数据结构之二叉搜索树
概念
二叉搜索树又叫二叉查找树,二叉排序树;特性:任意一个点的左子树小于该点,右子树大于该点
为什么又叫做二叉排序树呢?
中序遍历一定有序,上图中序遍历为0 3 4 5 6 8
为什么叫二叉查找树?
左子树<父节点,右子树>父节点,二分查找算法,可以排除一半的空间
操作性能
| 删除 | 1、要删除的结点是叶子结点 O(1) 2、要删除的结点只有一个子树(左或者右)O(1) 3、要删除的结点有两颗子树:找后继结点,而且后继结点的左子树一定为空【后继节点:删除节点右子树最左边的节点】 |
|---|---|
| 查找 | logn |
| 插入 | logn 插入的时候每次都是和根结点比较。一直要找到它应该插入的位置。肯定会插在叶子结点。那么其实大家可以看到 插入其实就是查找 |
用途
二叉搜索树有哪些应用呢?主要用于搜索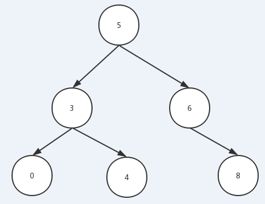 退化
退化 这也叫二叉树
这也叫二叉树
为什么(退化了)?怎么解决呢?不要变成一个链条一样
通过上面两个图我们发现,二叉树的结构就决定了其搜索的性能,那么我们应该怎么优化呢?
因此就有了AVL树和红黑树
- AVL树(自平衡二叉树):AVL属于实验室状态的,红黑树才是我们项目中用的
AVL树:平衡二叉树,它的左右子树高度之差不超过1这样确实可以避免一条直线型的结构
- 红黑树
实现二叉搜索树
MyTreeNode.java
BinarySearchTree.java
演示网站:https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/BST.html
节点定义
package datastructure.tree;
import datastructure.queue.LinkedListQueue;
/**
* 节点
*
* @author zw
* @create 2023-04-03 16:12
*/
public class MyTreeNode<T extends Comparable<T>> {
public int color; // 红黑树颜色
public int weight; //表示是频率(权重),哈夫曼树
public T data;
public MyTreeNode<T> left;
public MyTreeNode<T> right;
public MyTreeNode<T> parent;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [color=" + color + ", left=" + left.data + ", right=" + right.data + ", parent="
+ parent.data + "]" + "\r\n";
}
public MyTreeNode(T data, MyTreeNode<T> left, MyTreeNode<T> right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public MyTreeNode(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
public MyTreeNode(T data, int weight) {
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
// 用于节点的层数
public int getNodeDepth(BinaryNode root) {
return root.equals(this) ? 0 : (1 + Math.max(getNodeDepth(root.left), getNodeDepth(root.right)));
}
/**
* 查找后继节点
*
* @return
*/
public MyTreeNode findSuccessorsNode() { // 查找node的后继节点
if (this.right == null) { // 表示没有右边 那就没有后继
return this;
}
MyTreeNode cur = this.right;
MyTreeNode pre = this.right; // 开一个额外的空间 用来返回后继节点,因为我们要找到为空的时候,那么其实返回的是上一个节点
while (cur != null) {
pre = cur;
cur = cur.left; // 注意后继节点是要往左边找,因为右边的肯定比左边的大,我们要找的是第一个比根节点小的,所以只能往左边
}
return pre; // 因为cur会变成null,实际我们是要cur的上一个点,所以就是pre来代替
}
/**
* 前序遍历:根(输出) 左 右 时间复杂度?O(n) N^2 O(2*n)=>O(n);
*/
public void pre(MyTreeNode root) {
System.out.print(root.data); // 根
if (root.left != null) pre(root.left); // 左
if (root.right != null) pre(root.right); // 右
}
public void pre() {
pre(this);
}
/**
* 中序遍历:左 根(输出) 右
*/
public void in(MyTreeNode root) {
if (root.left != null) in(root.left); // 左
System.out.print(root); // 根
if (root.right != null) in(root.right); // 右
}
public void in() {
in(this);
}
/**
* 后序遍历:左 右 根(输出)
*/
public void post(MyTreeNode root) {
if (root.left != null) post(root.left); // 左
if (root.right != null) post(root.right); // 右
System.out.print(root.data); // 根
}
public void post() {
post(this);
}
/**
* 广度优先遍历:层次遍历
* 算法思想:
* (1)我们定义一个队列,先将根结点入队;
* (2)当前结点是队头结点,将其出队并访问;
* (3)若当前结点的左结点不为空将左结点入队;若当前结点的右结点不为空将其入队即可。
*/
private void bfs(MyTreeNode root) {
LinkedListQueue<MyTreeNode> queue = new LinkedListQueue<MyTreeNode>(100);
// 添加元素到队尾
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 取出队头元素
MyTreeNode head = queue.poll();
System.out.print(head.data);
// 将左节点添加到队列
if (head.left != null) queue.add(head.left);
// 将右边节点添加队列
if (head.right != null) queue.add(head.right);
}
}
public void bfs() {
bfs(this);
}
/**
* 兄弟节点
*
* @return
*/
public MyTreeNode brotherNode() {
if (this.isLeftNode()) return this.parent.right;
if (this.isRightNode()) return this.parent.left;
return null;
}
/**
* 叔叔节点
*
* @return
*/
public MyTreeNode uncleNode() {
if (this.parent == null) return null;
else if (this.parent.isLeftNode()) return this.parent.parent.right;
else if (this.parent.isRightNode()) return this.parent.parent.left;
return null;
}
/**
* 大于
*
* @param data
* @return
*/
public boolean gt(T data) {
return this.data.compareTo(data) > 0;
}
public boolean gt(MyTreeNode<T> node) {
return this.data.compareTo(node.data) > 0;
}
/**
* 等于
*
* @param data
* @return
*/
public boolean equals(T data) {
return this.data.compareTo(data) == 0;
}
/**
* 小于
*
* @param data
* @return
*/
public boolean lt(T data) {
return this.data.compareTo(data) < 0;
}
public boolean lt(MyTreeNode<T> node) {
return this.data.compareTo(node.data) < 0;
}
public boolean isRootNode() {
return this.parent == null;
}
public boolean isLeftNode() {
return this.equals(this.parent.left);
}
public boolean isRightNode() {
return this.equals(this.parent.right);
}
public boolean isLeaf() {
return this.left == null && this.right == null;
}
public boolean isLeftLeaf() {
return (this.left == null && this.right == null)
&& this.equals(this.parent.left);
}
public boolean isRightLeaf() {
return (this.left == null && this.right == null)
&& this.equals(this.parent.right);
}
/**
* 存在2个子节点
*
* @return
*/
public boolean have2ChildNode() {
return this.left != null && this.right != null;
}
/**
* 只存在左子节点
*
* @return
*/
public boolean onlyLeftChildNode() {
return this.left != null && this.right == null;
}
/**
* 只存在右子节点
*
* @return
*/
public boolean onlyRightChildNode() {
return this.left == null && this.right != null;
}
/**
* 打印当前节点树
*/
public void show() {
// 得到树的深度
int treeDepth = getTreeDepth(this);
// 最后一行的宽度为2的(n - 1)次方乘3,再加1
// 作为整个二维数组的宽度
int arrayHeight = treeDepth * 2 - 1;
int arrayWidth = (2 << (treeDepth - 2)) * 3 + 1;
// 用一个字符串数组来存储每个位置应显示的元素
String[][] res = new String[arrayHeight][arrayWidth];
// 对数组进行初始化,默认为一个空格
for (int i = 0; i < arrayHeight; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arrayWidth; j++) {
res[i][j] = " ";
}
}
// 从根节点开始,递归处理整个树
writeArray(this, 0, arrayWidth / 2, res, treeDepth);
// 此时,已经将所有需要显示的元素储存到了二维数组中,将其拼接并打印即可
for (String[] line : res) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < line.length; i++) {
sb.append(line[i]);
if (line[i].length() > 1 && i <= line.length - 1) {
i += line[i].length() > 4 ? 2 : line[i].length() - 1;
}
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
private void writeArray(MyTreeNode<T> currNode, int rowIndex, int columnIndex, String[][] res, int treeDepth) {
// 保证输入的树不为空
if (currNode == null) return;
// 先将当前节点保存到二维数组中
res[rowIndex][columnIndex] = String.valueOf(currNode.data)+"|" + String.valueOf(currNode.color);
// 计算当前位于树的第几层
int currLevel = ((rowIndex + 1) / 2);
// 若到了最后一层,则返回
if (currLevel == treeDepth)
return;
// 计算当前行到下一行,每个元素之间的间隔(下一行的列索引与当前元素的列索引之间的间隔)
int gap = treeDepth - currLevel - 1;
// 对左儿子进行判断,若有左儿子,则记录相应的"/"与左儿子的值
if (currNode.left != null) {
res[rowIndex + 1][columnIndex - gap] = "/";
writeArray(currNode.left, rowIndex + 2, columnIndex - gap * 2, res, treeDepth);
}
// 对右儿子进行判断,若有右儿子,则记录相应的"\"与右儿子的值
if (currNode.right != null) {
res[rowIndex + 1][columnIndex + gap] = "\\";
writeArray(currNode.right, rowIndex + 2, columnIndex + gap * 2, res, treeDepth);
}
}
/**
* 用于获得树的层数
*
* @return
*/
public int getTreeDepth(MyTreeNode<T> currNode) {
return currNode == null ? 0 : (1 + Math.max(getTreeDepth(currNode.left), getTreeDepth(currNode.right)));
}
}
查询操作
/**
* 查询data是否存在
*/
public MyTreeNode<T> find(MyTreeNode<T> root, T data) {
MyTreeNode<T> current = root;
while (current != null) {
if (current.gt(data)) {
current = current.left;
} else if (current.lt(data)) {
current = current.right;
} else {
return current;
}
}
return null;
}
插入操作
/**
* 插入
*
* @param currNode
* @param data
*/
public void insert(MyTreeNode<T> currNode, T data) {
// 判断应该插入左边还是右边
if (currNode.gt(data)) { // 根节点currNode >插入节点:插入左边
if (currNode.left == null) { // 左边为空则插入
MyTreeNode insertNode = new MyTreeNode(data);
currNode.left = insertNode;
insertNode.parent = currNode;
} else { // 否则继续往下查找插入位置
insert(currNode.left, data);
}
} else { // 根节点< 插入节点:插入右边
if (currNode.right == null) { // 左边为空则插入
MyTreeNode insertNode = new MyTreeNode(data);
currNode.right = insertNode;
insertNode.parent = currNode;
} else { // 否则继续往下查找插入位置
insert(currNode.right, data);
}
}
}
删除操作(必须会)
/**
* 删除节点
*
* @param root 从root节点开始查询删除
* @param data
* @return
*/
public void remove(MyTreeNode<T> root, T data) {
// 查找删除的节点
MyTreeNode<T> delNode = find(root, data);
if (delNode == null) {
return; // 要删除的值不在树中
}
// 要删除的结点是叶子结点 O(1)
System.out.println(String.format("叶子:%s\t有左子树:%s\t有右子树:%s\t有2子树:%s",
delNode.isLeaf(),delNode.onlyLeftChildNode(), delNode.onlyRightChildNode(),delNode.have2ChildNode()));
removeLeafNode(delNode);
// 要删除的结点只有一个子树(左或者右)O(1)
removeNodeOnlyOneNode(delNode);
// 要删除的结点有两颗子树:找后继结点,而且后继结点的左子树一定为空
removeNodeHaveTwoNode(delNode);
}
删除叶子节点
/**
* 删除叶子节点
*
* @param delNode
*/
private void removeLeafNode(MyTreeNode<T> delNode) {
if (delNode.isLeaf()) {
// 判断当前节点是根节点,还是左节点、右节点
if (delNode.isRootNode()) {
root = null;
} else if (delNode.isLeftNode()) { // 左节点
delNode.parent.left = null;
} else if (delNode.isRightNode()) { // 右节点
delNode.parent.right = null;
}
}
}
要删除的结点只有一个子树
/**
* 要删除的结点只有一个子树(左或者右)O(1)
*
* @param delNode
*/
private void removeNodeOnlyOneNode(MyTreeNode<T> delNode) {
// -----------删除节点只存在左节点---------------
if (delNode.onlyLeftChildNode()) {
if (delNode.isRootNode()) {
root = delNode.left;
root.parent = null;
}
// 删除节点是左节点
// parentNode
// delNode null
// leftNode
else if (delNode.isLeftNode()) { // 左节点
delNode.parent.left = delNode.left;
delNode.left.parent = delNode.parent;
}
// 删除节点是右节点
// parentNode
// null delNode
// leftNode
else if (delNode.isRightNode()) { // 右节点
delNode.parent.right = delNode.left;
delNode.left.parent = delNode.parent;
}
}
// ----------删除节点存在右节点--------------
if (delNode.onlyRightChildNode()) {
if (delNode.isRootNode()) {
root = root.right;
root.parent = null;
}
// 删除节点是左节点
// parentNode
// delNode null
// rightNode
else if (delNode.isLeftNode()) {
delNode.parent.left = delNode.right;
delNode.right.parent = delNode.parent;
}
// 删除节点是右节点
// parentNode
// null delNode
// leftNode
else if (delNode.isRightNode()) {
delNode.parent.right = delNode.right;
delNode.right.parent = delNode.parent;
}
}
}
要删除的结点有两颗子树
/**
* 要删除的结点有两颗子树
*
* @param delNode
* @param delNode
*/
private void removeNodeHaveTwoNode(@NotNull MyTreeNode<T> delNode) {
if (delNode.have2ChildNode()) {
// 查找当前节点的后继节点【第一个右节点的最左节点,后继节点左节点一定为null】
MyTreeNode<T> successorsNode = delNode.findSuccessorsNode();
System.out.println(String.format("后继节点= 叶子:%s\t有左子树:%s\t有右子树:%s\t有2子树:%s",
successorsNode.isLeaf(),successorsNode.onlyLeftChildNode(), successorsNode.onlyRightChildNode(),successorsNode.have2ChildNode()));
// 后继节点和删除节点进行交换,首先后继节点的左节点是肯定为空的
delNode.data = successorsNode.data;
// 1. 删除后继节点
// 1.1 要删除的结点是叶子结点 O(1)
// root
// a b 删除b:后继节点为f,将f和b交换,在删除b
// c d e f
removeLeafNode(successorsNode);
// 1.2 要删除的结点只有一个子树(左或者右)O(1)
// root
// a b 删除b:后继节点为h,将h和b交换,在删除b
// c d e f
// g h
removeNodeOnlyOneNode(successorsNode);
}
}
测试用例
完整代码BinarySearchTree.javaMyTreeNode.java
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchTree binarySearchTree = new BinarySearchTree();
int[] input = {15, 10, 19, 8, 13, 16, 28, 5, 9, 12, 14, 20, 30, 25};
for (int data : input) {
binarySearchTree.insert(data);
System.out.println(String.format("-------插入%s--------", data));
binarySearchTree.root.show();
}
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
int[] remove = {15, 8, 5, 12, 19, 16, 14, 30, 9, 13, 20, 28, 25, 10};
for (int data : remove) {
System.out.println(String.format("-------删除%s--------", data));
binarySearchTree.remove(data);
MyTreeNode root = binarySearchTree.root;
if (root != null) root.show();
}
}
运行结果
-------插入15--------
15
-------插入10--------
15
/
10
-------插入19--------
15
/ \
10 19
-------插入8--------
15
/ \
10 19
/
8
-------插入13--------
15
/ \
10 19
/ \
8 13
-------插入16--------
15
/ \
10 19
/ \ /
8 13 16
-------插入28--------
15
/ \
10 19
/ \ / \
8 13 16 28
-------插入5--------
15
/ \
10 19
/ \ / \
8 13 16 28
/
5
-------插入9--------
15
/ \
10 19
/ \ / \
8 13 16 28
/ \
5 9
-------插入12--------
15
/ \
10 19
/ \ / \
8 13 16 28
/ \ /
5 9 12
-------插入14--------
15
/ \
10 19
/ \ / \
8 13 16 28
/ \ / \
5 9 12 14
-------插入20--------
15
/ \
10 19
/ \ / \
8 13 16 28
/ \ / \ /
5 9 12 14 20
-------插入30--------
15
/ \
10 19
/ \ / \
8 13 16 28
/ \ / \ / \
5 9 12 14 20 30
-------插入25--------
15
/ \
10 19
/ \ / \
8 13 16 28
/ \ / \ / \
5 9 12 14 20 30
\
25
----------------------------------
-------删除15--------
叶子:false 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:true
后继节点= 叶子:true 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:false
16
/ \
10 19
/ \ \
8 13 28
/ \ / \ / \
5 9 12 14 20 30
\
25
-------删除8--------
叶子:false 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:true
后继节点= 叶子:true 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:false
16
/ \
10 19
/ \ \
9 13 28
/ / \ / \
5 12 14 20 30
\
25
-------删除5--------
叶子:true 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:false
16
/ \
10 19
/ \ \
9 13 28
/ \ / \
12 14 20 30
\
25
-------删除12--------
叶子:true 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:false
16
/ \
10 19
/ \ \
9 13 28
\ / \
14 20 30
\
25
-------删除19--------
叶子:false 有左子树:false 有右子树:true 有2子树:false
16
/ \
10 28
/ \ / \
9 13 20 30
\ \
14 25
-------删除16--------
叶子:false 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:true
后继节点= 叶子:false 有左子树:false 有右子树:true 有2子树:false
20
/ \
10 28
/ \ / \
9 13 25 30
\
14
-------删除14--------
叶子:true 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:false
20
/ \
10 28
/ \ / \
9 13 25 30
-------删除30--------
叶子:true 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:false
20
/ \
10 28
/ \ /
9 13 25
-------删除9--------
叶子:true 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:false
20
/ \
10 28
\ /
13 25
-------删除13--------
叶子:true 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:false
20
/ \
10 28
/
25
-------删除20--------
叶子:false 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:true
后继节点= 叶子:true 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:false
25
/ \
10 28
-------删除28--------
叶子:true 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:false
25
/
10
-------删除25--------
叶子:false 有左子树:true 有右子树:false 有2子树:false
10
-------删除10--------
叶子:true 有左子树:false 有右子树:false 有2子树:false
EMPTY!