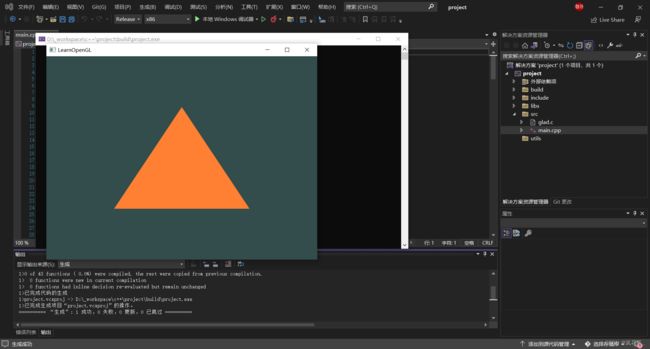
基于 Visual Studio 配置 opengl 环境
基于 Visual Studio 配置 opengl 环境
下载内容
- Visual Studio 2022
- glfw
- glad
Visual Studio 2022
傻瓜式安装即可,如果不知道需要安装什么环境,可以什么都不装。
glfw
注意下载 win32 版本。
glad
打开链接,看到如下界面:
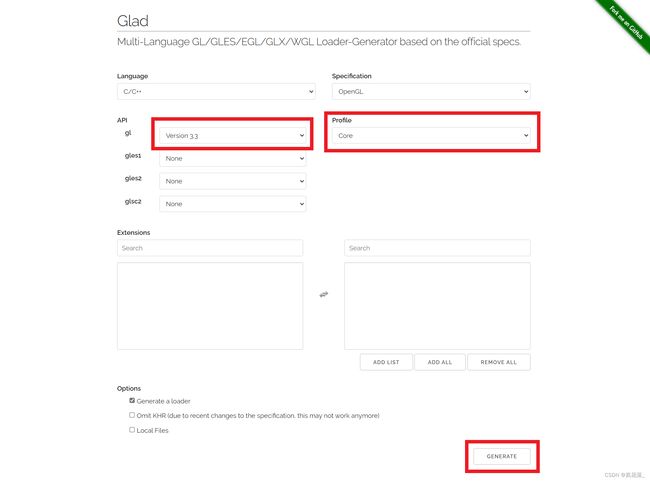
选择上述内容后,点击 generate。跳转后下载出现的安装包即可。
环境配置
调整 Visual Studio
首先打开 Visual Studio Installer,点击修改,安装如下两个环境:


创建项目
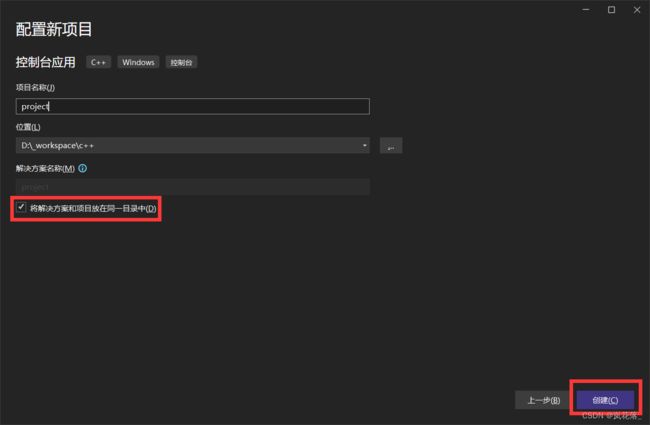
打开 Visual Studio,并创建项目:
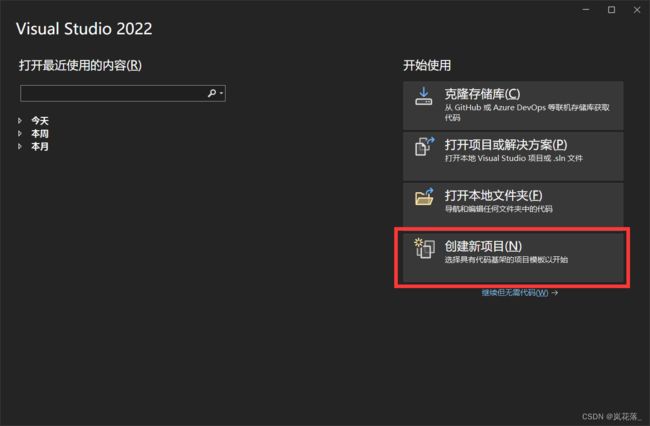
这里选控制台应用:

放置项目文件
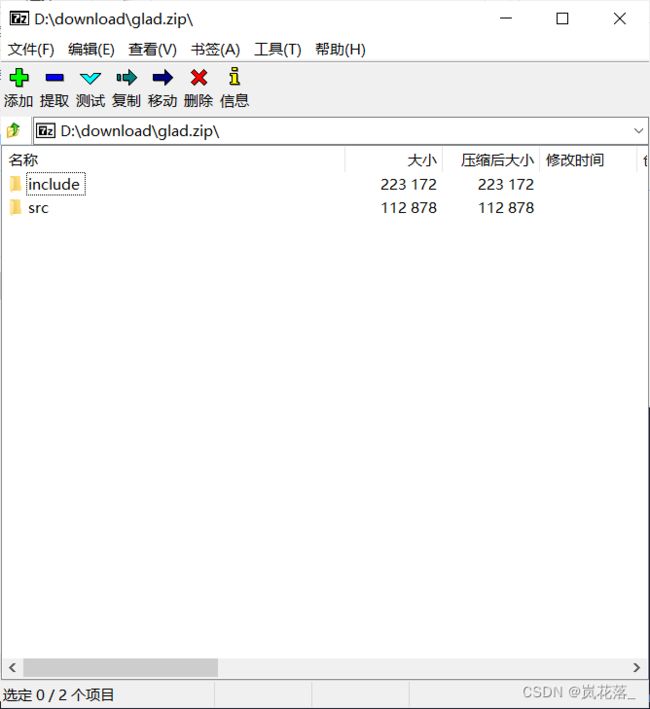
打开之前下载的 glad 压缩包:
打开之前下载的 glfw 压缩包:
顺便,你可以删除 project.cpp 文件。
现在项目如下所示:

设置项目
注意将位于窗口顶部的配置选项设为所有配置,平台选项设为Win32。
c/c++ 部分:
在附加包含目录 处添加./include:

在附加依赖项处添加如下信息:
opengl32.lib
glfw3.lib
msvcrt.lib
点击右下角应用,即可保存。
测试
显示所有文件,在 ./src 中找到之前放入的 glad.c,将其包括到项目中:

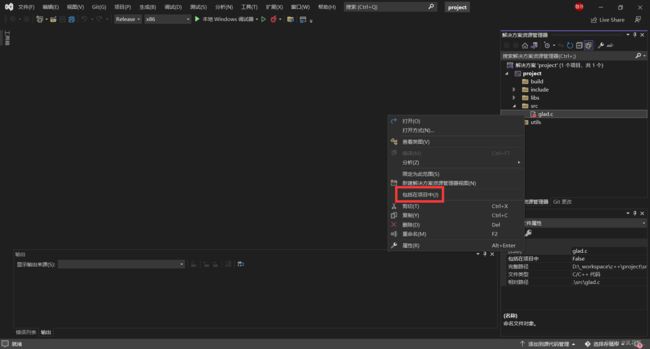
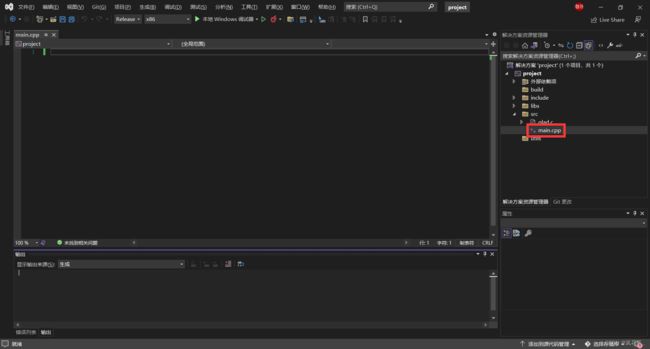
右击右侧空白,在 ./src 中创建 main.cpp 文件:
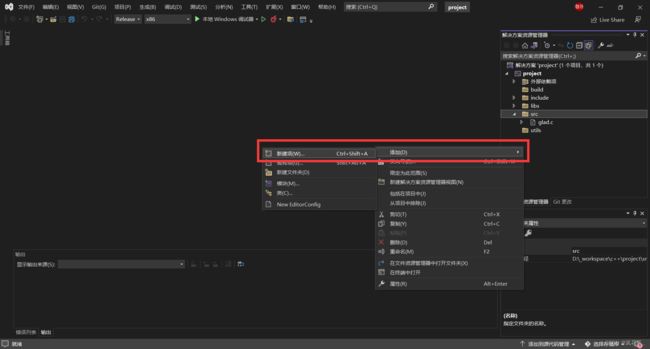
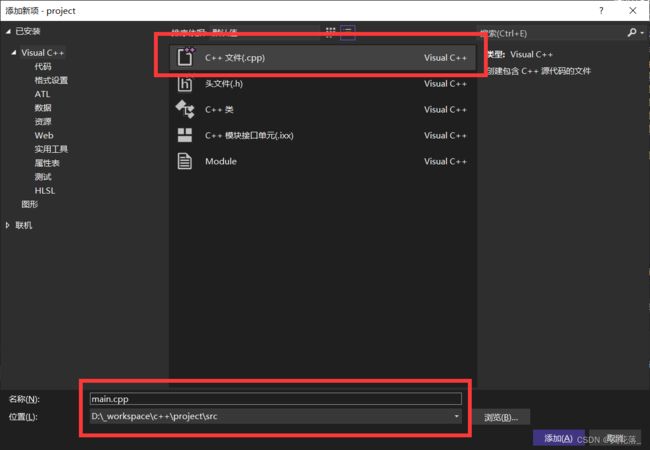
通过这种方式创建的文件,会被自动包含到项目中。
#include 参考资料
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44716867/article/details/110726972
- https://learnopengl-cn.github.io/01%20Getting%20started/02%20Creating%20a%20window/