【逆向】C与汇编的关系
程序1
使用 VC6.0 编译如下程序(使用 VC6.0 的原因是该编译器不会对代码进行过多的优化,因此适合逆向入门)
// 01.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
# include "stdafx.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
printf("Hello World!\n");
return 0;
}
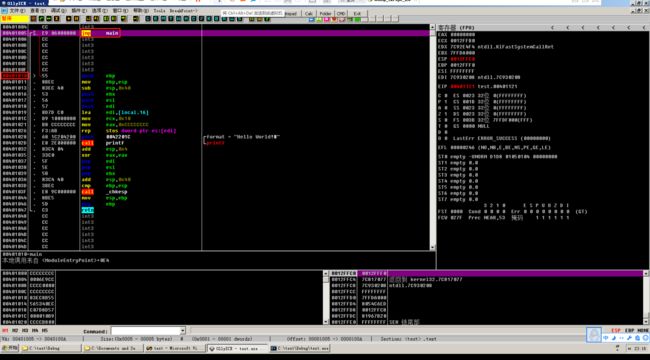
得到的程序使用 OllyICE 打开,找到 main 函数位置
可以看到 VC 将 printf 编译成了一个常量,也就是启用了全局堆来存放。
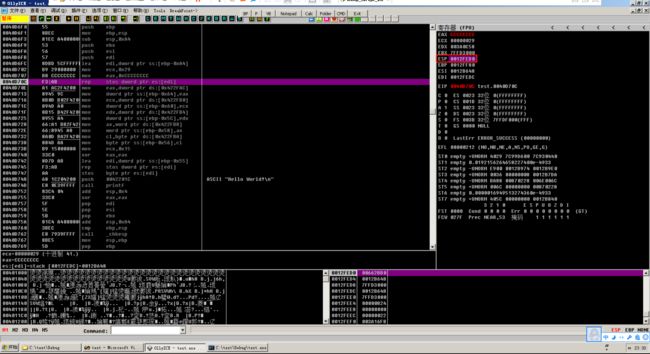
执行到 printf 后,右键选择在数据窗口跟随,可以看到该区段堆的结构
接下来修改程序
// 01.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
# include "stdafx.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
char buff[100] = {"sssssssssssss\0"};
printf("Hello World!\n");
return 0;
}
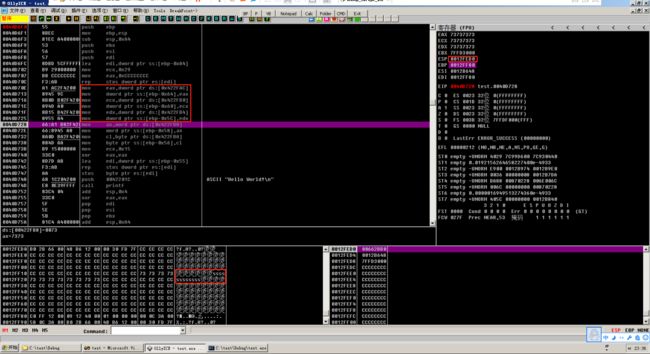
跟踪发现,VC 给程序分配了一段 0xA4 大小的堆栈空间,并且对这段空间进行了初始化
选中寄存器区域的 ESP,右键在数据区跟随,到达堆栈。继续执行可以看到首先堆栈被初始化,然后分三次将 13 个 ‘s’ 写入内存
程序2
再调试如下程序
// 01.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
# include "stdafx.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
int b = 0;
b = 15;
int i = b + 1;
printf("Hello World!\n");
return 0;
}
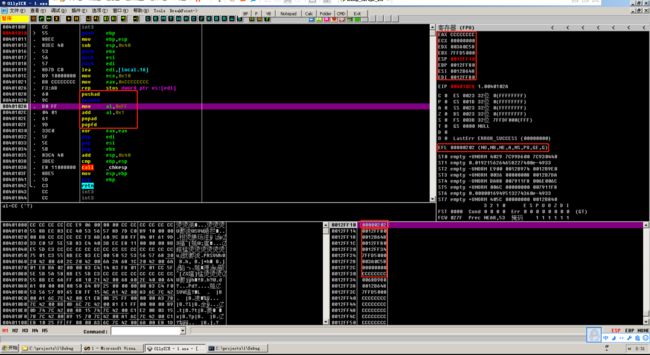
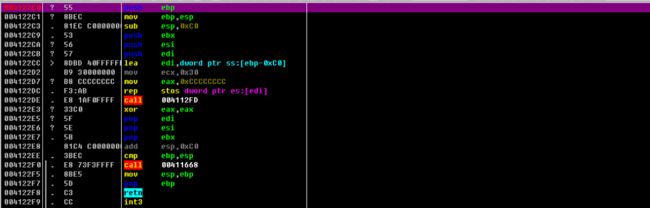
首先程序保存原来 EBP 的值,并分配新的堆栈空间。然后保存原来 EDI 的值,并分配新的数据区,使用rep指令对新数据区初始化。
使用内联汇编的方式编写程序并编译
#include "stdafx.h"
#include 可以看到,执行pushad会将所有寄存器的内容保存到栈里,执行pushfd会将所有标志位保存到栈里
条件分支语句
下面再编译一个包含if-else的程序
#include "stdafx.h"
#include 内联汇编
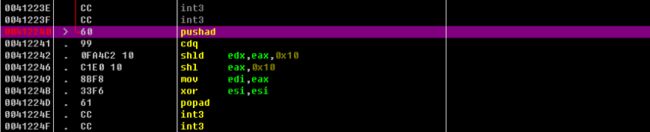
下面演示如何内联汇编。打开一段比较复杂的程序,比如 Wechat Setup.exe,跳过开头很多程序入口,假设想要使用如下一段汇编指令的原生态代码
cdq
shld edx,eax,0x10
shl eax,0x10
mov edi,eax
xor esi,esi
接下来打开 VC2008,新建项目;勾选Visual C+±控制台应用程序,勾选预编译头;右键左侧项目名,选择属性-配置属性-C/C+±代码生成-运行时库,选择多线程(/MT),这样就可以将 VC 库打到 exe 文件里去了;使用 VC2008 生成可执行文件。
// 04.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include 可以看到 VC2008 编译出文件的入口位置与 VC6.0 完全不一样
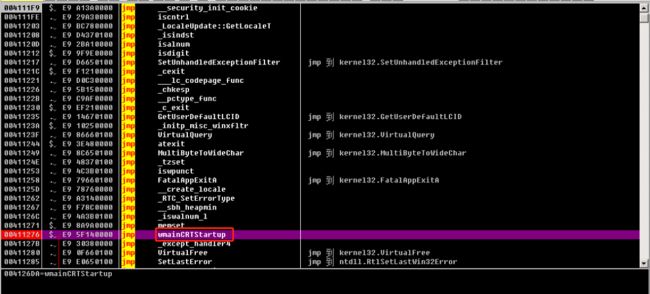
找到唯一一个 call 语句后设置断点并步入,在下面找到 wmainCRTStartup,双击跳转
双击 jump 语句跳转
找到我们的 main 函数,并双击跳转
再双击跳转
双击 call 指令跳转,找到我们定义的 Plus 函数
双击跳转,找到我们写的裸函数内容
可以看到完全没有堆栈初始化等内容,也就是说使用 naked 定义的裸函数,所有的堆栈初始化、保护恢复现场等,都是由我们自己来决定的。我们尝试不适用裸函数来定义一个函数。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include 可以看到编译器承包了所有工作。