.finishing && prev.frontOfTask) {
// 关闭Activity的分支,并且关闭Activity返回到桌面
1630 if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
1630 if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
1631 if (prevTask == nextTask) {
// 关闭的Activity上还有其他Activity,所以并不能返回到桌面,
// 设置其他Activity作为task的front activity。
1632 prevTask.setFrontOfTask();
1633 } else if (prevTask != topTask()) {
1634 // This task is going away but it was supposed to return to the home stack.
1635 // Now the task above it has to return to the home task instead.
// 要关闭的Task上面还有其他Task,设置其他task的关闭后返回到桌面
1636 final int taskNdx = mTaskHistory.indexOf(prevTask) + 1;
1637 mTaskHistory.get(taskNdx).setTaskToReturnTo(HOME_ACTIVITY_TYPE);
1638 } else if (!isOnHomeDisplay()) {
// 由于其他display上不能启动桌面stack,所以直接返回
1639 return false;
1640 } else if (!isHomeStack()){
1641 if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
1642 "resumeTopActivityLocked: Launching home next");
1643 final int returnTaskType = prevTask == null || !prevTask.isOverHomeStack() ?
1644 HOME_ACTIVITY_TYPE : prevTask.getTaskToReturnTo();
// 恢复桌面stack
1645 return isOnHomeDisplay() &&
1646 mStackSupervisor.resumeHomeStackTask(returnTaskType, prev, "prevFinished");
1647 }
1648 }
1649
......
1676 // The activity may be waiting for stop, but that is no longer
1677 // appropriate for it.
// 要设置next为resumed状态,所以从mStoppingActivities,
// mGoingToSleepActivities和mWaitingVisibleActivities中删除next。
// mStoppingActivities表示要设置为stoped的Activity,但是还没有请求客户端执行。
// 一般要等到栈顶Activity为idle状态才会设置被覆盖的Activity为stop状态,防止cpu争用。
// mGoingToSleepActivities 表示已经请求应用程序
// ActivityThread来stop该Activity,ActivityThread还没有stop完成的Activity。
// mWaitingVisibleActivities 表示要等待其他Activity可见来执行一些操作的Activity。
1678 mStackSupervisor.mStoppingActivities.remove(next);
1679 mStackSupervisor.mGoingToSleepActivities.remove(next);
1680 next.sleeping = false;
1681 mStackSupervisor.mWaitingVisibleActivities.remove(next);
1682
1683 if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH, "Resuming " + next);
1684
1685 // If we are currently pausing an activity, then don't do anything
1686 // until that is done.
1687 if (!mStackSupervisor.allPausedActivitiesComplete()) {
// 如果有其他Activity正在要进入paused状态,那么先等待其他Activity进入paused状态再来恢复焦点栈上的
// Activity。
1688 if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_PAUSE || DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE,
1689 "resumeTopActivityLocked: Skip resume: some activity pausing.");
1690 if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
1691 return false;
1692 }
1693
......
1725 // We need to start pausing the current activity so the top one
1726 // can be resumed...
// 因为系统同时只有一个焦点stack上的Activity可以作为焦点Activity为resumed状态,所以这里先把其他
// stack上的resumed状态的Activity设置为paused, 再把焦点栈上的Activity设置为paused状态。
1727 boolean dontWaitForPause = (next.info.flags&ActivityInfo.FLAG_RESUME_WHILE_PAUSING) != 0;
1728 boolean pausing = mStackSupervisor.pauseBackStacks(userLeaving, true, dontWaitForPause);
1729 if (mResumedActivity != null) {
1730 if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
1731 "resumeTopActivityLocked: Pausing " + mResumedActivity);
1732 pausing |= startPausingLocked(userLeaving, false, true, dontWaitForPause);
1733 }
1734 if (pausing) {
// 有Activity正在进入pause状态则等待pause完成,再来恢复焦点栈上Activity,这里直接返回了。
1735 if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG_STATES,
1736 "resumeTopActivityLocked: Skip resume: need to start pausing");
1737 // At this point we want to put the upcoming activity's process
1738 // at the top of the LRU list, since we know we will be needing it
1739 // very soon and it would be a waste to let it get killed if it
1740 // happens to be sitting towards the end.
1741 if (next.app != null && next.app.thread != null) {
1742 mService.updateLruProcessLocked(next.app, true, null);
1743 }
1744 if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
1745 return true;
1746 }
......
2012 }
resumeTopActivityInnerLocked代码比较长我们先分析前半部分, 前半部分主要检查stack上Activity恢复的可行性,不可行的情况要么直接返回了,要么就在其他stack上恢复了Activity返回。 经过检查后确定就要恢复当前stack上的Activity,在恢复Activity前如果发现当前stack还有resumed状态的Activity,要先将这个Activity设置成paused状态才能恢复Activity。 将resumed的Activity设置成paused状态调用的是startPausingLocked函数,我们先来分析startPausingLocked,后面再来看resumeTopActivityInnerLocked函数的后半部分(真正将Activity设置到resumed状态的代码)。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java
802 /**
803 * Start pausing the currently resumed activity. It is an error to call this if there
804 * is already an activity being paused or there is no resumed activity.
805 *
806 * @param userLeaving True if this should result in an onUserLeaving to the current activity.
807 * @param uiSleeping True if this is happening with the user interface going to sleep (the
808 * screen turning off).
809 * @param resuming True if this is being called as part of resuming the top activity, so
810 * we shouldn't try to instigate a resume here.
811 * @param dontWait True if the caller does not want to wait for the pause to complete. If
812 * set to true, we will immediately complete the pause here before returning.
813 * @return Returns true if an activity now is in the PAUSING state, and we are waiting for
814 * it to tell us when it is done.
815 */
816 final boolean startPausingLocked(boolean userLeaving, boolean uiSleeping, boolean resuming,
817 boolean dontWait) {
......
828 ActivityRecord prev = mResumedActivity;
......
// 设置 mResumedActivity为空。代表当前stack没有resumed状态的Activity.
844 mResumedActivity = null;
// mPausingActivity 为prev,表示正在pause的Activity
845 mPausingActivity = prev;
846 mLastPausedActivity = prev;
847 mLastNoHistoryActivity = (prev.intent.getFlags() & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_HISTORY) != 0
848 || (prev.info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_NO_HISTORY) != 0 ? prev : null;
849 prev.state = ActivityState.PAUSING;
850 prev.task.touchActiveTime();
851 clearLaunchTime(prev);
852 final ActivityRecord next = mStackSupervisor.topRunningActivityLocked();
853 if (mService.mHasRecents && (next == null || next.noDisplay || next.task != prev.task || uiSleeping)) {
854 prev.updateThumbnailLocked(screenshotActivities(prev), null);
855 }
856 stopFullyDrawnTraceIfNeeded();
857
858 mService.updateCpuStats();
859
860 if (prev.app != null && prev.app.thread != null) {
// Activity对应的进程还在, 调用ActivityThread.schedulePauseActivity()方法请求客户端将
// Activity设置成pause状态。
861 if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE, "Enqueueing pending pause: " + prev);
862 try {
863 EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_PAUSE_ACTIVITY,
864 prev.userId, System.identityHashCode(prev),
865 prev.shortComponentName);
866 mService.updateUsageStats(prev, false);
867 prev.app.thread.schedulePauseActivity(prev.appToken, prev.finishing,
868 userLeaving, prev.configChangeFlags, dontWait);
869 } catch (Exception e) {
870 // Ignore exception, if process died other code will cleanup.
871 Slog.w(TAG, "Exception thrown during pause", e);
872 mPausingActivity = null;
873 mLastPausedActivity = null;
874 mLastNoHistoryActivity = null;
875 }
876 } else {
// Activity对应的进程不存在,表示pause成功
877 mPausingActivity = null;
878 mLastPausedActivity = null;
879 mLastNoHistoryActivity = null;
880 }
881
882 // If we are not going to sleep, we want to ensure the device is
883 // awake until the next activity is started.
884 if (!uiSleeping && !mService.isSleepingOrShuttingDown()) {
885 mStackSupervisor.acquireLaunchWakelock();
886 }
887
888 if (mPausingActivity != null) {
889 // Have the window manager pause its key dispatching until the new
890 // activity has started. If we're pausing the activity just because
891 // the screen is being turned off and the UI is sleeping, don't interrupt
892 // key dispatch; the same activity will pick it up again on wakeup.
893 if (!uiSleeping) {
894 prev.pauseKeyDispatchingLocked();
895 } else if (DEBUG_PAUSE) {
896 Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE, "Key dispatch not paused for screen off");
897 }
898
899 if (dontWait) {
900 // If the caller said they don't want to wait for the pause, then complete
901 // the pause now.
// 不需要等待客户端完成pause,直接执行completePauseLocked表示Activity的pause已经完成。
902 completePauseLocked(false);
903 return false;
904
905 } else {
// 需要等待客户端pause完成,发送一个超时消息,防止客户端bug。
906 // Schedule a pause timeout in case the app doesn't respond.
907 // We don't give it much time because this directly impacts the
908 // responsiveness seen by the user.
909 Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(PAUSE_TIMEOUT_MSG);
910 msg.obj = prev;
911 prev.pauseTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
912 mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, PAUSE_TIMEOUT);
913 if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE, "Waiting for pause to complete...");
914 return true;
915 }
916
917 } else {
918 // This activity failed to schedule the
919 // pause, so just treat it as being paused now.
920 if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE, "Activity not running, resuming next.");
921 if (!resuming) {
// 如果不是resuming流程,那么恢复焦点task上的Activity可见
922 mStackSupervisor.getFocusedStack().resumeTopActivityLocked(null);
923 }
// 没有pausing状态的Activity,返回false。
924 return false;
925 }
926 }
startPausingLocked函数用于将stack中resumed状态的Activity(也就是mResumedActivity)设置为paused状态,我们都知道Activity的生命周期方法onPause,其实这个过程就是调用Activity的onPause方法。 所以这里通过调用ActivityThread的binder代理对象来完成,也就是887行代码。887行代码的第一个参数为appToken,通过这个token就可以在应用测找到对应的Activity。
899-904行如果不需要等待客户端完成activity的pause操作,则直接调用completePauseLocked函数来处理Activity pause完成的状态,返回false,表示pause已经完成。906到914行需要等待客户端pause完成,这时候客户端是不可靠的,可能由于某种bug不会通告Ams要pause的Activity已经完成,所以设置一个超时事件,客户端不反馈的话就按照pause完成来处理。最终都是调用completePauseLocked函数来完成Activity的pause处理。
我们来看看应用端的处理
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public final void schedulePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
boolean userLeaving, int configChanges, boolean dontReport) {
sendMessage(
finished ? H.PAUSE_ACTIVITY_FINISHING : H.PAUSE_ACTIVITY,
token,
(userLeaving ? 1 : 0) | (dontReport ? 2 : 0),
configChanges);
}
这里发送一个PAUSE_ACTIVITY消息给Android进程的主线程来处理Activity pause事件。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
private void handlePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
boolean userLeaving, int configChanges, boolean dontReport) {
ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token);
......
performPauseActivity(token, finished, r.isPreHoneycomb());
......
// Tell the activity manager we have paused.
if (!dontReport) {
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().activityPaused(token);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
}
}
}
应用端这测调用performPauseActivity函数来执行Activity.onPause 函数,然后调用ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().activityPaused(token)函数来通知Ams端Activity已经进入到paused状态。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
@Override
public final void activityPaused(IBinder token) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
synchronized(this) {
ActivityStack stack = ActivityRecord.getStackLocked(token);
if (stack != null) {
stack.activityPausedLocked(token, false);
}
}
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
找到Activity对应的stack,调用对用stack的activityPausedLocked方法。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java
928 final void activityPausedLocked(IBinder token, boolean timeout) {
929 if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE,
930 "Activity paused: token=" + token + ", timeout=" + timeout);
931
932 final ActivityRecord r = isInStackLocked(token);
933 if (r != null) {
934 mHandler.removeMessages(PAUSE_TIMEOUT_MSG, r);
935 if (mPausingActivity == r) {
936 if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG_STATES, "Moving to PAUSED: " + r
937 + (timeout ? " (due to timeout)" : " (pause complete)"));
938 completePauseLocked(true);
939 } else {
940 EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_FAILED_TO_PAUSE,
941 r.userId, System.identityHashCode(r), r.shortComponentName,
942 mPausingActivity != null
943 ? mPausingActivity.shortComponentName : "(none)");
944 if (r.finishing && r.state == ActivityState.PAUSING) {
945 if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG,
946 "Executing finish of failed to pause activity: " + r);
947 finishCurrentActivityLocked(r, FINISH_AFTER_VISIBLE, false);
948 }
949 }
950 }
951 }
activityPausedLocked函数有两个参数, 第一个参数token代表Activity的身份,通过token可以找到Ams对应的Activity 存根ActivityRecord, 第二个参数代表动用函数的原因,如果参数timeout为真表示activityPausedLocked函数是由于PAUSE_TIMEOUT消息触发的,客户端pause activity超时。 否则为客户端上报Activity pause完成。 代码934行首先清除该ActivityRecord对应的超时消息。然后判断mPausingActivity是否为参数token对应的Activity。 如果不是的话说明不是Ams端主动调用的Activity pause, 不需要处理pause activity完成,也就是说不需指定completePauseLocked,也可能是客户端别有意图的调用,如果这个Activity需要关闭则调用finishCurrentActivityLocked来执行Activity的后续生命周期。 completePauseLocked函数来处理Activity的pause状态完成。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java
994 private void completePauseLocked(boolean resumeNext) {
995 ActivityRecord prev = mPausingActivity;
996 if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE, "Complete pause: " + prev);
997
998 if (prev != null) {
999 prev.state = ActivityState.PAUSED;
1000 if (prev.finishing) {
1001 if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE, "Executing finish of activity: " + prev);
// Activity需要关闭的情况调用finishCurrentActivityLocked,注意这里不一定马上关闭Activity,
// 可能需要等待要启动的Activity进入idle状态再去执行Activity的后续生命周期方法
1002 prev = finishCurrentActivityLocked(prev, FINISH_AFTER_VISIBLE, false);
1003 } else if (prev.app != null) {
......
1009 if (prev.configDestroy) {
1010 // The previous is being paused because the configuration
1011 // is changing, which means it is actually stopping...
1012 // To juggle the fact that we are also starting a new
1013 // instance right now, we need to first completely stop
1014 // the current instance before starting the new one.
// 如果Activity的config发生变化,先销毁它准备重启
1015 if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE, "Destroying after pause: " + prev);
1016 destroyActivityLocked(prev, true, "pause-config");
1017 } else if (!hasVisibleBehindActivity() || mService.isSleepingOrShuttingDown()) {
1018 // If we were visible then resumeTopActivities will release resources before
1019 // stopping.
// 将Activity添加到mStoppingActivities中等待要启动的Activity进入idle状态后再
// 执行Activity的后续onStop生命周期。 默认情况下是等到要进入resumed状态的Activity
// 进入到idle状态后再去调用前边Activity的onStop和onDestoy等生命周期函数。
1020 mStackSupervisor.mStoppingActivities.add(prev);
1021 if (mStackSupervisor.mStoppingActivities.size() > 3 ||
1022 prev.frontOfTask && mTaskHistory.size() <= 1) {
// 这里检查如果等待执行stop生命周期的Activity超过
// 3个或者该Activity是stack中最后一个task上的最后一个Activity,执行scheduleIdleLocked尽快
// 处理Activity的后续生命周期方法。
1023 // If we already have a few activities waiting to stop,
1024 // then give up on things going idle and start clearing
1025 // them out. Or if r is the last of activity of the last task the stack
1026 // will be empty and must be cleared immediately.
1027 if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE, "To many pending stops, forcing idle");
// 发送IDLE_NOW_MSG消息
1028 mStackSupervisor.scheduleIdleLocked();
1029 } else {
// 检查是否由于其他情况需要提前执行Activity的onStop等生命周期方法
1030 mStackSupervisor.checkReadyForSleepLocked();
1031 }
1032 }
1033 } else {
1034 if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE, "App died during pause, not stopping: " + prev);
1035 prev = null;
1036 }
1037 // It is possible the activity was freezing the screen before it was paused.
1038 // In that case go ahead and remove the freeze this activity has on the screen
1039 // since it is no longer visible.
1040 prev.stopFreezingScreenLocked(true /*force*/);
1041 mPausingActivity = null;
1042 }
1043
1044 if (resumeNext) {
// 需要恢复下一个Activity的情况调用mStackSupervisor.resumeTopActivitiesLocked(
// topStack, prev, null)函数,来恢复焦点栈上顶部Activity到resumed状态,
// resumeTopActivitiesLocked这个函数前边我们分析过,最终调用到ActivityStack的
// resumeTopActivitiesLocked方法
1045 final ActivityStack topStack = mStackSupervisor.getFocusedStack();
1046 if (!mService.isSleepingOrShuttingDown()) {
1047 mStackSupervisor.resumeTopActivitiesLocked(topStack, prev, null);
1048 } else {
1049 mStackSupervisor.checkReadyForSleepLocked();
1050 ActivityRecord top = topStack.topRunningActivityLocked(null);
1051 if (top == null || (prev != null && top != prev)) {
1052 // If there are no more activities available to run,
1053 // do resume anyway to start something. Also if the top
1054 // activity on the stack is not the just paused activity,
1055 // we need to go ahead and resume it to ensure we complete
1056 // an in-flight app switch.
1057 mStackSupervisor.resumeTopActivitiesLocked(topStack, null, null);
1058 }
1059 }
1060 }
......
1086 }
completePauseLocked函数处理Activity完成pause的后续状态,会将paused状态的Activity添加到mStoppingActivities这个集合中,等待合适的时机来执行Activity的后续生命周期方法,本文一开始已经说明一般要等到要resume的Activity进程进入idle状态后再执行该Activity的onStop和onPuase方法,以免造成cpu的争抢。但是这里还是有些特殊的情况。 比如1021-1028行代码,当等待执行stop的Activity超过三个的时候,或者stack中最后一个Activity的时候。 另外ActivityStackSupervisor.checkReadyForSleepLocked函数也会检查一些情况,提前执行Activity的onStop等后续生命周期。 最后需要resume activity的情况调用mStackSupervisor.resumeTopActivitiesLocked(topStack, prev, null)函数来恢复焦点栈上的Activity。ActivityStackSupervisor的resumeTopActivitiesLocked这个函数前边我们分析过,最终调用到ActivityStack的
resumeTopActivitiesLocked方法,我们前面分析了一半ActivityStack.resumeTopActivitiesLocked方法,后面继续分析另一半
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java
1561 private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, Bundle options) {
......
// 设置相关动画
1859 ActivityStack lastStack = mStackSupervisor.getLastStack();
1860 if (next.app != null && next.app.thread != null) {
// Activity已经启动的情况next.app不为空
1861 if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH, "Resume running: " + next);
1862
1863 // This activity is now becoming visible.
1864 mWindowManager.setAppVisibility(next.appToken, true);
1865
1866 // schedule launch ticks to collect information about slow apps.
1867 next.startLaunchTickingLocked();
1868
1869 ActivityRecord lastResumedActivity =
1870 lastStack == null ? null :lastStack.mResumedActivity;
1871 ActivityState lastState = next.state;
1872
1873 mService.updateCpuStats();
1874
1875 if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG_STATES, "Moving to RESUMED: " + next + " (in existing)");
1876 next.state = ActivityState.RESUMED;
1877 mResumedActivity = next;
1878 next.task.touchActiveTime();
1879 mRecentTasks.addLocked(next.task);
1880 mService.updateLruProcessLocked(next.app, true, null);
1881 updateLRUListLocked(next);
1882 mService.updateOomAdjLocked();
1883
// 根据新的焦点Activity更新configuration
1884 // Have the window manager re-evaluate the orientation of
1885 // the screen based on the new activity order.
1886 boolean notUpdated = true;
1887 if (mStackSupervisor.isFrontStack(this)) {
1888 Configuration config = mWindowManager.updateOrientationFromAppTokens(
1889 mService.mConfiguration,
1890 next.mayFreezeScreenLocked(next.app) ? next.appToken : null);
1891 if (config != null) {
1892 next.frozenBeforeDestroy = true;
1893 }
1894 notUpdated = !mService.updateConfigurationLocked(config, next, false, false);
1895 }
1896
1897 if (notUpdated) {
// 由于配置更新导致Activity需要重新启动,计算下一个需要显示的Activity,调用
// scheduleResumeTopActivities 来进行恢复。否则返回false。
1898 // The configuration update wasn't able to keep the existing
1899 // instance of the activity, and instead started a new one.
1900 // We should be all done, but let's just make sure our activity
1901 // is still at the top and schedule another run if something
1902 // weird happened.
1903 ActivityRecord nextNext = topRunningActivityLocked(null);
1904 if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_STATES) Slog.i(TAG_STATES,
1905 "Activity config changed during resume: " + next
1906 + ", new next: " + nextNext);
1907 if (nextNext != next) {
1908 // Do over!
1909 mStackSupervisor.scheduleResumeTopActivities();
1910 }
1911 if (mStackSupervisor.reportResumedActivityLocked(next)) {
1912 mNoAnimActivities.clear();
1913 if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
1914 return true;
1915 }
1916 if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
1917 return false;
1918 }
1919
1920 try {
1921 // Deliver all pending results.
1922 ArrayList<ResultInfo> a = next.results;
1923 if (a != null) {
// 发送结果
1924 final int N = a.size();
1925 if (!next.finishing && N > 0) {
1926 if (DEBUG_RESULTS) Slog.v(TAG_RESULTS,
1927 "Delivering results to " + next + ": " + a);
1928 next.app.thread.scheduleSendResult(next.appToken, a);
1929 }
1930 }
1931
1932 if (next.newIntents != null) {
// 发送新intent
1933 next.app.thread.scheduleNewIntent(next.newIntents, next.appToken);
1934 }
1935
1936 EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_RESUME_ACTIVITY, next.userId,
1937 System.identityHashCode(next), next.task.taskId, next.shortComponentName);
1938
1939 next.sleeping = false;
1940 mService.showAskCompatModeDialogLocked(next);
1941 next.app.pendingUiClean = true;
1942 next.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(mService.mTopProcessState);
1943 next.clearOptionsLocked();
// 调用ActivityThread将Activity弄到resumed状态(因为Activity已经启动了)
1944 next.app.thread.scheduleResumeActivity(next.appToken, next.app.repProcState,
1945 mService.isNextTransitionForward(), resumeAnimOptions);
1946
1947 mStackSupervisor.checkReadyForSleepLocked();
1948
1949 if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES, "resumeTopActivityLocked: Resumed " + next);
1950 } catch (Exception e) {
1951 // Whoops, need to restart this activity!
1952 if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG_STATES, "Resume failed; resetting state to "
1953 + lastState + ": " + next);
1954 next.state = lastState;
1955 if (lastStack != null) {
1956 lastStack.mResumedActivity = lastResumedActivity;
1957 }
1958 Slog.i(TAG, "Restarting because process died: " + next);
1959 if (!next.hasBeenLaunched) {
1960 next.hasBeenLaunched = true;
1961 } else if (SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW && lastStack != null &&
1962 mStackSupervisor.isFrontStack(lastStack)) {
1963 mWindowManager.setAppStartingWindow(
1964 next.appToken, next.packageName, next.theme,
1965 mService.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(next.info.applicationInfo),
1966 next.nonLocalizedLabel, next.labelRes, next.icon, next.logo,
1967 next.windowFlags, null, true);
1968 }
// 异常了重新启动该Activity
1969 mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, false);
1970 if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
1971 return true;
1972 }
1973
1974 // From this point on, if something goes wrong there is no way
1975 // to recover the activity.
1976 try {
1977 next.visible = true;
// completeResumeLocked 完成resume activity的处理
1978 completeResumeLocked(next);
1979 } catch (Exception e) {
1980 // If any exception gets thrown, toss away this
1981 // activity and try the next one.
1982 Slog.w(TAG, "Exception thrown during resume of " + next, e);
1983 requestFinishActivityLocked(next.appToken, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null,
1984 "resume-exception", true);
1985 if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
1986 return true;
1987 }
1988 next.stopped = false;
1989
1990 } else {
// Activity 还没有启动,调用mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true)正式
// 启动Activity
1991 // Whoops, need to restart this activity!
1992 if (!next.hasBeenLaunched) {
1993 next.hasBeenLaunched = true;
1994 } else {
1995 if (SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW) {
1996 mWindowManager.setAppStartingWindow(
1997 next.appToken, next.packageName, next.theme,
1998 mService.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(
1999 next.info.applicationInfo),
2000 next.nonLocalizedLabel,
2001 next.labelRes, next.icon, next.logo, next.windowFlags,
2002 null, true);
2003 }
2004 if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH, "Restarting: " + next);
2005 }
2006 if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES, "resumeTopActivityLocked: Restarting " + next);
2007 mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true);
2008 }
2009
2010 if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
2011 return true;
2012 }
resumeTopActivityInnerLocked函数有两大分支,分别是Activity已经启动,恢复到resumed状态即可,该分支调用ActivityThread.scheduleResumeActivity 函数来执行Activity的生命周期方法到Activity的resumed状态。 第二个分支调用StackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked函数来启动Activity。 无论那个分支,最终Activity到resumed状态后都会调用completeResumeLocked函数来处理Activity进入resumed状态完成。
1088 /**
1089 * Once we know that we have asked an application to put an activity in
1090 * the resumed state (either by launching it or explicitly telling it),
1091 * this function updates the rest of our state to match that fact.
1092 */
1093 private void completeResumeLocked(ActivityRecord next) {
......
1109
// 设置IDLE超时消息,防止客户端一直不进入idle状态,等待stop的Activity无法回掉Activity的onStop方法。
1110 // schedule an idle timeout in case the app doesn't do it for us.
1111 mStackSupervisor.scheduleIdleTimeoutLocked(next);
......
1133 }
1134
void scheduleIdleTimeoutLocked(ActivityRecord next) {
if (DEBUG_IDLE) Slog.d(TAG_IDLE,
"scheduleIdleTimeoutLocked: Callers=" + Debug.getCallers(4));
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(IDLE_TIMEOUT_MSG, next);
mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, IDLE_TIMEOUT);
}
这里设置了一个等待Activity idle超时的消息。 我们前面说过Activity进入idle状态,或者IDLE_TIMEOUT,或者IDLE_NOW_MSG消息都会触发需要stop的activity的后续生命周期方法。 IDLE_TIMEOUT和 IDLE_NOW_MSG消息的发送我们前面都看到了。再来分析下应用何时进入IDLE状态。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
final void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token,
boolean clearHide, boolean isForward, boolean reallyResume) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
......
Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(new Idler());
......
在调用完Activity的onResume方法后会向应用主线程对应的MessageQueue中添加一个IdleHandler。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/MessageQueue.java
/**
* Add a new {@link IdleHandler} to this message queue. This may be
* removed automatically for you by returning false from
* {@link IdleHandler#queueIdle IdleHandler.queueIdle()} when it is
* invoked, or explicitly removing it with {@link #removeIdleHandler}.
*
* This method is safe to call from any thread.
*
* @param handler The IdleHandler to be added.
*/
public void addIdleHandler(@NonNull IdleHandler handler) {
if (handler == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("Can't add a null IdleHandler");
}
synchronized (this) {
mIdleHandlers.add(handler);
}
}
307 Message next() {
308 // Return here if the message loop has already quit and been disposed.
309 // This can happen if the application tries to restart a looper after quit
310 // which is not supported.
311 final long ptr = mPtr;
312 if (ptr == 0) {
313 return null;
314 }
315
316 int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iteration
317 int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
318 for (;;) {
319 if (nextPollTimeoutMillis != 0) {
320 Binder.flushPendingCommands();
321 }
322
323 nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);
324
325 synchronized (this) {
326 // Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found.
327 final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
328 Message prevMsg = null;
329 Message msg = mMessages;
330 if (msg != null && msg.target == null) {
331 // Stalled by a barrier. Find the next asynchronous message in the queue.
332 do {
333 prevMsg = msg;
334 msg = msg.next;
335 } while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous());
336 }
337 if (msg != null) {
338 if (now < msg.when) {
339 // Next message is not ready. Set a timeout to wake up when it is ready.
340 nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
341 } else {
342 // Got a message.
343 mBlocked = false;
344 if (prevMsg != null) {
345 prevMsg.next = msg.next;
346 } else {
347 mMessages = msg.next;
348 }
349 msg.next = null;
350 if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Returning message: " + msg);
351 msg.markInUse();
352 return msg;
353 }
354 } else {
355 // No more messages.
356 nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;
357 }
358
359 // Process the quit message now that all pending messages have been handled.
360 if (mQuitting) {
361 dispose();
362 return null;
363 }
364
365 // If first time idle, then get the number of idlers to run.
366 // Idle handles only run if the queue is empty or if the first message
367 // in the queue (possibly a barrier) is due to be handled in the future.
368 if (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0
369 && (mMessages == null || now < mMessages.when)) {
370 pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size();
371 }
372 if (pendingIdleHandlerCount <= 0) {
373 // No idle handlers to run. Loop and wait some more.
374 mBlocked = true;
375 continue;
376 }
377
378 if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) {
379 mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)];
380 }
381 mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers);
382 }
383
384 // Run the idle handlers.
385 // We only ever reach this code block during the first iteration.
386 for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) {
387 final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i];
388 mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handler
389
390 boolean keep = false;
391 try {
392 keep = idler.queueIdle();
393 } catch (Throwable t) {
394 Log.wtf(TAG, "IdleHandler threw exception", t);
395 }
396
397 if (!keep) {
398 synchronized (this) {
399 mIdleHandlers.remove(idler);
400 }
401 }
402 }
403
404 // Reset the idle handler count to 0 so we do not run them again.
405 pendingIdleHandlerCount = 0;
406
407 // While calling an idle handler, a new message could have been delivered
408 // so go back and look again for a pending message without waiting.
409 nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
410 }
411 }
MessageQueue的next()方法获取MessageQueue中的消息,如果没有马上要处理的消息就会执行308-403行代码。这段代码找到注册到系统中的mIdleHandlers调用它的queueIdle方法。
我们关注的IdleHandler是Activity的Idler,对应的MessageQueue为应用主线程的MessageQueue,也就是说等到应用主线程闲下来的时候调用Idler.queueIdle()方法。所以看下Idler如何处理吧。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
private class Idler implements MessageQueue.IdleHandler {
@Override
public final boolean queueIdle() {
ActivityClientRecord a = mNewActivities;
boolean stopProfiling = false;
if (mBoundApplication != null && mProfiler.profileFd != null
&& mProfiler.autoStopProfiler) {
stopProfiling = true;
}
if (a != null) {
mNewActivities = null;
IActivityManager am = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
ActivityClientRecord prev;
do {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, "Reporting idle of " + a +
" finished=" +
(a.activity != null && a.activity.mFinished));
if (a.activity != null && !a.activity.mFinished) {
try {
am.activityIdle(a.token, a.createdConfig, stopProfiling);
a.createdConfig = null;
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
}
prev = a;
a = a.nextIdle;
prev.nextIdle = null;
} while (a != null);
}
if (stopProfiling) {
mProfiler.stopProfiling();
}
ensureJitEnabled();
return false;
}
}
这里我们比较关注的方法就是am.activityIdle(a.token, a.createdConfig, stopProfiling),通知Ams 应用进入到了idle状态。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStackSupervisor.java
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case IDLE_TIMEOUT_MSG: {
if (DEBUG_IDLE) Slog.d(TAG_IDLE,
"handleMessage: IDLE_TIMEOUT_MSG: r=" + msg.obj);
if (mService.mDidDexOpt) {
mService.mDidDexOpt = false;
Message nmsg = mHandler.obtainMessage(IDLE_TIMEOUT_MSG);
nmsg.obj = msg.obj;
mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(nmsg, IDLE_TIMEOUT);
return;
}
// We don't at this point know if the activity is fullscreen,
// so we need to be conservative and assume it isn't.
activityIdleInternal((ActivityRecord)msg.obj);
} break;
case IDLE_NOW_MSG: {
if (DEBUG_IDLE) Slog.d(TAG_IDLE, "handleMessage: IDLE_NOW_MSG: r=" + msg.obj);
activityIdleInternal((ActivityRecord)msg.obj);
} break;
IDLE_TIMEOUT_MSG消息,IDLE_NOW_MSG和ActivityManagerService.activityIdle()方法最终都调用到了activityIdleInternal方法。
4017 void activityIdleInternal(ActivityRecord r) {
4018 synchronized (mService) {
4019 activityIdleInternalLocked(r != null ? r.appToken : null, true, null);
4020 }
4021 }
2522 // Checked.
2523 final ActivityRecord activityIdleInternalLocked(final IBinder token, boolean fromTimeout,
2524 Configuration config) {
2525 if (DEBUG_ALL) Slog.v(TAG, "Activity idle: " + token);
2526
2527 ArrayList<ActivityRecord> stops = null;
2528 ArrayList<ActivityRecord> finishes = null;
2529 ArrayList<UserState> startingUsers = null;
2530 int NS = 0;
2531 int NF = 0;
2532 boolean booting = false;
2533 boolean activityRemoved = false;
2534
2535 ActivityRecord r = ActivityRecord.forTokenLocked(token);
2536 if (r != null) {
// 移除IDLE_TIMEOUT_MSG消息
2537 if (DEBUG_IDLE) Slog.d(TAG_IDLE, "activityIdleInternalLocked: Callers="
2538 + Debug.getCallers(4));
2539 mHandler.removeMessages(IDLE_TIMEOUT_MSG, r);
2540 r.finishLaunchTickingLocked();
2541 if (fromTimeout) {
2542 reportActivityLaunchedLocked(fromTimeout, r, -1, -1);
2543 }
2544
2545 // This is a hack to semi-deal with a race condition
2546 // in the client where it can be constructed with a
2547 // newer configuration from when we asked it to launch.
2548 // We'll update with whatever configuration it now says
2549 // it used to launch.
2550 if (config != null) {
2551 r.configuration = config;
2552 }
2553
2554 // We are now idle. If someone is waiting for a thumbnail from
2555 // us, we can now deliver.
2556 r.idle = true;
2557
2558 //Slog.i(TAG, "IDLE: mBooted=" + mBooted + ", fromTimeout=" + fromTimeout);
2559 if (isFrontStack(r.task.stack) || fromTimeout) {
2560 booting = checkFinishBootingLocked();
2561 }
2562 }
2563
2564 if (allResumedActivitiesIdle()) {
2565 if (r != null) {
// 所有Activity都进入idle状态,调用app进行gc
2566 mService.scheduleAppGcsLocked();
2567 }
2568
2569 if (mLaunchingActivity.isHeld()) {
2570 mHandler.removeMessages(LAUNCH_TIMEOUT_MSG);
2571 if (VALIDATE_WAKE_LOCK_CALLER &&
2572 Binder.getCallingUid() != Process.myUid()) {
2573 throw new IllegalStateException("Calling must be system uid");
2574 }
2575 mLaunchingActivity.release();
2576 }
2577 ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null, 0);
2578 }
2579
2580 // Atomically retrieve all of the other things to do.
// 收集等待执行stop的activity到stops集合,收集要finish的activity到finishes集合
2581 stops = processStoppingActivitiesLocked(true);
2582 NS = stops != null ? stops.size() : 0;
2583 if ((NF = mFinishingActivities.size()) > 0) {
2584 finishes = new ArrayList<>(mFinishingActivities);
2585 mFinishingActivities.clear();
2586 }
2587
2588 if (mStartingUsers.size() > 0) {
2589 startingUsers = new ArrayList<>(mStartingUsers);
2590 mStartingUsers.clear();
2591 }
2592
2593 // Stop any activities that are scheduled to do so but have been
2594 // waiting for the next one to start.
2595 for (int i = 0; i < NS; i++) {
2596 r = stops.get(i);
2597 final ActivityStack stack = r.task.stack;
2598 if (stack != null) {
2599 if (r.finishing) {
// 立即执行Activity的finish后续生命周期(为什么有些情况不立即执行finish呢,因为需要切换动画)
2600 stack.finishCurrentActivityLocked(r, ActivityStack.FINISH_IMMEDIATELY, false);
2601 } else {
// 执行Activity的stop生命周期。
2602 stack.stopActivityLocked(r);
2603 }
2604 }
2605 }
2606
2607 // Finish any activities that are scheduled to do so but have been
2608 // waiting for the next one to start.
2609 for (int i = 0; i < NF; i++) {
2610 r = finishes.get(i);
2611 final ActivityStack stack = r.task.stack;
2612 if (stack != null) {
// 已经进入finishes的Activity是延迟finish的,已经吊用过finishCurrentActivityLocked,
// 这里直接调用destoy方法。
2613 activityRemoved |= stack.destroyActivityLocked(r, true, "finish-idle");
2614 }
2615 }
2616
2617 if (!booting) {
2618 // Complete user switch
2619 if (startingUsers != null) {
2620 for (int i = 0; i < startingUsers.size(); i++) {
2621 mService.finishUserSwitch(startingUsers.get(i));
2622 }
2623 }
2624 // Complete starting up of background users
2625 if (mStartingBackgroundUsers.size() > 0) {
2626 startingUsers = new ArrayList<UserState>(mStartingBackgroundUsers);
2627 mStartingBackgroundUsers.clear();
2628 for (int i = 0; i < startingUsers.size(); i++) {
2629 mService.finishUserBoot(startingUsers.get(i));
2630 }
2631 }
2632 }
2633
2634 mService.trimApplications();
2635 //dump();
2636 //mWindowManager.dump();
2637
2638 if (activityRemoved) {
2639 resumeTopActivitiesLocked();
2640 }
2641
2642 return r;
2643 }
这里主要处理等待stop的Activity和等待finish的Activity。分别调用Activity的生命周期方法来执行Activity的生命周期。不过我这里有个脑洞,手动调用Activity的一些状态上报函数来使Ams进入错乱状态来执行拒绝服务攻击。
应该写了不少错别字,希望csdn什么时候支持语法错误检查。要么准备到别处写去了。