C# 字符串(System.String)知识点总结
环境:Visual Studio 2015,.NET Framework 4.0
本文参考MSDN : https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/
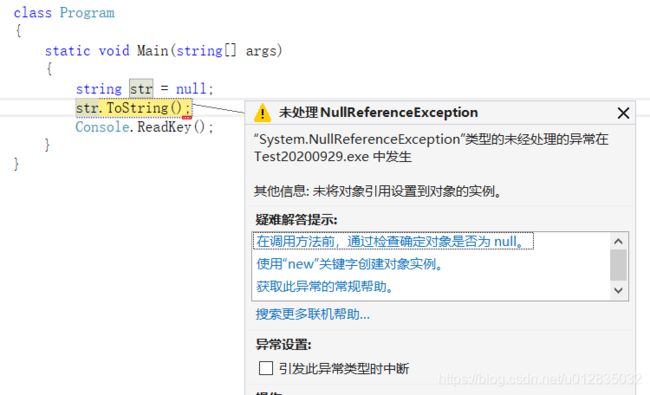
C#中的字符串,即System.String,一般用string表示。应用类型,可以为null。
为什么要强调说可以为null呢?
因为它会导致调用ToString()是报空引用错误。。。
String与string是什么关系?
在C#中,string是System.String的别名,String是公共库的语法,据说把string写成String之后,编译的时候就不用把string转成String了有一点性能提升。但是string才是C#的语法规范,个人推荐用string。
怎么定义字符串?
string str1 = "A123B";这就是定义字符串,并给他赋值A123B。
字符串等于""和null有什么不同?
string str1 = ""; → 空字符串,定义一个string的引用并且分配内存空间
string str2 = null; → 定义一个string的引用,只在栈上分配了空间,在堆上没有分配,直接使用该变量会报空引用错误
字符串常用操作
一、object to string
1、ToString()
调用ToString()方法把object转成字符串,如果object为null会报空引用错误。
介绍几种常用类型转字符串:
(1)、int to string,
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int i = 101;
string s = i.ToString();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
(2)、decimal to string,或者说小数转字符串
ToString("0.##")在把小数转字符串时去掉后面的0,也就是保留有效小数位。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
decimal d = 101.0000M;
string s = d.ToString();
Console.WriteLine(s);
string s2 = d.ToString("0.##");
Console.WriteLine(s2);
decimal d2 = 101.55000M;
s = d2.ToString();
Console.WriteLine(s);
s2 = d2.ToString("0.##");
Console.WriteLine(s2);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
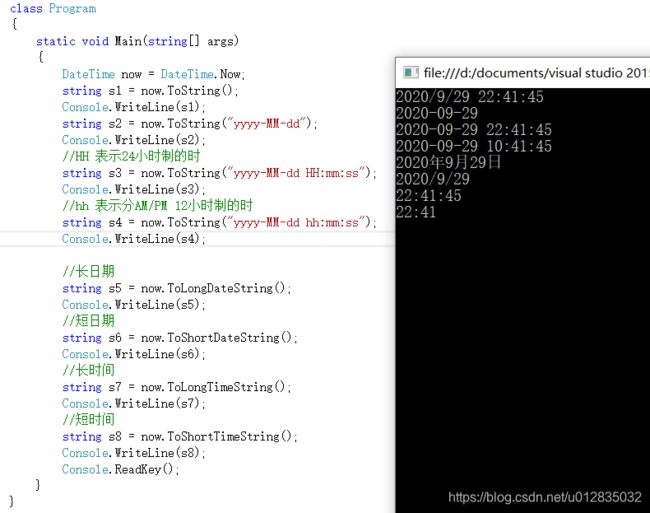
(3)、datetime to string,
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
DateTime now = DateTime.Now;
string s1 = now.ToString();
Console.WriteLine(s1);
string s2 = now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd");
Console.WriteLine(s2);
//HH 表示24小时制的时
string s3 = now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Console.WriteLine(s3);
//hh 表示分AM/PM 12小时制的时
string s4 = now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
Console.WriteLine(s4);
//长日期
string s5 = now.ToLongDateString();
Console.WriteLine(s5);
//短日期
string s6 = now.ToShortDateString();
Console.WriteLine(s6);
//长时间
string s7 = now.ToLongTimeString();
Console.WriteLine(s7);
//短时间
string s8 = now.ToShortTimeString();
Console.WriteLine(s8);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
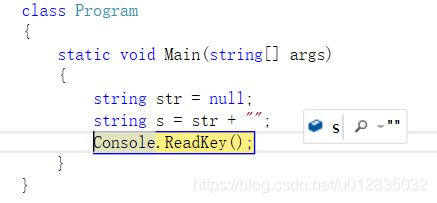
2、obj + ""
除了ToString()外,也可以在利用object+""把object转成字符串,如果字符串为null就把字符串转成"",并且那怕object为null也不会报异常。
二、字符串拼接
1、+
利用+把多个字符串连接成一个字符串
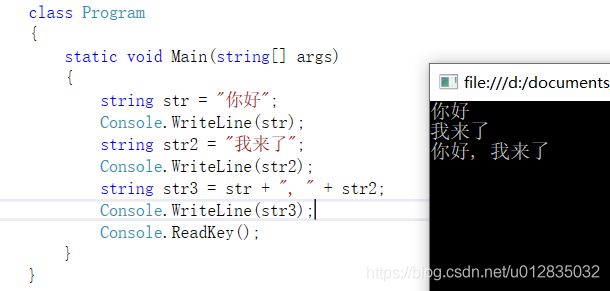
2、Format()
第一个参数是字符串模板,利用{}表数字括起来表示要在当前位置插入一个字符串,下标从0开始,Format()第二个参数起是模板的第一个参数。{0}表示模板的第一个参数,{1}表示模板的第二个参数。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str = "你好";
Console.WriteLine(str);
string str2 = "我来了";
Console.WriteLine(str2);
string str3 = string.Format("{0}, {1}。", str, str2);
Console.WriteLine(str3);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
三、判断字符串是否为""、null
1、str == "",str == null
2、IsNullOrEmpty()
用法如下,把要判断的字符串作参数传入,字符串为 ""、null、string.Empty 是返回true,否则返回false。
// 摘要:
// 指示指定的字符串是 null 还是 System.String.Empty 字符串。
//
// 参数:
// value:
// 要测试的字符串。
//
// 返回结果:
// 如果 value 参数为 null 或空字符串 (""),则为 true;否则为 false。
[TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline across NGen image boundaries")]
public static bool IsNullOrEmpty(String value);
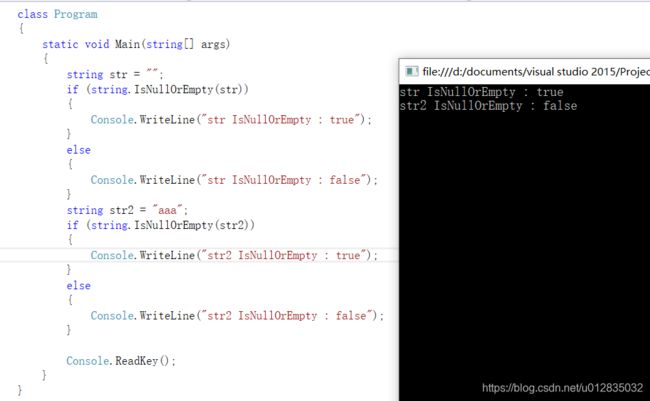
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str = "";
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(str))
{
Console.WriteLine("str IsNullOrEmpty : true");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("str IsNullOrEmpty : false");
}
string str2 = "aaa";
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(str2))
{
Console.WriteLine("str2 IsNullOrEmpty : true");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("str2 IsNullOrEmpty : false");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
3、IsNullOrWhiteSpace()
基本定义用法同上IsNullOrEmpty(),但是IsNullOrEmpty() 标注了"Performance critical to inline across NGen image boundaries",所以推荐用IsNullOrWhiteSpace()。
// 摘要:
// 指示指定的字符串是 null、空还是仅由空白字符组成。
//
// 参数:
// value:
// 要测试的字符串。
//
// 返回结果:
// 如果 value 参数为 null 或 System.String.Empty,或者如果 value 仅由空白字符组成,则为 true。
public static bool IsNullOrWhiteSpace(String value);
四、Substring(),截取字符串
1、Substring(int startIndex),从指定位置开始截取字符串
// 摘要:
// 从此实例检索子字符串。子字符串从指定的字符位置开始。
//
// 参数:
// startIndex:
// 此实例中子字符串的起始字符位置(从零开始)。
//
// 返回结果:
// 与此实例中在 startIndex 处开头的子字符串等效的一个字符串;如果 startIndex 等于此实例的长度,则为 System.String.Empty。
//
// 异常:
// T:System.ArgumentOutOfRangeException:
// startIndex 小于零或大于此实例的长度。
[TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline across NGen image boundaries")]
public String Substring(int startIndex);
2、Substring(int startIndex, int length),从指定的位置开始,截取给定长度的字符串
// 摘要:
// 从此实例检索子字符串。子字符串从指定的字符位置开始且具有指定的长度。
//
// 参数:
// startIndex:
// 此实例中子字符串的起始字符位置(从零开始)。
//
// length:
// 子字符串中的字符数。
//
// 返回结果:
// 与此实例中在 startIndex 处开头、长度为 length 的子字符串等效的一个字符串,如果 startIndex 等于此实例的长度且 length
// 为零,则为 System.String.Empty。
//
// 异常:
// T:System.ArgumentOutOfRangeException:
// startIndex 加 length 之和指示的位置不在此实例中。- 或 -startIndex 或 length 小于零。
[SecuritySafeCritical]
[TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline across NGen image boundaries")]
public String Substring(int startIndex, int length);
代码示例:
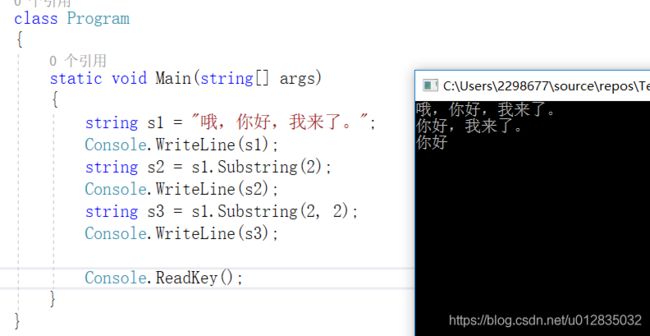
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string s1 = "哦,你好,我来了。";
Console.WriteLine(s1);
string s2 = s1.Substring(2);
Console.WriteLine(s2);
string s3 = s1.Substring(2, 2);
Console.WriteLine(s3);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
五、Replace(),替换字符串
1、用新字符串替换旧字符串
// 摘要:
// 返回一个新字符串,其中当前实例中出现的所有指定字符串都替换为另一个指定的字符串。
//
// 参数:
// oldValue:
// 要被替换的字符串。
//
// newValue:
// 要替换出现的所有 oldValue 的字符串。
//
// 返回结果:
// 与当前字符串等效的一个字符串,但其中 oldValue 的所有实例都替换为 newValue。
//
// 异常:
// T:System.ArgumentNullException:
// oldValue 为 null。
//
// T:System.ArgumentException:
// oldValue 是空字符串 ("")。
[SecuritySafeCritical]
[TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline across NGen image boundaries")]
public String Replace(String oldValue, String newValue);
2、用新字符替换旧字符
// 摘要:
// 返回一个新字符串,其中此实例中出现的所有指定 Unicode 字符都替换为另一个指定的 Unicode 字符。
//
// 参数:
// oldChar:
// 要被替换的 Unicode 字符。
//
// newChar:
// 要替换出现的所有 oldChar 的 Unicode 字符。
//
// 返回结果:
// 与此实例等效的一个字符串,但其中 oldChar 的所有实例都替换为 newChar。
[SecuritySafeCritical]
public String Replace(char oldChar, char newChar);
代码示例:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string s1 = "哦,你好,我来了。";
Console.WriteLine(s1);
string s2 = s1.Replace("哦,", "Oh ");
Console.WriteLine(s2);
string s3 = s1.Replace('哦', 'O');
Console.WriteLine(s3);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
六、Split(),字符串转成字符串数组
Split(params char[] separator),Split()方法有很多个重载,这个是最基础的,也是用的比较多的。
// 摘要:
// 返回的字符串数组包含此实例中的子字符串(由指定 Unicode 字符数组的元素分隔)。
//
// 参数:
// separator:
// 分隔此实例中子字符串的 Unicode 字符数组、不包含分隔符的空数组或 null。
//
// 返回结果:
// 一个数组,其元素包含此实例中的子字符串,这些子字符串由 separator 中的一个或多个字符分隔。有关更多信息,请参见“备注”部分。
public String[] Split(params char[] separator);
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string s1 = "哦,你好,我来了。";
Console.WriteLine(s1);
string[] s2 = s1.Split(',');
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
七、Join(),字符串数组转字符串
Join(String separator, params String[] value)
// 摘要:
// 串联字符串数组的所有元素,其中在每个元素之间使用指定的分隔符。
//
// 参数:
// separator:
// 要用作分隔符的字符串。
//
// value:
// 一个数组,其中包含要连接的元素。
//
// 返回结果:
// 一个由 value 中的元素组成的字符串,这些元素以 separator 字符串分隔。
//
// 异常:
// T:System.ArgumentNullException:
// value 为 null。
public static String Join(String separator, params String[] value);
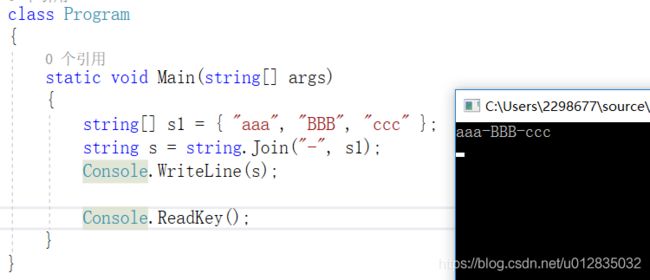
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string[] s1 = { "aaa", "BBB", "ccc" };
string s = string.Join("-", s1);
Console.WriteLine(s);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
八、ToLower() and ToUpper(),大小写转换
1、ToLower(),把字符串转成小写
// 摘要:
// 返回此字符串转换为小写形式的副本。
//
// 返回结果:
// 一个小写字符串。
public String ToLower();
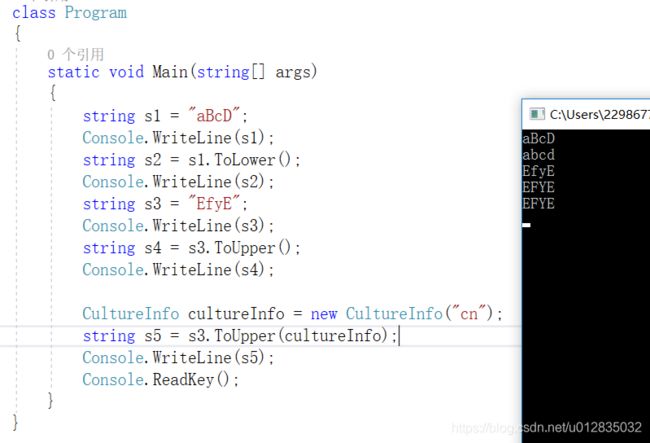
string s2 = s1.ToLower();
2、ToUpper(),把字符串转成大写
// 摘要:
// 返回此字符串转换为大写形式的副本。
//
// 返回结果:
// 当前字符串的大写形式。
public String ToUpper();
string s4 = s3.ToUpper();
3、CultureInfo,指定区域规则
// 摘要:
// 根据指定区域性的大小写规则返回此字符串转换为小写形式的副本。
//
// 参数:
// culture:
// 一个对象,用于提供区域性特定的大小写规则。
//
// 返回结果:
// 当前字符串的等效小写形式。
//
// 异常:
// T:System.ArgumentNullException:
// culture 为 null。
[TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline across NGen image boundaries")]
public String ToLower(CultureInfo culture);
// 摘要:
// 根据指定区域性的大小写规则返回此字符串转换为大写形式的副本。
//
// 参数:
// culture:
// 一个对象,用于提供区域性特定的大小写规则。
//
// 返回结果:
// 当前字符串的大写形式。
//
// 异常:
// T:System.ArgumentNullException:
// culture 为 null。
[TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline across NGen image boundaries")]
public String ToUpper(CultureInfo culture);
CultureInfo cultureInfo = new CultureInfo("cn");
string s5 = s3.ToUpper(cultureInfo);
九、Trim() and TrimEnd() and TrimStart(),去掉字符串前后指定的字符或字符数组
1、Trim()
// 摘要:
// 从当前 System.String 对象移除所有前导空白字符和尾部空白字符。
//
// 返回结果:
// 从当前字符串的开头和结尾删除所有空白字符后剩余的字符串。
public String Trim();
//
// 摘要:
// 从当前 System.String 对象移除数组中指定的一组字符的所有前导匹配项和尾部匹配项。
//
// 参数:
// trimChars:
// 要删除的 Unicode 字符的数组,或 null。
//
// 返回结果:
// 从当前字符串的开头和结尾删除所出现的所有 trimChars 参数中的字符后剩余的字符串。如果 trimChars 为 null 或空数组,则改为删除空白字符。
[TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline across NGen image boundaries")]
public String Trim(params char[] trimChars);
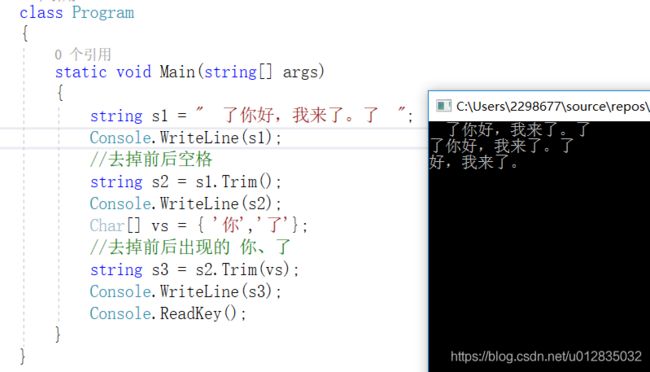
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string s1 = " 了你好,我来了。了 ";
Console.WriteLine(s1);
//去掉前后空格
string s2 = s1.Trim();
Console.WriteLine(s2);
Char[] vs = { '你','了'};
//去掉前后出现的 你、了
string s3 = s2.Trim(vs);
Console.WriteLine(s3);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
2、TrimEnd(),去掉字符串末尾出现的字符或字符数组
// 摘要:
// 从当前 System.String 对象移除数组中指定的一组字符的所有尾部匹配项。
//
// 参数:
// trimChars:
// 要删除的 Unicode 字符的数组,或 null。
//
// 返回结果:
// 从当前字符串的结尾删除所出现的所有 trimChars 参数中的字符后剩余的字符串。如果 trimChars 为 null 或空数组,则改为删除 Unicode
// 空白字符。
[TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline across NGen image boundaries")]
public String TrimEnd(params char[] trimChars);
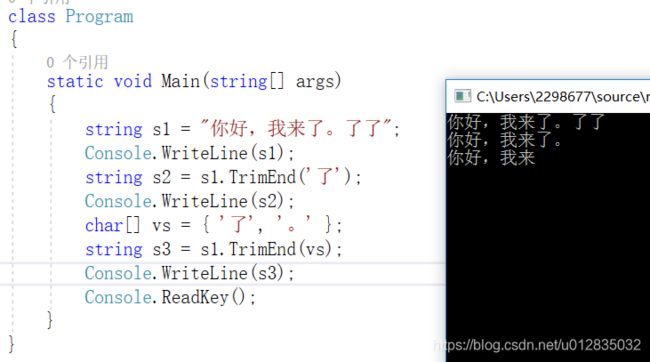
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string s1 = "你好,我来了。了了";
Console.WriteLine(s1);
string s2 = s1.TrimEnd('了');
Console.WriteLine(s2);
char[] vs = { '了', '。' };
string s3 = s1.TrimEnd(vs);
Console.WriteLine(s3);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
3、TrimStart(),去掉头部出现的字符或字符数组
// 摘要:
// 从当前 System.String 对象移除数组中指定的一组字符的所有前导匹配项。
//
// 参数:
// trimChars:
// 要删除的 Unicode 字符的数组,或 null。
//
// 返回结果:
// 从当前字符串的开头删除所出现的所有 trimChars 参数中的字符后剩余的字符串。如果 trimChars 为 null 或空数组,则改为删除空白字符。
[TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline across NGen image boundaries")]
public String TrimStart(params char[] trimChars);
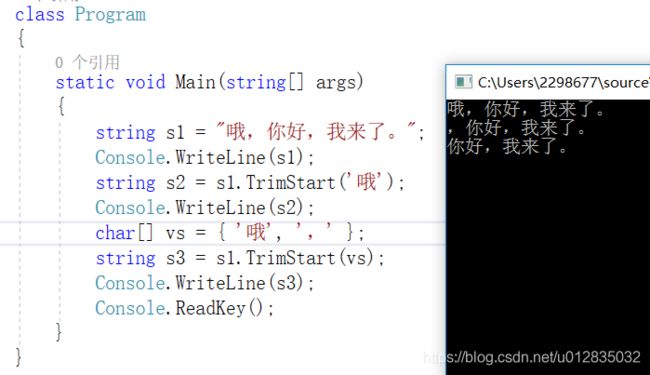
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string s1 = "哦,你好,我来了。";
Console.WriteLine(s1);
string s2 = s1.TrimStart('哦');
Console.WriteLine(s2);
char[] vs = { '哦', ',' };
string s3 = s1.TrimStart(vs);
Console.WriteLine(s3);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
十、判断字符串是否包含指定字符串
1、Contains(),字符串是否包含指定的字符串
// 摘要:
// 返回一个值,该值指示指定的 System.String 对象是否出现在此字符串中。
//
// 参数:
// value:
// 要搜寻的字符串。
//
// 返回结果:
// 如果 value 参数出现在此字符串中,或者 value 为空字符串 (""),则为 true;否则为 false。
//
// 异常:
// T:System.ArgumentNullException:
// value 为 null。
[TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline across NGen image boundaries")]
public bool Contains(String value);
2、IndexOf(),返回指定字符串在字符串中的位置
// 摘要:
// 报告指定字符串在此实例中的第一个匹配项的索引。
//
// 参数:
// value:
// 要搜寻的字符串。
//
// 返回结果:
// 如果找到该字符串,则为 value 的从零开始的索引位置;如果未找到该字符串,则为 -1。如果 value 为 System.String.Empty,则返回值为
// 0。
//
// 异常:
// T:System.ArgumentNullException:
// value 为 null。
public int IndexOf(String value);
3、StartsWith(),字符串头部是否包含指定字符串
// 摘要:
// 确定此字符串实例的开头是否与指定的字符串匹配。
//
// 参数:
// value:
// 要比较的字符串。
//
// 返回结果:
// 如果 value 与此字符串的开头匹配,则为 true;否则为 false。
//
// 异常:
// T:System.ArgumentNullException:
// value 为 null。
[TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline across NGen image boundaries")]
public bool StartsWith(String value);
4、EndsWith(),字符串末尾是否包含指定字符串
// 摘要:
// 确定此字符串实例的结尾是否与指定的字符串匹配。
//
// 参数:
// value:
// 要与此实例末尾的子字符串进行比较的字符串。
//
// 返回结果:
// 如果 value 与此实例的末尾匹配,则为 true;否则为 false。
//
// 异常:
// T:System.ArgumentNullException:
// value 为 null。
public bool EndsWith(String value);
代码示例:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string s1 = "哦,你好,我来了。";
bool b1 = s1.Contains("你好");
int i1 = s1.IndexOf("你好");
bool b2 = s1.StartsWith("哦");
bool b3 = s1.EndsWith("了。");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
到这里,本文就结束了,篇幅好像有点长了。。。
本来是想好好总结一下字符串的各个小知识点,尽可能的详细点、全面点,然后真写起来发现东西有点多。。。
还有一些东西想不起来了。。。
等想起来再补充。。。