【Qt- C++ & Qml 交互】
Qt编程指南 VX:hao541022348
- ■ 将C++对象注册到 QML中,在QML使用C++对象(Q_INVOKABLE宏)
-
- ■ C++对象注册到元对象系统
- ■ Q_INVOKABLE 宏
- ■ 演示步骤
- ■ 将C++对象注册到 QML中,在QML使用C++对象(Q_PROPERTY宏 属性绑定)
-
- ■ C++对象注册到元对象系统
- ■ Q_PROPERTY 宏
- ■ 演示代码
- ■ 将 C++类注册到 QML,并在QML声明一个对象并进行访问
-
- ■ C++类注册到qml中
- ■ 演示代码
- ■ 将 C++类注册到 QML,信号与槽进行交互
-
- ■ C++类注册到qml中
- ■ 演示代码
- ■ 将C++中的数据模型注册到C++中,qml进行访问 --- 模型视图
-
- ■ C++数据模型对象注册到元对象系统
- ■ 演示代码
- ■ C++使用QML
-
- ■ 代码演示
■ 将C++对象注册到 QML中,在QML使用C++对象(Q_INVOKABLE宏)
在 C++ 里定义了一个对象,然后将这个对象注册到 QML 里面。在 QML 里面访问的就是 C++ 定义的对象。
■ C++对象注册到元对象系统
QQmlApplicationEngine::rootContext()->setContextProperty()
■ Q_INVOKABLE 宏
Q_INVOKABLE
Q_INVOKABLE 是个宏定义,这个宏将 函数 声明为元对象系统可调用的函数
- Q_INVOKABLE 是个宏定义
- 这个宏定义 针对的是 函数, 不是变量
- 经过Q_INVOKABLE 声明过得函数 可以被元对象系统调用
- QtQuick 也在元对象系统内,所以在 QML 中也可以访问这个被声明了的函数
■ 演示步骤
- 新建qml工程,里面只有一个main.cpp 与一个默认的 main.qml
- 创建一个C++ 的类 MyQmlClass 来与 QML 进行交互(重点关注 函数 Q_INVOKABLE宏 )
- 将 C++ 的对象,注册到 QML中去 QQmlApplicationEngine::rootContext()->setContextProperty()
- 做完了这两步,我们就做了 C++ 的工作,在 QML 中 就可以 直接拿到对象 myQmlImp 来调用使用 Q_INVOKABLE 定义的方法了。
- 改造 QML (定义一个“获取”的 Button 与 显示获取值得 Label, 点击 Button 就会获取 C++ 中的 m_value 值, 在 Lable 上进行展示。)
MyQmlClass.h
#ifndef MYQMLCLASS_H
#define MYQMLCLASS_H
#include MyQmlClass.cpp
#include "MyQmlClass.h"
MyQmlClass::MyQmlClass(QObject *parent) : QObject(parent)
{
}
void MyQmlClass::setValue(int value)
{
m_Value = value;
}
int MyQmlClass::getValue()
{
return m_Value;
}
打开 main.cpp ,通过 QML 引擎 QQmlApplicationEngine 进行注册。
#include main.qml我们的思路很简单,就是 QML 中来调用上面 C++ 暴露出来的读写函数。所以我们在QML 中定义一个 “获取” Button ,点击它我们就来调用C++中的 getValue() 函数,然后我们需要一个Label 将获取的 C++ 的值进行展示
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.3
Window {
visible: true
width: 640
height: 480
title: qsTr("Hello World")
Label{ //Label用于显示获取C++的值
id: label //显示控件,唯一标识ID:label
text: "" //初始化内容清空
anchors.bottom: getBtn.top //显示控件的下方放到btn的上方
anchors.left: getBtn.left //显示控件的左方与btn的左侧对齐
}
Button{ //Button 用于获取值
id: getBtn //按钮控件,唯一标识ID:getBtn
text: "获取" //按钮显示文字
width: 120 //按钮宽度
height: 40 //按钮高度
anchors.centerIn: parent //按钮放到窗口中心
onClicked: { //点击按钮事件;
label.text = myQmlImp.getValue()
}
}
}

到这里,我们就在 QML 中获取了 C++ 代码中的值。可能到这里还有老师感觉不太真实,那么我们就继续进行验证,我们的思路是这样的:
- 我们增加一个 TextFiled 用于输入我们想给 。
- 再增加一个 “设置” 按钮,将 1中输入的值,给C++ 中的 m_Value 设值。
- 然后我们再点击刚才的 “获取” 按钮,将 C++ 中的 m_Value 值读取并显示出来。
这时候我们需要对原来的QML进行改造,新增加一个输入框TextField ,进行数值输入; 还需要新增加一个“设置” 按钮,点击按钮将值赋给 C++ 中的 m_Value
main.qml
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.3
Window {
visible: true
width: 640
height: 480
title: qsTr("Hello World")
Label{ //Label用于显示获取C++的值
id: label //显示控件,唯一标识ID:label
text: "" //初始化内容清空
anchors.bottom: getBtn.top //显示控件的下方放到btn的上方
anchors.left: getBtn.left //显示控件的左方与btn的左侧对齐
}
Button{ //Button 用于获取值
id: getBtn //按钮控件,唯一标识ID:getBtn
text: "获取" //按钮显示文字
width: 120 //按钮宽度
height: 40 //按钮高度
anchors.centerIn: parent //按钮放到窗口中心
onClicked: { //点击按钮事件;
label.text = myQmlImp.getValue()
}
}
TextField{ //文字输入控件
id: textField //唯一ID
width: getBtn.width //也可以直接设置成120
height: getBtn.height //也可以直接设置成40
anchors.top: getBtn.bottom //放到“获取”按钮下方10个像素
anchors.topMargin: 10
anchors.left: getBtn.left //与“获取”按钮左对齐
}
Button{
id: setBtn
text: "设置"
width: textField.width //可以设置成getBtn.width或者120
height: textField.height //可以设置成getBtn.height或者40
anchors.top: textField.bottom
anchors.left: textField.left
onClicked: {
var value = textField.text
myQmlImp.setValue(value)
}
}
}
■ 将C++对象注册到 QML中,在QML使用C++对象(Q_PROPERTY宏 属性绑定)
在 C++ 里定义了一个对象,然后将这个对象注册到 QML 里面。在 QML 里面访问的就是 C++ 定义的对象。
■ C++对象注册到元对象系统
QQmlApplicationEngine::rootContext()->setContextProperty()
■ Q_PROPERTY 宏
使用 Q_PROPERTY 定义交互的属性
Q_PROPERTY:用于声明属性的宏
■ 演示代码
person.h
#ifndef PERSON_H
#define PERSON_H
#include main.cpp
#include main.qml
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.5
Window {
visible: true
width: 480
height: 800
title: qsTr("Hello World")
Column {
spacing: 10
TextField {
placeholderText: "请输入姓名"
text: person.name // 与Person对象的name属性绑定
onTextChanged: person.name = text // 当文本改变时,更新Person对象的name属性
}
Slider {
from: 0
to: 100
value: person.age // 与Person对象的age属性绑定
onValueChanged: person.age = value // 当滑块值改变时,更新Person对象的age属性
}
Text {
text: "姓名:" + person.name
}
Text {
text: "年龄:" + person.age
}
}
}
■ 将 C++类注册到 QML,并在QML声明一个对象并进行访问
■ C++类注册到qml中
qmlRegisterType 就是一个函数模板。将 C++ 的类型注册到 QML 系统中,并且带有版本号,方便版本管理。 我们就把main.cpp 中的函数改造一下:
■ 演示代码
#include 其中:qmlRegisterType 模板函数中的 “com.company.myqmlclass” 为自定义的控件名称类似于C++中的库名称。我们在 QML 中需要 import 这个控件名, “MyQmlClass” 为 C++ 注册的类名, 1和0 为自定义版本号,方便版本管理。

import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.3
import com.company.myqmlclass 1.0
Window {
visible: true
width: 640
height: 480
title: qsTr("Hello World")
MyQmlClass{
id: myQmlImp
}
Label{ //Label用于显示获取C++的值
id: label //显示控件,唯一标识ID:label
text: "" //初始化内容清空
anchors.bottom: getBtn.top //显示控件的下方放到btn的上方
anchors.left: getBtn.left //显示控件的左方与btn的左侧对齐
}
Button{ //Button 用于获取值
id: getBtn //按钮控件,唯一标识ID:getBtn
text: "获取" //按钮显示文字
width: 120 //按钮宽度
height: 40 //按钮高度
anchors.centerIn: parent //按钮放到窗口中心
onClicked: { //点击按钮事件;
label.text = myQmlImp.getValue()
}
}
TextField{ //文字输入控件
id: textField //唯一ID
width: getBtn.width //也可以直接设置成120
height: getBtn.height //也可以直接设置成40
anchors.top: getBtn.bottom //放到“获取”按钮下方10个像素
anchors.topMargin: 10
anchors.left: getBtn.left //与“获取”按钮左对齐
}
Button{
id: setBtn
text: "设置"
width: textField.width //可以设置成getBtn.width或者120
height: textField.height //可以设置成getBtn.height或者40
anchors.top: textField.bottom
anchors.left: textField.left
onClicked: {
var value = textField.text
myQmlImp.setValue(value)
}
}
}
■ 将 C++类注册到 QML,信号与槽进行交互
C++ 对象可以发出信号,而QML中的元素可以连接到这些信号上。这样,当C++ 对象的状态发生变化时,可以通过信号与槽机制将这些变化传递给QML界面。
■ C++类注册到qml中
qmlRegisterType 就是一个函数模板。将 C++ 的类型注册到 QML 系统中,并且带有版本号,方便版本管理。 我们就把main.cpp 中的函数改造一下:
■ 演示代码
myobject.h
#include main.cpp
#include main.qml
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.5
import com.example 1.0
Window {
visible: true
width: 480
height: 800
title: qsTr("Hello World")
/* 定义 sendToCpp 信号 */
signal sendToCpp(string message)
/* Connections 组件用于连接 myObject 的 onMySignal 信号 */
Connections {
target: myObject
onMySignal: console.log("Received message from C++:", message)
}
MyObject {
id: myObject
/* 将 onMySignal 信号传递到 sendToCpp信号上,便于 QML 处理 */
onMySignal: sendToCpp(message)
}
Button {
text: "Send message to C++"
anchors.centerIn: parent
/* 单击按钮时,会将信号传递到 C++ 的 mySlot 槽上 */
onClicked: myObject.mySlot("Hello from QML")
}
}
■ 将C++中的数据模型注册到C++中,qml进行访问 — 模型视图
模型视图(Model-View):可以使用C++ 中的数据模型(QStandardItemModel)来提供数据给QML界面。
QML中的视图元素(如ListView或GridView)可以使用这些模型来显示数据。
■ C++数据模型对象注册到元对象系统
QQmlApplicationEngine::rootContext()->setContextProperty()
■ 演示代码
mymodel.h
#ifndef MYMODEL_H
#define MYMODEL_H
#include mymodel.cpp
#include "mymodel.h"
MyModel::MyModel(QObject *parent)
: QAbstractListModel(parent)
{
// 初始化一些数据
m_persons.append({"Alice", 25, "[email protected]"});
m_persons.append({"Bob", 30, "[email protected]"});
m_persons.append({"Charlie", 35, "[email protected]"});
}
int MyModel::rowCount(const QModelIndex &parent) const
{
Q_UNUSED(parent);
return m_persons.count();
}
QVariant MyModel::data(const QModelIndex &index, int role) const
{
if (!index.isValid())
return QVariant();
if (index.row() >= m_persons.count() || index.row() < 0)
return QVariant();
const Person &person = m_persons[index.row()];
if (role == NameRole)
return person.name;
else if (role == AgeRole)
return person.age;
else if (role == EmailRole)
return person.email;
return QVariant();
}
QHash<int, QByteArray> MyModel::roleNames() const
{
QHash<int, QByteArray> roles;
roles[NameRole] = "name";
roles[AgeRole] = "age";
roles[EmailRole] = "email";
return roles;
}
main.cpp
#include main.qml
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.5
Window {
visible: true
width: 480
height: 800
title: qsTr("Hello World")
ListView {
anchors.fill: parent
model: myModel
delegate: Item {
width: parent.width
height: 60
Column {
Text { text: name }
Text { text: age }
Text { text: email }
}
}
}
}
■ C++使用QML
■ 代码演示
main.qml
import QtQuick 2.7
import QtQuick.Window 2.2
Item {
id: root
visible: true
width: 640
height: 480
//title: qsTr("Hello World")
property string msg: "I am QML Item"
signal callCpp(string arg1, string arg2)
MainForm {
anchors.fill: parent
mouseArea.onClicked: {
Qt.quit();
}
}
Rectangle {
anchors.fill: parent
color: "blue"
objectName: "rect"
}
MouseArea {
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: {
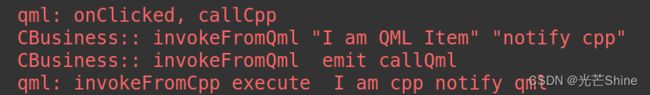
console.log("onClicked, callCpp")
root.callCpp(root.msg, "notify cpp")
}
}
onHeightChanged: {
console.log("onHeightChanged execute")
}
onWidthChanged: {
console.log("onWidthChanged execute")
}
//QML中的方法可以被cpp调用,也可以作为槽函数
function qmlFun(val_arg) {
console.log("qmlFun execute", val_arg, "return qmlFun_return_result")
return "qmlFun_return_result"
}
//注意槽函数参数为var类型
function invokeFromCpp(arg1, arg2) {
console.log("invokeFromCpp execute ", arg1, arg2)
}
}
cbusiness.h
#ifndef CBUSINESS_H
#define CBUSINESS_H
#include cbusiness.cpp
#include "cbusiness.h"
#include main.cpp
#include 测试结果

信号和槽的绑定在c++代码中完成,在c++中可以修改qml的属性,获取qml的属性,调用qml的方法,传递和获取参数均可以