Java8新特性 Stream
1、stream概述
Stream 使用一种类似用 SQL 语句从数据库查询数据的直观方式来提供一种对 Java 集合运算和表达的高阶抽象。
Stream API可以极大提高Java程序员的生产力,让程序员写出高效率、干净、简洁的代码。
这种风格将要处理的元素集合看作一种流, 流在管道中传输, 并且可以在管道的节点上进行处理, 比如筛选, 排序,聚合等。
元素流在管道中经过中间操作(intermediate operation)的处理,最后由最终操作(terminal operation)得到前面处理的结果。
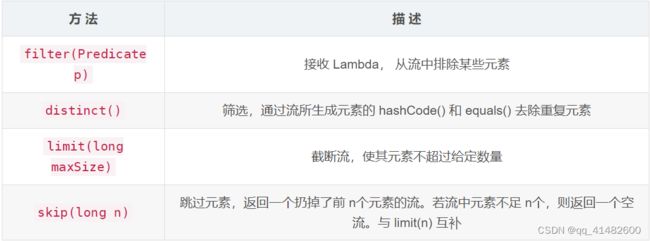
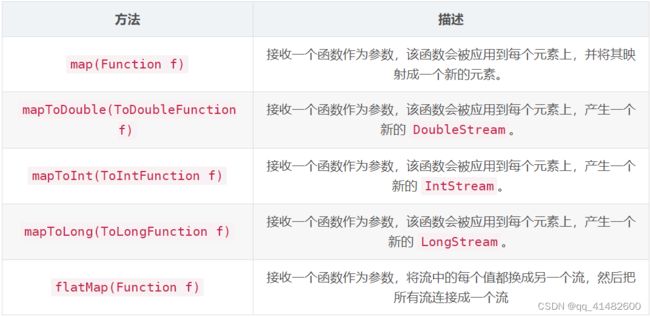
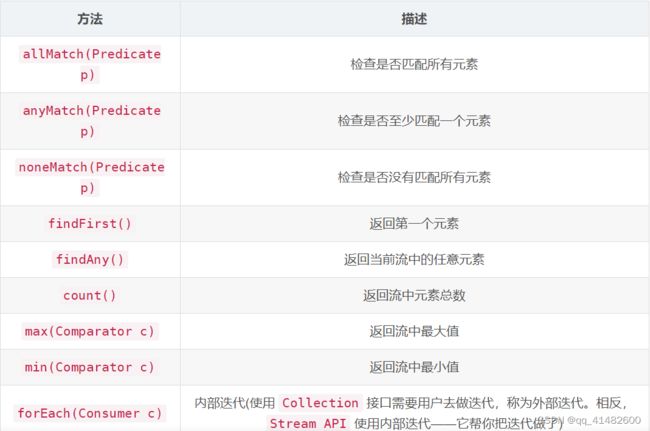
2、stream方法描述
3、stream方法实例
- 首先创建一个用户的实体类,包括姓名、年龄、性别、地址、赏金 几个属性
@Data
public class User {
//姓名
private String name;
//年龄
private Integer age;
//性别
private Integer sex;
//地址
private String address;
//赏金
private BigDecimal money;
public User(String name, Integer age, Integer sex, String address,BigDecimal money) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.address = address;
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex=" + sex +
", money=" + money +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- 我们在创建一个测试类,包含主方法,并创建一个数据源,作为我们测试的对象
public class Stream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public static List users(){
List list = Arrays.asList(
new User("赵", 18, 0, "安徽",new BigDecimal(1000)),
new User("钱", 16, 1, "江苏",new BigDecimal(500)),
new User("孙", 17, 1, "山东",new BigDecimal(800)),
new User("李", 99, 0, "河南",new BigDecimal(100000)),
new User("周", 19, 0, "陕西",new BigDecimal(900)),
new User("武", 45, 0, "上海",new BigDecimal(600)),
new User("郑", 48, 0, "北京",new BigDecimal(1100)),
new User("王", 18, 1, "广西",new BigDecimal(800))
);
return list;
}
}
3.1、stream方法1
- stream使用
- filter
- distinct
- sorted
- limit
- skip
- map
- flatMap
- allMatch
- anyMatch
- noneMatch
- findFirst
- findAny
- count
- max
- min
- avg
- sum
- join
- group
- partition
/*filter过滤(T-> boolean)*/
public static void filter(){
List list = users();
List newlist = list.stream()
.filter(user -> user.getAge() > 20)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
for (User user : newlist) {
System.out.println(user.getName()+" --> "+ user.getAge());
}
}
/*distinct 去重*/
数据源中复制new User("赵", 18, 0, "安徽",new BigDecimal(1000)) 并粘贴两个
public static void distinct(){
List list = users();
List newlist = list.stream()
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
for (User user : newlist) {
System.out.println(user.getName()+" --> "+ user.getAge());
}
}
/*sorted排序*/
public static void sorted(){
List list = users();
List newlist = list.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(User::getAge))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
for (User user : newlist) {
System.out.println(user.getName()+" --> "+ user.getAge());
}
}
/*limit返回前n个元素*/
public static void limit(){
List list = users();
List newlist = list.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(User::getAge))
.limit(2)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
for (User user : newlist) {
System.out.println(user.getName()+" --> "+ user.getAge());
}
}
/*skip去除前n个元素*/
public static void skip(){
List list = users();
List newlist = list.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(User::getAge))
.skip(2)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
for (User user : newlist) {
System.out.println(user.getName()+" --> "+ user.getAge());
}
}
/*map(T->R)*/
public static void map(){
List list = users();
List newlist = list.stream()
.map(User::getName)
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
for (String add : newlist) {
System.out.println(add);
}
}
/*flatMap(T -> Stream)*/
public static void flatmap(){
List flatmap = new ArrayList<>();
flatmap.add("赵,钱");
flatmap.add("孙,李,周");
/*
这里原集合中的数据由逗号分割,使用split进行拆分后,得到的是Stream,
字符串数组组成的流,要使用flatMap的Arrays::stream
将Stream转为Stream,然后把流相连接
*/
flatmap = flatmap.stream()
.map(s -> s.split(","))
.flatMap(Arrays::stream)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
for (String name : flatmap) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
---结果---
赵
钱
孙
李
周
/*allMatch(T->boolean)检测是否全部满足参数行为*/
public static void allMatch(){
List list = users();
boolean flag = list.stream()
.allMatch(user -> user.getAge() >= 17);
System.out.println(flag);
}
---结果---
false
/*anyMatch(T->boolean)检测是否有任意元素满足给定的条件*/
public static void anyMatch(){
List list = users();
boolean flag = list.stream()
.anyMatch(user -> user.getSex() == 1);
System.out.println(flag);
}
---结果---
true
/*noneMatchT->boolean)流中是否有元素匹配给定的 T -> boolean条件*/
public static void noneMatch(){
List list = users();
boolean flag = list.stream()
.noneMatch(user -> user.getAddress().contains("郑州"));
System.out.println(flag);
}
---结果---
true
/*findFirst( ):找到第一个元素*/
public static void findfirst(){
List list = users();
Optional optionalUser = list.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(User::getAge))
.findFirst();
System.out.println(optionalUser.toString());
}
---结果---
Optional[User{name='赵', age=16, sex=1, money=500, address='安徽'}]
/*findAny( ):找到任意一个元素*/
public static void findAny(){
List list = users();
// Optional optionalUser = list.stream()
.findAny();
Optional optionalUser = list.stream()
.findAny();
System.out.println(optionalUser.toString());
}
---结果---
Optional[User{name='钱', age=18, sex=0, money=1000, address='江苏'}]
/*计算总数*/
public static void count(){
List list = users();
long count = list.stream().count();
System.out.println(count);
}
---结果---
8
/*最大值最小值*/
public static void max_min(){
List list = users();
Optional max = list.stream()
.collect(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(User::getAge)));
Optional min = list.stream()
.collect(Collectors.minBy(Comparator.comparing(User::getAge)));
System.out.println("max--> " + max+" min--> "+ min);
}
---结果---
max--> Optional[User{name='李', age=99, sex=0, money=100000, address='山东'}]
min--> Optional[User{name='钱', age=16, sex=1, money=500, address='江苏'}]
/*求和_平均值*/
public static void sum_avg(){
Listlist = users();
int totalAge = list.stream()
.collect(Collectors.summingInt(User::getAge));
System.out.println("totalAge--> "+ totalAge);
/*获得列表对象金额, 使用reduce聚合函数,实现累加器*/
BigDecimal totalMpney = list.stream()
.map(User::getMoney)
.reduce(BigDecimal.ZERO, BigDecimal::add);
System.out.println("totalMpney--> " + totalMpney);
double avgAge = list.stream()
.collect(Collectors.averagingInt(User::getAge));
System.out.println("avgAge--> " + avgAge);
}
---结果---
totalAge--> 280
totalMpney--> 105700
avgAge--> 35.0
/*一次性得到元素的个数、总和、最大值、最小值*/
public static void allVlaue(){
List list = users();
IntSummaryStatistics statistics = list.stream()
.collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(User::getAge));
System.out.println(statistics);
}
---结果---
IntSummaryStatistics{count=8, sum=280, min=16, average=35.000000, max=99}
/*拼接*/
public static void join(){
List list = users();
String names = list.stream()
.map(User::getName)
.collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
System.out.println(names);
}
---结果---
赵, 钱, 孙, 李, 周, 武, 郑, 王
/*分组*/
public static void group(){
Map> map = users().stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User::getSex));
System.out.println(new Gson().toJson(map));
System.out.println();
Map>> map2 = users().stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User::getSex,
Collectors.groupingBy(User::getAge)));
System.out.println(new Gson().toJson(map2));
}
---结果---
{
"0":[
{"name":"赵","age":18,"sex":0,"address":"安徽","money":1000},
{"name":"钱","age":99,"sex":0,"address":"山东","money":100000},
{"name":"孙","age":19,"sex":0,"address":"河南","money":900},
{"name":"李","age":45,"sex":0,"address":"江苏","money":600},
{"name":"周","age":48,"sex":0,"address":"陕西","money":1100}
],
"1":[
{"name":"武","age":16,"sex":1,"address":"上海","money":500},
{"name":"郑","age":17,"sex":1,"address":"北京","money":800},
{"name":"王","age":18,"sex":1,"address":"深圳","money":800}
]
}
{"0":
{"48":[{"name":"赵","age":48,"sex":0,"address":"安徽","money":1100}],
"18":[{"name":"钱","age":18,"sex":0,"address":"山东","money":1000}],
"19":[{"name":"孙","age":19,"sex":0,"address":"河南","money":900}],
"99":[{"name":"李","age":99,"sex":0,"address":"江苏","money":100000}],
"45":[{"name":"周","age":45,"sex":0,"address":"陕西","money":600}]},
"1":
{"16":[{"name":"武","age":16,"sex":1,"address":"上海","money":500}]
,"17":[{"name":"郑","age":17,"sex":1,"address":"北京","money":800}],
"18":[{"name":"王","age":18,"sex":1,"address":"深圳","money":800}]}}
/*分组合计*/
public static void groupCount(){
Map num = users().stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User::getSex, Collectors.counting()));
System.out.println(num);
Map num2 = users().stream()
.filter(user -> user.getAge()>=18)
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User::getSex, Collectors.counting()));
System.out.println(num2);
}
---结果---
{0=5, 1=3}
{0=5, 1=1}
/*分区*/
public static void partitioningBy(){
List list = users();
Map> part = list.stream()
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(user -> user.getAge() <= 30));
System.out.println(new Gson().toJson(part));
}
---结果---
{"false":
[
{"name":"赵","age":99,"sex":0,"address":"江苏","money":100000},
{"name":"钱","age":45,"sex":0,"address":"山东","money":600},
{"name":"孙","age":48,"sex":0,"address":"河南","money":1100}],
"true":
[
{"name":"李","age":18,"sex":0,"address":"陕西","money":1000},
{"name":"周","age":16,"sex":1,"address":"安徽","money":500},
{"name":"武","age":17,"sex":1,"address":"上海","money":800},
{"name":"郑","age":19,"sex":0,"address":"北京","money":900},
{"name":"王","age":18,"sex":1,"address":"深圳","money":800}]
}
3.2、stream方法2
- for
- filter
- map
- toList
- toMap
- distinct
- sorted
- group
package stream;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class StreamApplication {
static class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public User(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List userList = Arrays.asList(
new User(1, "a"),
new User(2, "b"),
new User(3, "c"),
new User(4, "d"));
// for 循环
userList.forEach(
user -> System.out.println(user.getId())
);
// map键拼接
Map map = new HashMap();
userList.stream().forEach(
user -> map.put(user.getId() +"_"+user.getName(),user.getName() );
);
// 遍历map
map.stream().foreach(
(key,value) -> {
System.out.println(key+value)
}
);
// filter
// 数字比较
List userList = userList.stream()
.filter(user -> user.getId() > 2)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 字符串
List userList = userList.stream()
.filter(user -> "a".equals(user.getName()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// List name
List userList = userList.stream()
.filter(user -> user.getId() > 2)
.map(User::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// count
long count = userList.stream()
.filter(user -> user.getId() > 2)
.count()
// map 用法
List users = userList.stream()
.map(User::getId)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// toList用法
List list = userList.stream()
.map(User::getId)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// toMap 用法
Map map = userList.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(User::getId, User::getName));
// 使用distinct()方法去重
List list = new ArrayList<>();
List distinctList = list.stream()
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// sorted()方法对元素进行排序
List list = new ArrayList<>();
// 按照分数升序排序
List sortedList = list.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparingDouble(Student::getScore))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 按照年龄降序排序
List reversedList = list.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(Student::getAge).reversed())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// groupingBy()方法对元素进行分组
List list = new ArrayList<>();
Map> groupByMajor = list.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getMajor));
}
}
3.3、stream方法3
-
sort
// 排序
List list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new User("a", "1"));
list.add(new User("b", "2"));
// 正序排序
list.sort((user1,user2)->user1.getUserId() - user2.getUserId());
list.forEach(user -> {
System.out.println(user);
});
// 倒序排序
list.sort((((o1, o2) -> o2.getUserId() - o1.getUserId())));
list.forEach(user -> {
System.out.println(user);
});
// 多字段排序
ArrayList oldList1 = oldList.stream()
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(
Collectors.toCollection(
()-> new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(table -> table.getAge() + ";" + table.getNo())))
, ArrayList::new)
); -
List --> Map
// List-->Map
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new User("赵", 16, "安徽"));
list.add(new User("钱", 18, "山东"));
list.add(new User("孙", 20, "江苏"));
// key-value (String-String) key对应字符
Map userMap = list.stream()
.collect(
Collectors.toMap(User::getName, User::getStockCode,(k1, k2) -> k2)
);
// key-value (String-entity) key对应对象
Map list2 = list.stream()
.collect(
Collectors.toMap(User::getName, Function.identity(), (key1, key2) -> key2)
);
// key-value (String-entity) 多字段拼接key对应对象
Map list3 = list.stream()
.collect(
Collectors.toMap(user->user.getName()+"_"+user.getAge(),Function.identity(), (key1, key2) -> key2)
);
// key-value (String-List) key对应list
Map> list4= list.stream()
.collect(
Collectors.groupingBy(User::getName)
);
-
List 去重
// List去重
List list1 = list.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
// List对象一个属性去重
List list2 = list.stream()
.collect(
Collectors.collectingAndThen(
Collectors.toCollection(() -> new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(User::getName))),
ArrayList::new)
);
// List对象多属性去重
List list3 = list.stream()
.collect(
Collectors.collectingAndThen(
Collectors.toCollection(() -> new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(user -> user.getName() + ";" + user.getAge()))),
ArrayList::new)
);
-
List交集 、差集
Student s1 = new Student("a",10);
Student s2 = new Student("b",11);
Student s3 = new Student("c",12);
Student s4 = new Student("d",13);
Student s5 = new Student("a",10);
List oldList = new ArrayList() {{
add(s1);
add(s2);
add(s3);
}};
List oldAgeList = oldList.stream().map(x -> x.getAge()).collect(Collectors.toList());
List newList = new ArrayList() {{
add(s4);
add(s5);
}};
List newAgeList = newList.stream().map(x -> x.getAge()).collect(Collectors.toList());
// List 根据Bean的一个属性求两个list的交集 差集
// 交集
List updList = newList.stream()
.filter(item ->
oldList.stream()
.map(e -> e.getAge())
.collect(Collectors.toList())
.contains(item.getAge())
)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 差集 (new - old)
List addList = newList.stream()
.filter(item ->
!oldList.stream()
.map(e -> e.getAge())
.collect(Collectors.toList())
.contains(item.getAge())
)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 差集 (old - new)
List delList = oldList.stream()
.filter(item ->
!newList.stream()
.map(e -> e.getAge())
.collect(Collectors.toList())
.contains(item.getAge())
)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// list 和 List 取差集
List list3 = new ArrayList() {{
add("a");
add("b");
add("b");
}};
List listStr = list3.stream()
.filter(item ->
!newList.stream()
.map(e -> e.getHaircolor())
.collect(Collectors.toList())
.contains(item)
)
.collect(Collectors.toList());