JUC之CompletableFuture
Future接口理论
Future接口定义了异步任务执行的一些方法,包括异步任务执行结果,异步任务执行是否中断,异步任务是否完毕等。
Future接口常用实现类FutureTask异步任务
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<String>( () -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t -----come in");
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "task over";
});
Thread t1 = new Thread(futureTask, "t1");
t1.start();
CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture对Future的改进
- CompletableFuture异步线程发生异常,不会影响到主线程,用来记录日志特别方便。
- CompletableFuture出现的原因:Future的get方法是阻塞方法,当异步线程计算完成之前一直会阻塞,isDone()方法判断异步线程又特别消耗CPU资源。对于真正的异步处理我们希望传入回调函数,在Future结束时,自动调用该回调函数。这样我们就不用等待结果 。
- CompletableFuture提供了一种观察者模式,可以让任务完成后通知监听的一方。
CompletionStage
- CompltionStage是异步执行的一个阶段。一个阶段执行完成之后可能触发另一个阶段。
- 一个阶段的执行可以是一个Function,Comsumer或者Runnable。比如
stage.thenApply(x -> square(x)).thenAccept(×->System.out.print(x)).thenRun(( ->system.out.println())
- 一个阶段可能会是另一个阶段完成后触发。也可能是其他多个阶段完成后触发。
CompletableFuture的方法

主要是runAsync和supplyAsnc方法。一个无返回值。一个有返回值。
CompletableFuture的优点
- 异步任务执行完成后,会自动调用某个对象的方法
- 异步任务出异常后,会自动调用某个对象的方法
- 主线程设置好回调后,不用关心异步任务的执行。异步任务之间可以顺序执行。
案例 - 前言
join和get的区别。get必须处理异常。join不需要处理异常
jdk8新特性: lambda表达式,stream流,chain链式调用,函数式编程

有参数,有返回值:Function
有参数,无返回值:Consume, BiConsumer(两个参数)
无参数,有返回值:Supplier
无参数,无返回值:Runnable
案例-从电商网站的比价需求
原来的写法,串行的方式:
/**
* step by step 一家家搜查
* List ----->map------> List
* @param list
* @param productName
* @return
*/
public static List<String> getPrice(List<NetMall> list,String productName)
{
//《mysql》 in taobao price is 90.43
return list
.stream()
.map(netMall ->
String.format(productName + " in %s price is %.2f",
netMall.getNetMallName(),
netMall.calcPrice(productName)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
使用CompletableFuture,异步的方式:
/**
* List ----->List>------> List
* @param list
* @param productName
* @return
*/
public static List<String> getPriceByCompletableFuture(List<NetMall> list,String productName)
{
return list.stream().map(netMall ->
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> String.format(productName + " in %s price is %.2f",
netMall.getNetMallName(),
netMall.calcPrice(productName))))
.collect(Collectors.toList())
.stream()
.map(s -> s.join())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
耗时:比串行的方式快得多!!!
CompletableFuture 常用方法
获得结果和触发计算
获得结果:
- public T get() 一直等
- public T get(long timeout,TimeUnit unit) 过时不候,到了时间没拿到结果会报异常
- public T join():join和get都是用来获取CompletableFuture异步之后的返回值。join是unchecked异常(即运行时异常)。get是checked异常(经过检查的异常)
- public T getNow(T valuelfAbsent):没有计算完,给我默认的结果。计算完,返回实际的结果。
主动触发计算:
- public boolean complete(T value) 如果CompletableFuture没有完成,将get结果修改为value,返回值为true。如果完成了,不修改get,返回值为false.
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello CompletableFuture";
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.getNow("心急吃不了热豆腐"));
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
System.out.println(completableFuture.get(1500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
System.out.println(completableFuture.join());
System.out.println(completableFuture.complete("未雨绸缪")+"\t"+completableFuture.join());
}
}
对计算结果进行处理
thenApply(常用)
两个计算结果存在依赖关系,这两个线程串行化。
出现异常,直接跳到whenComplete和exceptionally执行。(不再执行后续的thenApply)
public class CompletableFutureTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 6;
},executorService).thenApply((r)-> {
int i=2/0;
return r * 5;
}).thenApply((r)-> {
System.out.println(r);
return r - 2;
}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {
System.out.println("计算结果:"+v);
}).exceptionally(e -> {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.out.println(e);
return null;
});
System.out.println("============主线程==========");
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
handle
计算机结果存在依赖关系,两个线程串行化
handle出现异常,会往下一个handle走,同时也会走到whenComplete和exceptionally
public class CompletableFutureTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 6;
},executorService).handle((r,e)-> {
int i=2/0;
return r * 5;
}).handle((r,e)-> {
System.out.println(r);
return r - 2;
}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {
System.out.println("计算结果:"+v);
}).exceptionally(e -> {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.out.println(e);
return null;
});
System.out.println("============主线程==========");
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
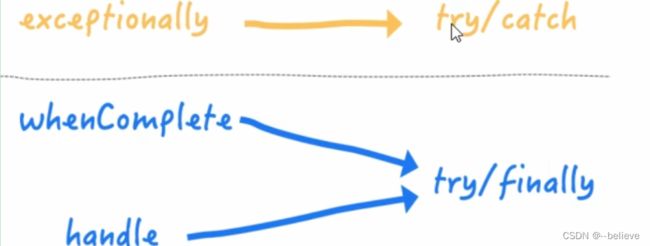
exceptionally相当于try catch
whenComplete和handler相当于try finally
对计算结果进行消费
接受任务的处理结果,消费处理。thenAccept无返回结果。(thenApply是有返回结果的)
public class CompletableFutureTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
return 3;
}).thenApply(r->{
return r*8;
}).thenApply(r->{
return r/2;
}).thenAccept(r-> System.out.println(r));
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->"6666").thenRun(()->{}).join());
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->"6666").thenAccept(r-> System.out.println(r)).join());
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->"6666").thenApply(r->r+"9999").join());
}
}
12
null
6666
null
66669999
对计算速度进行选用与对计算结果进行合并
applyToEither:谁快用谁
thenCombine: 两个completionStage任务都完成后,将结果交给thenCombine。先完成的先等着,等待其他分支任务。
public class CompletableFutureTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<String> first = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "1号选手";
});
CompletableFuture<String> second = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "2号选手";
});
CompletableFuture<String> result = first.applyToEither(second, r -> r + "is winner");
CompletableFuture<String> res = first.thenCombine(second, (x, y) -> x + y);
System.out.println(result.join());
System.out.println(res.join());
}
}
并行执行
allOf():当所有给定的CompletableFuture完成时, 返回一个新的CompletableFuture
anyOf():当任何一个给定的CompletableFuture完成时,返回一个新的CompletableFuture
public static void testAllOf(){
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future1执行完成");
});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future2执行完成");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> all = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2);
try {
all.get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
completableFuture和线程池说明
以thenRun和thenRunAsync为例,有什么区别?
- 没有传入自定义线程池,默认是ForkJoinPool.
- 如果第一个执行的任务传入了一个自定义线程池,调用thenRun执行第二个任务,则第一个和第二个都是用自定义的线程池。
- 如果第一个执行的任务传入了一个自定义线程池,调用thenRunAsyn执行第二个任务,则第一个用自定义。第二个用ForkJoinPool(后面也都是ForkJoinPool)