矢量,矢量化的梯度下降以及多元线性回归
一、矢量
定义:按照特定顺序排列的元素集合。可以被视为一维数组。
在机器学习中的作用:
- 特征表示:在机器学习任务中,输入数据通常以矢量的形式表示。例如,图像可以表示为像素值的矢量,文本可以表示为词向量的矢量。矢量工具可以用来处理和表示这些特征向量,以便机器学习模型能够对其进行处理和学习。
- 模型参数表示:在机器学习模型中,参数通常以矢量的形式表示。例如,线性回归模型的参数可以表示为一个包含权重和偏置的矢量。矢量工具可以用来对模型参数进行操作和更新,以便模型能够进行学习和预测。
- 矩阵运算:在机器学习中,矩阵运算是非常常见的操作。例如,矩阵乘法在神经网络中经常用于计算输入数据和模型参数之间的线性变换。矢量工具可以用来进行高效的矩阵运算,以便加速机器学习模型的训练和推断过程。
优势:
- 高效地表示和处理大量的数据特征和模型参数。
- 方便进行数学运算
- 高校利用内存和处理器资源
- 简化编程
二、numpy
在编程中常用numpy库来创建和运行矢量数组。以下为常见的使用方式:
1.使用形状元组(shape tuple)生成矢量
注:numpy.zeros((4,))和numpy.zeros(4)的效果相同,但是numpy.zeros((4,1))会生成4行一列的矩阵。
# NumPy routines which allocate memory and fill arrays with value
a = np.zeros(4); print(f"np.zeros(4) : a = {a}, a shape = {a.shape}, a data type = {a.dtype}")
a = np.zeros((4,)); print(f"np.zeros(4,) : a = {a}, a shape = {a.shape}, a data type = {a.dtype}")
a = np.random.random_sample(4); print(f"np.random.random_sample(4): a = {a}, a shape = {a.shape}, a data type = {a.dtype}")
# 运行结果
#np.zeros(4) : a = [0. 0. 0. 0.], a shape = (4,), a data type = float64
#np.zeros(4,) : a = [0. 0. 0. 0.], a shape = (4,), a data type = float64
#np.random.random_sample(4): a = [0.49722532 0.51600241 0.11757225 0.65462113], a shape = (4,), a data type = float642.不使用形状元组生成矢量
a = np.arange(4.); print(f"np.arange(4.): a = {a}, a shape = {a.shape}, a data type = {a.dtype}")
a = np.random.rand(4); print(f"np.random.rand(4): a = {a}, a shape = {a.shape}, a data type = {a.dtype}")
#运行结果
#np.arange(4.): a = [0. 1. 2. 3.], a shape = (4,), a data type = float64
#np.random.rand(4): a = [0.54342577 0.79334353 0.74999339 0.43430988], a shape = (4,), a data type = float643.手动创建矢量
# NumPy routines which allocate memory and fill with user specified values
a = np.array([5,4,3,2]); print(f"np.array([5,4,3,2]): a = {a}, a shape = {a.shape}, a data type = {a.dtype}")
a = np.array([5.,4,3,2]); print(f"np.array([5.,4,3,2]): a = {a}, a shape = {a.shape}, a data type = {a.dtype}")
#运行结果:
#np.array([5,4,3,2]): a = [5 4 3 2], a shape = (4,), a data type = int32
#np.array([5.,4,3,2]): a = [5. 4. 3. 2.], a shape = (4,), a data type = float64numpy的矢量实际上属于数组,所以拥有数组的一般性质,可以进行索引、切片、删除等操作。 但是矢量的加法与列表的加法却有所不同,矢量是对位相加,列表是两个列表连接形成新的列表:
#矢量相加
a = np.array([ 1, 2, 3, 4])
b = np.array([-1,-2, 3, 4])
print(f"Binary operators work element wise: {a + b}")
#列表相加
c = [1,2,3,4]
d = [-1,-2, 3, 4]
print(f"Binary operators work element wise:{c + d}")
#运行结果
#Binary operators work element wise: [0 0 6 8]
#Binary operators work element wise:[1, 2, 3, 4, -1, -2, 3, 4]三、多元线性回归&矢量化
在之前学习过一元线性回归模型,接下来学习和总结多元线性模型。
一般来说,我们分析一个问题时往往会考虑多个不同的因素,我们在建立模型时会将这些影响因素作为变量x,影响的权重作为系数w,得到下图中的改变:
我们可以发现,f(x)可以改写为向量形式:
由于![]()
所以![]()
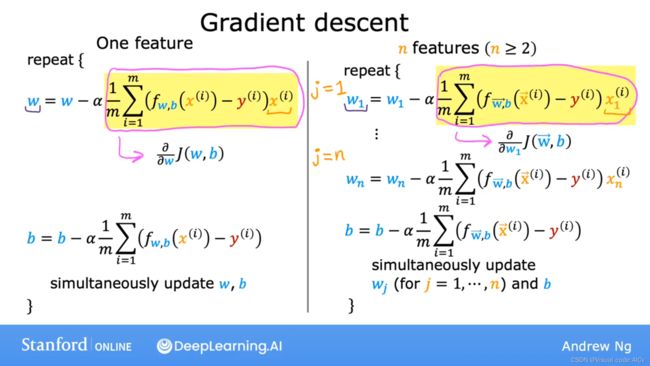
四、多元线性回归的矢量化梯度下降法
按照老师的讲解如下进行变换:(其实也没多难,就是把运算的部分换成矢量运算)
下面是算法实现:
X_train = np.array([[2104, 5, 1, 45], [1416, 3, 2, 40], [852, 2, 1, 35]])
y_train = np.array([460, 232, 178])
def compute_gradient(X, y, w, b):
"""
Computes the gradient for linear regression
Args:
X (ndarray (m,n)): Data, m examples with n features
y (ndarray (m,)) : target values
w (ndarray (n,)) : model parameters
b (scalar) : model parameter
Returns:
dj_dw (ndarray (n,)): The gradient of the cost w.r.t. the parameters w.
dj_db (scalar): The gradient of the cost w.r.t. the parameter b.
"""
m,n = X.shape #(number of examples, number of features)
dj_dw = np.zeros((n,))
dj_db = 0.
for i in range(m):
err = (np.dot(X[i], w) + b) - y[i]
for j in range(n):
dj_dw[j] = dj_dw[j] + err * X[i, j]
dj_db = dj_db + err
dj_dw = dj_dw / m
dj_db = dj_db / m
return dj_db, dj_dw
#Compute and display gradient
tmp_dj_db, tmp_dj_dw = compute_gradient(X_train, y_train, w_init, b_init)
print(f'dj_db at initial w,b: {tmp_dj_db}')
print(f'dj_dw at initial w,b: \n {tmp_dj_dw}')
#显示结果如下:
#dj_db at initial w,b: -1.673925169143331e-06
#dj_dw at initial w,b:
#[-2.73e-03 -6.27e-06 -2.22e-06 -6.92e-05]