当应用程序含有事务管理时,xmlApplicationContext的调试
读取通知配置的类是:TxAdviceBeanDefinitionParser。
这个类将xml中配置的通知标签读取到bean定义中去,也就是将事务属性读取到bean定义中。
<tx:advice id="tx-advice">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="add*" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="DEFAULT" read-only="false" timeout="10"/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
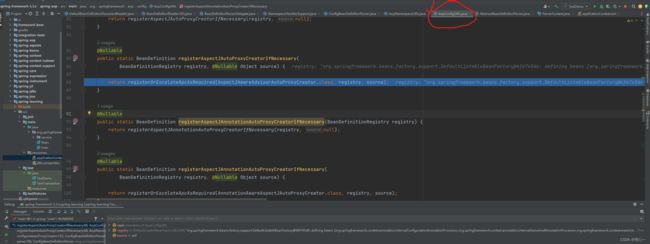
上面的配置读取到的bean定义实际是如下的TransactionInterceptor拦截器,如下图中的definition所示:
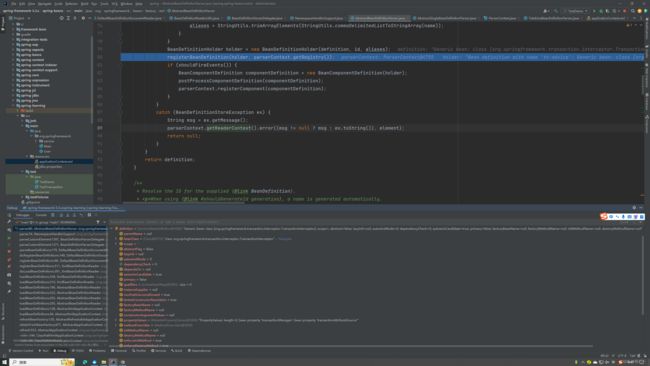
切点和切面的配置·读取,配置代码如下:
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="tx-pt" expression="execution(* org.springframework.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="tx-advice" pointcut-ref="tx-pt">aop:advisor>
aop:config>
首先根据xml的命名空间获取对应的处理器:
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd) {
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele);
if (namespaceUri == null) {
return null;
}
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
}
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}
这里获取到的handler是一个AopNamespaceHandler,如下:
实际的解析,还需要调用NamespaceHandlerSupport的findParserForElement方法获取解析器:
@Override
@Nullable
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
BeanDefinitionParser parser = findParserForElement(element, parserContext);
return (parser != null ? parser.parse(element, parserContext) : null);
}
最终进行解析的类是ConfigBeanDefinitionParser,这个类解析的是aop的配置信息,
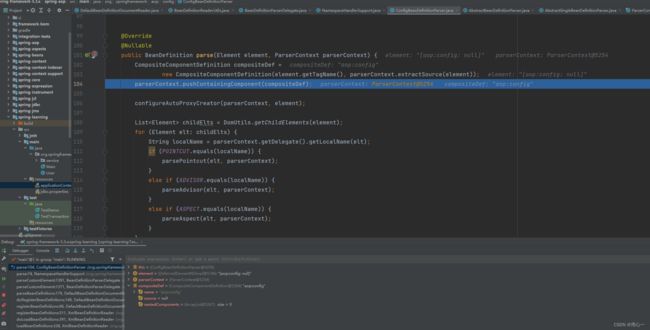
配置自动代理创建器:
/**
* Configures the auto proxy creator needed to support the {@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions}
* created by the '{@code private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(
Class<?> cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition apcDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
if (!cls.getName().equals(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName())) {
int currentPriority = findPriorityForClass(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName());
int requiredPriority = findPriorityForClass(cls);
if (currentPriority < requiredPriority) {
apcDefinition.setBeanClassName(cls.getName());
}
}
return null;
}
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls);
beanDefinition.setSource(source);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("order", Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME, beanDefinition);
return beanDefinition;
}
上述方法将注册名为:org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator 的自动代理创建器。
注册配置了自动代理创建器之后,ConfigBeanDefinition的parse方法将读取aop-config的其它属性配置,如切点,通知和切面。
如下图进入解析pointcut切点的代码:

切点对应的类是: AspectJExpressionPointcut
需要注意的是这是一个原型类:

上述方法将切点bean定义注册到容器。
然后是解析aop-config标签的’通知’元素:

解析通知的方法如下:
private void parseAdvisor(Element advisorElement, ParserContext parserContext) {
AbstractBeanDefinition advisorDef = createAdvisorBeanDefinition(advisorElement, parserContext);
String id = advisorElement.getAttribute(ID);
try {
this.parseState.push(new AdvisorEntry(id));
String advisorBeanName = id;
if (StringUtils.hasText(advisorBeanName)) {
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(advisorBeanName, advisorDef);
}
else {
advisorBeanName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(advisorDef);
}
Object pointcut = parsePointcutProperty(advisorElement, parserContext);
if (pointcut instanceof BeanDefinition) {
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add(POINTCUT, pointcut);
parserContext.registerComponent(
new AdvisorComponentDefinition(advisorBeanName, advisorDef, (BeanDefinition) pointcut));
}
else if (pointcut instanceof String) {
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add(POINTCUT, new RuntimeBeanReference((String) pointcut));
parserContext.registerComponent(
new AdvisorComponentDefinition(advisorBeanName, advisorDef));
}
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
创建通知器bean定义的代码如下:
private AbstractBeanDefinition createAdvisorBeanDefinition(Element advisorElement, ParserContext parserContext) {
RootBeanDefinition advisorDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor.class);
advisorDefinition.setSource(parserContext.extractSource(advisorElement));
String adviceRef = advisorElement.getAttribute(ADVICE_REF);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(adviceRef)) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().error(
"'advice-ref' attribute contains empty value.", advisorElement, this.parseState.snapshot());
}
else {
advisorDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(
ADVICE_BEAN_NAME, new RuntimeBeanNameReference(adviceRef));
}
if (advisorElement.hasAttribute(ORDER_PROPERTY)) {
advisorDefinition.getPropertyValues().add(
ORDER_PROPERTY, advisorElement.getAttribute(ORDER_PROPERTY));
}
return advisorDefinition;
}
上述代码会读取通知引用,然后设置到通知器的属性“adviceBeanName”中去。
由于我们没有未通知命名,框架会自动生成一个名字:

parsePointcutProperty解析通知的切点属性:
private Object parsePointcutProperty(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
if (element.hasAttribute(POINTCUT) && element.hasAttribute(POINTCUT_REF)) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().error(
"Cannot define both 'pointcut' and 'pointcut-ref' on tag." ,
element, this.parseState.snapshot());
return null;
}
else if (element.hasAttribute(POINTCUT)) {
// Create a pointcut for the anonymous pc and register it.
String expression = element.getAttribute(POINTCUT);
AbstractBeanDefinition pointcutDefinition = createPointcutDefinition(expression);
pointcutDefinition.setSource(parserContext.extractSource(element));
return pointcutDefinition;
}
else if (element.hasAttribute(POINTCUT_REF)) {
String pointcutRef = element.getAttribute(POINTCUT_REF);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(pointcutRef)) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().error(
"'pointcut-ref' attribute contains empty value.", element, this.parseState.snapshot());
return null;
}
return pointcutRef;
}
else {
parserContext.getReaderContext().error(
"Must define one of 'pointcut' or 'pointcut-ref' on tag." ,
element, this.parseState.snapshot());
return null;
}
}
完成bean的定义读取之后,在容器里有以下bean定义:
回到AbstractApplicationContext类的refresh方法,

在refresh方法的registerBeanPostProcessors方法中调用PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate的方法注册后处理器,如下:
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// WARNING: Although it may appear that the body of this method can be easily
// refactored to avoid the use of multiple loops and multiple lists, the use
// of multiple lists and multiple passes over the names of processors is
// intentional. We must ensure that we honor the contracts for PriorityOrdered
// and Ordered processors. Specifically, we must NOT cause processors to be
// instantiated (via getBean() invocations) or registered in the ApplicationContext
// in the wrong order.
//
// Before submitting a pull request (PR) to change this method, please review the
// list of all declined PRs involving changes to PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate
// to ensure that your proposal does not result in a breaking change:
// https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues?q=PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate+is%3Aclosed+label%3A%22status%3A+declined%22
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
在上面的中可以看到调用beanFactory的getBean方法,这里会创建后处理器postProcessor。
创建代理bean
事务代理bean的创建,在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类的protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException 方法中,调用:
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
上述方法中applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法会为事务bean创建代理,创建代理的处理器就是在aop配置中配置的bean:
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
调用的是AbstractAutoProxyCreator的以下方法:
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
在warpIfNecessary中创建代理对象。
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
这个wrapIfNecessary会调用getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean,获取对应bean的通知,在这个过程中会创建通知,具体的是TransactionInterceptor实例。在创建这个拦截器实例的过程中,有一系列的匹配方法来确定这个bean是否有对应的拦截器。
Eligible:符合条件的
在后处理器中,对每一个bean,代理创建器会在后置处理器方法中判断当前类是否配置了通知,具体的匹配过程比较复杂,最终调用的方法如下(在AopUtils类中):
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass));
}
classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
对于匹配上的通知,会创建拦截器,代码如下:

可以看到,拦截器的创建也是通过beanFactory的getBean方法创建的。
为上述txUserServiceImpl找到的两个通知器如下:
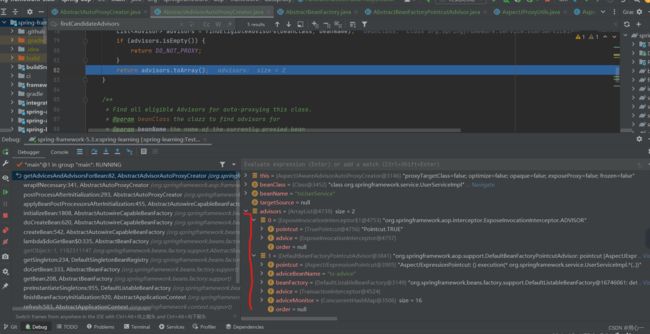
回到wrapIfNecessary方法,里面的createProxy方法,具体的是调用类AbstractAutoProxyCreator的aop代理创建方法:
/**
* Create an AOP proxy for the given bean.
* @param beanClass the class of the bean
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param specificInterceptors the set of interceptors that is
* specific to this bean (may be empty, but not null)
* @param targetSource the TargetSource for the proxy,
* already pre-configured to access the bean
* @return the AOP proxy for the bean
* @see #buildAdvisors
*/
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
// Explicit handling of JDK proxy targets and lambdas (for introduction advice scenarios)
if (Proxy.isProxyClass(beanClass) || ClassUtils.isLambdaClass(beanClass)) {
// Must allow for introductions; can't just set interfaces to the proxy's interfaces only.
for (Class<?> ifc : beanClass.getInterfaces()) {
proxyFactory.addInterface(ifc);
}
}
}
else {
// No proxyTargetClass flag enforced, let's apply our default checks...
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// Use original ClassLoader if bean class not locally loaded in overriding class loader
ClassLoader classLoader = getProxyClassLoader();
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader && classLoader != beanClass.getClassLoader()) {
classLoader = ((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).getOriginalClassLoader();
}
return proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader);
}
在上面的方法中有一个判断是代理类还是接口的逻辑。