操作系统OS-Lab2-FAT12文件读取
OS-Lab2
问题
PPT相关内容
-
什么是实模式,什么是保护模式?
PPT: * 实模式:基地址+偏移量可以直接获得物理地址的模式 * 缺点:非常不安全 * 保护模式:不能直接拿到物理地址,需要进行地址转换 * 从80286开始,是现代操作系统的主要模式 2: 实模式是早期x86处理器的一种工作模式,它可以直接使用物理地址来访问内存,但是只能识别1MB内存地址范围。实模式只能使用16位寻址方式,不支持多任务,也无法进行内存保护,程序可以相互篡改,因此不适合开发大型操作系统。 相比之下,保护模式是一种新的工作模式,它对内存进行了保护和隔离,使得多个程序可以同时运行,相互之间互不干扰,可以共享硬件资源。保护模式可以使用32位和64位寻址方式,支持虚拟存储器和内存保护。保护模式是现代操作系统的基础,例如Windows和Linux等操作系统都是在保护模式下运行的。 -
什么是选择子?
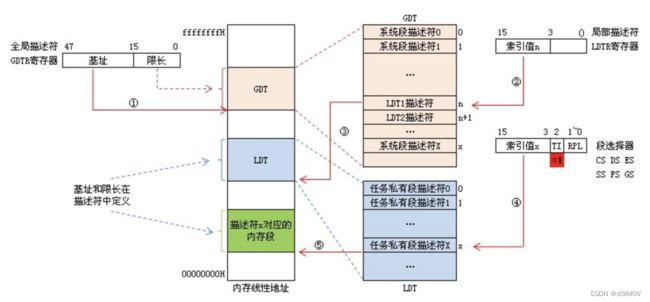
选择子是在x86架构的计算机中使用的一种数据结构,用于访问内存中的段。 选择子由16位构成 包含了段的索引、段的特权级别和其他标志信息。 当CPU需要访问内存中的数据时,它需要使用选择子来确定需要访问的段。 选择子中包含的段的索引信息确定了CPU需要访问的段在全局描述符表(GDT)或局部描述符表(LDT)中的位置,而特权级别的信息则用于检查当前正在执行的代码是否有访问该段的权限。 同时通过选择子和段的切换,操作系统可以实现虚拟内存,将虚拟地址映射到物理地址。 放在段选择寄存器里 * 低2位表示请求特权级 * 第3位表示选择GDT还是LDT方式 * 高13位表示在描述符表中的偏移 * 故描述符表的项数最多是2的13次方 -
PPT: 是GDT或LDT描述符表中的一个数据结构项 包含了一个段的大小、位置、特权级别等信息 每个段描述符占用8byte,64bit,包含段基地址、段线长、段属性等 * 段基址:开始地址,线性地址,偏移为0 * 段线长:长度,最大可用 * DPL:描述符特权级,目标段特权集 * CPL:当前段特权集 * GDT:全局描述符表,是全局唯一的。 * 存放一些公用的描述符,和包含**各进程局部描述符表**首地址的描述符。 * LDT:局部描述符表,每个进程都可以有一个。 * 存放本进程内使用的描述符。 * GDTR:全局描述符表寄存器 * 48位寄存器,高32位放置GDT首地址,低16位放置GDT限长 * 限长决定了可寻址的大小,**注意低16位放的不是选择子** * LDTR:16位寄存器,放置一个特殊的选择子,用于查找当前进程的LDT首地址。 描述符是计算机中一种结构化的数据结构,通常用于描述各种资源的属性和特征。 在计算机中,最常见的描述符有段描述符和系统描述符。 段描述符在保护模式下使用,用于描述内存中的段。 段描述符包含了该段的基地址、限制、特权级别、类型、状态等信息, 这些信息可以帮助操作系统实现内存保护和虚拟内存等特性。 在选择子中包含的段索引信息可以用来在全局描述符表或局部描述符表中找到对应的段描述符。 系统描述符是在x86架构中用于描述各种系统资源和特殊处理器状态的数据结构。它们包括门描述符、任务状态段描述符、中断描述符和TSS描述符等。这些特殊描述符包含了特定的处理器状态信息,可以被系统调用、中断和异常处理例程使用。 -
什么是GDT,什么是LDT?
GDT和LDT都是描述符表,用于记录计算机内存中的段描述符信息。 GDT是全局描述符表,是一个全局的描述符表,其中包含了操作系统所管理的所有内存段的描述符信息。 GDT对于整个操作系统是唯一的,在操作系统启动时通过将其加载到内存中来启用。 它可以包含多个段描述符,这些描述符描述了操作系统所管理的内存中的所有段, 包括各个用户进程的代码段、数据段、堆栈段等。 LDT是局部描述符表,每个任务可以设定自己的LDT。 LDT和GDT的作用相同,用于记录任务在内存中的段描述符信息。 与GDT不同的是,LDT是每个任务独有的,每个任务都可以为自己定义一个LDT,来描述其代码、数据、堆栈等内存段。 在任务切换时,也需要重新装载LDT。 这使得在多任务操作系统中,每个任务都有自己独立的内存空间,提高了操作系统的安全性和稳定性。 -
请分别说明GDTR和LDTR的结构。
GDTR和LDTR都是x86处理器中的寄存器,它们用于记录全局描述符表(GDT)和局部描述符表(LDT)在内存中的地址和大小信息。 GDTR即全局描述符表寄存器(Global Descriptor Table Register),是由48位线性地址和16位限制大小组成的一个64位寄存器。其中,低16位表示GDT的限制大小(即GDT可存储的描述符数量),高48位表示GDT的起始地址。在x86处理器的保护模式下,GDTR的值由操作系统进行初始化,并且不应该被用户程序修改。 LDTR即局部描述符表寄存器(Local Descriptor Table Register),是一个16位寄存器,它包含了当前任务(进程)所使用的局部描述符表的选择子,这个选择子指向一个LDT描述符。LDT描述符包含了LDT在内存中的起始地址和大小信息,其中LDT的大小限制最多为64KB。当需要在任务之间切换时,操作系统会根据任务的LDT选择子将对应的LDT加载到内存中,以便更改任务内存地址空间的映射关系,从而使程序得以运行。 总之,GDTR和LDTR都是用于管理描述符表的寄存器,其中GDTR用于全局描述符表的地址和大小信息,LDTR用于局部描述符表的选择子和LDT大小和地址信息。它们是实现内存保护、虚拟内存和多任务等操作系统功能的基础。 -
PPT: 如果是GDT查找方式,会从GDTR全局描述符表寄存器中获取全局描述符表首地址,利用选择子中高13位偏移量作为索引,从GDT中获取段描述符。如果查询合法且有权限,就会用**描述符中的段首地址+偏移量找到物理地址(线性地址)** 在不分页的情况下,线性地址即物理地址 -
PPT: * 给出段选择子(放在段选择寄存器中)+ 偏移量 * 若选择了LDT方式,则从GDTR获取GDT首地址,**用LDTR中的偏移量做偏移**,拿到GDT中的描述符1 * 从描述符1中获取LDT首地址,用段选择子中的13位做偏移,拿到LDT中的描述符2 * 如果合法且有权限,用描述符2中的段首地址加上1.中的偏移量找到物理地址。寻址结束 -
根目录区大小一定么?扇区号是多少?为什么?
根目录区的大小并不一定,它取决于磁盘容量、簇大小和根目录项大小等因素,不同的文件系统可能会有不同的根目录区大小限制。 起始扇区号:1(引导) + 9(fat1)+9(fat2) = 19 -
数据区第一个簇号是多少?为什么?
默认情况下第一个簇号是2。 因为0号簇表示这个目录项没有分配簇,1号簇被保留作为文件系统保留区域。因此,分配数据时需要跳过这两个号码。 -
FAT表的作用?
FAT表的作用是记录存储设备上每个文件与相应数据所在簇的对应关系。 * 12位地址,最大容量16MB * 为软盘设计的文件系统 * FAT文件系统把存储介质看成一维的数组,基本单位是**簇**(cluster) 存储介质被划分为3个区域:boot record、FAT、directory and data area **一个簇包含一个扇,大小为512B** -
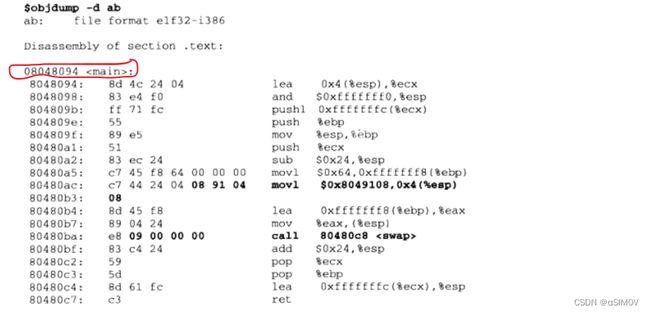
解释静态链接的过程。 解释动态链接的过程。
静态链接: 静态链接是指在编译时将所有被使用的库函数(如标准 C 库)和对象文件都被拷贝到可执行文件中,生成一个完整的可执行文件。程序在运行时不需要再加载任何其他的外部库或对象文件,因为所有需要的代码都已经包含在可执行文件中。 静态链接的过程如下: 1.编译源代码,生成目标文件; 2.把这些目标文件中的符号链接合并成一个可执行文件; 3.把合并后的可执行文件中未定义的符号链接到系统提供的函数库中。 它的主要缺点是它会增加可执行文件的大小,并且如果多个程序都使用相同的库,则会在磁盘上重复存储多次,浪费存储空间。 动态链接: 动态链接是指在程序运行时在内存中加载共享库,程序运行时只需要加载导入库的地址表,而不需要把整个库都加载到内存中,共享库的代码可以被不同的进程共享使用,从而节省系统资源。 动态链接的过程如下: 1.编译源代码时,不进行链接操作; 2.运行程序时,系统会在内存中将程序的硬件指令读入,同时加载程序所需要的动态链接库。这些库会被映射到进程的地址空间中; 3.进行重定位操作,动态链接库和主程序中的未定义符号进行链接,生成可执行文件; 4.程序开始运行。 它的主要优点是它可以减小可执行文件的大小,减少磁盘和内存空间的浪费。此外,动态链接可以提供更新和修复旧版本库的机制,带给了系统更大的灵活性。 -
静态链接相关PPT中为什么使用ld链接⽽不是gcc?
将.c文件编译成目标文件,但是gcc -c生成的.obj文件是只与源代码对应的,printf函数在源代码中是通过#include引入的,相当于只有声明没有定义,-c选项指定了不进行链接过程,所以找不到printf函数 需要ld添加参数来引用标准c库。不过简单的作法是把ld的过程交给gcc命令 gcc -o -
linux下可执行文件的虚拟地址空间默认从哪里开始分配。
在Linux下,可执行文件的虚拟地址空间默认从0x08048000开始分配。这个地址被称为程序的“基地址(base address)”。 在32位的Linux系统中,用户空间的地址范围是0x00000000-0xFFFFFFFF(共4GB),其中用户空间前1GB(0x00000000-0x3FFFFFFF)是保留给用户程序使用的,剩余部分则是保留给内核使用的。 可执行文件在运行时,操作系统把可执行文件映射至进程的虚拟地址空间,其中text段、data段和bss段等代码和数据段从程序的基地址开始连续映射,堆、栈和共享库等则被映射到内存的相应位置。 需要注意的是,基地址也可以通过动态链接或运行时链接的方式被修改,这通常需要在程序中显式声明或使用一些特定的链接选项。
实验相关内容
-
BPB指定字段的含义 :见代码
-
如何进⼊子目录并输出(说明方法调用)
-
如何获得指定文件的内容,即如何获得数据区的内容(比如使用指针等)
-
如何进行C代码和汇编之间的参数传递和返回值传递
在C代码和汇编之间进行参数传递和返回值传递,需要使用一些特殊的方法和约定,具体步骤如下: 1.参数传递 1.1 C代码将参数按照调用约定(如cdecl、stdcall、fastcall等)压栈或者存放在寄存器中; 1.2 C代码调用汇编函数时,传递参数的顺序和方式必须与被调用函数的参数类型和个数一致; 1.3 汇编函数从栈顶或者寄存器中获取参数,并进行相应的操作; 1.4 若需要将修改后的值返回给C代码,需要遵循相应的返回值传递约定。 2.返回值传递 2.1 汇编函数在处理过程中需要将返回值存放在某个特定的寄存器或者栈中; 2.2 若返回值为单一的紧凑型数据类型(如整数、字符、指针等),则可直接将结果存放在紧凑型返回值寄存器或者栈中,返回时则直接读取即可; 2.3 若返回值为结构体或其他较复杂的数据类型,则需要返回一个指向结果的指针或引用; 2.4 若返回值需要通过栈传递,则需要对返回的栈空间进行内存管理和数据的提取。 需要注意的是,C代码和汇编代码之间的参数传递、返回值传递等约定可能因操作系统、编译器、CPU架构等因素而异,需要根据具体情况进行设置和调整。在实际应用中,可以使用C声明的内联汇编(inline assembly)语句、宏指令、外部接口等方法实现C和汇编之间的交互和调用。 -
汇编代码中对I/O的处理方式,说明指定寄存器所存值的含义
*在主函数main.cpp中,调用myPrint函数时,会将字符串的起始地址(由指针p指向)作为参数传递给myPrint函数。 * 在myPrint函数内部,由于参数传递采用的是cdecl调用约定,即先压栈后由调用者负责清理栈的方式,所以第一个参数p被压入栈中。 * 然后,在my_print.asm中,首先将当前的栈帧指针ebp保存到堆栈中, * 再将栈指针移动到保存第一个参数的位置(ebp+8),即将p的地址保存到ecx寄存器中, * 然后将字符串的长度计算得出,并保存到edx寄存器中, * 接下来调用可打印sys_call, * 其中将打印的信息通过eax寄存器中的数值传递给了Linux系统的sys_call, * 1表示stdout流,print函数立即把消息写到控制台输出,最后通过pop指令恢复栈顶指针并返回。 * 这样,myPrint函数内部的asm_print函数就完成了字符串的输出。
gcc + nasm
基础原理
-
如果函数的定义在其它文件,比如说你想要复用之前用汇编写的函数,那么要通过extern指定。(gcc如果发现函数只有声明没有定义,默认是extern,不需要专门指定了)
-
gcc main.c 编译且链接或者链接
-
gcc -c main.c 只编译,生成中间文件,链接时只要同时给出.c文件中没有给出的定义的代码就可以了
-
gcc hello.c –o hello.bin其实是先编译成obj文件hello.out,再连接成hello.bin
gcc编译生成的obj文件和nasm汇编生成的obj文件是统一的格式。
所以,可以使用gcc编译c语言,nasm汇编汇编语言,最后使用链接器(通常是ld命令)将多个obj文件链接成可执行文件。
但是,obj文件和可执行文件都是平台相关的,比如linux下面是ELF格式,mac下面是maco格式。
示例
主程序为c语言,子程序为一个函数,返回3个参数的最大值。
主程序为main.c文件
声明maxofthree函数,但不给出定义。(gcc会默认为extern)
子程序为func.asm文件
通过global关键字,表明这个标签是对外的函数标签。
通过global关键字,nasm在汇编时会把global的这个函数的信息写到中间文件里,链接器链接时就可以看到。
- 将.asm文件编译成目标文件
- 将.c文件编译成目标文件,但是gcc -c生成的.obj文件是只与源代码对应的,printf函数在源代码中是通过#include
引入的,相当于只有声明没有定义,-c选项指定了不进行链接过程,所以找不到printf函数 - 需要ld添加参数来引用标准c库。不过简单的作法是把ld的过程交给gcc命令,如下
- 运行‘
错误运行方式:
nasm -f elf -o func.o func.asm
gcc -c -o main.o main.c
ld -o hello main.o func.o
./hello
正确方式:
nasm -f elf -o func.o func.asm
gcc -o hello main.c func.o
./hello
安装库
- 64位ubuntu:首先安装32位库
sudo apt-get install gcc-multilib
nasm -f elf32 func.asm
gcc -m32 main.c func.o
-
mac系统:nasm的参数需要修改为maco
-
nasm -hf 可以查看各个平台的参数。
-
windows为win32
-
nasm 命令
- 参见nasmdoc第二章
-
gcc 命令
- http://man.linuxde.net/gcc
静态链接与动态链接
-
静态链接:静态链接就是在编译链接时直接将需要的执行代码拷贝到调用处,使用静态链接生成的可执行文件体积较大,包含相同的公共代码,造成浪费
-
动态链接:使用这种方式的程序并不在一开始就完成动态链接,而是直到真正调用动态库代码(调用未被本文件实现的函数代码)时,载入程序才计算(被调用的那部分)动态代码的逻辑地址。
这种方式使程序初始化时间较短,但运行期间的性能比不上静态链接的程序
-
静态链接是指在编译阶段直接把静态库加入到可执行文件中去,这样可执行文件会比较大。
而动态链接则是指链接阶段仅仅只加入一些描述信息,而程序执行时再从系统中把相应动态库加载到内存中去。
动态链接两种方法
- 装载时动态链接:这种用法的前提是在编译之前已经明确知道要调用DLL中的哪几个函数,编译时在目标文件中只保留必要的链接信息,而不含DLL函数的代码;当程序执行时,调用函数的时候利用链接信息加载DLL函数代码并在内存中将其链接入调用程序的执行空间中(全部函数加载进内存),其主要目的是便于代码共享。(动态加载程序,处在加载阶段,主要为了共享代码,共享代码内存)
- 运行时动态链接(Run-time Dynamic Linking):这种方式是指在编译之前并不知道将会调用哪些DLL函数,完全是在运行过程中根据需要决定应调用哪个函数,将其加载到内存中(只加载调用的函数进内存),并标识内存地址,其他程序也可以使用该程序,并用LoadLibrary和GetProcAddress动态获得DLL函数的入口地址。(dll在内存中只存在一份,处在运行阶段)
静态链接指令
my_lib为库
gcc -c my_lib.c -o my_lib.o
gcc -c test.c -o test.o
使用objdump –h查看test.o、my_lib.o(或libmylib.a)以及最终的可执行文件的所有节信息。
静态链接时发生了什么?
-
空间和地址分配
-
符号解析和重定位
-
符号解析主要使用elf里面的符号表节来完成
Elf格式文件符号表参考博客ELF格式文件符号表全解析及readelf命令使用方法_忧郁的废物_Addy的博客-CSDN博客
-
一旦链接器完成符号解析这一步骤,它就把代码中的每一个符号引用和定义联系起来,在此时,链接器就知道它的输入目标文件中的代码节和数据节的确切大小,就可以进行重定位了,在这个步骤中将合并输入模块,并为每个符号分配运行时地址
-
重定位信息
执行指令
gcc –c a.c -o a.o
gcc –c b.c -o b.o
gcc -o ab a.o b.o
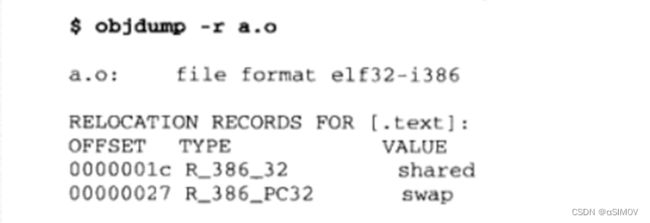
obdump -r a.o
- Offset:要修改的位置在.text节的偏移量
- Type:重定位类型
- Value:重定位符号的名称
- R_386_32:绝对寻址修正
- R_386_PC32:相对寻址修正
链接操作前,此时并没有分配存储器运行时地址,因为目前基址部分显示为00000000
链接操作后,静态链接操作之后就找到shared和swap的具体运行时地址了
重定位
重定位的工作就是修改偏移处的内容
静态链接指令
头文件信息:
运行命令:
gcc -fPIC -c my_lib.c -o my_lib.o
gcc -shared my_lib.o -o libd.so
gcc -c -g dynamic_a.c -o da.o
gcc -c -g dynamic_b.c -o db.o
gcc -o da da.o -L./ -ld
gcc -o db db.o -L./ -ld
-
-fPIC 作用于编译阶段,告诉编译器产生与位置无关代码(Position-Independent Code),则产生的代码中,没有绝对地址,全部使用相对地址,故而代码可以被加载器加载到内存的任意位置,都可以正确的执行。
-
-shared:产生共享对象文件
-
Dynamic_a.c和dynamic_b.c都调用了my_lib.c中的变量和函数,为了在内存中加载一次Lib.c,使a.c 和b.c共享,我们可以将my_lib.c编译成共享对象,共享的并不是my_lib.c中整个内容,而是特指共享他的代码部分
-
对于my_lib.c中的数据部分,每个进程都需要一份自己的拷贝,因为他们可能需要独立地修改my_lib.c中的数据
-
六个指令的最后两个,编译时还是要带上libd.so,因为虽然是动态链接,但是编译的时候总要告诉程序有函数和变量是动态链接,而他们的符号信息就在libd.so中,所以这里编译时还是要带上libd.so
-
执行时,操作系统会首先在我们的虚拟进程空间中加载进一个动态链接器,动态链接器帮我们完成链接任务,然后我们的程序就开始执行了
动态链接
1.动态链接器自举
动态链接器本身也是一个不依赖其他共享对象的共享对象,需要完成自举。
2.装载共享对象
将可执行文件和链接器自身的符号合并成为全局符号表,开始寻找依赖对象。加载对象的过程可以看做图的遍历过程;新的共享对象加载进来后,其符号将合并入全局符号表;加载完毕后,全局符号表将包含进程动态链接所需全部符号。
3.重定位和初始化
链接器遍历可执行文件和共享对象的重定位表,将它们GOT/PLT中每个需要重定位的位置进行修正。完成重定位后,链接器执行.init段的代码,进行共享对象特有的初始化过程(例如C++里全局对象的构造函数)。
4.转交控制权
完成所有工作,将控制权转交给程序的入口开始执行。
ref:https://www.cnblogs.com/linhaostudy/p/10544917.html
《程序员的自我修养》——链接、装载与库
动态链接的指令
ldd: 查看引用的动态库的链接和名字
objdump和readelf:查看目标代码,查看各节地址和符号表等信息
gdb:调试,查看运行时地址等信息
cat /proc/pid/maps: 查看内存映像,其中pid为进程id。可以看到是否正确加载到所需要的动态库以及程序的内存分布。
实模式和保护模式
-
实模式:基地址+偏移量可以直接获得物理地址的模式
- 缺点:非常不安全
-
保护模式:不能直接拿到物理地址,需要进行地址转换
- 从80286开始,是现代操作系统的主要模式
选择子
放在段选择寄存器里
-
低2位表示请求特权级
-
第3位表示选择GDT还是LDT方式
-
高13位表示在描述符表中的偏移
-
故描述符表的项数最多是2的13次方
段描述符
是GDT或LDT描述符表中的一个数据结构项
包含了一个段的大小、位置、特权级别等信息
每个段描述符占用8byte,64bit,包含段基地址、段线长、段属性等
- 段基址:开始地址,线性地址,偏移为0
- 段线长:长度,最大可用
- DPL:描述符特权级,目标段特权集
- CPL:当前段特权集
- GDT:全局描述符表,是全局唯一的。
- 存放一些公用的描述符,和包含各进程局部描述符表首地址的描述符。
- LDT:局部描述符表,每个进程都可以有一个。
- 存放本进程内使用的描述符。
- GDTR:全局描述符表寄存器
- 48位寄存器,高32位放置GDT首地址,低16位放置GDT限长
- 限长决定了可寻址的大小,注意低16位放的不是选择子
- LDTR:16位寄存器,放置一个特殊的选择子,用于查找当前进程的LDT首地址。
GDT查询物理地址
给出段选择子和偏移量
段选择子在段选择寄存器中
查询方式
如果是GDT查找方式,会从GDTR全局描述符表寄存器中获取全局描述符表首地址,利用选择子中高13位偏移量作为索引,从GDT中获取段描述符。如果查询合法且有权限,就会用描述符中的段首地址+偏移量找到物理地址(线性地址)
在不分页的情况下,线性地址即物理地址
-
给出段选择子(放在段选择寄存器里)+ 偏移量
-
若选择了GDT方式,则从GDTR获取GDT首地址,用段选择子中的13位做偏 移,拿到GDT中的描述符
-
如果合法且有权限,用描述符中的段首地址加上1.中的偏移量找到物理地址, 寻址结束
LDT查询物理地址
查询方式
- 给出段选择子(放在段选择寄存器中)+ 偏移量
- 若选择了LDT方式,则从GDTR获取GDT首地址,用LDTR中的偏移量做偏移,拿到GDT中的描述符1
- 从描述符1中获取LDT首地址,用段选择子中的13位做偏移,拿到LDT中的描述符2
- 如果合法且有权限,用描述符2中的段首地址加上1.中的偏移量找到物理地址。寻址结束
FAT12
FAT(File Allocation Table)文件配置表。用来记录文件所在位置的表格。假若丢失文件分配表,那么硬盘上的数据就会因无法定位而无法使用。
在DOS v1.0时代就引入了,是最基本的文件系统之一。
FAT家族:FAT12、FAT16、FAT32、ExFAT、VFAT
FAT12介绍
-
12位地址,最大容量16MB
-
为软盘设计的文件系统
-
FAT文件系统把存储介质看成一维的数组,基本单位是簇(cluster)
存储介质被划分为3个区域:boot record、FAT、directory and data area
一个簇包含一个扇区,大小为512B
FAT结构
Boot Record
引导扇区包含了数据和代码,数据被称为BPB(BIOS Parameter Block)
![]()
-
FAT1和FAT2互为备份。
-
文件分配表被划分为紧密排列的若干个表项,每个表项都与数据区中的一个簇相对应,而且表项的序号也是与簇号一一对应的。
-
每12位成为一个FAT项(FATEntry),代表一个簇。所以2个FAT项会占用3个字节
-
**在1.44M软盘上,FAT前三个字节的值是固定的0xF0、0xFF、0xFF,用于表示这是一个应用在1.44M软盘上的FAT12文件系统。**本来序号为0和1的FAT表项应该对应于簇0和簇1,但是由于这两个表项被设置成了固定值,簇0和簇1就没有存在的意义了,所以数据区就起始于簇2
-
FAT项的值代表文件的下一个簇号
-
值大于或等于0xFF8,表示当前簇已经是本文件的最后一个簇值为0xFF7, 表示它是一个坏簇
读取过程
目录区
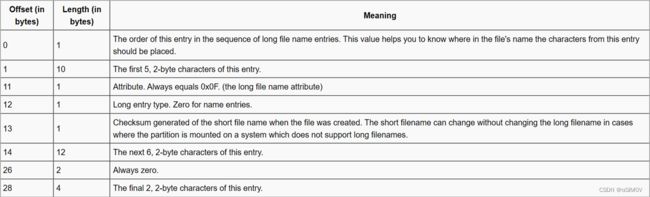
根目录区由目录项(entry)组成,一个目录项占32个字节。
如果文件名过长,在原本的目录项前面会立即跟一个LFN项,同样也是32个字节。
-
数据区开始扇区号=根目录开始扇区号+根目录所占扇区数。
-
若为目录,格式同根目录项。
-
https://wiki.osdev.org/FAT#File_Allocation_Table
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39654127/article/details/88429461#main-toc
制作FAT12镜像
Linux
1.在当前目录(.)下创建一个新的软盘镜像a.img
mkfs.fat -C a.img 1440
- 1440:大小
- -C:创建一个新的文件
- mkfs.fat:创建fat类型镜像
2.在当前目录下创建一个新目录(./mount)作为挂载点
mkdir mount
3.将镜像./a.img挂载到./mount下
sudo mount a.img mount
- 然后就可以在挂载目录添加文件,可以从文件夹操作读取镜像的内容
- 挂载目录进行操作需要root权限
实验要求
实验内容 - FAT12镜像查看工具
用C/C++和nasm编写一个FAT12镜像查看工具,读取一个.img格式的文件并响 应用户输入。
功能列表
[见文件]
实验过程
创建结构体
- BS_jmpBoot:从上表可以看出,在引导程序的起始处,首先定义的是BS_jmpBoot字段。从字面意思可知,它是一句跳转代码,这是由于BS_jmpBoot字段后面的数据不是可执行程序,而是FAT12文件系统的组成结构信息,故此必须跳过这部分内容。字段长度为3,说明汇编代码jmp short Label_start;nop经过编译后,一共生成三个字节的机器码,其中nop会生成一个字节的机器码,jmp shortLabel_start会生成两个字节的机器码。
- BS_OEMName:记录制造商的名字,亦可自行为文件系统命名。
- BPB_SecPerClus:描述了每簇扇区数。由于每个扇区的容量只有512B,过小的扇区容量可能会导致软盘读写次数过于频繁,从而引入簇(Cluster)这个概念。簇将2的整数次方个扇区作为一个“原子”数据存储单元,也就是说簇是FAT类文件系统的最小数据存储单位。
- BPB_RsvdsecCnt:指定保留扇区的数量,此域值不能为0。保留扇区起始于FAT12文件系统的第一个扇区,对于FAT12而言此位必须为1,也就意味着引导扇区包含在保留扇区内,所以FAT表从软盘的第二个扇区开始。
- BPB_NumFATs:指定FAT12文件系统中FAT表的份数,任何FAT类文件系统都建议此域设置为2。设置为2主要是为了给FAT表准备一个备份表,因此FAT表1与FAT表2内的数据是一样的,FAT表2是FAT表1的数据备份表。
- BPB_RootEntCnt:指定根目录可容纳的目录项数。对于FAT12文件系统而言,这个数值乘以32必须是BPB_BytesPersec的偶数倍。
- BPB_Totsec16:记录着总扇区数。这里的总扇区数包括保留扇区(内含引导扇区)、FAT表、根目录区以及数据区占用的全部扇区数,如果此域值为0,那么BPB_Totsec32字段必须是非0值。
- BPB_Media:描述存储介质类型。对于不可移动的存储介质而言,标准值是0xF8。对于可移动的存储介质,常用值为0xF0,此域的合法值是0xF0、0xF8、0xF9、0xFA、0xFB、0xFC、0xFD、0xFE、0xFF:另外提醒一点,无论该字段写入了什么数值,同时也必须向FAT[O]的低字节写入相同值。
- BPB_FATSz16:记录着FAT表占用的扇区数。FAT表1和FAT表2拥有相同的容量,它们的容量均由此值记录。
- Bs_volLab:指定卷标。它就是Windows或Linux系统中显示的磁盘名。
- BS_FilesysType:描述文件系统类型。此处的文件系统类型值为’FAT12 ',这个类型值只是一个字符串而已,操作系统并不使用该字段来鉴别FAT类文件系统的类型。
#include 处理命令行
-
打开FAT12的映像文件
-
创建根节点
-
载入BPB:fillBPB(fat12, bpb_ptr);
-
初始化各个全局变量和RootEntry
-
构建文件链表:ReadFiles(fat12, rootEntry_ptr, root);
-
解析输入的命令:
- 第一次split,按空格分割:split(input, inputCommandList, ’ ')
- 删除数组中空格产生的空位置
-
处理exit:exit 退出情况
-
是ls系列命令:
- ls后面无内容:最直接printList(root);
- ls后面有内容:
- 三个flag:hasL hasPath error
- 遍历所有参数:-l可以出现在任意位置、任意多次
- 出现不是-的,则只可能是路径,路径只能出现一次
- if已经hasPath了,报错,error为true
- else还没有路径参数:需要在路径前后确认有无/,没有需要加上:pathAdd(inputCommandList[i])
- 是-,说明是ls -参数
- if ls -后面为空:报错,error为true
- else不为空
- ls -后面不是l,报错,error为true
- hasL为true
- 如果error为true,本行命令不执行
- 接下来是ls -l的处理:
- 新创建一个flag:exist,exist == 1有L没有path;exist == 2没有L有path && 文件,无法打开
- 有hasL没有Path:exist为1:printList_L(root);
- 没有hasL有Path(ls NJU): *printListWithPath(root, path, exist, false);
- 有hasL有Path:*printListWithPath(root, path, exist, true);
- 没有hasL没有Path:**printList(root);**并跳到下一个命令执行
- exist == 0: **myPrint(ERR_NO_DIR);**并跳到下一个命令执行
- exist == 2:**myPrint(ERR_CANT_OPEN);**并跳到下一个命令执行
-
是cat指令
-
cat path
- cat后无参数或者参数过多,error
-
其他错误的不支持的指令
-
报错
main.cpp
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
//user地址需要替换
/**
*user地址需要替换
*/
string img = "/home/user/OS-Lab/lab2/1/a.img";
FILE *fat12;
fat12 = fopen("./a.img", "rb"); //打开FAT12的映像文件
struct BPB bpb;
//bpb_ptr是指向BPB的指针
struct BPB *bpb_ptr = &bpb;
//创建根节点
Node *root = new Node();
root->name = "";
root->path = "/";
//载入BPB
fillBPB(fat12, bpb_ptr);
//初始化各个全局变量
BytsPerSec = bpb_ptr->BPB_BytsPerSec;
SecPerClus = bpb_ptr->BPB_SecPerClus;
RsvdSecCnt = bpb_ptr->BPB_RsvdSecCnt;
NumFATs = bpb_ptr->BPB_NumFATs;
RootEntCnt = bpb_ptr->BPB_RootEntCnt;
if (bpb_ptr->BPB_FATSz16 != 0) {
FATSz = bpb_ptr->BPB_FATSz16;
} else {
//BPB_FATSz16为0,该值为FAT扇区数
FATSz = bpb_ptr->BPB_TotSec32;
}
struct RootEntry rootEntry;
struct RootEntry *rootEntry_ptr = &rootEntry; //pointer of rootEntry
ReadFiles(fat12, rootEntry_ptr, root);//*****构建文件链表
while (true) { //解析输入的命令
//cout << "> ";
myPrint(">");
string input;
getline(cin, input);
vector<string> inputCommandList;
split(input, inputCommandList, ' ');
for (auto it = inputCommandList.begin(); it != inputCommandList.end();) {
//删除数组中空格产生的空位置
if (*it == "") {
it = inputCommandList.erase(it);
} else {
it++;
}
}
if (inputCommandList[0].compare("exit") == 0) {
//exit 退出情况
myPrint("Exit accept!exe down.\n");
fclose(fat12);
return 0;
} else if (inputCommandList[0].compare("ls") == 0) {
//ls系列命令
//情况1: ls
if (inputCommandList.size() == 1) {
printList(root);
} else {
bool hasL = false;
bool hasPath = false;
bool error = false;
string *path = NULL;
for (int i = 1; i < inputCommandList.size(); i++) {
//遍历所有参数
string s = inputCommandList[i];
// -l可以出现在任意位置、任意多次
if (s[0] != '-') {
// != - 则只可能是路径,路径只能出现一次
//路径
if (hasPath) {
//路径出现多次
myPrint(ERR_HAS_PATH);
error = true;
break;
} else {
//还没有路径参数
hasPath = true;
//需要在路径前后确认有无/
//没有需要加上
pathAdd(inputCommandList[i]);
path = &inputCommandList[i];
}
} else {
//ls -参数
if (s.length() == 1) {
//ls -后面为空:报错
myPrint(ERR_PARAMETER_WRONG);
error = true;
break;
}
//不为空
for (int j = 1; j < s.length(); j++) {
if (s[j] != 'l') {
//不为ls -l:报错
error = true;
myPrint(ERR_PARAMETER_WRONG);
break;
}
}
hasL = true;
}
}
if (error) {
continue;
}
//情况2 ls -l
int exist = 0; //exist == 1有L没有path exist == 2没有L有path && 文件,无法打开
if (hasL && !hasPath) {
exist = 1;
printList_L(root);
} else if (!hasL && hasPath) {
//情况3 ls NJU
printListWithPath(root, *path, exist, false);
} else if (hasL && hasPath) {
printListWithPath(root, *path, exist, true);
} else {
//!hasL && !hashPath
printList(root);
continue;
}
if (exist == 0) {
myPrint(ERR_NO_DIR);
continue;
} else if (exist == 2) {
myPrint(ERR_CANT_OPEN);
continue;
}
}
} else if (inputCommandList[0].compare("cat") == 0) {
//cat系列命令
//输出文件名对应文件的内容,若路径不存在或不是一个普通文件则报错,给出提示
if (inputCommandList.size() == 2 && inputCommandList[1][0] != '-') {
//cat path
int exist = 0;
pathAdd(inputCommandList[1]);
Cat(root, inputCommandList[1], exist); //执行cat
if (exist == 0) {
myPrint(ERR_NO_FILE);
continue;
} else if (exist == 2) {
myPrint(ERR_CANT_OPEN);
continue;
}
} else {
//cat后无参数或者参数过多,error
myPrint(ERR_PARAMETER_WRONG);
continue;
}
} else {
//错误命令
myPrint(ERR_COMMAND_WRONG);
continue;
}
}
return 0;
}
split(const string &s, vector &sv, const char flag)
void split(const string &s, vector<string> &sv, const char flag) {
sv.clear();
//初始化输入字符串流istringstream
istringstream iss(s);
string temp;
//使用 getline 函数通过 iss 对字符串进行分割
while (getline(iss, temp, flag)) {
sv.push_back(temp);
}
return;
}
pathAdd
void pathAdd(string &s) {
//给path的首尾加上'/'
if (s[0] != '/') {
s = "/" + s;
}
if (s[s.length() - 1] != '/') {
s += '/';
}
}
读取软盘文件系统信息
载入BPB:
fillBPB(fat12, bpb_ptr):
void fillBPB(FILE *fat12, struct BPB *bpb_ptr) { //读取boot信息
int check;
//BPB从偏移11个字节处开始
//C 库函数 int fseek(FILE *stream, long int offset, int whence)
// 设置流 stream 的文件位置为给定的偏移 offset,参数 offset 意味着从给定的 whence 位置查找的字节数。
check = fseek(fat12, 11, SEEK_SET);
if (check == -1)
myPrint("fseek in fillBPB failed!\n");
//BPB长度为25字节
check = fread(bpb_ptr, 1, 25, fat12);
if (check != 25)
myPrint("fread in fillBPB failed!\n");
}
构建文件链表:在根目录中查找目标文件
ReadFiles(fat12, rootEntry_ptr, root)
-
读文件的base基质的单位都是字节
-
读出来的文件用DIR_Attr&0x10判断,结果为0是文件,否则为文件夹
-
文件:
- 文件的名字中间空格用“.”代替
- 新建该文件的节点,并将其加入父节点的子结点集合中,子节点数量自增
- 每个节点的path默认加上/作为结尾
- 读取文件的内容:getFileContent(fat12, rootEntry_ptr->DIR_FstClus, son);
-
目录
- 把目录名提取出来放到了realName
- creatDirectoryNode(son, fatherNode);
- 读取目录的内容:readChildren(fat12, rootEntry_ptr->DIR_FstClus, son);
ReadFiles(FILE *fat12, struct RootEntry *rootEntry_ptr, Node *fatherNode)
void ReadFiles(FILE *fat12, struct RootEntry *rootEntry_ptr, Node *fatherNode) {
//根目录首字节的偏移数
//base = (boot扇区数 + fat数量 * 每个fat表占用扇区数) * 每个扇区字节数
int base = (RsvdSecCnt + NumFATs * FATSz) * BytsPerSec;
int check;
char realName[12]; //暂存文件名
//依次处理根目录中的各个条目
for (int i = 0; i < RootEntCnt; i++) {
check = fseek(fat12, base, SEEK_SET);
if (check == -1)
myPrint("fseek in printFiles failed!\n");
//每个元素1byte,一共32元素,即一个根目录区的目录项
check = fread(rootEntry_ptr, 1, 32, fat12);
if (check != 32)
myPrint("fread in printFiles failed!\n");
//base后移32byte
base += 32;
if (rootEntry_ptr->DIR_Name[0] == '\0') continue; //空条目不输出
//过滤非目标文件
int boolean = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 11; j++) {
if (!(((rootEntry_ptr->DIR_Name[j] >= 48) && (rootEntry_ptr->DIR_Name[j] <= 57)) ||
((rootEntry_ptr->DIR_Name[j] >= 65) && (rootEntry_ptr->DIR_Name[j] <= 90)) ||
((rootEntry_ptr->DIR_Name[j] >= 97) && (rootEntry_ptr->DIR_Name[j] <= 122)) ||
(rootEntry_ptr->DIR_Name[j] == ' '))) {
boolean = 1; //非英文及数字、空格
break;
}
}
if (boolean == 1) continue; //非目标文件不输出
int k; //名字的处理
//用DIR_Attr&0x10判断,结果为0是文件,否则为文件夹。
//文件 0x20 文件夹0x10
if ((rootEntry_ptr->DIR_Attr & 0x10) == 0) {
//文件
//从0开始
int name_len = -1; //name_len中存储了是name的下标
for (k = 0; k < 11; k++) {
if (rootEntry_ptr->DIR_Name[k] != ' ') {
name_len++;
realName[name_len] = rootEntry_ptr->DIR_Name[k];
} else {
//name[k]为空,名字加上. ,跳过剩下的空格
name_len++;
realName[name_len] = '.';
while (rootEntry_ptr->DIR_Name[k] == ' ') k++;
k--;
}
}
name_len++;
realName[name_len] = '\0';
//到此为止,把文件名提取出来放到了realName里
//新建该文件的节点,并将其加入父节点的子结点集合中
Node *son = new Node();
fatherNode->next.push_back(son); //存到father的next数组中
son->name = realName;
son->FileSize = rootEntry_ptr->DIR_FileSize;
son->isfile = true;
//每个节点的path默认加上/作为结尾
son->path = fatherNode->path + realName + "/";
fatherNode->file_count++;
getFileContent(fat12, rootEntry_ptr->DIR_FstClus, son);//读取文件的内容
} else {
//目录
int tempLong = -1;
for (k = 0; k < 11; k++) {
if (rootEntry_ptr->DIR_Name[k] != ' ') {
tempLong++;
realName[tempLong] = rootEntry_ptr->DIR_Name[k];
} else {
tempLong++;
realName[tempLong] = '\0';
break;
}
} //到此为止,把目录名提取出来放到了realName
Node *son = new Node();
fatherNode->next.push_back(son);
son->name = realName;
son->path = fatherNode->path + realName + "/";
fatherNode->dir_count++;
creatDirectoryNode(son, fatherNode);
//输出目录及子文件
readChildren(fat12, rootEntry_ptr->DIR_FstClus, son); //读取目录的内容
}
}
}
creatDirectoryNode(son, fatherNode);
void creatDirectoryNode(Node *p, Node *father) {
//每个目录里自带 . 和 ..
Node *q = new Node();
q->name = ".";
q->isval = false;
p->next.push_back(q);
q = new Node();
q->name = "..";
q->isval = false;
p->next.push_back(q);
}
readChildren(fat12, rootEntry_ptr->DIR_FstClus, son);
- getFATValue(fat12, currentClus);//查FAT表获取下一个簇号
- 0xFF8:最后一个簇;0xFF7:坏簇
- 按照每簇的字节数读取内容:几乎和readFile的内容差不多
- 用查表查到的下一个簇号作为地址继续读取,直到读到最后,一个根目录区的目录里的内容全部读完了,建成树林存储起来了
void readChildren(FILE *fat12, int startClus, Node *father) {
//数据区的第一个簇(即2号簇)的偏移字节
int dataBase = BytsPerSec * (RsvdSecCnt + FATSz * NumFATs + (RootEntCnt * 32 + BytsPerSec - 1) / BytsPerSec);
int currentClus = startClus;
int value = 0;//value用来查看是否存在多个簇(查FAT表)
while (value < 0xFF8) {
value = getFATValue(fat12, currentClus);//查FAT表获取下一个簇号
if (value == 0xFF7) {
myPrint("坏簇,读取失败!\n");
break;
}
int startByte = dataBase + (currentClus - 2) * SecPerClus * BytsPerSec;
int check;
int count = SecPerClus * BytsPerSec; //每簇的字节数
int loop = 0;
while (loop < count) {
int i;
RootEntry sonEntry;//读取目录项
RootEntry *sonEntryP = &sonEntry;
check = fseek(fat12, startByte + loop, SEEK_SET);
if (check == -1)
myPrint("fseek in readchildren failed!\n");
check = fread(sonEntryP, 1, 32, fat12);
if (check != 32)
myPrint("fread in readchildren failed!\n");//读取完毕
loop += 32;
if (sonEntryP->DIR_Name[0] == '\0')
continue;
//空条目不输出
//过滤非目标文件
int j;
int boolean = 0;
for (j = 0; j < 11; j++) {
if (!(((sonEntryP->DIR_Name[j] >= 48) && (sonEntryP->DIR_Name[j] <= 57)) ||
((sonEntryP->DIR_Name[j] >= 65) && (sonEntryP->DIR_Name[j] <= 90)) ||
((sonEntryP->DIR_Name[j] >= 97) && (sonEntryP->DIR_Name[j] <= 122)) ||
(sonEntryP->DIR_Name[j] == ' '))) {
boolean = 1; //非英文及数字、空格
break;
}
}
if (boolean == 1)
continue;
if ((sonEntryP->DIR_Attr & 0x10) == 0) {
//文件处理
char tempName[12]; //暂存替换空格为点后的文件名
int k;
int tempLong = -1;
for (k = 0; k < 11; k++) {
if (sonEntryP->DIR_Name[k] != ' ') {
tempLong++;
tempName[tempLong] = sonEntryP->DIR_Name[k];
} else {
tempLong++;
tempName[tempLong] = '.';
while (sonEntryP->DIR_Name[k] == ' ') k++;
k--;
}
}
tempLong++;
tempName[tempLong] = '\0'; //到此为止,把文件名提取出来放到tempName里
Node *son = new Node();
father->next.push_back(son);
son->name = tempName;
son->FileSize = sonEntryP->DIR_FileSize;
son->isfile = true;
son->path = father->path + tempName + "/";
father->file_count++;
getFileContent(fat12, sonEntryP->DIR_FstClus, son);
} else {
char tempName[12];
int count = -1;
for (int k = 0; k < 11; k++) {
if (sonEntryP->DIR_Name[k] != ' ') {
count++;
tempName[count] = sonEntryP->DIR_Name[k];
} else {
count++;
tempName[count] = '\0';
}
}
Node *son = new Node();
father->next.push_back(son);
son->name = tempName;
son->path = father->path + tempName + "/";
father->dir_count++;
creatDirectoryNode(son, father);
readChildren(fat12, sonEntryP->DIR_FstClus, son);
}
}
currentClus = value;//下一个簇
}
}
getFATValue(fat12, currentClus)
int getFATValue(FILE *fat12, int num) {
//FAT1的偏移字节
int fatBase = RsvdSecCnt * BytsPerSec;
//FAT项的偏移字节
//一个fat项1.5字节
int fatPos = fatBase + num * 3 / 2;
//奇偶FAT项处理方式不同,分类进行处理,从0号FAT项开始
//type == 0 偶数
//typ3 == 1 奇数
int type = 0;
if (num % 2 == 0) {
type = 0;
} else {
type = 1;
}
//先读出FAT项所在的两个字节
u16 bytes;
u16 *bytes_ptr = &bytes;
int check;
check = fseek(fat12, fatPos, SEEK_SET);
if (check == -1)
myPrint("fseek in getFATValue failed!");
check = fread(bytes_ptr, 1, 2, fat12);
if (check != 2)
myPrint("fread in getFATValue failed!");
//u16为short,结合存储的小尾顺序和FAT项结构可以得到
//wiki的写法
if (type == 0) {
bytes = bytes << 4; //这里原文错误,原理建议看网上关于FAT表的文章
return bytes >> 4;
} else {
return bytes >> 4;
}
}
getFileContent(fat12, rootEntry_ptr->DIR_FstClus, son);
void getFileContent(FILE *fat12, int startClus, Node *son) {//获取文件内容
//步骤:
// (1)在根目录区查找目标文件对应的项
// (2)获取目标文件的起始簇号和文件大小
// (3)根据FAT表中记录的逻辑先后关系读取数据
//计算每簇的字节数,每个区域的初始位置的偏移量。
//每簇字节数 = 每簇扇区数 * 每扇区字节数。
//fatBase = Boot记录占用的扇区数 * 每扇区字节数
//fileRootBase =(Boot记录占用的扇区数+FAT表个数 * FAT扇区数)* 每扇区字节数
//dataBase =(Boot记录占用的扇区数+FAT表个数 * FAT扇区数 +(根目录最大文件数* 32byte + 每扇区字节数 - 1)/ 每扇区字节数)* 每扇区字节数。
//数据区的偏移量又乘又除可不可以等于fileRootBase+根目录最大文件数*32?不行!
//dataBase初始位置 = FileRootBase最后一个簇的结束位置。如果根目录没有填满最后一个簇,数据区也是从下一个簇开始的,而不是默认于最后一个根目录的结束位置开始。
//用 "(根目录最大文件数 * 32 + 每扇区字节数 - 1)/ 每扇区字节数 "可以得到根目录区占用的真正扇区数。
//原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43242836/article/details/103056431
int dataBase = BytsPerSec * (RsvdSecCnt + FATSz * NumFATs + (RootEntCnt * 32 + BytsPerSec - 1) / BytsPerSec);
int currentClus = startClus;
int value = 0; //这里用value来进行不同簇的读取(超过512字节)
char *p = son->content;
if (startClus == 0) {
return;
}
//while循环读取簇,即便大于512byte也可以,直到该文件的最后一个簇
while (value < 0xFF8) {//如果表项值大于等于0xFF8,则说明已经到达最后一个簇
value = getFATValue(fat12, currentClus);//获取下一个簇
if (value == 0xFF7) {
myPrint("坏簇,读取失败!\n");
break;
}
char *str = (char *) malloc(SecPerClus * BytsPerSec); //暂存从簇中读出的数据,大小为每簇扇区数 * 每扇区字节数
char *content = str;
// 字节开始处 = 数据基址 + (目前簇 - 2)* 每簇扇区数 * 每扇区字节数
// 数据区起始地址所对应的编号为2(不为0)(有了起始地址,这里可以用偏移地址)
// FAT12文件系统的前两个簇是固定簇,而实际表示数据的簇号——或者更确切的说,是FAT12表项的序号从2开始,实际表示数据的“簇”仍然是从0开始。
int startByte = dataBase + (currentClus - 2) * SecPerClus * BytsPerSec;
int check;
check = fseek(fat12, startByte, SEEK_SET);
if (check == -1)
myPrint("fseek in printChildren failed!");
check = fread(content, 1, SecPerClus * BytsPerSec, fat12);//提取数据
//fread:return the number of items read or written. This number equals the number of bytes transferred only when size is 1.
// If an error occurs, or the end of the file is reached, the return value is a short item count (or zero)
if (check != SecPerClus * BytsPerSec)
myPrint("fread in printChildren failed!");
int count = SecPerClus * BytsPerSec;
int loop = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {//读取赋值
*p = content[i];
p++;
}
free(str);
currentClus = value;
}
}
根目录区的大小和位置
根目录区的目录项
根目录区由目录项构成,每一个目录项代表根目录中的一个文件索引。
读取目标文件到内存的注意事项
加载FAT12中的文件数据
小贴士
-
FAT表中的每个表项只占用12比特(1.5字节)
-
FAT表一共记录了BPB_BytsPerSec * 9 * 2 / 3个表项 (9个扇区 * 512 /1.5)
-
可以使用一个short表示一个表项的值
-
如果表项值大于等于0xFF8,则说明已经到达最后一个簇
-
如果表项值等于0xFF7,则说明当前簇已经损坏
-
数据区起始簇(扇区)号为33,地址为0x4200(33 * 512)
-
数据区起始地址所对应的编号为2(不为0)(有了起始地址,这里可以用偏移地址)
FAT12文件系统的前两个簇是固定簇,而实际表示数据的簇号——或者更确切的说,是FAT12表项的序号从2开始,实际表示数据的“簇”仍然是从0开始。
- 因此,DIR_FstClus对应的地址为:0×4200+(DIR_FstClus-2)*512
计算每簇的字节数,每个区域的初始位置的偏移量:
每簇字节数 = 每簇扇区数 * 每扇区字节数。
fatBase = Boot记录占用的扇区数 * 每扇区字节数
fileRootBase =(Boot记录占用的扇区数+FAT表个数 * FAT扇区数)* 每扇区字节数
dataBase =(Boot记录占用的扇区数+FAT表个数 * FAT扇区数+(根目录最大文件数* 32+每扇区字节数-1)/每扇区字节数)* 每扇区字节数。
数据区的偏移量又乘又除是不是吃饱了撑的0.0?可不可以等于fileRootBase+根目录最大文件数*32?
不行!
dataBase初始位置=FileRootBase最后一个簇的结束位置。如果根目录没有填满最后一个簇,数据区也是从下一个簇开始的,而不是默认于最后一个根目录的结束位置开始。
用 (根目录最大文件数 32+每扇区字节数-1)/每扇区字节数* 可以得到根目录区占用的真正扇区数。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43242836/article/details/103056431
又:读取fat项内容的时候最好参照wiki百科的写法,有一些PPT和CSDN上的图是有点问题的
打印
打印的过程也是查找的过程:
如果需要打印,就把string放入str_print,然后传给 myPrint(str_print.c_str()),最后clear str_print
查找带路径的节点:cat与printListWithPath相同的逻辑
- 如果递归前发现需要的路径source和目前root的path相同,则判断是否为文件,如果文件内容不为空,就打印
- 如果没找到:
- 判读是否需要的路径source长度已经小于目前root的path,如果是,则不可能在后面的子结点找到;如果不是,则继续
- 判断是否当前节点的path部分与source相同,如果相同则继续递归查询当前节点的所有符合子结点;如果不同,则返回
void printList(Node *r) {
Node *father = r;//通过root节点,遍历所有的节点
if (father->isfile == true) {
return;
} else {
//首先输出路径名,加一个冒号: , 换行,再输出路径下的文件和目录列表。路径下的目录包括. 和..
//cout << father->path << ":" << endl;
str_print = father->path + ":\n";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
//打印每个next
//使用红色(\033[31m)颜色输出目录名,不添加特殊颜色输出文件的文件名。
Node *node;
int lens = father->next.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lens; i++) {
node = father->next[i];
//当用户不添加任何选项执行ls命令时,每个文件/目录项之间用两个空格隔开。
if (!node->isfile) {
// 文件夹
// cout << "\033[31m" << node->name << "\033[0m" << " ";
// cout << node->name << " ";
str_print = "\033[31m" + node->name + "\033[0m" + " ";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
} else {
// 文件
// cout << node->name << " ";
str_print = node->name + " ";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
}
}
//cout << endl;
str_print = "\n";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
//进行递归
for (int i = 0; i < lens; i++) {
if (father->next[i]->isval) {
printList(father->next[i]);
}
}
}
}
void printList_L(Node *root) {
Node *father = root;
if (father->isfile) {
//如果该Node是文件,不处理
return;
} else {
//在路径名后,冒号前,另输出此目录下直接子目录和直接子文件的数目,两个数字之间用空格连接。两个数字不添加特殊颜色
//cout << father->path <<" "<dir_count<<" "<file_count<< ":" << endl;
str_print = father->path + " " + to_string(father->dir_count) + " " + to_string(father->file_count) + ":\n";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
//打印每个next
Node *node;
int lens = father->next.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lens; i++) {
node = father->next[i];
if (!node->isfile) {
// 文件夹
// cout << "\033[31m" <name << "\033[0m" << " ";
if (node->isval) {
// 若项为目录,输出此目录下直接子目录和直接子文件的数目,
// 两个数字之间用空格连接。这两个数字不添加特殊颜色
// cout << node->name << " " << node->dir_count << " " << node->file_count << endl;
// 用红色( \033[31m )颜色输出目录名
str_print = "\033[31m" + node->name + "\033[0m" + " " + to_string(node->dir_count) + " " +
to_string(node->file_count) + "\n";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
} else {
//处理. ..
//cout << node->name << " "<
str_print = "\033[31m" + node->name + "\033[0m" + " \n";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
}
} else {
// 文件
// cout << node->name << " " << node->FileSize << endl;
str_print = node->name + " " + to_string(node->FileSize) + "\n";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
}
}
//cout << endl;
myPrint("\n");
//进行递归
for (int i = 0; i < lens; i++) {
//不输出.和..目录的子目录和子文件数目
if (father->next[i]->isval) printList_L(father->next[i]);
}
}
}
void printListWithPath(Node *root, string path, int &exist, bool hasL) {
if (path.compare(root->path) == 0) { //路径完全相同,说明就是该节点
//查找到
if (root->isfile) {
//如果是文件,无法打开
exist = 2;
return;
} else {
exist = 1;//状态正常,无需报错
if (hasL) {
printList_L(root);
} else {
printList(root);
}
}
return;
}
if (path.length() <= root->path.length()) { //出现该情况直接出去
return;
}
string temp = path.substr(0, root->path.length());
//截取输入的path的部分字符串,和当前节点的path比较,如果相同,说明目标在该节点下级
if (temp.compare(root->path) == 0) {
//路径部分匹配
for (Node *q: root->next) {
//递归查找,找到就打印
printListWithPath(q, path, exist, hasL);
}
}
}
void Cat(Node *root, string source, int &exist) {
//与printListWithPath相同的逻辑
//如果递归前发现需要的路径source和目前root的path相同,则判断是否为文件,如果文件内容不为空,就打印
//如果没找到:
//判读是否需要的路径source长度已经小于目前root的path,如果是,则不可能在后面的子结点找到;如果不是,则继续
//判断是否当前节点的path部分与source相同,如果相同则继续递归查询当前节点的所有符合子结点;如果不同,则返回
if (source.compare(root->path) == 0) {
//查找到
if (root->isfile) {
exist = 1;
if (root->content[0] != 0) {
//cout << root->content << endl;
myPrint(root->content);
myPrint("\n");
}
return;
} else {
exist = 2;
return;
}
}
if (source.length() <= root->path.length()) {
return;
}
string temp = source.substr(0, root->path.length());
if (temp.compare(root->path) == 0) {
//路径部分匹配
for (Node *node: root->next) {
Cat(node, source, exist);
}
}
}
*myPrint(const char p)
void myPrint(const char *p) {
asm_print(p, strlen(p));
}
实验完全代码
#include dir_count<<" "<file_count<< ":" << endl;
str_print = father->path + " " + to_string(father->dir_count) + " " + to_string(father->file_count) + ":\n";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
//打印每个next
Node *node;
int lens = father->next.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lens; i++) {
node = father->next[i];
if (!node->isfile) {
// 文件夹
// cout << "\033[31m" <name << "\033[0m" << " ";
if (node->isval) {
// 若项为目录,输出此目录下直接子目录和直接子文件的数目,
// 两个数字之间用空格连接。这两个数字不添加特殊颜色
// cout << node->name << " " << node->dir_count << " " << node->file_count << endl;
// 用红色( \033[31m )颜色输出目录名
str_print = "\033[31m" + node->name + "\033[0m" + " " + to_string(node->dir_count) + " " +
to_string(node->file_count) + "\n";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
} else {
//处理. ..
//cout << node->name << " "<
str_print = "\033[31m" + node->name + "\033[0m" + " \n";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
}
} else {
// 文件
// cout << node->name << " " << node->FileSize << endl;
str_print = node->name + " " + to_string(node->FileSize) + "\n";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
}
}
//cout << endl;
myPrint("\n");
//进行递归
for (int i = 0; i < lens; i++) {
//不输出.和..目录的子目录和子文件数目
if (father->next[i]->isval) printList_L(father->next[i]);
}
}
}
void printListWithPath(Node *root, string path, int &exist, bool hasL) {
if (path.compare(root->path) == 0) { //路径完全相同,说明就是该节点
//查找到
if (root->isfile) {
//如果是文件,无法打开
exist = 2;
return;
} else {
exist = 1;//状态正常,无需报错
if (hasL) {
printList_L(root);
} else {
printList(root);
}
}
return;
}
if (path.length() <= root->path.length()) { //出现该情况直接出去
return;
}
string temp = path.substr(0, root->path.length());
//截取输入的path的部分字符串,和当前节点的path比较,如果相同,说明目标在该节点下级
if (temp.compare(root->path) == 0) {
//路径部分匹配
for (Node *q: root->next) {
//递归查找,找到就打印
printListWithPath(q, path, exist, hasL);
}
}
}
void Cat(Node *root, string source, int &exist) {
//与printListWithPath相同的逻辑
//如果递归前发现需要的路径source和目前root的path相同,则判断是否为文件,如果文件内容不为空,就打印
//如果没找到:
//判读是否需要的路径source长度已经小于目前root的path,如果是,则不可能在后面的子结点找到;如果不是,则继续
//判断是否当前节点的path部分与source相同,如果相同则继续递归查询当前节点的所有符合子结点;如果不同,则返回
if (source.compare(root->path) == 0) {
//查找到
if (root->isfile) {
exist = 1;
if (root->content[0] != 0) {
//cout << root->content << endl;
myPrint(root->content);
myPrint("\n");
}
return;
} else {
exist = 2;
return;
}
}
if (source.length() <= root->path.length()) {
return;
}
string temp = source.substr(0, root->path.length());
if (temp.compare(root->path) == 0) {
//路径部分匹配
for (Node *node: root->next) {
Cat(node, source, exist);
}
}
}
/**
*
* @param fat12
* @param startClus : 开始簇号
* @param son
*/
void getFileContent(FILE *fat12, int startClus, Node *son) {//获取文件内容
//步骤:
// (1)在根目录区查找目标文件对应的项
// (2)获取目标文件的起始簇号和文件大小
// (3)根据FAT表中记录的逻辑先后关系读取数据
//计算每簇的字节数,每个区域的初始位置的偏移量。
//每簇字节数 = 每簇扇区数 * 每扇区字节数。
//fatBase = Boot记录占用的扇区数 * 每扇区字节数
//fileRootBase =(Boot记录占用的扇区数+FAT表个数 * FAT扇区数)* 每扇区字节数
//dataBase =(Boot记录占用的扇区数+FAT表个数 * FAT扇区数 +(根目录最大文件数* 32byte + 每扇区字节数 - 1)/ 每扇区字节数)* 每扇区字节数。
//数据区的偏移量又乘又除可不可以等于fileRootBase+根目录最大文件数*32?不行!
//dataBase初始位置 = FileRootBase最后一个簇的结束位置。如果根目录没有填满最后一个簇,数据区也是从下一个簇开始的,而不是默认于最后一个根目录的结束位置开始。
//用 "(根目录最大文件数 * 32 + 每扇区字节数 - 1)/ 每扇区字节数 "可以得到根目录区占用的真正扇区数。
//原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43242836/article/details/103056431
int dataBase = BytsPerSec * (RsvdSecCnt + FATSz * NumFATs + (RootEntCnt * 32 + BytsPerSec - 1) / BytsPerSec);
int currentClus = startClus;
int value = 0; //这里用value来进行不同簇的读取(超过512字节)
char *p = son->content;
if (startClus == 0) {
return;
}
//while循环读取簇,即便大于512byte也可以,直到该文件的最后一个簇
while (value < 0xFF8) {//如果表项值大于等于0xFF8,则说明已经到达最后一个簇
value = getFATValue(fat12, currentClus);//获取下一个簇
if (value == 0xFF7) {
myPrint("坏簇,读取失败!\n");
break;
}
char *str = (char *) malloc(SecPerClus * BytsPerSec); //暂存从簇中读出的数据,大小为每簇扇区数 * 每扇区字节数
char *content = str;
// 字节开始处 = 数据基址 + (目前簇 - 2)* 每簇扇区数 * 每扇区字节数
// 数据区起始地址所对应的编号为2(不为0)(有了起始地址,这里可以用偏移地址)
// FAT12文件系统的前两个簇是固定簇,而实际表示数据的簇号——或者更确切的说,是FAT12表项的序号从2开始,实际表示数据的“簇”仍然是从0开始。
int startByte = dataBase + (currentClus - 2) * SecPerClus * BytsPerSec;
int check;
check = fseek(fat12, startByte, SEEK_SET);
if (check == -1)
myPrint("fseek in printChildren failed!");
check = fread(content, 1, SecPerClus * BytsPerSec, fat12);//提取数据
//fread:return the number of items read or written. This number equals the number of bytes transferred only when size is 1.
// If an error occurs, or the end of the file is reached, the return value is a short item count (or zero)
if (check != SecPerClus * BytsPerSec)
myPrint("fread in printChildren failed!");
int count = SecPerClus * BytsPerSec;
int loop = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {//读取赋值
*p = content[i];
p++;
}
free(str);
currentClus = value;
}
}
int getFATValue(FILE *fat12, int num) {
//FAT1的偏移字节
int fatBase = RsvdSecCnt * BytsPerSec;
//FAT项的偏移字节
//一个fat项1.5字节
int fatPos = fatBase + num * 3 / 2;
//奇偶FAT项处理方式不同,分类进行处理,从0号FAT项开始
//type == 0 偶数
//typ3 == 1 奇数
int type = 0;
if (num % 2 == 0) {
type = 0;
} else {
type = 1;
}
//先读出FAT项所在的两个字节
u16 bytes;
u16 *bytes_ptr = &bytes;
int check;
check = fseek(fat12, fatPos, SEEK_SET);
if (check == -1)
myPrint("fseek in getFATValue failed!");
check = fread(bytes_ptr, 1, 2, fat12);
if (check != 2)
myPrint("fread in getFATValue failed!");
//u16为short,结合存储的小尾顺序和FAT项结构可以得到
//wiki的写法
if (type == 0) {
bytes = bytes << 4; //这里原文错误,原理建议看网上关于FAT表的文章
return bytes >> 4;
} else {
return bytes >> 4;
}
}
可以使用…的版本
#include dir_count<<" "<file_count<< ":" << endl;
str_print = father->path + " " + to_string(father->dir_count) + " " + to_string(father->file_count) + ":\n";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
//打印每个next
Node *node;
int lens = father->next.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lens; i++) {
node = father->next[i];
if (!node->isfile) {
// 文件夹
// cout << "\033[31m" <name << "\033[0m" << " ";
if (node->isval) {
// 若项为目录,输出此目录下直接子目录和直接子文件的数目,
// 两个数字之间用空格连接。这两个数字不添加特殊颜色
// cout << node->name << " " << node->dir_count << " " << node->file_count << endl;
// 用红色( \033[31m )颜色输出目录名
str_print = "\033[31m" + node->name + "\033[0m" + " " + to_string(node->dir_count) + " " +
to_string(node->file_count) + "\n";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
} else {
//处理. ..
//cout << node->name << " "<
str_print = "\033[31m" + node->name + "\033[0m" + " \n";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
}
} else {
// 文件
// cout << node->name << " " << node->FileSize << endl;
str_print = node->name + " " + to_string(node->FileSize) + "\n";
myPrint(str_print.c_str());
str_print.clear();
}
}
//cout << endl;
myPrint("\n");
//进行递归
for (int i = 0; i < lens; i++) {
//不输出.和..目录的子目录和子文件数目
if (father->next[i]->isval) printList_L(father->next[i]);
}
}
}
void printListWithPath(Node *root, string path, int &exist, bool hasL) {
if (path.compare(root->path) == 0) { //路径完全相同,说明就是该节点
//查找到
if (root->isfile) {
//如果是文件,无法打开
exist = 2;
return;
} else {
exist = 1;//状态正常,无需报错
if (hasL) {
printList_L(root);
} else {
printList(root);
}
}
return;
}
if (path.length() <= root->path.length()) { //出现该情况直接出去
return;
}
string temp = path.substr(0, root->path.length());
//截取输入的path的部分字符串,和当前节点的path比较,如果相同,说明目标在该节点下级
if (temp.compare(root->path) == 0) {
//路径部分匹配
for (Node *q: root->next) {
//递归查找,找到就打印
printListWithPath(q, path, exist, hasL);
}
}
}
void Cat(Node *root, string source, int &exist) {
//与printListWithPath相同的逻辑
//如果递归前发现需要的路径source和目前root的path相同,则判断是否为文件,如果文件内容不为空,就打印
//如果没找到:
//判读是否需要的路径source长度已经小于目前root的path,如果是,则不可能在后面的子结点找到;如果不是,则继续
//判断是否当前节点的path部分与source相同,如果相同则继续递归查询当前节点的所有符合子结点;如果不同,则返回
if (source.compare(root->path) == 0) {
//查找到
if (root->isfile) {
exist = 1;
if (root->content[0] != 0) {
//cout << root->content << endl;
myPrint(root->content);
myPrint("\n");
}
return;
} else {
exist = 2;
return;
}
}
if (source.length() <= root->path.length()) {
return;
}
string temp = source.substr(0, root->path.length());
if (temp.compare(root->path) == 0) {
//路径部分匹配
for (Node *node: root->next) {
Cat(node, source, exist);
}
}
}
/**
*
* @param fat12
* @param startClus : 开始簇号
* @param son
*/
void getFileContent(FILE *fat12, int startClus, Node *son) {//获取文件内容
//步骤:
// (1)在根目录区查找目标文件对应的项
// (2)获取目标文件的起始簇号和文件大小
// (3)根据FAT表中记录的逻辑先后关系读取数据
//计算每簇的字节数,每个区域的初始位置的偏移量。
//每簇字节数 = 每簇扇区数 * 每扇区字节数。
//fatBase = Boot记录占用的扇区数 * 每扇区字节数
//fileRootBase =(Boot记录占用的扇区数+FAT表个数 * FAT扇区数)* 每扇区字节数
//dataBase =(Boot记录占用的扇区数+FAT表个数 * FAT扇区数 +(根目录最大文件数* 32byte + 每扇区字节数 - 1)/ 每扇区字节数)* 每扇区字节数。
//数据区的偏移量又乘又除可不可以等于fileRootBase+根目录最大文件数*32?不行!
//dataBase初始位置 = FileRootBase最后一个簇的结束位置。如果根目录没有填满最后一个簇,数据区也是从下一个簇开始的,而不是默认于最后一个根目录的结束位置开始。
//用 "(根目录最大文件数 * 32 + 每扇区字节数 - 1)/ 每扇区字节数 "可以得到根目录区占用的真正扇区数。
//原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43242836/article/details/103056431
int dataBase = BytsPerSec * (RsvdSecCnt + FATSz * NumFATs + (RootEntCnt * 32 + BytsPerSec - 1) / BytsPerSec);
int currentClus = startClus;
int value = 0; //这里用value来进行不同簇的读取(超过512字节)
char *p = son->content;
if (startClus == 0) {
return;
}
//while循环读取簇,即便大于512byte也可以,直到该文件的最后一个簇
while (value < 0xFF8) {//如果表项值大于等于0xFF8,则说明已经到达最后一个簇
value = getFATValue(fat12, currentClus);//获取下一个簇
if (value == 0xFF7) {
myPrint("坏簇,读取失败!\n");
break;
}
char *str = (char *) malloc(SecPerClus * BytsPerSec); //暂存从簇中读出的数据,大小为每簇扇区数 * 每扇区字节数
char *content = str;
// 字节开始处 = 数据基址 + (目前簇 - 2)* 每簇扇区数 * 每扇区字节数
// 数据区起始地址所对应的编号为2(不为0)(有了起始地址,这里可以用偏移地址)
// FAT12文件系统的前两个簇是固定簇,而实际表示数据的簇号——或者更确切的说,是FAT12表项的序号从2开始,实际表示数据的“簇”仍然是从0开始。
int startByte = dataBase + (currentClus - 2) * SecPerClus * BytsPerSec;
int check;
check = fseek(fat12, startByte, SEEK_SET);
if (check == -1)
myPrint("fseek in printChildren failed!");
check = fread(content, 1, SecPerClus * BytsPerSec, fat12);//提取数据
//fread:return the number of items read or written. This number equals the number of bytes transferred only when size is 1.
// If an error occurs, or the end of the file is reached, the return value is a short item count (or zero)
if (check != SecPerClus * BytsPerSec)
myPrint("fread in printChildren failed!");
int count = SecPerClus * BytsPerSec;
int loop = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {//读取赋值
*p = content[i];
p++;
}
free(str);
currentClus = value;
}
}
int getFATValue(FILE *fat12, int num) {
//FAT1的偏移字节
int fatBase = RsvdSecCnt * BytsPerSec;
//FAT项的偏移字节
//一个fat项1.5字节
int fatPos = fatBase + num * 3 / 2;
//奇偶FAT项处理方式不同,分类进行处理,从0号FAT项开始
//type == 0 偶数
//typ3 == 1 奇数
int type = 0;
if (num % 2 == 0) {
type = 0;
} else {
type = 1;
}
//先读出FAT项所在的两个字节
u16 bytes;
u16 *bytes_ptr = &bytes;
int check;
check = fseek(fat12, fatPos, SEEK_SET);
if (check == -1)
myPrint("fseek in getFATValue failed!");
check = fread(bytes_ptr, 1, 2, fat12);
if (check != 2)
myPrint("fread in getFATValue failed!");
//u16为short,结合存储的小尾顺序和FAT项结构可以得到
//wiki的写法
if (type == 0) {
bytes = bytes << 4; //这里原文错误,原理建议看网上关于FAT表的文章
return bytes >> 4;
} else {
return bytes >> 4;
}
}
my_print.sam
global asm_print
section .text
asm_print:
push ebp
mov ebp, esp
mov edx, [ebp+12]
mov ecx, [ebp+8]
mov ebx, 1
mov eax, 4
int 80h
pop ebp
ret
Makefile
Main: main.cpp my_print.asm
nasm -f elf32 my_print.asm
g++ -m32 main.cpp my_print.o -o main
rm -rf my_print.o
clean:
rm -rf main
置开始。
//用 "(根目录最大文件数 * 32 + 每扇区字节数 - 1)/ 每扇区字节数 "可以得到根目录区占用的真正扇区数。
//原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43242836/article/details/103056431
int dataBase = BytsPerSec * (RsvdSecCnt + FATSz * NumFATs + (RootEntCnt * 32 + BytsPerSec - 1) / BytsPerSec);
int currentClus = startClus;
int value = 0; //这里用value来进行不同簇的读取(超过512字节)
char *p = son->content;
if (startClus == 0) {
return;
}
//while循环读取簇,即便大于512byte也可以,直到该文件的最后一个簇
while (value < 0xFF8) {//如果表项值大于等于0xFF8,则说明已经到达最后一个簇
value = getFATValue(fat12, currentClus);//获取下一个簇
if (value == 0xFF7) {
myPrint("坏簇,读取失败!\n");
break;
}
char *str = (char *) malloc(SecPerClus * BytsPerSec); //暂存从簇中读出的数据,大小为每簇扇区数 * 每扇区字节数
char *content = str;
// 字节开始处 = 数据基址 + (目前簇 - 2)* 每簇扇区数 * 每扇区字节数
// 数据区起始地址所对应的编号为2(不为0)(有了起始地址,这里可以用偏移地址)
// FAT12文件系统的前两个簇是固定簇,而实际表示数据的簇号——或者更确切的说,是FAT12表项的序号从2开始,实际表示数据的“簇”仍然是从0开始。
int startByte = dataBase + (currentClus - 2) * SecPerClus * BytsPerSec;
int check;
check = fseek(fat12, startByte, SEEK_SET);
if (check == -1)
myPrint("fseek in printChildren failed!");
check = fread(content, 1, SecPerClus * BytsPerSec, fat12);//提取数据
//fread:return the number of items read or written. This number equals the number of bytes transferred only when size is 1.
// If an error occurs, or the end of the file is reached, the return value is a short item count (or zero)
if (check != SecPerClus * BytsPerSec)
myPrint("fread in printChildren failed!");
int count = SecPerClus * BytsPerSec;
int loop = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {//读取赋值
*p = content[i];
p++;
}
free(str);
currentClus = value;
}
}
int getFATValue(FILE *fat12, int num) {
//FAT1的偏移字节
int fatBase = RsvdSecCnt * BytsPerSec;
//FAT项的偏移字节
//一个fat项1.5字节
int fatPos = fatBase + num * 3 / 2;
//奇偶FAT项处理方式不同,分类进行处理,从0号FAT项开始
//type == 0 偶数
//typ3 == 1 奇数
int type = 0;
if (num % 2 == 0) {
type = 0;
} else {
type = 1;
}
//先读出FAT项所在的两个字节
u16 bytes;
u16 *bytes_ptr = &bytes;
int check;
check = fseek(fat12, fatPos, SEEK_SET);
if (check == -1)
myPrint("fseek in getFATValue failed!");
check = fread(bytes_ptr, 1, 2, fat12);
if (check != 2)
myPrint("fread in getFATValue failed!");
//u16为short,结合存储的小尾顺序和FAT项结构可以得到
//wiki的写法
if (type == 0) {
bytes = bytes << 4; //这里原文错误,原理建议看网上关于FAT表的文章
return bytes >> 4;
} else {
return bytes >> 4;
}
}
my_print.sam
~~~nasm
global asm_print
section .text
asm_print:
push ebp
mov ebp, esp
mov edx, [ebp+12]
mov ecx, [ebp+8]
mov ebx, 1
mov eax, 4
int 80h
pop ebp
ret
Makefile
Main: main.cpp my_print.asm
nasm -f elf32 my_print.asm
g++ -m32 main.cpp my_print.o -o main
rm -rf my_print.o
clean:
rm -rf main