前端调试,模拟数据利器之Mock Server使用教程来啦~
文章目录
- 1 MockServer是什么
- 2 为什么要使用MockServer
- 3 MockServer的作用
- 4 搭建MockServer服务
-
- 4.1 部署MockServer服务详细步骤
-
- 4.1.1 第一种方式(推荐)
- 4.1.2 第二种方式
- 4.2 启动Shell脚本
- 4.3 访问MockServer UI界面
- 5 MockServer服务的基础使用
-
- 5.1 项目启动时,初始化Expectations
- 5.2 访问模拟的数据
- 5.3 Creating Expectations && Query Expectations
-
- 5.3.1 Creating Expectations
- 5.3.2 Query Expectations
- 5.4 clear某个不需要的path
- 5.5 clear所有的path
- 6 数据持久化
1 MockServer是什么
MockServer其实就是一个用来模拟http(https)请求响应结果数据的服务器。通过这个MockServer服务,我们可以极大地方便接口的调试。
2 为什么要使用MockServer
如今的业务系统模块越来越多,功能也越来越复杂。及时的与前端调试也迎来了一些小的挑战。
假设有一个场景:
新项目刚开始启动时,这时候后台部分的接口都没有开发完成,这时候如果前端需要调试页面,该怎么调试呢?
傻傻的等着后台开发完成再进行调试?不可能的,这样你会影响项目正常上线。那么模拟数据就显得非常重要了,如何快速有效的模拟真实场景的数据?
有两种方案:
- 通常情况下,后台会把请求接口Api的结果先定义好,写死在action层,然后返回给前端,但是这种方案现在已经不怎么用了,效率太低
- 现在比较流行的方案,一般会
搭建一些server来进行mock,这样可以使得被开发功能的调试和测试功能能够正常进行下去。而MockServer就可以有效的解决这个问题,这也是MockServer的出现的原因
网上找了张图片,可以很好的说明使用MockServer前后的不同,如下图所示:
使用mock之前:

使用mock之后:

使用了Mock Server之后,前端可以不再依赖与后台的业务接口,在后台接口未开发完成时,可以模拟一些业务数据,来进行前台页面的调试,极大的节省了调试的成本。
3 MockServer的作用
对于通过HTTP或HTTPS与之集成的任何系统,MockServer都可以用作以下用途:
-
对于任何的http或者https请求,可以结合具体的业务场景,配置mock,来模拟接口Api,返回一个具体的响应结果
-
代理一个记录,并且可以选择修改请求路径和响应的结果
-
同时代理某些请求和模拟其他请求(both a proxy for some requests and a mock for other requests at the same time)
When MockServer receives a request it matches the request against active expectations that have been configured, if no matches are found it proxies the request if appropriate otherwise a 404 is returned.
首先我们会配置active expectations,当MockServer接收到与之匹配的http或者https请求时,就会返回匹配到的模拟的响应结果。如果没有匹配到active expectations,那么就会看看是否有合适的代理,有的话会代理这些http请求,否则返回404:
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
content-length: 0
connection: keep-alive
<Response body is empty>
Response code: 404 (Not Found); Time: 33ms; Content length: 0 bytes
4 搭建MockServer服务
4.1 部署MockServer服务详细步骤
4.1.1 第一种方式(推荐)
-
添加maven依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.mock-servergroupId> <artifactId>mockserver-nettyartifactId> <version>5.11.1version> dependency> -
启动MockServer
@PostConstruct public void startMockServer() { mockServer = startClientAndServer(1080); System.out.println("mock server【" + mockServer + "】 start..."); }
这样,即可实现基础的mock server服务部署。
4.1.2 第二种方式
-
从github上下载源码
git clone https://github.com/jamesdbloom/mockservice.git -
进入项目根目录
cd mockservice -
通过maven构建一个包含所有依赖的可执行jar包
./mvnw clean package -
成功生成的可执行jar包,在
mockserver-netty/target/目录下
mockserver-netty/target/mockserver-netty-5.11.1-jar-with-dependencies.jar -
将打包好的可执行jar包,上传到Linux服务器上,启动成功后,MockServer即部署完成
4.2 启动Shell脚本
这里送给老铁们一个shell脚本,方便启动jar项目服务:
#!/bin/sh
DIR=$(dirname $(readlink -f "$0"))
JAR_NAME="mockserver-netty-5.11.1-jar-with-dependencies"
JAR_FILE=${DIR}/${JAR_NAME}.jar
PID_FILE=${DIR}/${JAR_NAME}.pid
PID=$(cat ${PID_FILE})
if [ $PID -gt 0 ];then
kill -9 $PID
rm -f ${PID_FILE}
echo "mock server stop finished"
fi
java -Xms256m -Xmx256m -jar ${JAR_FILE} -serverPort 1001 & echo $! > ${PID_FILE}
4.3 访问MockServer UI界面
- 使用以下命令访问MockServer UI界面
http(s)://: /mockserver/dashboard
MockServer UI界面可以看到MockServer内部的运行状态,主要包括以下部分:
- logs
- active expectations
- requests received
- proxied requests
5 MockServer服务的基础使用
5.1 项目启动时,初始化Expectations
-
首先创建一个配置类
ExpectationInit,把需要初始化的期望初始化:package cn.smilehappiness.mockserver.expectation; import org.mockserver.mock.Expectation; import org.mockserver.server.initialize.ExpectationInitializer; import static org.mockserver.model.HttpRequest.request; import static org.mockserver.model.HttpResponse.response; /** ** Expectation Initializer Class,用来初始化 expectation *
* * @author smilehappiness * @Date 2020/8/16 17:13 */ public class ExpectationInit implements ExpectationInitializer { @Override public Expectation[] initializeExpectations() { return new Expectation[]{ new Expectation( request().withPath("/simpleFirst")).thenRespond(response().withBody("some first response") ), new Expectation( request().withPath("/simpleSecond")).thenRespond(response().withBody("some second response") ) }; } } -
启动mock server服务时,初始化期望配置类
@PostConstruct public void startMockServer() { ConfigurationProperties.enableCORSForAPI(true); //初始化期望配置类 ConfigurationProperties.initializationClass(ExpectationInit.class.getName()); //持久化期望数据 ConfigurationProperties.persistExpectations(true); mockServer = startClientAndServer(1080); System.out.println("mock server【" + mockServer + "】 start..."); }
以上两步,即可在MockServer服务启动时,初始化期望模拟数据。
5.2 访问模拟的数据
项目启动时,设置了两个简单的期望数据,可以通过Restful Api访问数据,访问格式:http://ip:port/path
比如: 访问http://localhost:1080/simpleFirst
【请求结果】
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
connection: keep-alive
content-length: 19
some first response
Response code: 200 (OK); Time: 32ms; Content length: 19 bytes
5.3 Creating Expectations && Query Expectations
创建和获取模拟的Expectations期望数据
5.3.1 Creating Expectations
可以使用postman等工具,添加expectations,比如:
使用put请求,http://localhost:1080/mockserver/expectation(/mockserver/expectation为固定写法)
请求json串内容:
{
"id": "test_mock",
"httpRequest" : {
"path" : "/hello/mock",
"method":"POST"
},
"httpResponse" : {
"body" : {
"status": 200,
"result": "Welcome to mock server!"
}
},
"priority" : 10
}
需要说明的是,这里id需要保证唯一,因为同一个path,会根据这个主键id修改之前的内容
5.3.2 Query Expectations
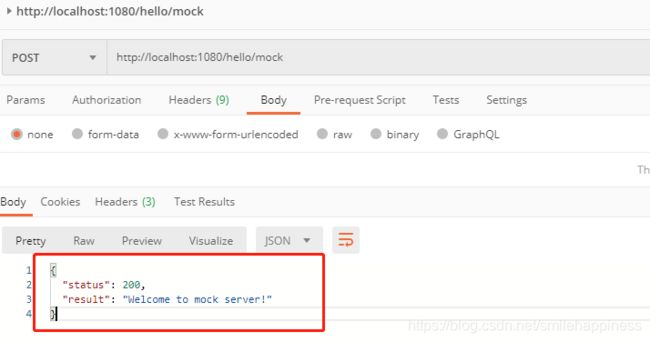
访问刚才创建的期望数据:
使用post请求,访问链接http://localhost:1080/hello/mock,即可访问到刚才创建的期望数据,如下图所示:
5.4 clear某个不需要的path
使用url:http://localhost:1080/mockserver/clear?type=EXPECTATIONS
例如:

日志如下:

5.5 clear所有的path
格式: curl -v -X PUT "http://localhost:1080/mockserver/reset
比如,笔者使用postman操作:

所有的期望数据都被清空了,这个操作需要谨慎呀

至此,基础使用已经ok了,但是有个小问题,如果mock server重启了,那么UI界面上,数据都丢失了,那么,数据持久化也是需要解决的一个问题,下面介绍下,MockServer expectations 数据如何持久化。
6 数据持久化
In MockServer expectations are only held in memory by default. However, it is possible to persist expectations to the local file system to ensure that they survive a restart of MockServer.
上面这句话意思是,MockServer expectations默认把数据保存在内存中,但是,你可以把数据持久化到文件中,这样,再重启MockServer之后,数据不会丢失。
持久化大致需要三个步骤:
-
persistExpectations属性,需要使用以下方式开启(true)
ConfigurationProperties.persistExpectations(boolean persistExpectations) -
使用以下方法,设置expectations持久化的路径
ConfigurationProperties.persistedExpectationsPath(String persistedExpectationsPath)
The file path used to save persisted expectations as json, which is updated whenever the expectation state is updated (i.e. add, clear, expires, etc)比如: 设置path为
persistedExpectations.json -
当MockServer服务启动时,会通过以下方法加载持久化文件,并初始化文件中每一组的期望数据,The expected format of the file is a
JSON arrayof expectations
ConfigurationProperties.initializationJsonPath(String initializationJsonPath)注意:为了确保下次MockServer启动时初始化JsonPath时加载持久化的期望,那么persistedExpectationsPath应该匹配,并且persistExpectations需要设置为true
配置后,重启MockServer,出现以下界面,说明持久化配置成功:

好啦,本部分内容先介绍到这里了,后续有用到代理(比如使用代理,隔离单个服务等等)相关的内容再更新吧,这里面说的,基本上可以满足日常使用了,希望对老铁们有所帮助哈。
本文涉及到的相关代码已上传GitHub,需要的小伙伴们可以下载Code
如果GitHub网速不好的话,也可以使用另一个下载链接下载
参考资料链接:
https://github.com/mock-server/mockserver
https://www.mock-server.com/
写博客是为了记住自己容易忘记的东西,另外也是对自己工作的总结,希望尽自己的努力,做到更好,大家一起努力进步!
如果有什么问题,欢迎大家评论,一起探讨,代码如有问题,欢迎各位大神指正!
给自己的梦想添加一双翅膀,让它可以在天空中自由自在的飞翔!

