LeetCode算法题4:DFS和BFS
文章目录
- 前言
-
- 深度优先搜索算法伪代码:
- 广度优先搜索算法伪代码:
- 一、图像渲染
-
- DFS:
- BFS:
-
- 上面BFS算法存在的问题:
- 修改 1:
- 修改 2:
- 二、岛屿的最大面积
-
- DFS:
- BFS :
- 三、合并二叉树
-
- DFS:
- BFS:
-
- 上面BFS算法存在的问题:
- 修改 1:
- 修改 2:
- 四、填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
-
- 思路 1:
-
- 树的层序遍历
- 思路 2:
- 五、01矩阵
-
- BFS:
- DP:
- 六、腐烂的橘子
-
- BFS:
- 总结
前言
Leetcode算法系列:https://leetcode-cn.com/study-plan/algorithms/?progress=njjhkd2
简单总结一下DFS、BFS相关的算法题:
深度优先搜索算法伪代码:
一般需要建立一个 visited 数组来标记访问过的元素。从一个节点开始,访问它;找到它未被访问过的后续节点,递归执行此算法。以下图的二叉树为例:访问节点的顺序依次为:A->B->C->D->E->F 类似于树的先序遍历。遍历方式类似于先死磕一个方向打开缺口,再由缺口处扩散来扩大战果,直至结束。
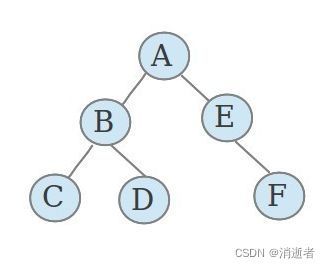
递归实现的伪代码为:
function dfs(node, visited) {
visit(node);//访问元素
visited[node]=true;//标记已访问
for (node in node.children()) {
if (visited[node]==false) //防止重复访问同一个元素。
dfs(node, visited);
}
}
广度优先搜索算法伪代码:
此算法和树的层序遍历基本一致。一般需要建立一个辅助队列。搜索方法为:一圈圈扩散,从内圈开始直到最外围,队列用来保持内外圈的搜索顺序(内圈遍历结束才能到外圈)。以上图的二叉树为例:访问节点的顺序依次为:A->B->E->C->D->F 类似于树的层序遍历。
伪代码 1:
function bfs(graph, root) {
queue = [];
queue.add([root]);
int [] visited;
visited[root]=true;
while (!queue.isEmpty())
node = queue.pop();
visit(node);
for (node in node.children()&&visited[node]==false) {
queue.add(node);
visited[node]=true;
}
伪代码 2:
function bfs(graph, root) {
queue = [];
queue.add([root]);
visit(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty())
node = queue.pop();
for (node in node.children()) {
queue.add(node);
visit(node);
}
广度优先伪代码 1 和 2 的差别后面在具体的问题中会讲到,一般常采用伪代码 2的写法(即建议应该采用入队时访问,并且在某些情况下在出队时访问会造成错误)。
一、图像渲染
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flood-fill/
题目描述:有一幅以 m x n 的二维整数数组表示的图画 image ,其中 image[i][j] 表示该图画的像素值大小。
你也被给予三个整数 sr , sc 和 newColor 。你应该从像素 image[sr][sc] 开始对图像进行 上色填充 。
为了完成 上色工作 ,从初始像素开始,记录初始坐标的 上下左右四个方向上 像素值与初始坐标相同的相连像素点,接着再记录这四个方向上符合条件的像素点与他们对应 四个方向上 像素值与初始坐标相同的相连像素点,……,重复该过程。将所有有记录的像素点的颜色值改为 newColor 。
最后返回 经过上色渲染后的图像 。
DFS:
其中 oldColor 表示整个二维数组中值为 oldColor 的元素需要被更改为 newColor 。**下面的算法没有采用 visited 数组来标记访问过的元素,因为一旦发现元素的值为 oldColor,就会改变它的值为 newColor,不会造成程序多次访问同一个值为 oldColor 的元素,**也不会导致程序陷入循环。因此:参考上面的 DFS 模板,如果 visit() 方法不会对访问的元素造成改变,那么就需要一个 visited 数组来进行标记,否则如本题这样不需要 visited 数组的存在。参考算法如下:
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
int oldColor=image[sr][sc];
if(oldColor!=newColor)
floodFill0(image,sr,sc,oldColor,newColor);
return image;
}
public void floodFill0(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int oldColor, int newColor) {
if(sr<0||sc<0||sr>=image.length||sc>=image[0].length||image[sr][sc]!=oldColor)
return; //退出条件为数组元素越界或碰到不符合要求的元素(元素值不等于 oldColor)
image[sr][sc]=newColor;
floodFill0(image,sr+1,sc,oldColor,newColor);
floodFill0(image,sr-1,sc,oldColor,newColor);
floodFill0(image,sr,sc+1,oldColor,newColor);
floodFill0(image,sr,sc-1,oldColor,newColor);
}
稍微修改一下代码,如下:
int[] x={1,0,-1,0};
int[] y={0,1,0,-1};
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
int oldColor=image[sr][sc];
if(oldColor!=newColor)
floodFill0(image,sr,sc,oldColor,newColor);
return image;
}
public void floodFill0(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int oldColor, int newColor) {
if(sr<0||sc<0||sr>=image.length||sc>=image[0].length||image[sr][sc]!=oldColor)
return;
image[sr][sc]=newColor;
for(int i=0;i<x.length;i++)
floodFill0(image,sr+x[i],sc+y[i],oldColor,newColor);
}
BFS:
从起点开始一圈圈往外扩散。参考算法如下:
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
int oldColor=image[sr][sc];
if(oldColor!=newColor){
int[] dx={1,0,-1,0};
int[] dy={0,1,0,-1};
Queue<int[]> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{sr,sc});
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] cell=queue.poll();
int x=cell[0],y=cell[1];
image[x][y]=newColor;
for(int i=0;i<dx.length;i++){
int mx=x+dx[i],my=y+dy[i];
if(mx<0||my<0||mx>=image.length||my>=image[0].length||image[mx][my]!=oldColor){
continue;
}
queue.offer(new int[]{mx,my});
}
}
}
return image;
}
上面BFS算法存在的问题:
按照本题描述中的示例,左上角 (0,0) 处的 1 会被添加进队列两次,分别由(0,1) 处的 1 添加一次,(1,0) 处的 1 再添加一次。上述算法有可能导致同一个元素入队多次,这是我们不希望看到的。而伪代码 2 保证了 BFS 中每个元素只能入队一次。
修改 1:
伪代码 2:在每个元素入队时改变它的值为 newColor。参考如下:
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
int oldColor=image[sr][sc];
if(oldColor!=newColor){
int[] dx={1,0,-1,0};
int[] dy={0,1,0,-1};
Queue<int[]> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{sr,sc});
image[sr][sc]=newColor;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] cell=queue.poll();
int x=cell[0],y=cell[1];
for(int i=0;i<dx.length;i++){
int mx=x+dx[i],my=y+dy[i];
if(mx<0||my<0||mx>=image.length||my>=image[0].length||image[mx][my]!=oldColor){
continue;
}
queue.offer(new int[]{mx,my});
image[mx][my]=newColor;
}
}
}
return image;
}
修改 2:
另一种方式即采用标记数组,这样需要在每次入队时标记元素为 true,修改如下:
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
boolean[][] visited=new boolean[image.length][image[0].length];
int oldColor=image[sr][sc];
if(oldColor!=newColor){
int[] dx={1,0,-1,0};
int[] dy={0,1,0,-1};
Queue<int[]> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{sr,sc});
visited[sr][sc]=true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] cell=queue.poll();
int x=cell[0],y=cell[1];
image[x][y]=newColor;
for(int i=0;i<dx.length;i++){
int mx=x+dx[i],my=y+dy[i];
if(mx<0||my<0||mx>=image.length||my>=image[0].length||image[mx][my]!=oldColor||visited[mx][my]==true){
continue;
}
queue.offer(new int[]{mx,my});
visited[mx][my]=true;
}
}
}
return image;
}
为了防止BFS中同一个元素多次入队的情况产生,需要在每个元素入队时采用操作(比如修改,单纯的访问是不行的),其实更通用的方式是采用标记数组来实现。即像 DFS 那样。
二、岛屿的最大面积
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/max-area-of-island/
题目描述:给你一个大小为 m x n 的二进制矩阵 grid 。
岛屿 是由一些相邻的 1 (代表土地) 构成的组合,这里的「相邻」要求两个 1 必须在 水平或者竖直的四个方向上 相邻。你可以假设 grid 的四个边缘都被 0(代表水)包围着。
岛屿的面积是岛上值为 1 的单元格的数目。
计算并返回 grid 中最大的岛屿面积。如果没有岛屿,则返回面积为 0 。
DFS:
本题不会对访问的元素造成改变,所以需要 visited 数组来标记是否访问过该元素。参考代码如下:(当然也可以仿照上一题修改访问过元素的值,比如将访问过的 1 均变为 2,这样就不需要使用 visited 数组了。缺点是会对原来的数组状态造成破环。)
int count=0;
int[] x={1,0,0,-1};
int[] y={0,1,-1,0};
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int re=0,m=grid.length,n=grid[0].length;
boolean[][] visited=new boolean[m][n];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(grid[i][j]==1&&visited[i][j]==false){//找到每一个未被访问过的岛屿。计算并比较其面积
count=0;
DFS(grid,i,j,visited);
if(count>re)
re=count;
}
}
}
return re;
}
public void DFS(int[][] grid,int i,int j,boolean[][] visited){
if(i<0||j<0||i>=grid.length||j>=grid[0].length||grid[i][j]!=1||visited[i][j]==true)
return;
visited[i][j]=true;
count++;
for(int k=0;k<x.length;k++)
DFS(grid,i+x[k],j+y[k],visited);
}
不带有 visited 数组的 DFS 如下:
int count=0;
int[] x={1,0,0,-1};
int[] y={0,1,-1,0};
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int re=0,m=grid.length,n=grid[0].length;
int newValue=2;//用 2 来表示已经探查过的岛屿。
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(grid[i][j]==1){
count=0;
DFS(grid,i,j,newValue);
if(count>re)
re=count;
}
}
}
return re;
}
public void DFS(int[][] grid,int i,int j,int newValue){
if(i<0||j<0||i>=grid.length||j>=grid[0].length||grid[i][j]!=1)
return;
grid[i][j]=newValue;
count++;
for(int k=0;k<x.length;k++)
DFS(grid,i+x[k],j+y[k],newValue);
}
BFS :
和上一题类似,需要在元素入队的时候进行标记或修改操作(比如将值也置为 2 )来防止同一个元素多次入队;否则采用伪代码 1 的解法会导致同一个元素多次入队,会造成多次计数,这样就不能得到正确结果了。
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int count=0;
int[] x={1,0,0,-1};
int[] y={0,1,-1,0};
int re=0,m=grid.length,n=grid[0].length;
boolean[][] visited=new boolean[m][n];
Queue<int[]> queue=new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(grid[i][j]==1&&visited[i][j]==false){
count=0;
queue.offer(new int[]{i,j});
visited[i][j]=true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] tmp=queue.poll();
count++;
for(int k=0;k<x.length;k++){
int newX=tmp[0]+x[k],newY=tmp[1]+y[k];
if(newX<0||newY<0||newX>=m||newY>=n||grid[newX][newY]!=1||visited[newX][newY]==true)
continue;
queue.offer(new int[]{newX,newY});
visited[newX][newY]=true;
}
}
if(count>re)
re=count;
}
}
}
return re;
}
三、合并二叉树
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-binary-trees/
题目描述:给你两棵二叉树: root1 和 root2 。
想象一下,当你将其中一棵覆盖到另一棵之上时,两棵树上的一些节点将会重叠(而另一些不会)。你需要将这两棵树合并成一棵新二叉树。合并的规则是:如果两个节点重叠,那么将这两个节点的值相加作为合并后节点的新值;否则,不为 null 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
返回合并后的二叉树。
注意: 合并过程必须从两个树的根节点开始。
DFS:
参考先序遍历,先计算当前节点的最终值,在递归进行左右孩子节点值的判断,在这里需要分情况计算的。参考算法如下(这个算法完全重建了一个新的树):
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if(root1!=null&&root2!=null)
return new TreeNode(root1.val+root2.val,mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left),mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right));
else if(root1==null&&root2!=null)
return new TreeNode(root2.val,mergeTrees(null,root2.left),mergeTrees(null,root2.right));
else if(root2==null&&root1!=null)
return new TreeNode(root1.val,mergeTrees(root1.left,null),mergeTrees(root1.right,null));
else
return null;
}
不完全重建一个新的树的算法如下:
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if(root1!=null&&root2!=null)
return new TreeNode(root1.val+root2.val,mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left),mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right));
else if(root1==null&&root2!=null)
return root2;
else if(root2==null&&root1!=null)
return root1;
else
return null;
}
或者下面这种,思路更加清晰一些,更加像树的先序遍历。
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null) {
return t2;
}
if (t2 == null) {
return t1;
}
TreeNode merged = new TreeNode(t1.val + t2.val);
merged.left = mergeTrees(t1.left, t2.left);
merged.right = mergeTrees(t1.right, t2.right);
return merged;
}
BFS:
有两个不算问题的问题:1,两个数中的节点入队,如何保持相应节点的一致性?2,假设已经得到了最终树的层序遍历,如何恢复出一个树?但其实问题并没有想象中那么复杂,关键在于元素出队之后要对此元素的左右孩子做判断,来得到该位置上的最终节点。在这里只关心相应的两个节点均不为空的情形,若任意一个节点为空,新节点置为另一个不为空的节点。另外也不需要从层序遍历恢复出一个树,最终的目标树结构在每一次元素出队时都会建立一部分,直至结束。参考算法如下:()
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
LinkedList<TreeNode> q1=new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<TreeNode> q2=new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<TreeNode> q=new LinkedList<>();
if(root1!=null&&root2!=null)
q.offer(new TreeNode(root1.val+root2.val));
else if(root1!=null)
return root1;
else if(root2!=null)
return root2;
else
return null;
TreeNode re=q.peek();
q1.offer(root1);
q2.offer(root2);
while(!q1.isEmpty()){//这里的循环条件只要 q1 或 q2 不为空即可。
TreeNode a=q1.poll(),b=q2.poll(),c=q.poll();
TreeNode al=a.left,ar=a.right,bl=b.left,br=b.right;
if(al!=null&&bl!=null){
TreeNode tmp=new TreeNode(al.val+bl.val);
c.left=tmp;
q.offer(tmp);
q1.offer(al);
q2.offer(bl);
}
else if(al!=null)
c.left=al;
else if(bl!=null)
c.left=bl;
if(ar!=null&&br!=null){
TreeNode tmp=new TreeNode(ar.val+br.val);
c.right=tmp;
q.offer(c.right);
q1.offer(ar);
q2.offer(br);
}
else if(ar!=null)
c.right=ar;
else if(br!=null)
c.right=br;
}
return re;
}
上面BFS算法存在的问题:
按照本题描述中的示例,左上角 (0,0) 处的 1 会被添加进队列两次,分别由(0,1) 处的 1 添加一次,(1,0) 处的 1 再添加一次。上述算法有可能导致同一个元素入队多次,这是我们不希望看到的。而伪代码 2 保证了 BFS 一定要保证一个元素只能入队一次。
修改 1:
如果采用标记数组的话,需要在每次入队时标记元素为 true,修改如下:
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
boolean[][] visited=new boolean[image.length][image[0].length];
int oldColor=image[sr][sc];
if(oldColor!=newColor){
int[] dx={1,0,-1,0};
int[] dy={0,1,0,-1};
Queue<int[]> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{sr,sc});
visited[sr][sc]=true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] cell=queue.poll();
int x=cell[0],y=cell[1];
image[x][y]=newColor;
for(int i=0;i<dx.length;i++){
int mx=x+dx[i],my=y+dy[i];
if(mx<0||my<0||mx>=image.length||my>=image[0].length||image[mx][my]!=oldColor||visited[mx][my]==true){
continue;
}
queue.offer(new int[]{mx,my});
visited[mx][my]=true;
}
}
}
return image;
}
修改 2:
本题另一种更好的修改方式为:在每个元素入队时改变它的值为 newColor,这样在功能上可以做到和标记数组一样的效果。参考如下:
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
int oldColor=image[sr][sc];
if(oldColor!=newColor){
int[] dx={1,0,-1,0};
int[] dy={0,1,0,-1};
Queue<int[]> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{sr,sc});
image[sr][sc]=newColor;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] cell=queue.poll();
int x=cell[0],y=cell[1];
for(int i=0;i<dx.length;i++){
int mx=x+dx[i],my=y+dy[i];
if(mx<0||my<0||mx>=image.length||my>=image[0].length||image[mx][my]!=oldColor){
continue;
}
queue.offer(new int[]{mx,my});
image[mx][my]=newColor;
}
}
}
return image;
}
为了防止BFS中同一个元素多次入队的情况产生,需要在每个元素入队时采用操作(采用标记数组或别的方式),DFS 不会存在这样的问题,类似于先序遍历,它是先对元素进行操作,然后进行递归调用的。
四、填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/
题目描述:给定一个 完美二叉树 ,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
思路 1:
树的层序遍历
在此给出一段代码:用来分层打印出二叉树结点信息。如何分层是通过两个辅助变量做到的,其中 remainingNode 表示当前层还未打印的结点数量,nextLayerN 表示下一层的结点数量。
public void printTree(){//分层打印树节点。
if(root==null)
return;
ArrayDeque<BinaryNode<T>> queue=new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offerLast(root);
int remainingNode=1,nextLayerN=0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
BinaryNode<T> tmp=queue.pollFirst();
System.out.print(tmp.element+" ");
remainingNode--;
if(tmp.left!=null){
queue.offerLast(tmp.left);
nextLayerN++;
}
if(tmp.right!=null){
queue.offerLast(tmp.right);
nextLayerN++;
}
if(remainingNode==0){
System.out.println();
remainingNode=nextLayerN;
nextLayerN=0;
}
}
}
参考上面树的分层打印,可得到算法如下:
public Node connect(Node root) {
if(root==null)
return root;
LinkedList<Node> q=new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
int remain=1,nextLayer=0;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Node tmp=q.poll();
remain--;
if(remain>=1)//所有最右侧结点的 next 值在初始化时都为 null
tmp.next=q.peek();
if(tmp.left!=null){
q.offer(tmp.left);
nextLayer++;
}
if(tmp.right!=null){
q.offer(tmp.right);
nextLayer++;
}
if(remain==0){
remain=nextLayer;
nextLayer=0;
}
}
return root;
}
思路 2:
在该完全二叉树上,如果一个结点(node)存在左右结点,那么直接令 node.left.next=node.right 即可,那么 node.right.next 的值呢?如果右边没有结点,该值为 null;如果右边存在结点,那么 node.right.next=node.next.left;注意:在这里我们都是在上一层构建当前层的 next 关系的。可参考算法:
public Node connect(Node root) {
if(root==null)
return root;
Node beforeL=root,tmp;//保存上一层的最左侧结点
while(beforeL.left!=null){
tmp=beforeL;
while(tmp!=null){//构建当前层的 next 指针关系
tmp.left.next=tmp.right;
if(tmp.next!=null)
tmp.right.next=tmp.next.left;
tmp=tmp.next;
}
beforeL=beforeL.left;
}
return root;
}
五、01矩阵
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/01-matrix/
题目描述:给定一个由 0 和 1 组成的矩阵 mat ,请输出一个大小相同的矩阵,其中每一个格子是 mat 中对应位置元素到最近的 0 的距离。
两个相邻元素间的距离为 1 。
BFS:
一般来讲,BFS 算法可以参考树的层序遍历算法(分层遍历),之前讲过,BFS 可以看作是一圈圈扩散的,在本题中,初始值(初始入队值的数量)并非只有 1 个,而是 n 个 0,但是这 n 个 0 可以抽象为一个,称为超级源点。
因为它是多个源点的抽象,对它的处理方法和只有一个源点的方法没有本质上的区别。然后需要将这些 0 周围距离为 1 的点设置为 1,将这些 1 周围距离为 1 的点设置为 2 ,以此类推。
需要注意 BFS 一定需要防止同一个元素多次入队,用标记数组的话需要在入队时更改元素标记,而不是在出队时。参考算法如下:
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] mat) {
if(mat==null||mat.length==0||mat[0].length==0)
return new int[0][0];
int m=mat.length,n=mat[0].length;
LinkedList<int[]> queue=new LinkedList<>();
boolean[][] flag=new boolean[m][n];//用来防止重复入队
int numCurr=0,numNext=0,valueCurr=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)//将超级源点入队(即所有为 0 的点)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
if(mat[i][j]==0){
queue.add(new int[]{i,j});
flag[i][j]=true;
numCurr++;
}
int[] tmp;
int i,j;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
tmp=queue.poll();
numCurr--;
i=tmp[0];
j=tmp[1];
if(j+1<n&&flag[i][j+1]==false){
queue.add(new int[]{i,j+1});
flag[i][j+1]=true;
numNext++;
}
if(j-1>=0&&flag[i][j-1]==false){
queue.add(new int[]{i,j-1});
flag[i][j-1]=true;
numNext++;
}
if(i+1<m&&flag[i+1][j]==false){
queue.add(new int[]{i+1,j});
flag[i+1][j]=true;
numNext++;
}
if(i-1>=0&&flag[i-1][j]==false){
queue.add(new int[]{i-1,j});
flag[i-1][j]=true;
numNext++;
}
mat[i][j]=valueCurr;
if(numCurr==0){
valueCurr++;
numCurr=numNext;
numNext=0;
}
}
return mat;
}
上面代码是在出队的时候重新设置 mat 数组的值,为了和入队时设置 flag 统一,将其也放在入队的时候。顺便也换一种写法,如下:
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] mat) {
if(mat==null||mat.length==0||mat[0].length==0)
return new int[0][0];
int[] x={1,0,0,-1},y={0,1,-1,0};
int m=mat.length,n=mat[0].length;
LinkedList<int[]> queue=new LinkedList<>();
boolean[][] flag=new boolean[m][n];
int numCurr=0,numNext=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
if(mat[i][j]==0){
queue.add(new int[]{i,j});
flag[i][j]=true;
numCurr++;
}
int[] tmp;
int i,j;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
tmp=queue.poll();
numCurr--;
i=tmp[0];
j=tmp[1];
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
int newI=i+x[k],newJ=j+y[k];
if(newI>=0&&newI<m&&newJ>=0&&newJ<n&&flag[newI][newJ]==false){
queue.add(new int[]{newI,newJ});
numNext++;
flag[newI][newJ]=true;
mat[newI][newJ]=mat[i][j]+1;
}
}
if(numCurr==0){
numCurr=numNext;
numNext=0;
}
}
return mat;
}
DP:
动态规划的做法是请参考题解。它不需要从所有为 0 的点处开始计算,而是取决于状态转移:dp[i][j]=Math.min(dp[i][j],dp[i-1][j]+1,dp[i+1][j]+1,dp[i][j-1]+1,dp[i][j+1]+1),其中 dp[i][j]表示在(i,j)处的元素距离最近的 0 处的距离,即任意一个位置的距离是它本身和周围四个格子的距离加一之间的最小值。实现的算法比较巧妙,第一次遍历实现一半的状态转移(从任意位置的左上方开始),另一次遍历实现另一半的转台转移(从右下方开始),从而得到最终结果。参考算法如下:
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] mat) {
int i,j,m=mat.length,n=mat[0].length;
int[][] dp=new int[m][n];
for(i=0;i<m;i++) //初始化 dp 数组,
for(j=0;j<n;j++){
if(mat[i][j]!=0)
dp[i][j]=Integer.MAX_VALUE/2;
}
for(i=0;i<m;i++) //从左上方开始遍历
for(j=0;j<n;j++){
if(i-1>=0)
dp[i][j]=Math.min(dp[i][j],dp[i-1][j]+1);
if(j-1>=0)
dp[i][j]=Math.min(dp[i][j],dp[i][j-1]+1);
}
for(i=m-1;i>=0;i--) //从左上方开始遍历
for(j=n-1;j>=0;j--){
if(i+1<m)
dp[i][j]=Math.min(dp[i][j],dp[i+1][j]+1);
if(j+1<n)
dp[i][j]=Math.min(dp[i][j],dp[i][j+1]+1);
}
return dp;
}
六、腐烂的橘子
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotting-oranges/
题目描述:在给定的 m x n 网格 grid 中,每个单元格可以有以下三个值之一:
值 0 代表空单元格;
值 1 代表新鲜橘子;
值 2 代表腐烂的橘子。
每分钟,腐烂的橘子 周围 4 个方向上相邻 的新鲜橘子都会腐烂。
返回 直到单元格中没有新鲜橘子为止所必须经过的最小分钟数。如果不可能,返回 -1 。
BFS:
这道题很适合用 BFS,因为从一圈到另一圈,刚好 time 加一。所以采用超级源点的 BFS,在入队的时候更改相应的 grid 值。参考算法如下:
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
int[] xa={0,1,0,-1};
int[] ya={1,0,-1,0};
int m=grid.length,n=grid[0].length;
int[][] store=new int[m][n];
LinkedList<int[]> queue=new LinkedList<>();
int currT=0,num1=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(grid[i][j]==2){
queue.add(new int[]{i,j});
currT++;
}
else if(grid[i][j]==1)
num1++;
}
if(num1==0) //特殊情况。
return 0;
int time=-1,x,y,nextT=0,xx,yy;
int[] tmp;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
tmp=queue.poll();
x=tmp[0];
y=tmp[1];
currT--;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
xx=x+xa[i];
yy=y+ya[i];
if(xx>=0&&xx<m&&yy>=0&&yy<n&&grid[xx][yy]==1){
grid[xx][yy]=2;
queue.add(new int[]{xx,yy});
nextT++;
num1--;
}
}
if(currT==0){
time++;
currT=nextT;
nextT=0;
}
}
if(num1!=0)
return -1;
return time;
}
总结
完。