(源码解析)mybatis调用链之XMLMapperBuilder解析Mapper
创建XMLMapperBuilder对象
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());XMLMapperBuilder继承于BaseBuilder
public XMLMapperBuilder(InputStream inputStream, Configuration configuration, String resource, Map sqlFragments) {
this(new XPathParser(inputStream, true, configuration.getVariables(), new XMLMapperEntityResolver()),
configuration, resource, sqlFragments);
} 初始化一个XPathParser对象,该对象使用dom和xpath技术解析xml文件
private XMLMapperBuilder(XPathParser parser, Configuration configuration, String resource, Map sqlFragments) {
super(configuration);
this.builderAssistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource);
this.parser = parser;
this.sqlFragments = sqlFragments;
this.resource = resource;
} 进入XMLMapperBuilder另外构造函数,首先调用父类构造函数,为configuration、typeAliasRegistry、typeHandlerRegistry对象赋值。
其次创建MapperBuilderAssistant对象,用于辅助XMLMapperBuilder和XMLStatementBuilder解析mapper.xml文件,完善属性信息,并注册到configuration对象。
MapperBuilderAssistant同样继承于BaseBuilder。 在创建对象时,调用父类构造函数,为configuration、typeAliasRegistry、typeHandlerRegistry对象赋值。
最终给XMLMapperBuilder对象的parser、sqlFragments、resource属性赋值,XMLMapperBuilder对象构建完成。
mapperParser.parse();调用XMLMapperBuilder的parse方法,方法如下:
public void parse() {
//判断是否已经加载该配置文件
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));//处理mapper节点
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);//将mapper文件添加到configuration.loadedResources中
bindMapperForNamespace();//注册mapper接口
}
//处理解析失败的ResultMap节点
parsePendingResultMaps();
//处理解析失败的CacheRef节点
parsePendingCacheRefs();
//处理解析失败的Sql语句节点
parsePendingStatements();
}parse方法中,首先判断判断是否已经加载该配置文件,若未加载,贼进入configurationElement方法,开始处理mapper节点。
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
//获取mapper节点的namespace属性
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
//设置builderAssistant的namespace属性
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
//解析cache-ref节点
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
//重点分析 :解析cache节点----------------1-------------------
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
//解析parameterMap节点(已废弃)
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
//重点分析 :解析resultMap节点(基于数据结果去理解)----------------2-------------------
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
//解析sql节点
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
//重点分析 :解析select、insert、update、delete节点 ----------------3-------------------
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}configurationElement方法主要作用就是解析mapper中的各个节点,此处一一说明。
1、获取mapper节点的namespace属性
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
2、设置builderAssistant的namespace属性
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
3、cacheRefElement解析cache-ref节点
private void cacheRefElement(XNode context) {
if (context != null) {
configuration.addCacheRef(builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(), context.getStringAttribute("namespace"));
CacheRefResolver cacheRefResolver = new CacheRefResolver(builderAssistant, context.getStringAttribute("namespace"));
try {
cacheRefResolver.resolveCacheRef();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteCacheRef(cacheRefResolver);
}
}
}4、cacheElement解析cache节点
private void cacheElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
//获取cache节点的type属性,默认为PERPETUAL
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
//找到type对应的cache接口的实现
Class typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
//读取eviction属性,既缓存的淘汰策略,默认LRU
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
//根据eviction属性,找到装饰器
Class evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
//读取flushInterval属性,既缓存的刷新周期
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
//读取size属性,既缓存的容量大小
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
//读取readOnly属性,既缓存的是否只读
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
//读取blocking属性,既缓存的是否阻塞
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
//通过builderAssistant创建缓存对象,并添加至configuration
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
}上述cache解析即为解析二级缓存,若是配置了二级缓存,则会通过builderAssistant创建缓存对象,并添加至configuration
//通过builderAssistant创建缓存对象,并添加至configuration
public Cache useNewCache(Class typeClass,
Class evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
//经典的建造起模式,创建一个cache对象
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
//将缓存添加至configuration,注意二级缓存以命名空间为单位进行划分
configuration.addCache(cache);
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}经典的建造者模式,创建一个cache对象,
public Cache build() {
//设置缓存的主实现类为PerpetualCache
setDefaultImplementations();
//通过反射实例化PerpetualCache对象
Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id);
setCacheProperties(cache);//根据cache节点下的信息,初始化cache
// issue #352, do not apply decorators to custom caches
if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) {//如果cache是PerpetualCache的实现,则为其添加标准的装饰器
for (Class decorator : decorators) {//为cache对象添加装饰器,这里主要处理缓存清空策略的装饰器
cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache);
setCacheProperties(cache);
}
//通过一些属性为cache对象添加装饰器
cache = setStandardDecorators(cache);
} else if (!LoggingCache.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())) {
//如果cache不是PerpetualCache的实现,则为其添加日志的能力
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
}
return cache;
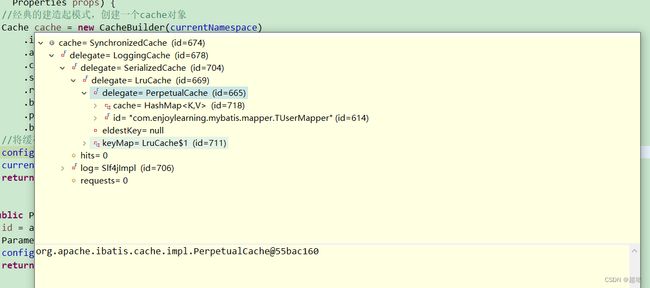
} 观察下图可以看到,整体的Cache使用了装饰器模式进行层层嵌套。
可以看到,最终将二级缓存添加到configuration中,二级缓存以命名空间为单位进行划分。以及将该cache设置为MapperBuilderAssistant对象的currentCache属性值。在后续XMLStatementBuilder解析sql语句生成MappedStatement对象时会使用到。
5、parameterMapElement解析parameterMap节点
private void parameterMapElement(List list) throws Exception {
for (XNode parameterMapNode : list) {
String id = parameterMapNode.getStringAttribute("id");
String type = parameterMapNode.getStringAttribute("type");
Class parameterClass = resolveClass(type);
List parameterNodes = parameterMapNode.evalNodes("parameter");
List parameterMappings = new ArrayList<>();
for (XNode parameterNode : parameterNodes) {
String property = parameterNode.getStringAttribute("property");
String javaType = parameterNode.getStringAttribute("javaType");
String jdbcType = parameterNode.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String resultMap = parameterNode.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String mode = parameterNode.getStringAttribute("mode");
String typeHandler = parameterNode.getStringAttribute("typeHandler");
Integer numericScale = parameterNode.getIntAttribute("numericScale");
ParameterMode modeEnum = resolveParameterMode(mode);
Class javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaType);
JdbcType jdbcTypeEnum = resolveJdbcType(jdbcType);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class> typeHandlerClass = (Class>) resolveClass(typeHandler);
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = builderAssistant.buildParameterMapping(parameterClass, property, javaTypeClass, jdbcTypeEnum, resultMap, modeEnum, typeHandlerClass, numericScale);
parameterMappings.add(parameterMapping);
}
builderAssistant.addParameterMap(id, parameterClass, parameterMappings);
}
} 6、resultMapElements解析resultMap节点
//解析resultMap节点,实际就是解析sql查询的字段与pojo属性之间的转化规则
private void resultMapElements(List list) throws Exception {
//遍历所有的resultmap节点
for (XNode resultMapNode : list) {
try {
//解析具体某一个resultMap节点
resultMapElement(resultMapNode);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// ignore, it will be retried
}
}
}
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode) throws Exception {
return resultMapElement(resultMapNode, Collections. emptyList());
}
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode, List additionalResultMappings) throws Exception {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("processing " + resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
//获取resultmap节点的id属性
String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("id",
resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
//获取resultmap节点的type属性
String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("type",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("ofType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType"))));
//获取resultmap节点的extends属性,描述继承关系
String extend = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("extends");
//获取resultmap节点的autoMapping属性,是否开启自动映射
Boolean autoMapping = resultMapNode.getBooleanAttribute("autoMapping");
//从别名注册中心获取entity的class对象
Class typeClass = resolveClass(type);
Discriminator discriminator = null;
//记录子节点中的映射结果集合
List resultMappings = new ArrayList<>();
resultMappings.addAll(additionalResultMappings);
//从xml文件中获取当前resultmap中的所有子节点,并开始遍历
List resultChildren = resultMapNode.getChildren();
for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren) {
if ("constructor".equals(resultChild.getName())) {//处理节点
processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else if ("discriminator".equals(resultChild.getName())) {//处理节点
discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else {//处理 节点
List flags = new ArrayList<>();
if ("id".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);//如果是id节点,向flags中添加元素
}
//创建ResultMapping对象并加入resultMappings集合中
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags));
}
}
//实例化resultMap解析器
ResultMapResolver resultMapResolver = new ResultMapResolver(builderAssistant, id, typeClass, extend, discriminator, resultMappings, autoMapping);
try {
//通过resultMap解析器实例化resultMap并将其注册到configuration对象
return resultMapResolver.resolve();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteResultMap(resultMapResolver);
throw e;
}
}
7、解析sql节点
private void sqlElement(List list) throws Exception {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
sqlElement(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
sqlElement(list, null);
}
private void sqlElement(List list, String requiredDatabaseId) throws Exception {
for (XNode context : list) {
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
if (databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, requiredDatabaseId)) {
sqlFragments.put(id, context);
}
}
} 8、解析select、insert、update、delete节点
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
具体详情请查看mybatis调用链之XMLStatementBuilder解析解析sql语句节点
处理完mapper节点后,将将mapper文件添加到configuration.loadedResources属性中,
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
然后需要注册mapper接口,
bindMapperForNamespace();
//注册mapper接口
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
//获取命名空间
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class boundType = null;
try {
//通过命名空间获取mapper接口的class对象
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//ignore, bound type is not required
}
if (boundType != null) {
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {//是否已经注册过该mapper接口?
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag
// to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface
// look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource
//将命名空间添加至configuration.loadedResource集合中
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
//将mapper接口添加到mapper注册中心
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
}上述方法,具体步骤:
1、获取mapper接口的命名空间
2、将命名空间添加至configuration.loadedResources集合中
3、将mapper接口添加到mapper注册中心MapperRegistry的knownMappers中
//记录了mapper接口与对应MapperProxyFactory之间的关系
private final Map, MapperProxyFactory> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
......
//将mapper接口的工厂类添加到mapper注册中心
public void addMapper(Class type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
//实例化Mapper接口的代理工程类,并将信息添加至knownMappers
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
//解析接口上的注解信息,并添加至configuration对象
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
} 最后,
处理解析失败的ResultMap节点 parsePendingResultMaps();
private void parsePendingResultMaps() {
Collection incompleteResultMaps = configuration.getIncompleteResultMaps();
synchronized (incompleteResultMaps) {
Iterator iter = incompleteResultMaps.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
try {
iter.next().resolve();
iter.remove();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// ResultMap is still missing a resource...
}
}
}
} 处理解析失败的CacheRef节点 parsePendingCacheRefs();
private void parsePendingCacheRefs() {
Collection incompleteCacheRefs = configuration.getIncompleteCacheRefs();
synchronized (incompleteCacheRefs) {
Iterator iter = incompleteCacheRefs.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
try {
iter.next().resolveCacheRef();
iter.remove();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// Cache ref is still missing a resource...
}
}
}
} 处理解析失败的Sql语句节点 parsePendingStatements();
private void parsePendingStatements() {
Collection incompleteStatements = configuration.getIncompleteStatements();
synchronized (incompleteStatements) {
Iterator iter = incompleteStatements.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
try {
iter.next().parseStatementNode();
iter.remove();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// Statement is still missing a resource...
}
}
}
}