字节校园精选 66 道高频经典笔面试题(含多种思路)(上)
目录
- 前言
- 第一天
-
- 21. 合并两个有序链表(简单)
- 146. LRU 缓存(中等)**
- 25. K 个一组翻转链表(困难)**
- 第二天
-
- 14. 最长公共前缀(简单)
- 3. 无重复字符的最长子串(中等)
- 124. 二叉树中的最大路径和(困难)
- 第三天
-
- 206. 反转链表(简单)
- 199. 二叉树的右视图(中等)
- bytedance-016. 最短移动距离(简单)???
- 第四天
-
- 1. 两数之和(简单)
- 15. 三数之和(中等)
- 42. 接雨水(困难)*
- 第五天
-
- 7. 整数反转(中等)
- 215. 数组中的第K个最大元素(中等)
- 23. 合并K个升序链表(困难)*
- 第六天
-
- 33. 搜索旋转排序数组(中等)*
- 54. 螺旋矩阵(中等)
- bytedance-006. 夏季特惠(简单)**
- 第七天
-
- 53. 最大子数组和(中等)
- 152. 乘积最大子数组(中等)
- 41. 缺失的第一个正数(困难)
- 第八天
-
- 20. 有效的括号(简单)
- 200. 岛屿数量(中等)
- 76. 最小覆盖子串(困难)******
- 第九天
-
- 105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树(中等)**
- 103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历(中等)
- bytedance-010. 数组组成最大数(简单)
- 第十天
-
- 94. 二叉树的中序遍历(简单)
- 102. 二叉树的层序遍历(中等)
- 394. 字符串解码(中等)
- 第十一天
-
- 415. 字符串相加(简单)
- 5. 最长回文子串(中等)**
- 72. 编辑距离(困难)**
前言
该算法链接来源于
冲刺春招-精选笔面试 66 题大通关
![]()
以下为我的学习笔记以及汇总,也为了方便其他人更加快速的浏览
第一天
21. 合并两个有序链表(简单)
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
![]()
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
提示:
两个链表的节点数目范围是 [0, 50]
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
l1 和 l2 均按 非递减顺序 排列
思路
通过递归遍历合并两个有序链表
if(list1 == null){
return list2;
}else if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}else if(list1.val >= list2.val){
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1,list2.next);
return list2;
}else if(list1.val < list2.val){
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
}
return list1;
或者通过创建头节点进行遍历
遍历的同时,头节点 和l1 l2 的下一个位置移动
以及最后谁先结束 prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
最后返回的值是头结点的下一个next
通过创建一个头节点,以及头指针遍历
关于怎么创建头节点的知识点可看我之前的文章
java中new ListNode(0)常见用法详细区别(全)
代码可能有的bug:
- 创建临时节点prehead,最后要返回这个节点的next
list1==null?pre.next=list2:pre.next=list1;这种写法错误,要写成list1==null?pre.next=list2:list1;
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// 创建头结点,一个用来存储值,一个用来遍历整个链表节点
ListNode prehead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode pre = prehead;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null){
if(list1.val >= list2.val){
pre.next = list2;
list2 =list2.next;
}else {
pre.next = list1;
list1 =list1.next;
}
// 公共的部分放在此处
pre = pre.next;
}
// 合并后 l1 和 l2 最多只有一个还未被合并完,我们直接将链表末尾指向未合并完的链表即可
pre.next = list1 == null ? list2:list1;
return prehead.next;
}
}
146. LRU 缓存(中等)**
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity) 以 正整数 作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存
int get(int key) 如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1 。
void put(int key, int value) 如果关键字 key 已经存在,则变更其数据值 value ;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组 key-value 。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过 capacity ,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例:
输入
[“LRUCache”, “put”, “put”, “get”, “put”, “get”, “put”, “get”, “get”, “get”]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
输出
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
解释
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
提示:
1 <= capacity <= 3000
0 <= key <= 10000
0 <= value <= 105
最多调用 2 * 105 次 get 和 put
思路
主要的思路是 通过哈希表加上双向链表
在java中有一个类也是这样,可以通过继承实现它来写
java之LinkedHashMap源码详细解析
public class LRUCache {
class DLinkedNode {
int key;
int value;
DLinkedNode prev;
DLinkedNode next;
public DLinkedNode() {}
public DLinkedNode(int key, int value) {this.key = key; this.value = value;}
}
private Map<Integer, DLinkedNode> map = new HashMap<Integer, DLinkedNode>();
private int size;
private int capacity;
private DLinkedNode head, tail;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
// 注意此处的差异
this.size = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
// 使用伪头部和伪尾部节点
head = new DLinkedNode();
tail = new DLinkedNode();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
DLinkedNode node= map.get(key);
if(node==null) return -1 ;
// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再移到头部
removeNode(node);
addToHead(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
DLinkedNode node=map.get(key);
if(node == null){
// 如果 key 不存在,创建一个新的节点
DLinkedNode newnode=new DLinkedNode(key,value);
// 添加进哈希表
map.put(key,newnode);
//添加头部 并且size加1
addToHead(newnode);
size++;
if(size>capacity){
//移除尾部,map删除
DLinkedNode tail=removeTail();
map.remove(tail.key);
size--;
}
}
else{
// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再修改 value,并移到头部
node.value = value;//不可省略
removeNode(node);
addToHead(node);
}
}
private void addToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
node.prev = head;
node.next = head.next;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
}
private void removeNode(DLinkedNode node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
private DLinkedNode removeTail() {
DLinkedNode res = tail.prev;
removeNode(res);
return res;
}
}
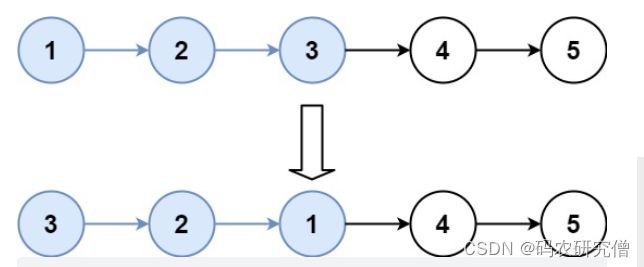
25. K 个一组翻转链表(困难)**
给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。
如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
进阶:
你可以设计一个只使用常数额外空间的算法来解决此问题吗?
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 1
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 4:
输入:head = [1], k = 1
输出:[1]
提示:
列表中节点的数量在范围 sz 内
1 <= sz <= 5000
0 <= Node.val <= 1000
1 <= k <= sz
思路:
关于这篇文章的思路,主要结合反转链表的一部分
具体在于中间的衔接点怎么使用,以及k个,前后顺序的状态
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummy=new ListNode(0);
dummy.next=head;
ListNode pre=dummy;
ListNode end=dummy;
while(end.next!=null){
for(int i=0;i<k&&end!=null;i++){
end=end.next;
}
if(end==null)break;
ListNode next=end.next;
end.next=null;
ListNode start= pre.next;
pre.next=reverse(start);
start.next=next;
pre=start;
end=start;
}
return dummy.next;
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode rear){
ListNode prev=null;
ListNode rev=rear;
while(rev!=null){
ListNode next=rev.next;
rev.next=prev;
prev=rev;
rev=next;
}
return prev;
}
}
关于以上代码可看如下类似的注解解释:
或者看官方的解释,比较易懂
图解k个一组翻转链表的解释
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//定义一个假的节点。
ListNode dummy=new ListNode(0);
//假节点的next指向head。
// dummy->1->2->3->4->5
dummy.next=head;
//初始化pre和end都指向dummy。pre指每次要翻转的链表的头结点的上一个节点。end指每次要翻转的链表的尾节点
ListNode pre=dummy;
ListNode end=dummy;
while(end.next!=null){
//循环k次,找到需要翻转的链表的结尾,这里每次循环要判断end是否等于空,因为如果为空,end.next会报空指针异常。
//dummy->1->2->3->4->5 若k为2,循环2次,end指向2
for(int i=0;i<k&&end != null;i++){
end=end.next;
}
//如果end==null,即需要翻转的链表的节点数小于k,不执行翻转。
if(end==null){
break;
}
//先记录下end.next,方便后面链接链表
ListNode next=end.next;
//然后断开链表
end.next=null;
//记录下要翻转链表的头节点
ListNode start=pre.next;
//翻转链表,pre.next指向翻转后的链表。1->2 变成2->1。 dummy->2->1
pre.next=reverse(start);
//翻转后头节点变到最后。通过.next把断开的链表重新链接。
start.next=next;
//将pre换成下次要翻转的链表的头结点的上一个节点。即start
pre=start;
//翻转结束,将end置为下次要翻转的链表的头结点的上一个节点。即start
end=start;
}
return dummy.next;
}
//链表翻转
// 例子: head: 1->2->3->4
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
//单链表为空或只有一个节点,直接返回原单链表
if (head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//前一个节点指针
ListNode preNode = null;
//当前节点指针
ListNode curNode = head;
//下一个节点指针
ListNode nextNode = null;
while (curNode != null){
nextNode = curNode.next;//nextNode 指向下一个节点,保存当前节点后面的链表。
curNode.next=preNode;//将当前节点next域指向前一个节点 null<-1<-2<-3<-4
preNode = curNode;//preNode 指针向后移动。preNode指向当前节点。
curNode = nextNode;//curNode指针向后移动。下一个节点变成当前节点
}
return preNode;
}
}
第二天
14. 最长公共前缀(简单)
题目:
编写一个函数来查找字符串数组中的最长公共前缀。
如果不存在公共前缀,返回空字符串 “”。
示例 1:
输入:strs = [“flower”,“flow”,“flight”]
输出:“fl”
示例 2:
输入:strs = [“dog”,“racecar”,“car”]
输出:“”
解释:输入不存在公共前缀。
提示:
1 <= strs.length <= 200
0 <= strs[i].length <= 200
strs[i] 仅由小写英文字母组成
思路:
通过对比所有的列,一列一列比较
终止条件有两个(通过两个for进行遍历,而且实时刻刻都是只有一个第一行的每一列进行比较strs[0].charAt(j)
- 这一列的长度等于其遍历的当前列的长度
strs[i].length()==j - 不同列的相同位置
strs[i].charAt(j)!=strs[0].charAt(j)
如果执行完都不返回的话,最后就是本身,输出strs【0】即可
字符串数组,有两个区别,取全部的字符串长度,则为strs.length;,取单个数组内部的字符串则为strs[0].length()(容易弄混)
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
int m = strs.length;
// 长度返回需要注意,此处为字符串的长度
int n = strs[0].length();
for(int j = 0;j < n;j++){
// 不从1开始,自动把第一行作为基准进行比较
for(int i = 1;i < m;i++){
// 提前结束的条件,一个是判断结束,一个是不相等提前结束
if(strs[i].length() == j || strs[i].charAt(j) != strs[0].charAt(j)){
// substring 而不是subString
return strs[0].substring(0,j);
}
}
}
return strs[0];
}
}
另外一种思路是,对比每一行的,一行一行的比较。最后输出其结果即可
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
int m = strs.length;
String prefix = strs[0];
for(int i = 1;i < m;i++){
// strs[i].length() 此处为字符串的数组长度,为length()
int length = Math.min(strs[i].length(),prefix.length());
int j;
// 此处的长度,为两者字符串的最小值
for(j = 0;j < length;j++){
if(strs[i].charAt(j) != prefix.charAt(j)){
break;
}
}
//int index=0;
//while(index
//prefix=strs[i].substring(0,index);
prefix = strs[i].substring(0,j);
}
return prefix;
}
}
3. 无重复字符的最长子串(中等)
题目:
给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
示例 1:
输入: s = “abcabcbb”
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “abc”,所以其长度为 3。
示例 2:
输入: s = “bbbbb”
输出: 1
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “b”,所以其长度为 1。
示例 3:
输入: s = “pwwkew”
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “wke”,所以其长度为 3。
请注意,你的答案必须是 子串 的长度,“pwke” 是一个子序列,不是子串。
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
s 由英文字母、数字、符号和空格组成
思路:
通过遍历数组,为了减少一次遍历,可以通过set集合进行遍历
如果出现重复,则删除第一个节点,继续开始从第二个节点开始遍历(因为从第一个节点到查重重复 是不能算入子串的)
集合已经添加进入了,第二个指针可以不用挪到最开始的地方。
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
Set<Character>set=new HashSet<>();
int n=s.length();
int ans=0,rk=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(i!=0) set.remove(s.charAt(i-1));
while(rk<n&&!set.contains(s.charAt(rk))){
set.add(s.charAt(rk));
rk++;
}
ans=Math.max(ans,rk-i);
}
return ans;
}
}
以上是因为rk的节点,每次都会往右在挪一个节点位置,所以不用减1
如果rk节点要想减1,可以通过下面的代码设置
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
// 哈希集合,记录每个字符是否出现过
Set<Character> occ = new HashSet<Character>();
int n = s.length();
// 右指针,初始值为 -1,相当于我们在字符串的左边界的左侧,还没有开始移动
int rk = -1, ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (i != 0) {
// 左指针向右移动一格,移除一个字符
occ.remove(s.charAt(i - 1));
}
while (rk + 1 < n && !occ.contains(s.charAt(rk + 1))) {
// 不断地移动右指针
occ.add(s.charAt(rk + 1));
++rk;
}
// 第 i 到 rk 个字符是一个极长的无重复字符子串
ans = Math.max(ans, rk - i + 1);
}
return ans;
}
}
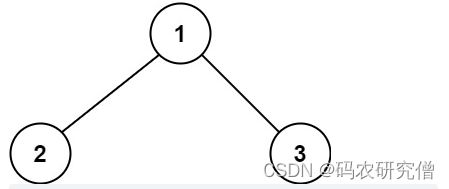
124. 二叉树中的最大路径和(困难)
题目:124. 二叉树中的最大路径和
路径 被定义为一条从树中任意节点出发,沿父节点-子节点连接,达到任意节点的序列。同一个节点在一条路径序列中 至多出现一次 。该路径 至少包含一个 节点,且不一定经过根节点。
路径和 是路径中各节点值的总和。
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其 最大路径和 。
输入:root = [1,2,3]
输出:6
解释:最优路径是 2 -> 1 -> 3 ,路径和为 2 + 1 + 3 = 6
输入:root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:42
解释:最优路径是 15 -> 20 -> 7 ,路径和为 15 + 20 + 7 = 42
提示:
树中节点数目范围是 [1, 3 * 104]
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
class Solution {
// 可以为负值,所以最大值设置为 Integer.MIN_VALUE
int maxsum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
maxGain(root);
return maxsum;
}
public int maxGain(TreeNode node){
// 递归的终止条件,如果没有终止条件无法递归
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
// 自上而下的递归
int leftGain = Math.max(maxGain(node.left),0);
int rightGain = Math.max(maxGain(node.right),0);
// 全局变量赋值求cur 的maxsum
int cur = leftGain + rightGain + node.val;
maxsum = Math.max(cur,maxsum);
// 递归的返回值,一个节点不能同时走两个方向,求一个方向最大值即可
return node.val + Math.max(leftGain,rightGain);
}
}
第三天
206. 反转链表(简单)
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
![]()
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
![]()
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 5000]
-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
1.思路一:
ListNode rear可以在任何时刻定义
也可直接使用ListNode rear=cur.next;
返回的是pre指针,而不是cur指针也不是head指针
具体的逻辑思路如下
![]()
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 定义三个指针,前中后
ListNode cur = head,pre = null;
ListNode rear = null;
// 这种判断只需要 纠正一个方向即可,如果纠正两个方向,条件需要改变
while(cur != null){
rear = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = rear;
}
return pre;
}
}
中途的错误做法:
只截取上面片段代码作为讲解:
将rear=cur.next;放在while里面最后定义,rear已经越界了
ListNode cur=head,pre=null;
ListNode rear;
while(cur!=null){
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=rear;
rear=cur.next;
}
2.思路二:
使用递归的条件进行反转
递这个用法用在了层层递进
归这个用法用在了每一层的特殊情节,也就是两个链表地址空间的反转
![]()
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 终止条件,特别是head.next == null 这个 条件不可少
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 用head.next遍历递归,利用指针记住当前位置
ListNode newhead = reverseList(head.next);
// 遍历的交换
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newhead;
}
}
199. 二叉树的右视图(中等)
题目:
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
示例 1:
输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
输出: [1,3,4]
示例 2:
输入: [1,null,3]
输出: [1,3]
示例 3:
输入: []
输出: []
提示:
二叉树的节点个数的范围是 [0,100]
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
思路:
主要的思路是层次遍历的应用,在每一层的最后一个节点输出即可
对层次遍历熟悉就好操作
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null)return list;
LinkedList<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(root);
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int n = que.size();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
TreeNode node = que.poll();
if(i == n - 1)list.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) que.offer(node.left);
if(node.right != null) que.offer(node.right);
}
}
return list;
}
}
bytedance-016. 最短移动距离(简单)???
题目:bytedance-016. 最短移动距离
这道题没想出来
给出如下题目,如果有大佬想出来,可评论区留言
给定一棵 n 个节点树。节点 1 为树的根节点,对于所有其他节点 i,它们的父节点编号为 floor(i/2) (i 除以 2 的整数部分)。在每个节点 i 上有 a[i] 个房间。此外树上所有边均是边长为 1 的无向边。
树上一共有 m 只松鼠,第 j 只松鼠的初始位置为 b[j],它们需要通过树边各自找到一个独立的房间。请为所有松鼠规划一个移动方案,使得所有松鼠的总移动距离最短。
格式:
输入:
- 输入共有三行。
- 第一行包含两个正整数 n 和 m,表示树的节点数和松鼠的个数。
- 第二行包含 n 个自然数,其中第 i 个数表示节点 i 的房间数 a[i]。
- 第三行包含 m 个正整数,其中第 j 个数表示松鼠 j 的初始位置 b[j]。
输出:- 输出一个数,表示 m 只松鼠各自找到独立房间的最短总移动距离。
示例:
输入:
5 4
0 0 4 1 1
5 4 2 2
输出:4
解释:前两只松鼠不需要移动,后两只松鼠需要经节点 1 移动到节点 3
提示:
对于 30% 的数据,满足 n,m <=100。
对于 50% 的数据,满足 n,m <=1000。
对于所有数据,满足 n,m<=100000,0<=a[i]<=m, 1<=b[j]<=n。
由于样例太少,给出两个反例:
31 2
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0
13 26
输出为3
63 2
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 13
输出为4
有想出来的大佬可评论留言
第四天
1. 两数之和(简单)
题目:
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
输出:[0,1]
解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
输出:[1,2]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [3,3], target = 6
输出:[0,1]
提示:
2 <= nums.length <= 104
-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
-109 <= target <= 109
只会存在一个有效答案
进阶:你可以想出一个时间复杂度小于 O(n2) 的算法吗?
思路:
常规的思路可以使用暴力遍历,但是复杂度比较高
可以使用哈希表的存储进行存取
此处不可用set,因为返回的类型为下标值,所以用map最合适,可以通过map。get获取下标
通过target-nums【i】进行获取
而且map哈希中是containsKey,返回一个数组类型是new int[]{map.get(target-nums[i]),i};
如果为空值则为return new int[0];
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int n = nums.length;
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
// 对应如果只存在,则进行添加两个值
if(map.containsKey(target - nums[i])){
return new int[]{map.get(target - nums[i]),i};
}
map.put(nums[i],i);
}
// 返回初始数组的默认值
return new int[0];
}
}
15. 三数之和(中等)
题目:
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [0]
输出:[]
提示:
0 <= nums.length <= 3000
-105 <= nums[i] <= 105
思路:
先排序,步步逼近双指针
最主要的条件是 去重而且一开始大于0都要去掉
通过判定总值 跟0的比较,移动指针的位置,使用while一直移动指针,而且最后还要前进一个,如果是L++ 最后要在进一个L。++L是最合适的。再者使用while的同时 一直不会跳出大循环,所以每个小循环都要L 列表中添加数组,主要通过这个函数进行转换: 关于这部分的解答 更详细的题解 可看如下链接: 题目:42. 接雨水 给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。 示例 1: 输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 示例 2: 输入:height = [4,2,0,3,2,5] 提示: n == height.length 思路: 动态规划:(下雨后水能到达的最大高度等于下标 i两边的最大高度的最小值,下标 i处能接的雨水量等于下标 i 处的水能到达的最大高度减去 height[i]) 题目 给你一个 32 位的有符号整数 x ,返回将 x 中的数字部分反转后的结果。 如果反转后整数超过 32 位的有符号整数的范围 [−231, 231 − 1] ,就返回 0。 假设环境不允许存储 64 位整数(有符号或无符号)。 示例 1: 输入:x = 123 示例 2: 输入:x = -123 示例 3: 输入:x = 120 示例 4: 输入:x = 0 提示: -231 <= x <= 231 - 1 思路一: 【leetcode】数学 - 回文数 但是有个前提条件,而且可以是负数 题目: 给定整数数组 nums 和整数 k,请返回数组中第 k 个最大的元素。 请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。 示例 1: 输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4] 和 k = 2 示例 2: 输入: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6] 和 k = 4 提示: 1 <= k <= nums.length <= 104 思路: 使用快排的思路将其遍历出来 其快排代码思路如下: 也可使用堆的思想,本身优先队列就有堆的思想:(具体可看我以下文章) 题目:23. 合并K个升序链表 给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。 请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。 示例 1: 输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] 示例 2: 输入:lists = [] 示例 3: 输入:lists = [[]] 提示: k == lists.length 用优先队列的思想 题目: 整数数组 nums 按升序排列,数组中的值 互不相同 。 在传递给函数之前,nums 在预先未知的某个下标 k(0 <= k < nums.length)上进行了 旋转,使数组变为 [nums[k], nums[k+1], …, nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], …, nums[k-1]](下标 从 0 开始 计数)。例如, [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 在下标 3 处经旋转后可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] 。 给你 旋转后 的数组 nums 和一个整数 target ,如果 nums 中存在这个目标值 target ,则返回它的下标,否则返回 -1 。 示例 1: 输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0 示例 2: 输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3 示例 3: 输入:nums = [1], target = 0 提示: 1 <= nums.length <= 5000 进阶:你可以设计一个时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的解决方案吗? 思路: 采用二分查找的方法 将数组一分为二,其中一定有一个是有序的,另一个可能是有序,也能是部分有序。 题目: 给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。 示例 1: 输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] 示例 2: 输入:matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]] 提示: m == matrix.length n == matrix[i].length 思路: 一个循环一个循环的输出,同时要在每个循环中加一个判断,随时计数器结束就停止循环,不然会出现下方某个错误 每个条件中要加入 题目:bytedance-006. 夏季特惠 某公司游戏平台的夏季特惠开始了,你决定入手一些游戏。现在你一共有X元的预算,该平台上所有的 n 个游戏均有折扣,标号为 i 的游戏的原价 ai元,现价只要 bi 元(也就是说该游戏可以优惠 ai - bi元)并且你购买该游戏能获得快乐值为 wi。由于优惠的存在,你可能做出一些冲动消费导致最终买游戏的总费用超过预算,但只要满足获得的总优惠金额不低于超过预算的总金额,那在心理上就不会觉得吃亏。现在你希望在心理上不觉得吃亏的前提下,获得尽可能多的快乐值。 格式: 输入: 示例 1: 输入: 示例 2: 输入: 示例 3: 输入: 提示: 所有输入均为整型数 题目: 子数组 是数组中的一个连续部分。 示例 1: 输入:nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4] 示例 2: 输入:nums = [1] 示例 3: 输入:nums = [5,4,-1,7,8] 提示: 1 <= nums.length <= 105 进阶:如果你已经实现复杂度为 O(n) 的解法,尝试使用更为精妙的 分治法 求解。 具体思路如下: 通过动态规划的思路进行滚动数组 题目: 给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你找出数组中乘积最大的非空连续子数组(该子数组中至少包含一个数字),并返回该子数组所对应的乘积。 测试用例的答案是一个 32-位 整数。 子数组 是数组的连续子序列。 示例 1: 输入: nums = [2,3,-2,4] 示例 2: 输入: nums = [-2,0,-1] 提示: 1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 104 因为可能为负数,所以要保存最大值和最小值。再者,定义的总数一开始就不应该为0,而是 具体代码如下: 题目:41. 缺失的第一个正数 给你一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,请你找出其中没有出现的最小的正整数。 请你实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 并且只使用常数级别额外空间的解决方案。 示例 1: 输入:nums = [1,2,0] 示例 2: 输入:nums = [3,4,-1,1] 示例 3: 输入:nums = [7,8,9,11,12] 提示: 1 <= nums.length <= 5 * 105 原地置换的思想: 还有一种思路是哈希表: 题目: 给定一个只包括 ‘(’,‘)’,‘{’,‘}’,‘[’,‘]’ 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。 有效字符串需满足: 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。 示例 1: 输入:s = “()” 示例 2: 输入:s = “()[]{}” 示例 3: 输入:s = “(]” 示例 4: 输入:s = “([)]” 示例 5: 输入:s = “{[]}” 提示: 1 <= s.length <= 104 思路: 注意一个代码格式: 通过哈希表存储其键值对 不使用map集合: 题目: 给你一个由 ‘1’(陆地)和 ‘0’(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。 岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。 此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。 示例 1: 输入:grid = [ 示例 2: 输入:grid = [ 提示: m == grid.length n == grid[i].length 思路: 通过深度优先遍历,将其遍历过后的数字都变为一个0,也就是状态变量 上面的思路是修改了原数组,如果不想修改原数组,增加一个状态变量的数组,具体代码如下:(核心代码如下) 题目:76. 最小覆盖子串 给你一个字符串 s 、一个字符串 t 。返回 s 中涵盖 t 所有字符的最小子串。如果 s 中不存在涵盖 t 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 “” 。 注意: 对于 t 中重复字符,我们寻找的子字符串中该字符数量必须不少于 t 中该字符数量。 示例 1: 输入:s = “ADOBECODEBANC”, t = “ABC” 示例 2: 输入:s = “a”, t = “a” 示例 3: 输入: s = “a”, t = “aa” 提示: 1 <= s.length, t.length <= 105 进阶:你能设计一个在 o(n) 时间内解决此问题的算法吗? 这道题没啥思路,用的是官方题解: 题目: 给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历, inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。 示例 1: 输入: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1] 提示: 1 <= preorder.length <= 3000 思路一: 使用递归的思路,因为先序遍历的第一个头节点是关键,因为他是根节点,与中序遍历的根节点相同,中序遍历的左子树,以及右子树就可区分,以此类推,就可找到其构建的二叉树 题目: 给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 锯齿形层序遍历 。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。 输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 示例 2: 输入:root = [1] 示例 3: 输入:root = [] 提示: 树中节点数目在范围 [0, 2000] 内 思路: 通过层次遍历,在内部的列表中使用的是双端队列,如果存储1 23 的时候,通过存放为1 32.因为是双端队列,32 存放的时候是通过offerFirst进行存储 另一种思路是不使用双端队列 题目:bytedance-010. 数组组成最大数 自定义排序 给定一组非负整数,重新排列它们的顺序使之组成一个最大的整数。 示例 1: 输入:[10,1,2] 示例 2: 输入:[3,30,34,5,9] 题目: 给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它的 中序 遍历。 示例 1: 输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 示例 2: 输入:root = [] 示例 3: 输入:root = [1] 示例 4: 输入:root = [1,2] 示例 5: 树中节点数目在范围 [0, 100] 内 进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗? 思路一: 思路二: 通过迭代的方式进行 题目: 给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 层序遍历 。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。 示例 1: 输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 示例 2: 输入:root = [1] 示例 3: 输入:root = [] 提示: 树中节点数目在范围 [0, 2000] 内 思路: 通过列表以及队列的方式进行存储 具体大条件是判断其队列不为空 题目: 给定一个经过编码的字符串,返回它解码后的字符串。 编码规则为: k[encoded_string],表示其中方括号内部的 encoded_string 正好重复 k 次。注意 k 保证为正整数。 你可以认为输入字符串总是有效的;输入字符串中没有额外的空格,且输入的方括号总是符合格式要求的。 此外,你可以认为原始数据不包含数字,所有的数字只表示重复的次数 k ,例如不会出现像 3a 或 2[4] 的输入。 示例 1: 输入:s = “3[a]2[bc]” 示例 2: 输入:s = “3[a2[c]]” 示例 3: 输入:s = “2[abc]3[cd]ef” 示例 4: 输入:s = “abc3[cd]xyz” 提示: 思路: 通过栈的存储,以及StringBulider的存储 错误代码展示 少考虑了这种情况: 正确代码如下: 题目: 给定两个字符串形式的非负整数 num1 和num2 ,计算它们的和并同样以字符串形式返回。 你不能使用任何內建的用于处理大整数的库(比如 BigInteger), 也不能直接将输入的字符串转换为整数形式。 示例 1: 输入:num1 = “11”, num2 = “123” 示例 2: 输入:num1 = “456”, num2 = “77” 示例 3: 输入:num1 = “0”, num2 = “0” 提示: 1 <= num1.length, num2.length <= 104 思路: 通过模拟的思路,将其两个字符串从后往前加上,如果有进位就保留进位 通过StringBuilder添加进入,但是记得要 题目:5. 最长回文子串 给你一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串。 示例 1: 输入:s = “babad” 示例 2: 输入:s = “cbbd” 提示: 1 <= s.length <= 1000 中心拓展思路: 题目:72. 编辑距离 给你两个单词 word1 和 word2, 请返回将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数 。 你可以对一个单词进行如下三种操作: 插入一个字符 示例 1: 输入:word1 = “horse”, word2 = “ros” 示例 2: 输入:word1 = “intention”, word2 = “execution” 提示: 0 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 500Arrays.asList() 详解
而且需要使用ArrayList而不是List这个函数list.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[L],nums[R])));
三数之和(排序+双指针,易懂图解)
画解算法:15. 三数之和class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
int n = nums.length;
Arrays.sort(nums);
// < nums.length - 2是为了保证后面还能存在两个数字
for(int i = 0;i < n - 2;i++){
//大于0,则后面的数字也是大于零(排序后是递增的)
if(nums[i] > 0)break;
// 代表第一个值重复了,去重
if(i != 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1])continue;
int left = i + 1;
int right = n - 1;
while(left < right){
int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if(sum == 0){
//创建一个空的列表
/*
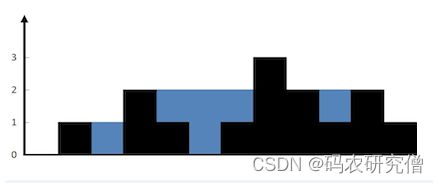
List42. 接雨水(困难)*
输出:6
解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。
输出:9
1 <= n <= 2 * 104
0 <= height[i] <= 105
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int n = height.length;
// 定义左边界最大的值,注意边界范围
int[] leftmax = new int[n];
leftmax[0] = height[0];
for(int i = 1;i < n;i++){
leftmax[i] = Math.max(leftmax[i - 1],height[i]);
}
// 定义右边界最大的值,注意边界范围
int[] rightmax = new int[n];
rightmax[n - 1] = height[n - 1];
for(int i = n - 2;i >= 0;i--){
rightmax[i] = Math.max(rightmax[i + 1],height[i]);
}
// 两者最小的边界,减去height即为蓄水池
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
sum += Math.min(leftmax[i],rightmax[i]) - height[i];
}
return sum;
}
}
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int n = height.length;
int left = 0;
int right = n - 1;
int leftmax = 0;
int rightmax = 0;
int sum = 0;
// 边界条件是 left < right
while(left < right){
// 保持左右边界最大的值,维护两个值
leftmax = Math.max(leftmax,height[left]);
rightmax = Math.max(rightmax,height[right]);
// 哪个边界小,就用这个边界 减去自身height的值
if(height[left] < height[right]){
sum += leftmax - height[left];
left++;
}else {
sum += rightmax - height[right];
right--;
}
}
return sum;
}
}
第五天
7. 整数反转(中等)
输出:321
输出:-321
输出:21
输出:0
这道题的思路很像之前那道算法
所以在要加以判断,否则会溢出class Solution {
public int reverse(int x) {
int res = 0;
while(x != 0){
// 一定要除以10,因为1534236469的输入,输出是0,而不是本身
// 如果反转后整数超过 32 位的有符号整数的范围 [−231, 231 − 1] ,就返回 0
if(res < Integer.MIN_VALUE / 10 || res > Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10){
return 0;
}
int ret = x % 10;
// 核心代码在这一步
res = res * 10 + ret;
x /= 10;
}
return res;
}
}
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素(中等)
输出: 5
输出: 4
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
具体快排的思路可看我这篇文章
【数据结构】常见排序算法详细分析(内含java与c++代码)class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
quicksort(nums,0,nums.length-1);
// 返回第k大的数组值
return nums[nums.length-k];
}
// 使用快排的思想进行排序
public void quicksort(int [] nums,int left,int right){
// 边界条件 特别要注意
if(left > right)return;
int l = left;
int r = right;
// 以左边的第一个为基准
int temp = nums[l];//基准的数字
// 筛选出一个有序数字的位置
while(l < r){
while(l < r && nums[r] >= temp)r--;
while(l < r && nums[l] <= temp)l++;
if(l < r){
int t = nums[l];
nums[l] = nums[r];
nums[r] = t;
}
}
//最后的基准 跟(i与j相等)i互换位置
nums[left] = nums[l];
nums[l] = temp;
// 遍历递归左右边界的值
quicksort(nums,left,l-1);
quicksort(nums,l+1,right);
}
}
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
// 使用优先队列,默认是小顶堆
PriorityQueue <Integer> que = new PriorityQueue<>();
for(int num :nums){
que.add(num);
if(que.size() > k){
// 去除最小的,因为是小顶堆
que.poll();
}
}
// 返回堆顶就是 第k个最大的
return que.peek();
}
}
23. 合并K个升序链表(困难)*
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
输出:[]
输出:[]
0 <= k <= 104
0 <= lists[i].length <= 500
-10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 104
lists[i] 按 升序 排列
lists[i].length 的总和不超过 104class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
// java lambda表达式新写法( Comparator.comparingInt(o->o.vaal) )
PriorityQueue<ListNode>pq=new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o->o.val));
int n=lists.length;
// 只添加每个list的第一个节点
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(lists[i]!=null) pq.offer(lists[i]);
}
// 创建头结点以及头指针
ListNode head=new ListNode(-1);
ListNode ans=head;
// 优先队列不为空,进入条件
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
// 将其出栈,通过头指针指向该节点,并且挪到头指针
ListNode cur=pq.poll();
ans.next=cur;
ans=ans.next;
// 判断该list 下一个的next是否为空,添加下个节点
if(cur.next!=null){
pq.offer(cur.next);
}
}
// 返回头结点的next
return head.next;
}
}
第六天
33. 搜索旋转排序数组(中等)*
输出:4
输出:-1
输出:-1
-104<= nums[i] <= 104
nums 中的每个值都 独一无二
题目数据保证 nums 在预先未知的某个下标上进行了旋转
-104 <= target <= 104
此时有序部分用二分法查找。无序部分再一分为二,其中一个一定有序,另一个可能有序,可能无序。就这样循环.

关于该题解看的是如下提示:
官方题解class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
// 处理边界问题
int n = nums.length;
int l = 0;
int r = n - 1;
// 总体大条件为 l 小于等于r
while(l <= r){
// 求出mid
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target)return mid;
// 主要分两种大情况,nums【mid】的值和第一个进行比较,查看是否落在哪个位置
if(nums[0] <= nums[mid]){
// 如果归于左边,则左边的target具体位置 判断落的地点在哪,好处理边界
if(nums[0] <= target && target < nums[mid]){
r = mid - 1;
}else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}else {
// 注意等于号的位置
if(nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[n - 1]){
l = mid + 1;
}else {
r = mid - 1;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
54. 螺旋矩阵(中等)
输出:[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
输出:[1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
1 <= m, n <= 10
-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
// 以下算法为模拟算法
int m =matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 定义四个边界值
int l = 0;
int r = n - 1;
int top = 0;
int bottom = m - 1 ;
// 通过计数判断
int num = 1;
int sum = m * n;
while(num <= sum){
// 定义的是n - 1,所以有等于号,在内部的遍历随时可能结束,所以要带上num <= sum 的条件
// 遍历注意起始条件
for(int i = l;i <= r && num <= sum;i++){
list.add(matrix[top][i]);
num++;
}
top++;//往下加1
for(int i = top;i <= bottom && num <= sum;i++){
list.add(matrix[i][r]);
num++;
}
r--;//往左减1
// ----注意遍历的i 是减减 ---
for(int i = r;i >= l && num <= sum;i--){
list.add(matrix[bottom][i]);
num++;
}
bottom--;//往上加1
for(int i = bottom;i >= top && num <= sum;i--){
list.add(matrix[i][l]);
num++;
}
l++;//往右加1
}
return list;
}
}
&&num<=sum,否则一个while出不了循环,特别是长方形会有错误class Solution {
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
int [][] ss = new int[n][n];
// 定义四个边界值
int l = 0;
int r = n - 1;
int top = 0;
int bottom = n - 1 ;
// 通过计数判断
int num = 1;
int sum = n * n;
while(num <= sum){
for(int i = l;i <= r;i++){
ss[top][i] = num++;
}
top++;//往下走
for(int i = top;i <= bottom;i++){
ss[i][r] = num++;
}
r--;//往左走
for(int i = r;i >= l;i--){
ss[bottom][i] = num++;
}
bottom--;//往上走
for(int i = bottom;i >= top;i--){
ss[i][l] = num++;
}
l++;//往右走
}
return ss;
}
}
bytedance-006. 夏季特惠(简单)**
输出:
4 100
100 73 60
100 89 35
30 21 30
10 8 10
输出:100
解释:买 1、3、4 三款游戏,获得总优惠 38 元,总金额 102 元超预算 2 元,满足条件,获得 100 快乐值。
3 100
100 100 60
80 80 35
21 21 30
输出:60
解释:只能买下第一个游戏,获得 60 的快乐值。
2 100
100 30 35
140 140 100
输出:135
解释:两款游戏都买,第一款游戏获得优惠 70 元,总开销 170 元,超过预算 70 元,超出预算金额不大于获得优惠金额满足条件,因此可以获得最大快乐值为 135。
1 <= n <= 500
0 <= x <= 10,000
0 <= b_i <= a_i <= 500
1 <= w_i <= 1,000,000,000
关于数据集:
前 30% 的数据, 小数据集 (n<=15)
中间 30% 的数据,中等数据集 (n<=100)
后 40% 的数据,大数据集 (n<=500)import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 输入数据
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int X = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n];
int[] b = new int[n];
int[] w = new int[n];
// 2. 去除重量 <= 0 物品
int num = 0;
long base = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[num] = sc.nextInt();
b[num] = sc.nextInt();
w[num] = sc.nextInt();
// 总优惠金额不低于超过预算的总金额 通过b【num】与0进行比较
b[num] = b[num] - (a[num] - b[num]); // 作为物品重量
if (b[num] <= 0) {
X += -b[num];
base += w[num];
} else {
num++;
}
}
// 3. 对剩余物品进行01背包求解
long[] dp = new long[X + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
for (int j = X; j >= b[i]; j--) {
dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - b[i]] + w[i]);
}
}
System.out.println(dp[X] + base); // 任何容量的背包都可以直接加上重量<=0 的物品的价值和
}
}
第七天
53. 最大子数组和(中等)
给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你找出一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
输出:6
解释:连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6 。
输出:1
输出:23
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
通过Math函数,将其一个个加上获取最大值
以及通过Math函数,存储各个区域中的最大子数组之和class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
// 最大的前缀值
int pre = 0;
// 遍历所有,所有值最大的一个,赋值为nums【0】,如果数组只有一个,则返回nums【0】
int max = nums[0];
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
pre = Math.max(pre+nums[i],nums[i]);
// 所有的遍历都筛选出最大的max
max = Math.max(pre,max);
}
return max;
}
}
152. 乘积最大子数组(中等)
输出: 6
解释: 子数组 [2,3] 有最大乘积 6。
输出: 0
解释: 结果不能为 2, 因为 [-2,-1] 不是子数组。
-10 <= nums[i] <= 10
nums 的任何前缀或后缀的乘积都 保证 是一个 32-位 整数
Integer.MIN_VALUE
如果下一个数为负数,则最大值和最小值互换class Solution {
public int maxProduct(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int max = 1;
int min = 1;
// 此处定义的sum 初始不应为0,如果只有一个nums,并且为负数,那么最大就会为0
int sum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
// 先判断nums小于0再进行判断
if(nums[i] < 0){
int temp = max;
max = min;
min = temp;
}
max=Math.max(nums[i]*max,nums[i]);
min=Math.min(nums[i]*min,nums[i]);
sum=Math.max(sum,max);
}
return sum;
}
}
41. 缺失的第一个正数(困难)
输出:3
输出:2
输出:1
-231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1class Solution {
public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
// 数组的原地置换,精髓在于 nums[nums[i] - 1] ,nums[i] 这两个交换
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
// 一直再这交换,前提的条件要大于0 小于n
while(nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] < n && nums[nums[i] - 1] != nums[i]){
int temp = nums[nums[i] - 1];
nums[nums[i] - 1] = nums[i];
nums[i] = temp;
}
}
// 如果不相等,直接返回i + 1
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
if(nums[i] != i + 1){
return i + 1;
}
}
// 返回最大的元素
return n + 1;
}
}
nums[num - 1] = -Math.abs(nums[num - 1]);变为负数class Solution {
public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (nums[i] <= 0) {
nums[i] = n + 1;
}
}
// 最主要的核心
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int num = Math.abs(nums[i]);
if (num <= n) {
nums[num - 1] = -Math.abs(nums[num - 1]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (nums[i] > 0) {
return i + 1;
}
}
return n + 1;
}
}
第八天
20. 有效的括号(简单)
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
输出:true
输出:true
输出:false
输出:false
输出:true
s 仅由括号 ‘()[]{}’ 组成
Map <Character,Character> map=new HashMap<>(){{
put(')','(');
}} ;
通过栈的形式防其值
((),不想此处判断栈是否为空的话,可以在一开始就判断是否为偶数个数)
代码如下:class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
if(s.length()%2==1)return false;
Deque <Character>stack=new LinkedList<>();
Map <Character,Character> map=new HashMap<>(){{
put(')','(');
put('}','{');
put(']','[');
}};
for(char c:s.toCharArray()){
if(map.containsKey(c)){
if(map.get(c)!=stack.peek()){
return false;
}
stack.pop();
}else {
stack.push(c);
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
// 不使用map结构,直接进行比较
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length();i++){
// 单个字符 无法使用equals进行比较判断
if(s.charAt(i) == '('){
stack.push(')');
}else if(s.charAt(i) == '{'){
stack.push('}');
}else if(s.charAt(i) == '['){
stack.push(']');
// 如果栈为空,或者对应的peek 不相等,则直接返回false
}else if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() != s.charAt(i) ){
return false;
}else {
// 右边的括号配对成功,就会将其右括号出栈
stack.pop();
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
200. 岛屿数量(中等)
[“1”,“1”,“1”,“1”,“0”],
[“1”,“1”,“0”,“1”,“0”],
[“1”,“1”,“0”,“0”,“0”],
[“0”,“0”,“0”,“0”,“0”]
]
输出:1
[“1”,“1”,“0”,“0”,“0”],
[“1”,“1”,“0”,“0”,“0”],
[“0”,“0”,“1”,“0”,“0”],
[“0”,“0”,“0”,“1”,“1”]
]
输出:3
1 <= m, n <= 300
grid[i][j] 的值为 ‘0’ 或 ‘1’
如果一开始进入的为1,则sum+1
在遍历的时候终止条件,一般有临界值,以及状态值class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if(grid == null || grid.length == 0)return 0;
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < n;j++){
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
sum++;
dfs(grid,i,j);
}
}
}
return sum;
}
public void dfs(char[][] grid,int i,int j){
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
// 临界条件不满足的return 返回
// grid[i][j] == '0' 这个条件需要放在后面,先处理越界问题
if(i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || grid[i][j] == '0' ){
return;
}
// 更改原数组,将其赋值为0
grid[i][j] = '0';
dfs(grid,i - 1,j);
dfs(grid,i + 1,j);
dfs(grid,i,j - 1);
dfs(grid,i,j + 1);
}
}
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if(grid == null || grid.length == 0)return 0;
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
// 默认一开始的初始值为0
int[][] visited = new int[m][n];
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < n;j++){
if(grid[i][j] == '1' && visited[i][j] != 1){
sum++;
dfs(grid,i,j,visited);
}
}
}
return sum;
}
public void dfs(char[][] grid,int i,int j,int[][] visited){
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
// 临界条件不满足的return 返回
// grid[i][j] == '0' 这个条件需要放在后面,先处理越界问题
if(i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || grid[i][j] == '0' || visited[i][j] == 1){
return;
}
// 更改原数组,将其赋值为0
visited[i][j] = 1;
dfs(grid,i - 1,j,visited);
dfs(grid,i + 1,j,visited);
dfs(grid,i,j - 1,visited);
dfs(grid,i,j + 1,visited);
}
}
76. 最小覆盖子串(困难)******
如果 s 中存在这样的子串,我们保证它是唯一的答案。
输出:“BANC”
输出:“a”
输出: “”
解释: t 中两个字符 ‘a’ 均应包含在 s 的子串中,
因此没有符合条件的子字符串,返回空字符串。
s 和 t 由英文字母组成
class Solution {
Map<Character, Integer> ori = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
Map<Character, Integer> cnt = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
int tLen = t.length();
for (int i = 0; i < tLen; i++) {
char c = t.charAt(i);
ori.put(c, ori.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}
int l = 0, r = -1;
int len = Integer.MAX_VALUE, ansL = -1, ansR = -1;
int sLen = s.length();
while (r < sLen) {
++r;
if (r < sLen && ori.containsKey(s.charAt(r))) {
cnt.put(s.charAt(r), cnt.getOrDefault(s.charAt(r), 0) + 1);
}
while (check() && l <= r) {
if (r - l + 1 < len) {
len = r - l + 1;
ansL = l;
ansR = l + len;
}
if (ori.containsKey(s.charAt(l))) {
cnt.put(s.charAt(l), cnt.getOrDefault(s.charAt(l), 0) - 1);
}
++l;
}
}
return ansL == -1 ? "" : s.substring(ansL, ansR);
}
public boolean check() {
Iterator iter = ori.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iter.next();
Character key = (Character) entry.getKey();
Integer val = (Integer) entry.getValue();
if (cnt.getOrDefault(key, 0) < val) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
第九天
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树(中等)**
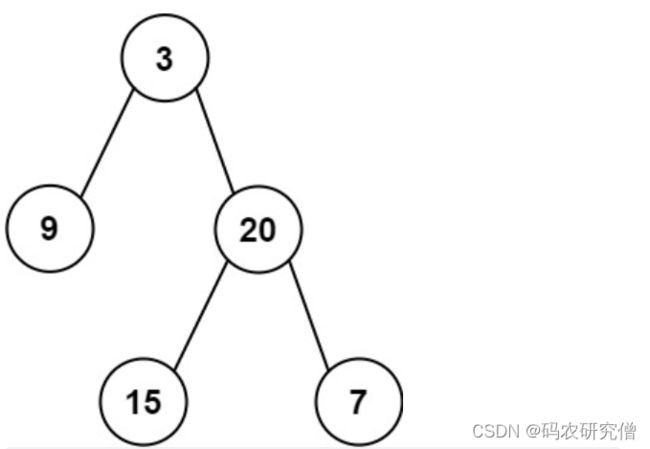
输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
输出: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
输出: [-1]
inorder.length == preorder.length
-3000 <= preorder[i], inorder[i] <= 3000
preorder 和 inorder 均 无重复 元素
inorder 均出现在 preorder
preorder 保证 为二叉树的前序遍历序列
inorder 保证 为二叉树的中序遍历序列
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[preorder_left]);/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
Map<Integer,Integer>map;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
map=new HashMap<>();
int n=inorder.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
map.put(inorder[i],i);
}
return mybuildTree(preorder,inorder,0,n-1,0,n-1);
}
public TreeNode mybuildTree(int []preorder,int [] inorder,int preorder_left,int preorder_right,int inorder_left,int inorder_right ){
// 通过判定前序的 left 指针大于 right指针
if(preorder_left>preorder_right)return null;
int inorder_root=map.get(preorder[preorder_left]);
int sum=inorder_root-inorder_left;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[preorder_left]);
root.left=mybuildTree(preorder,inorder,preorder_left+1,preorder_left+sum, inorder_left,inorder_root-1);
root.right=mybuildTree(preorder,inorder,preorder_left+sum+1,preorder_right, inorder_root+1,inorder_right);
return root;
}
}
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历(中等)
输出:[[3],[20,9],[15,7]]
输出:[[1]]
输出:[]
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
因为是双端队列,所以在添加的时候要强转list.add(new LinkedList/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root==null)return list;
Queue<TreeNode> que =new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(root);
boolean direction = true;
while(!que.isEmpty()){
Deque<Integer> sonlist=new LinkedList<>();
int n=que.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
TreeNode node=que.poll();
if(direction){
sonlist.offerLast(node.val);
}else{
sonlist.offerFirst(node.val);
}
if(node.left!=null)que.offer(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)que.offer(node.right);
}
direction=!direction;
list.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(sonlist));
}
return list;
}
}
直接使用列表的形式进行添加
特殊行使用Collection进行反转class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root == null)return list;
Deque<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(root);
boolean direction = true;
while(!que.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> sonlist = new ArrayList<>();
int n = que.size();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
TreeNode node = que.poll();
sonlist.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null)que.offer(node.left);
if(node.right != null)que.offer(node.right);
}
if(!direction){
Collections.reverse(sonlist);
}
direction = !direction;
list.add(sonlist);
}
return list;
}
}
bytedance-010. 数组组成最大数(简单)
输出:2110
输出:9534330import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = sc.nextLine();
String[] nums = s.substring(1,s.length() - 1).split(",");
// 第一种写法:lambda 表达式
// Arrays.sort(nums,(a,b) -> (b + a).compareTo(a + b));
// 改写Comparator钟的compare的方法,compareTO
Arrays.sort(nums,new Comparator<String>(){
@Override
public int compare(String a,String b){
return (b + a).compareTo(a + b);
}
});
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(String num : nums){
sb.append(num);
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
第十天
94. 二叉树的中序遍历(简单)
输出:[1,3,2]
输出:[]
输出:[1]
输出:[2,1]
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
通过递归 的方式
创建一个函数,将其res列表传入class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 调用函数
inorder(root,list);
return list;
}
// 中序遍历的递归,前中后,如果为null则直接return
public void inorder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> res){
if(root == null){
return ;
}
inorder(root.left,res);
res.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right,res);
}
}
利用栈的思想/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
// 两个条件,root不为空 或者 栈不为空
while(root != null ||!stack.isEmpty()){
// 对应的所有左子树先入栈
while(root != null){
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
// 添加栈中元素
root = stack.pop();
list.add(root.val);
// 遍历是否有右子树
root = root.right;
}
return list;
}
}
102. 二叉树的层序遍历(中等)
输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
输出:[[1]]
输出:[]
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
内部存储的是每一层的列表size
注意泛型的类型/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root == null)return list;
// 定义队列的格式
Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(root);
while(!que.isEmpty()){
// 定义子列表
List<Integer> sonlist = new ArrayList<>();
int n = que.size();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
TreeNode node = que.poll();
// poll的时候将其add进入
sonlist.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null)que.offer(node.left);
if(node.right != null)que.offer(node.right);
}
list.add(sonlist);
}
return list;
}
}
394. 字符串解码(中等)
输出:“aaabcbc”
输出:“accaccacc”
输出:“abcabccdcdcdef”
输出:“abccdcdcdxyz”
遇到】的时候都进栈class Solution {
public String decodeString(String s) {
Stack<Character>stack=new Stack<>();
StringBuilder res=new StringBuilder();
for(char c:s.toCharArray()){
if(c!=']'){
stack.push(c);
}else{
StringBuilder ans=new StringBuilder();
while(!stack.isEmpty()&&Character.isLetter(stack.peek()))
ans.insert(0,stack.pop());
String sub=ans.toString();
stack.pop();
ans = new StringBuilder();
while(!stack.isEmpty()&&Character.isDigit(stack.peek()))
ans.insert(0,stack.pop());
int count=Integer.valueOf(ans.toString());
while(count>0){
for(char h:sub.toCharArray()){
res.append(h);
}
count--;
}
}
}
return res.toString();
}
}

对此在前面的时候不着急直接输出添加进去
而是继续放到栈中,等全部放到栈中之后在一一添加进去
Character.isLetter(stack.peek()Character.isDigit(stack.peek()ans.insert(0,stack.pop());Integer.valueOf();toString();先转换为字符串class Solution {
public String decodeString(String s) {
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<>();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(char c : s.toCharArray()){
if(c != ']'){
// 不是这个括号的都进栈
stack.push(c);
}else {
// 找出对应的所有字母,从后往前弹出找
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
while(!stack.isEmpty() && Character.isLetter(stack.peek())){
ans.insert(0,stack.pop());
}
// 放入sub字符串中
String sub = ans.toString();
// 弹出一个括号
stack.pop();
// 在找出它的数字
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
while(!stack.isEmpty() && Character.isDigit(stack.peek())){
res.insert(0,stack.pop());
}
int count = Integer.valueOf(res.toString());
// 将其字母重新放入栈中 (以倍数)
while(count > 0){
for(char h : sub.toCharArray()){
stack.push(h);
}
count--;
}
}
}
// 将其栈按照原先进入的顺序 通过insert从前往后插入
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
sb.insert(0,stack.pop());
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
第十一天
415. 字符串相加(简单)
输出:“134”
输出:“533”
输出:“0”
num1 和num2 都只包含数字 0-9
num1 和num2 都不包含任何前导零
reverse反转,之后还要将其输出为字符串toString();class Solution {
public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {
// 临界值要计算,所以要减1
int i = num1.length() - 1;
int j = num2.length() - 1;
int add = 0;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while(i >= 0 || j >= 0 || add != 0){
// 在while 大条件下循环,如果小于0则直接返回0
int x = i >= 0 ? num1.charAt(i) - '0': 0;
int y = j >= 0 ? num2.charAt(j) - '0': 0;
int result = add + x + y;
sb.append(result % 10);
add = result / 10;
i--;
j--;
}
// 最后要反转
sb.reverse();
return sb.toString();
}
}
5. 最长回文子串(中等)**
输出:“bab”
解释:“aba” 同样是符合题意的答案。
输出:“bb”
s 仅由数字和英文字母组成class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() < 1) {
return "";
}
int start = 0,end = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < s.length();i++){
int len1 = expandAroundCenter(s,i,i);
int len2 = expandAroundCenter(s,i,i + 1);
int len = Math.max(len1,len2);
if(len > end - start){
// 之所以是len - 1,是处理奇数边界问题
start = i - (len - 1) / 2;
end = i + len / 2;
}
}
// 左闭右开,所以要end + 1
return s.substring(start,end + 1);
}
public int expandAroundCenter(String s, int left, int right) {
while (left >= 0 && right < s.length() && s.charAt(left) == s.charAt(right)) {
--left;
++right;
}
// 如果不匹配了
// 此处的left以及right是在匹配元素边界:left 【匹配元素】 right
// 因此回文串长度为:【left + 1,right - 1】,right - 1 - (left + 1)+ 1 = right - left - 1
return right - left - 1;
}
}
72. 编辑距离(困难)**
删除一个字符
替换一个字符
输出:3
解释:
horse -> rorse (将 ‘h’ 替换为 ‘r’)
rorse -> rose (删除 ‘r’)
rose -> ros (删除 ‘e’)
输出:5
解释:
intention -> inention (删除 ‘t’)
inention -> enention (将 ‘i’ 替换为 ‘e’)
enention -> exention (将 ‘n’ 替换为 ‘x’)
exention -> exection (将 ‘n’ 替换为 ‘c’)
exection -> execution (插入 ‘u’)
word1 和 word2 由小写英文字母组成class Solution {
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int m = word1.length();
int n = word2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
dp[0][0] = 0;
// word1删除元素,每删除一个,初始化都是下标删除的个数
for(int i = 1;i < m + 1;i++){
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for(int j = 1;j < n + 1;j++){
dp[0][j] = j;
}
for(int i = 1;i < m + 1;i++){
for(int j = 1;j < n + 1;j++){
//如果配对,则保存上一个的值
if(word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)){
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
}else {
//如果不配对要分三种情况,第一种是word1删除,第二种是word2删除,第三种是两者都删除。三者之间比较出最小值,记得每删除一个元素都是要加1
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], Math.min(dp[i - 1][j],dp[i][j - 1])) + 1;
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
}