创建 SSL证书并应用于WebSocket
写在前面
由于上一篇介绍 如何使用Fleck创建WebSocket服务器 ,感觉不够完善,因为生产环境中肯定是需要用到ssl的,而创建或申请ssl证书,相对而言是比较繁琐的事情,特别是本地如果要构建一个使用ssl的测试环境时,就难免要多费一番周折了。
本文介绍了如何创建一个 ssl 证书,用于test.com在本地环境中测试带安全验证的 WebSocket。
1.首先下载并安装 Win64 OpenSSL
建议把安装目录指定为 C:\OpenSSL-Win64\
2.然后创建openssl.cnf 并保存到如下目录:C:\OpenSSL-Win64\
内容如下:
[ req ]
default_bits = 2048
default_keyfile = server-key.pem
distinguished_name = subject
req_extensions = req_ext
x509_extensions = x509_ext
string_mask = utf8only
# The Subject DN can be formed using X501 or RFC 4514 (see RFC 4519 for a description).
# Its sort of a mashup. For example, RFC 4514 does not provide emailAddress.
[ subject ]
countryName = Country Name (2 letter code)
countryName_default = US
stateOrProvinceName = State or Province Name (full name)
stateOrProvinceName_default = NY
localityName = Locality Name (eg, city)
localityName_default = New York
organizationName = Organization Name (eg, company)
organizationName_default = Example, LLC
# Use a friendly name here because its presented to the user. The server's DNS
# names are placed in Subject Alternate Names. Plus, DNS names here is deprecated
# by both IETF and CA/Browser Forums. If you place a DNS name here, then you
# must include the DNS name in the SAN too (otherwise, Chrome and others that
# strictly follow the CA/Browser Baseline Requirements will fail).
commonName = Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name)
commonName_default = Example Company
emailAddress = Email Address
emailAddress_default = [email protected]
# Section x509_ext is used when generating a self-signed certificate. I.e., openssl req -x509 ...
[ x509_ext ]
subjectKeyIdentifier = hash
authorityKeyIdentifier = keyid,issuer
# You only need digitalSignature below. *If* you don't allow
# RSA Key transport (i.e., you use ephemeral cipher suites), then
# omit keyEncipherment because that's key transport.
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
subjectAltName = @alternate_names
nsComment = "OpenSSL Generated Certificate"
# RFC 5280, Section 4.2.1.12 makes EKU optional
# CA/Browser Baseline Requirements, Appendix (B)(3)(G) makes me confused
# In either case, you probably only need serverAuth.
# extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth, clientAuth
# Section req_ext is used when generating a certificate signing request. I.e., openssl req ...
[ req_ext ]
subjectKeyIdentifier = hash
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
subjectAltName = @alternate_names
nsComment = "OpenSSL Generated Certificate"
# RFC 5280, Section 4.2.1.12 makes EKU optional
# CA/Browser Baseline Requirements, Appendix (B)(3)(G) makes me confused
# In either case, you probably only need serverAuth.
# extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth, clientAuth
[ alternate_names ]
DNS.1 = test.com
DNS.2 = www.test.com
DNS.3 = mail.test.com
DNS.4 = ftp.test.com
# Add these if you need them. But usually you don't want them or
# need them in production. You may need them for development.
# DNS.5 = localhost
# DNS.6 = localhost.localdomain
# DNS.7 = 127.0.0.1
# IPv6 localhost
# DNS.8 = ::1详细步骤
打开命令提示符窗口:
1.执行 cd "c:\OpenSSL-Win64\bin"
2.执行 set OPENSSL_CONF=c:\OpenSSL-Win64\openssl.cnf
3.执行 openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -sha256 -nodes -keyout test.key -out test.crt -subj "/CN=test.com" -days 3650
如下图所示:
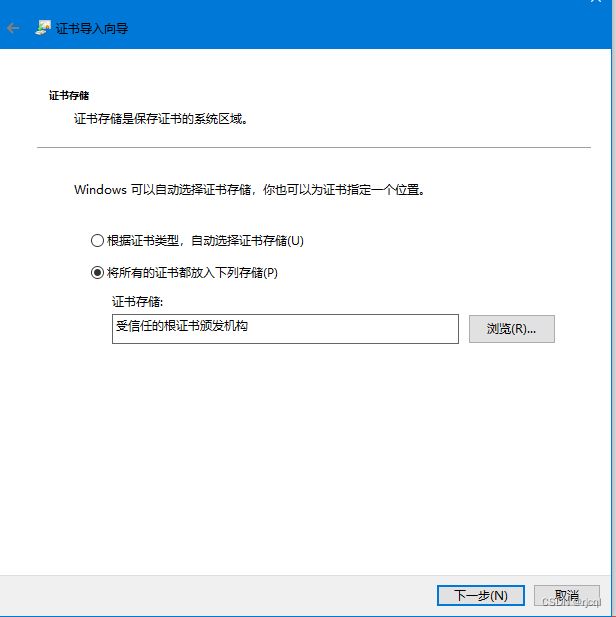
将C:\OpenSSL-Win64\bin目录下 test.crt 导入证书存储:
- 打开
certlm.msc - 转至受信任的根证书颁发机构 > 证书
- 右键单击某处,选择“所有任务”>“导入”
- 浏览刚刚创建的文件
test.crt(位于 C:\OpenSSL-Win32\bin 中) - 选择将所有证书放入以下存储中:受信任的根证书颁发机构
- 单击“完成”
从证书列表中导出此证书:
- 刷新受信任的根证书颁发机构 > 证书,找到并右键单击 test.com 证书
- 选择所有任务 > 导出
- 导出为
test.p7b并保存在C:\OpenSSL-Win64\bin\ - 删除
test.com证书存储中当前的证书
接着执行:openssl pkcs7 -in test.p7b -inform DER -out result.pem -print_certs
在执行:openssl pkcs12 -export -inkey test.key -in result.pem -name test.com -out final_result.pfx
过程中需要输入密码,后面要用到不要忘掉,建议保存一下。
将“final_result.pfx”导入证书存储区:
- 双击生成的
final_result.pfx文件运行安装程序 - 选择本地机器
- 输入密码
- 选择将此密钥标记为可导出
- 选择包括所有扩展属性
- 选择将所有证书放入以下存储中:受信任的根证书颁发机构
- 单击“完成”
再次重复上述导入步骤 1 到 7,但这次在步骤 6 中,将证书放置在“Web宿主”证书存储中(以便 IIS 在绑定到 https 时可以看到该证书)
从存储中导出此证书(以在套接字服务器应用程序中使用):
- 刷新受信任的根证书颁发机构 > 证书,找到并右键单击该
test.com证书 - 选择所有任务 > 导出
- 选择yes,导出私钥
- 选择个人信息交换
- 如果可能,选择包括所有证书
- 选择导出所有扩展属性
- 选择启用证书隐私
- 添加密码
- 添加文件名
test.com.pfx(将其保存到 C:\ 或“套接字服务器应用程序”将引用它的位置,请参见下文)X509Certificate2 certificate = new X509Certificate2("C:\\test.com.pfx", "password");
将test.com与本地电脑 IP 一起添加到主机文件中,C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
创建 IIS 网站并为 http 和 https 添加到 test.com 的绑定(并在 https 绑定中选择 test.com 证书)
访问 https://test.com/your-socket-client.htm (在 Chrome/Edge 中,当提示 ssl 警告时单击高级 > 继续)
套接字客户端现在应该使用 wss 成功连接wss://test.com:xxxx
注意事项
如果是用 Chrome 进行测试,则可能需要使用 TLS 1.2。因为Chrome貌似加强了可以使用的安全协议。另外要在套接字服务器上使用 TLS 1.2,请设置:
server.EnabledSslProtocols = SslProtocols.Tls12;
或更多选项,比如:
server.EnabledSslProtocols = SslProtocols.Tls12 | SslProtocols.Ssl3 | SslProtocols.Tls11 | SslProtocols.Tls;
在套接字服务器上,尝试监听 0.0.0.0
var server = new WebSocketServer("wss://0.0.0.0:7181");
在客户端,如果使用wss,则需要使用ssl证书注册的域的url,而不是ip地址:
window.ws = new wsImpl('wss://test.com:7181/');
代码实现
控制台代码
using Fleck;
using System.Security.Authentication;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
public class WebSocketServerDemo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
X509Certificate2 certificate = new X509Certificate2("C:\\test.com.pfx", "test");
var server = new WebSocketServer("wss://0.0.0.0:7181");
if (certificate != null)
{
server.Certificate = certificate;
server.EnabledSslProtocols = SslProtocols.Ssl3 | SslProtocols.Tls | SslProtocols.Tls11 | SslProtocols.Tls12;
//server.EnabledSslProtocols = SslProtocols.Tls12;
}
server.Start(socket =>
{
socket.OnOpen = () => Console.WriteLine("Open!");
socket.OnClose = () => Console.WriteLine("Close!");
socket.OnMessage = message =>
{
Console.WriteLine(message);
socket.Send(message + " from server");
};
});
Console.WriteLine("Server Started");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
客户端代码
WebSocket Demo
调用示例
IIS 站点配置