【MySQL数据库之多表关联关系(一对一、一对多、多对多)】
文章目录
-
-
- 多表关联关系的实现
- 多表关联关系的分类
- 一对多
- 多对多
- 一对一
-
多表关联关系的实现
外键是一列或一组列,用于强制两个表中的数据之间的链接。 在外键引用中,第一个表的主键列(或多个列)由第二个表的列(或列)引用。 第二个表的列(或列)成为外键。
在创建或更改表时,可以使用FOREIGN KEY约束创建外键。
多表关联关系的分类
一对多
一对多
1.以员工表与部门表为例
先站在员工表的角度
问:一个员工能否对应多个部门
答:不可以
再站在部门表的角度
问:一个部门能否对应多个员工
答:可以
结论:换位思考之后得出的答案是一个可以一个不可以
所以关系是"一对多" 部门是’一’员工是’多’
‘’‘关系表达只能用一对多 不能用多对一’‘’
一对多关系 外键字段建在"多"的一方(员工表)
员工表:
create table emp1(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '编号',
name varchar(32) comment '姓名',
age int comment '年龄',
dep_id int comment '部门编号',
foreign key(dep_id) references dep1(id)
on update cascade # 级联更新
on delete cascade # 级联删除
);
部门表:
create table dep1(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '编号',
dep_name varchar(32) comment '部门名称',
dep_desc varchar(32) comment '部门描述'
);
注意:
1.创建表的时候 应该先创建被关联表(没有外键字段的表)
2.插入数据的时候 应该先插入被关联表(没有外键字段的表)
外键字段填入的值只能是被关联表中已经存在的值
3.修改、删除被关联表数据都会出现障碍
on update cascade # 级联更新
on delete cascade # 级联删除
多对多
以图书与作者表为例
1.先站在图书表的角度
问:一本书籍能否对应多名作者
答:可以
2.再站在作者表的角度
问:一名作者能否对应多本书籍
答:可以
结论:换位思考之后两边都可以 那么就是"多对多"关系
图书表:
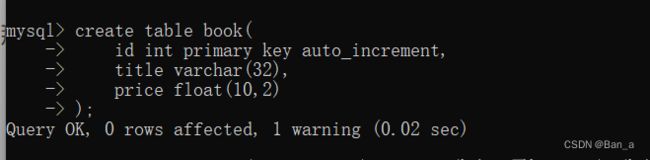
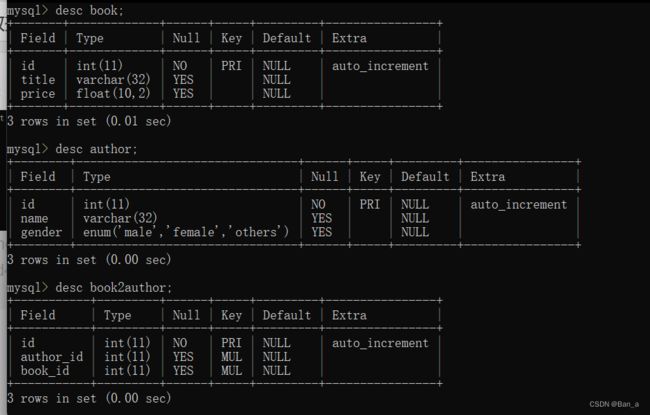
create table book(
id int primary key auto_increment,
title varchar(32),
price float(10,2)
);
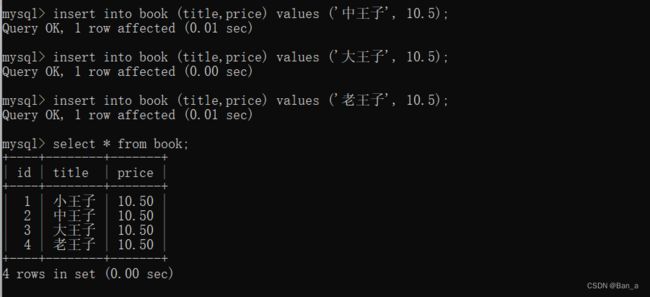
insert into book (title,price) values ('小王子', 10.5);
insert into book (title,price) values ('中王子', 10.5);
insert into book (title,price) values ('大王子', 10.5);
insert into book (title,price) values ('老王子', 10.5);
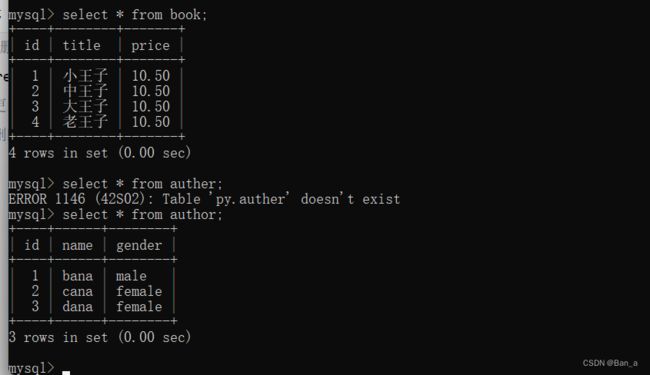
create table author(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(32),
gender enum('male','female','others')
);
添加数据:
insert into author (name,gender) values ('bana','male');
insert into author (name,gender) values ('cana','female');
insert into author (name,gender) values ('dana','female');
中间表:创建一个中间表,中间表的两个普通字段分别关联另两张表的主键。
create table book2author(
id int primary key auto_increment,
author_id int,
book_id int,
foreign key(author_id) references author(id)
on update cascade # 级联更新
on delete cascade, # 级联删除
foreign key(book_id) references book(id)
on update cascade # 级联更新
on delete cascade # 级联删除
);
一对一
用户表
存使用频率较高的数据字段
用户详情表
存使用频率较低的数据字段
1.先站在用户表的角度
问:一个用户数据能否对应多个用户详情数据
答:不可以
2.再站在用户详情表的角度
问:一个用户详情数据能否对应多个用户数据
答:不可以
结论:换位思考之后两边都不可以 那么关系可能有两种
‘没有关系’:用膝盖都能判断出来
‘一对一关系’
针对’一对一关系’外键字段建在任意一方都可以,但是推荐建在查询频率较高的较好的一方
用户表:
create table User(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(32),
gender enum('male','female','others'),
user_detail_id int unique, # 好好体会为什么加unique
foreign key(user_detail_id) references UserDetail(id)
on update cascade # 级联更新
on delete cascade # 级联删除
);
#插入信息
insert into User (name,gender,user_detail_id) values('bana','male',1);
insert into User (name,gender,user_detail_id) values('cana','female',2);
insert into User (name,gender,user_detail_id) values('dana','male',3);
用户详情表:
create table UserDetail(
id int primary key auto_increment,
phone bigint,
age int
);
# 插入信息
insert into UserDetail (phone,age) values (120,15);
insert into UserDetail (phone,age) values (110,16);
insert into UserDetail (phone,age) values (130,17);