算法基础12 —— 树进阶(二叉搜索树 + 堆—优先队列)
二叉搜索树
定义:
二叉搜索树,又叫二叉排序树、二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree)
它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树:
- 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树
性质:二叉搜索树的中序遍历结果为一个无重复数据的升序序列
判断方法:将待判断的二叉树采用中序遍历,结果保存在vector中,然后遍历vector,判断是否满足是升序并且无重复数据,不满足则不是二叉搜索树,反之则是搜索二叉树。
时间空间复杂度分析: 时间复杂度为O(N),空间复杂度为O(N)
下图就是一棵二叉搜索树
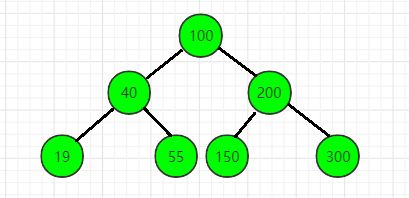
其先序遍历为(根左右):100 40 19 55 200 150 300
其中序遍历为(左根右):19 40 55 100 150 200 300
其后序遍历为(左右根):19 55 40 150 300 200 100
不难发现,其中序序列递增
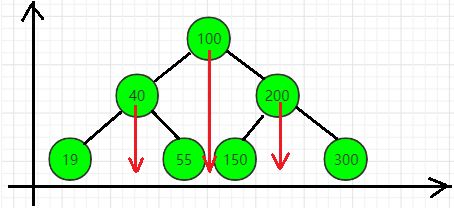
另外,对二叉搜索树进行垂直投影,可以直接得到其中序序列
代码实现:
堆 —— 优先队列
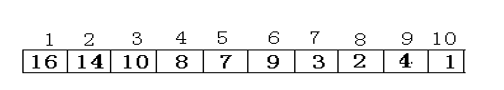
问题引入:假如有14个数,分别是99、5、36、7、22、17、46、12、2、19、25、28、1和92,请找出这14个数中最小的数。
暴力法:时间复杂度是O(N)
for(int i = 1;i <= 14;i++)
{
if (a[i] < min) min = a[i];
}
- 现在我们需要删除其中最小的数,并增加一个新数23,再次求这N个数中最小的一个数
- 该怎么办?
- 假设有N次这样的操作,那么整个时间复杂度为O(NxN)。
- 有没有效率更高的办法呢?
- 堆来解决,时间复杂度O(nlogn)
什么是堆?
定义以及存储方式:
堆结构是一种数组对象,它可以被视为一棵完全二叉树。如下图是一个大根堆:
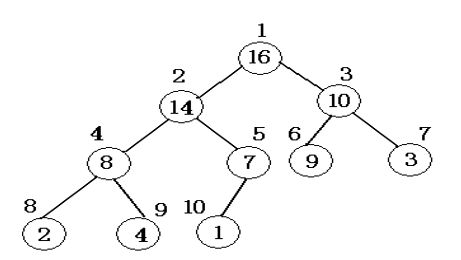
利用数组进行顺序存储:
堆的性质:
对于每个结点 i
- 如果每个结点都大于等于他的孩子结点,称为大根堆
- 反之,如果每个结点都小于等于他的孩子结点,称为小根堆
堆的操作(建堆):
一、往堆中加入一个元素的算法(put)如下:
(1) 在堆尾加入一个元素,并把这个结点置为当前结点
(2) 比较当前结点和它父结点的大小
- 如果当前结点小于父结点,则交换它们的值,并把父结点置为当前结点。转(2)
- 如果当前结点大于等于父结点,则转(3)
(3) 结束
重复n次put操作,即可建立一个小根堆。
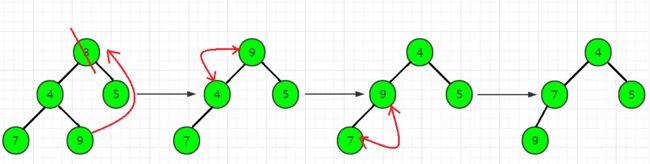
例:设n = 10,10个数依次为:3、5、1、7、6、4、2、5、4、1。建小根堆的过程如下:
第1步,读入一个数x = 3,len = 1,heap[len] = x,堆中只有一个数,必定会满足堆的性质:


第2步,读入一个数x = 5,len = 2,heap[len] = x,依然满足堆的性质:
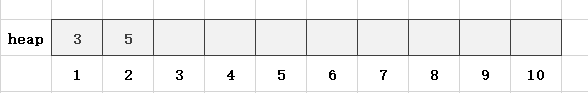

第3步,读入一个数x = 1,len = 3,heap[len] = x,此时heap[1] = 3,heap[3] = 1,不满足小根堆的性质,故需要交换heap[1]和heap[3]:
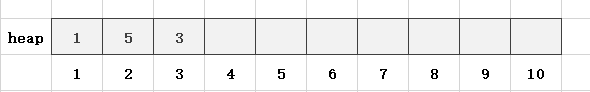

第4步,读入一个数x = 7,len = 4,heap[len] = x,满足堆的性质:
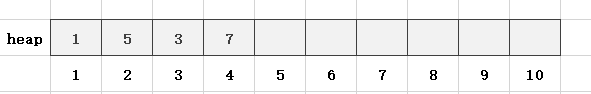
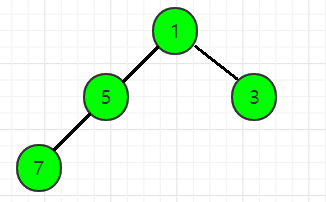
第5步,读入一个数x = 6,len = 5,heap[len] = x,满足堆的性质:
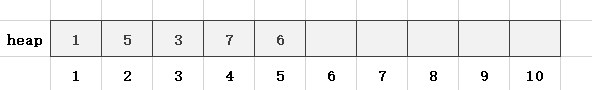

第6步,读入一个数x = 4,len = 6,heap[len] = x,满足堆的性质:
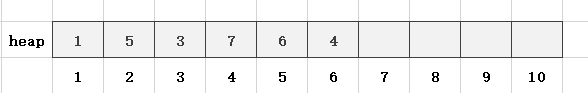
第7步,读入一个数x = 2,len = 7,heap[len] = x,此时heap[7] = 2,heap[3] = 3,不满足小根堆的性质,故需要交换heap[7]和heap[3]:
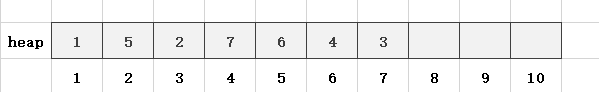

第8步,读入一个数x = 5,len = 8,heap[len] = x,此时heap[8] = 5,heap[4] = 7,不满足小根堆的性质,故需要交换heap[8]和heap[4]:
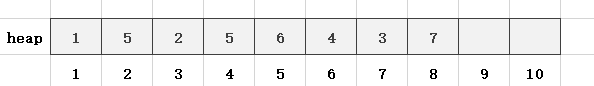
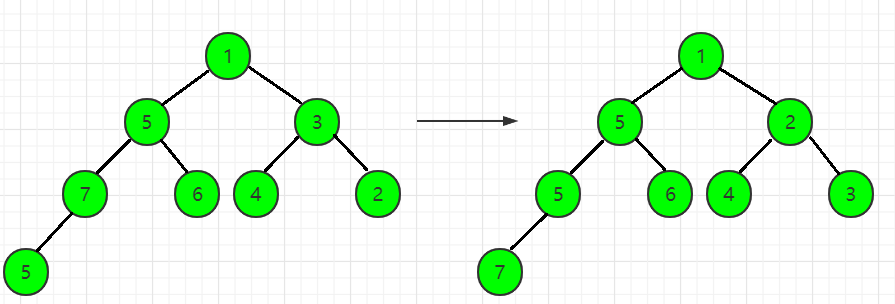
第9步,读入一个数x = 4,len = 9,heap[len] = x,此时heap[9] = 4,heap[4] = 7,不满足小根堆的性质,故需要先交换heap[9]和heap[4]:

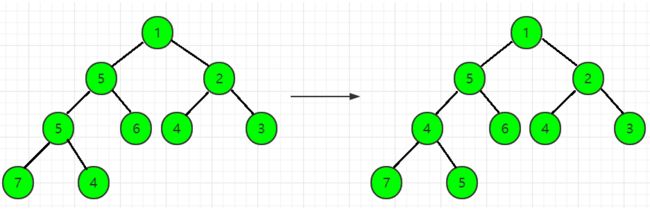
但是,经过上一步的转换之后,此时heap[2] = 5,heap[4] = 4,仍然不满足小根堆的性质,故需要继续交换heap[2]和heap[4]:
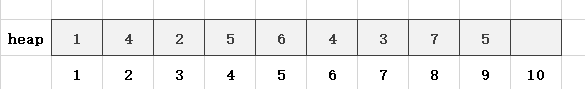
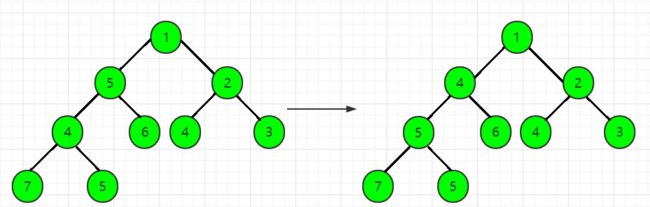
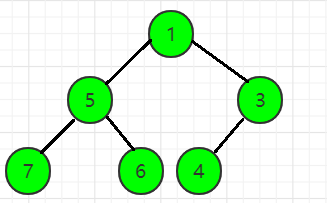
第10步,读入一个数x = 1,len = 10,heap[len] = x,先把1从heap[10]调整到heap[5],再把1从heap[5]调整到heap[2],得到最后的小根堆,如图所示:
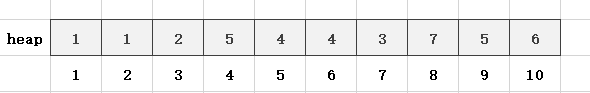

代码实现建立小根堆:
#include 输入
10
3 5 1 7 6 4 2 5 4 1
输出
1 1 2 5 4 4 3 7 5 6
堆的堆顶元素具有最值问题,例如对于一个小根堆,其堆顶元素即为最小值。同理,大根堆的堆顶元素即为最大值。当取出堆顶元素之后,剩下的n-1个结点如何继续构成一个小根堆,是一个很重要的问题。
二、从堆中取出并删除一个元素的算法(get)如下:
(1) 取出堆的根结点heap[1]的值。
(2) 把堆的最后一个结点(heap[heapSize])放到根的位置上,把根覆盖掉。把堆的长度减一
(3) 把根结点置为当前父结点pa
(4) 如果pa无儿子(2 * pa > len),则转(6);否则,把pa的两(或一)个儿子中值最小的那个置为当前的子结点son
(5) 比较pa与son的值:
- 如果pa的值小于或等于son,则转(6)
- 否则,交换这两个结点的值,把pa指向son,转(4)
(6) 结束
int get()//取出堆顶元素,heap[1]为堆顶
{
int now = 1,res = heap[1];
int next;
heap[1] = heap[heapSize];//将最后一个元素置于堆顶
heapSize --;
//重新调整为小根堆
while (now * 2 <= heapSize)//存在左孩子
{
next = now * 2;
//next < heapSize说明heapSize+1存在,然后找出左右孩子中较小的那个
if (next < heapSize && heap[next + 1] < heap[next]) next++;
if (heap[now] <= heap[next]) break;//当前结点小于等于左右孩子中较小的那个
else swap(heap[now],heap[next]);
now = next;
}
return res;
}
堆排序(heapsort)
假设n个数存放在a[1… …n]中,我们可以利用堆将它们从小到大进行排序,这种排序方法称为“堆排序”。将建堆与获取堆顶元素组合起来,就实现了堆排序。
#include 输入
10
3 5 1 7 6 4 2 5 4 1
输出
1 1 2 5 4 4 3 7 5 6
1 1 2 3 4 4 5 5 6 7
堆排序的时间复杂度为O(nlogn)