【elfboard linux开发板】6. uart 实现串口收发功能
1. 硬件连线
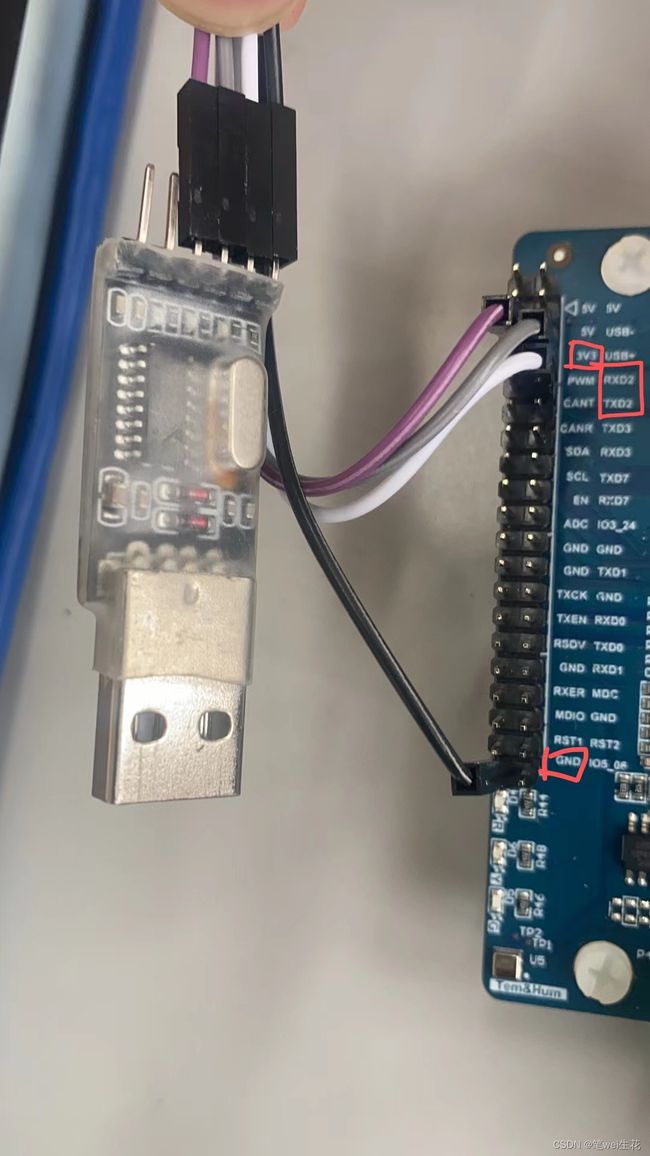
准备一个usb转ttl的模块, 对应的引脚的连接分为:
VCC - 3V3; GND - GND; RXD - TXD2; TXD - RXD2 ;
连接方式如下图,并且将ttl模块连接至电脑usb口:

2.发送功能实现(uart_send.c)
a. 初始化说明
open终端文件时,带上如下参数 O_RDWR, O_NOCTTY, O_NONBLOCK;
b. 程序说明:
编译生成uart_send_arm发送到开发板:
$CC uart_send.c -o uart_send_arm scp uart_send_arm [email protected]:/home/root/ ssh [email protected]
使用方式:
./uart_send_arm tty设备号 -b 波特率 -w 字符
补充说明:
发送的字符列表需要全部先置0,以防止乱码
需要使用tcflush(fd,TCIOFLUSH)将前面没读取和传输完的列表清空;
c. 实现
#include 打开串口工具,将串口工具的串口、波特率、停止位、数据位、奇偶校验保持和程序中设置的一致,然后打开串口,接着在嵌入式Linux上启动程序;串口工具可以收到数据。
发送字符串的实现效果如下:
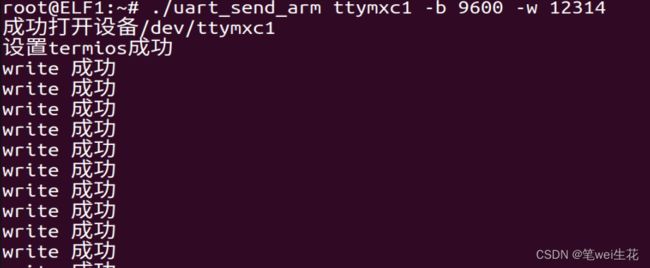

3. 接收功能实现(uart_receive.c)
a. 初始化补充说明
termios结构体中c_iflag的INPCK位需要被设置 : 使能输入校验码检测
termios_t->c_iflag |= INPCK;
termios中c_cflag中的CREAD位需要设置:
termios_t->c_cflag |= CREAD;
b. 具体程序
#include 
