ChatGPT生成的一些有趣的文件管理用python小程序
0.去除文件名中的空格
import os
def remove_spaces_recursive(directory):
# 遍历目录中的所有文件和子目录
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):
for file_name in files:
# 构建完整的文件路径
file_path = os.path.join(root, file_name)
# 移除文件名中的空格
new_file_name = file_name.replace(" ", "_")
new_file_path = os.path.join(root, new_file_name)
# 重命名文件
os.rename(file_path, new_file_path)
print(f"已重命名文件:{file_path} -> {new_file_path}")
def main():
# 获取当前工作目录
current_directory = os.getcwd()
# 调用递归函数处理当前目录
remove_spaces_recursive(current_directory)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
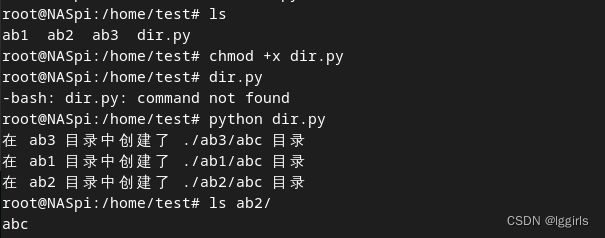
1. 在当前位置中的所有文件夹内增加一个名为 abc 的新文件夹
import os
def create_abc_directories(root_dir='.'):
# 获取当前目录下的所有目录
subdirectories = [d for d in os.listdir(root_dir) if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(root_dir, d))]
# 在每个目录中创建名为abc的子目录
for directory in subdirectories:
abc_dir = os.path.join(root_dir, directory, 'abc')
os.makedirs(abc_dir, exist_ok=True)
print(f"在 {directory} 目录中创建了 {abc_dir} 目录")
if __name__ == "__main__":
create_abc_directories()用法:保存为 *.py文件,增加x权限,执行命令: python *.py
2. 批量新建以文件 a.txt 内的名称命名的文件夹
import os
def create_folders_from_file(file_path='a.txt'):
# 检查文件是否存在
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
print(f"错误: 文件 '{file_path}' 不存在。")
return
# 打开文件并逐行读取文件名
with open(file_path, 'r') as file:
folder_names = [line.strip() for line in file.readlines()]
# 在当前位置创建文件夹,如果同名文件夹已存在则跳过
for folder_name in folder_names:
folder_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), folder_name)
if os.path.exists(folder_path) and os.path.isdir(folder_path):
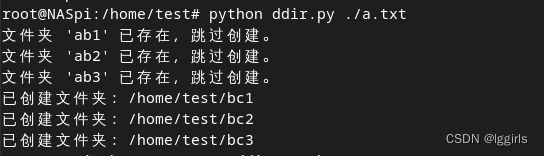
print(f"文件夹 '{folder_name}' 已存在,跳过创建。")
else:
os.makedirs(folder_path, exist_ok=True)
print(f"已创建文件夹: {folder_path}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
create_folders_from_file()
运行命令: python *.py ./a.txt
这个脚本首先检查文件a.txt是否存在,然后逐行读取该文件中的名称。对于每个名称,它构建文件夹路径并检查是否已经存在。如果存在,则输出提示信息并跳过创建;否则,它将创建新的文件夹。
3.检查当前位置中的所有空文件夹并将其删除,递归执行
import os
def remove_empty_directories(root_dir='.'):
# 获取当前目录下的所有子目录和文件
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(root_dir, topdown=False):
for directory in dirs:
folder_path = os.path.join(root, directory)
# 检查目录是否为空
if not os.listdir(folder_path):
print(f"删除空目录: {folder_path}")
os.rmdir(folder_path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
remove_empty_directories()这个脚本使用os.walk函数遍历目录树,从底层向上遍历目录。对于每个目录,它检查是否为空,如果是,则删除该目录。
4.为当前位置下的子文件夹 在/home/link/中的同名子文件夹内 创建软连接,软连接的名称是abcd
import os
# 获取当前目录
current_dir = os.getcwd()
# 设置链接目录
link_dir = "/home/link"
# 遍历当前目录中的子目录
for dir_name in os.listdir(current_dir):
# 检查是否是目录
if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(current_dir, dir_name)):
# 构建软链接的目标路径
link_target = os.path.join(link_dir, dir_name, "abcd")
# 创建软链接
os.symlink(os.path.join(current_dir, dir_name), link_target)
print(f"Created symlink for {dir_name} in {link_target}")5.为当前位置中所有文件夹内的同名子文件夹批量创建软连接,软连接名称以父文件夹来命名
编写一个python脚本,其功能是: 检查当前位置所有文件夹内是否有名称为abc的子文件夹,如果有,则在/home/link/中为子文件夹abc创建软链接,软链接的名称为其父文件夹的名称
import os
# 获取当前目录
current_dir = os.getcwd()
# 设置链接目录
link_dir = "/home/link"
# 遍历当前目录中的子目录
for dir_name in os.listdir(current_dir):
dir_path = os.path.join(current_dir, dir_name)
abc_dir_path = os.path.join(dir_path, "abc")
# 检查是否是目录且 abc 子目录存在
if os.path.isdir(dir_path) and os.path.exists(abc_dir_path) and os.path.isdir(abc_dir_path):
# 构建软链接的目标路径
link_target = os.path.join(link_dir, dir_name)
# 创建软链接
os.symlink(abc_dir_path, link_target)
print(f"Created symlink for {abc_dir_path} in {link_target}")例如,/home/test/中有两个文件夹 公司A 公司B,他们都有同样的文件夹abc,则运行该脚本后,会/home/link/中生成 公司A 公司B 两个软链接文件,分别指向各自文件夹内的 abc
该用法适用的场景: 在Company文件夹中有100个以公司名称命名的文件夹,每个公司的文件夹中,是以各种业务名称命名的子文件夹;如果想对各个公司的同一个项目创建软连接到Projetc文件夹中,则采用该脚本;这样在 Projetc/项目X/ 文件家内,就会出现以各个公司名为文件夹的软连接。
6. 查找具有相同名称关键字的文件夹
其功能是: 比较 /home/A 和 /home/B 两个文件夹内的文件夹名称,如果任意两个文件夹名称中有3个以上的中文字符相同,则在a.txt文本中的同一行记录正两个文件夹的路径
import os
def get_chinese_characters(s):
return [c for c in s if '\u4e00' <= c <= '\u9fff']
def compare_folders(folder_a, folder_b, output_file):
folders_a = os.listdir(folder_a)
folders_b = os.listdir(folder_b)
with open(output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as output:
for folder_name_a in folders_a:
for folder_name_b in folders_b:
chinese_chars_a = set(get_chinese_characters(folder_name_a))
chinese_chars_b = set(get_chinese_characters(folder_name_b))
common_chars = chinese_chars_a.intersection(chinese_chars_b)
if len(common_chars) >= 3:
path_a = os.path.join(folder_a, folder_name_a)
path_b = os.path.join(folder_b, folder_name_b)
output.write(f'{path_a}\t{path_b}\n')
if __name__ == "__main__":
folder_a_path = "/home/A"
folder_b_path = "/home/B"
output_file_path = "a.txt"
compare_folders(folder_a_path, folder_b_path, output_file_path)
print("Comparison completed. Results saved in a.txt.")
7. 找出当前位置下不在a.txt 名单内的文件夹,结果输出到 b.txt
import os
def find_non_listed_folders(base_folder, list_file, output_file):
# 获取a.txt中的文件夹名单
with open(list_file, 'r') as list_file:
listed_folders = {line.strip() for line in list_file}
# 获取当前位置下的所有文件夹
all_folders = [folder for folder in os.listdir(base_folder) if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(base_folder, folder))]
# 找出没有包含在a.txt名单内的文件夹
non_listed_folders = set(all_folders) - listed_folders
# 将结果输出到b.txt文件
with open(output_file, 'w') as output:
output.write('\n'.join(sorted(non_listed_folders)))
# 指定当前位置、a.txt和b.txt的路径
base_folder = '.' # 可以根据需要修改为你想要的文件夹路径
list_file = 'a.txt'
output_file = 'b.txt'
# 调用函数
find_non_listed_folders(base_folder, list_file, output_file)
8. 将A、B两个文本文档的内容,行对行进行合并
def merge_files(file_a, file_b, output_file):
with open(file_a, 'r') as file_a_content, open(file_b, 'r') as file_b_content:
lines_a = file_a_content.readlines()
lines_b = file_b_content.readlines()
with open(output_file, 'w') as output_content:
max_lines = max(len(lines_a), len(lines_b))
for i in range(max_lines):
line_a = lines_a[i].strip() if i < len(lines_a) else ""
line_b = lines_b[i].strip() if i < len(lines_b) else ""
merged_line = f"{line_a} {line_b}\n"
output_content.write(merged_line)
print(f"合并完成,并保存到 {output_file} 中。")
# 用法示例
merge_files('A.txt', 'B.txt', 'C.txt')注: 结果输出到了 C.txt 中
9. 在5分钟后运行脚本 abc.sh
你可以使用 Python 的 time 模块来实现延迟执行。下面是一个简单的脚本,它会等待5分钟后运行当前目录下的 abc.sh 脚本:
import time
import subprocess
# 等待5分钟
time.sleep(300)
# 运行 abc.sh 脚本
subprocess.run(["./abc.sh"])请确保在脚本所在的目录下有执行权限,并且 abc.sh 也有执行权限。你可以使用以下命令添加执行权限:
chmod +x abc.sh然后,将上面的 Python 脚本保存为一个 .py 文件,比如 run_after_five_minutes.py,然后在终端中运行:
python run_after_five_minutes.py这将在5分钟后执行 abc.sh 脚本。请注意,这个脚本中的时间延迟是以秒为单位的,因此 time.sleep(300) 表示等待300秒,即5分钟。
应用举例:
我通过frps服务登录了家中的服务器,计划升级frpc客户端,因为frpc文件在使用中,无法复制替换为新文件,所以编写一个 abc.sh 文档,配合上面的python脚本,实现在5分钟后自动复制frpc文件进行替换,并启动frpc服务。这样就可以在运行python脚本后,停止frpc服务,然后五分钟后再登录即可。