Shiro框架:Shiro SecurityManager安全管理器解析
目录
1. SecurityManager介绍
1.1 Authenticator
1.2 Authorizer
1.3 SessionManager
2. DefaultWebSecurityManager解析
2.1 Destroyable
2.2 CacheManagerAware
2.3 EventBusAware
2.4 CachingSecurityManager(聚合缓存管理和事件监听管理功能)
2.5 RealmSecurityManager(聚合Realm管理功能)
2.6 AuthenticatingSecurityManager(聚合登录认证功能)
2.7 AuthorizingSecurityManager(聚合访问控制功能)
2.8 SessionsSecurityManager(聚合Session管理功能)
2.9 DefaultSecurityManager
2.9.1 创建用户(Subject)功能
2.9.2 存储用户(Subject)功能
2.9.3 用户RememberMe管理功能
2.10 DefaultWebSecurityManager
Shiro作为一款比较流行的登录认证、访问控制安全框架,被广泛应用在程序员社区;Shiro登录验证、访问控制、Session管理等流程内部都是委托给SecurityManager安全管理器来完成的,在前述文章全面解析Shiro框架原理的基础之上,详见:Shiro框架:ShiroFilterFactoryBean过滤器源码解析-CSDN博客、Shiro框架:Shiro内置过滤器源码解析-CSDN博客,本篇文章继续深入解析Shiro SecurityManager安全管理器的结构和功能,为后续各处理流程的解析做好铺垫。
1. SecurityManager介绍
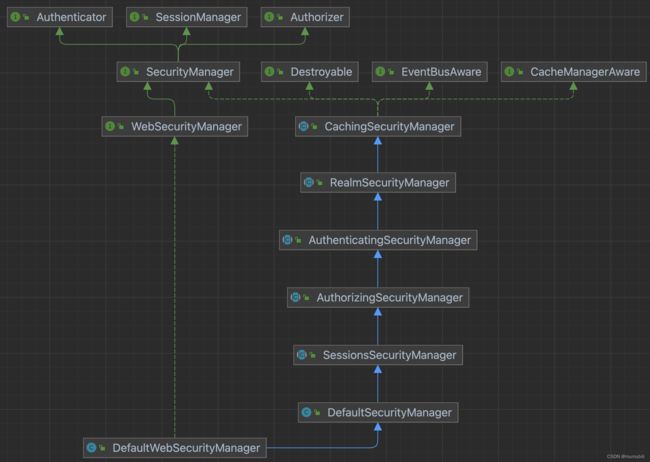
SecurityManager接口类图如下:
可以看到SecurityManager实际上整合了3部分功能:
- Authenticator:登录认证器
- Authorizer:访问控制器
- SessionManager:Session管理器
同时SecurityManager也定义了登录、退出以及创建用户的接口功能,如下:
public interface SecurityManager extends Authenticator, Authorizer, SessionManager {
/**
* Logs in the specified Subject using the given {@code authenticationToken}, returning an updated Subject
* instance reflecting the authenticated state if successful or throwing {@code AuthenticationException} if it is
* not.
*/
Subject login(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException;
/**
* Logs out the specified Subject from the system.
*/
void logout(Subject subject);
/**
* Creates a {@code Subject} instance reflecting the specified contextual data.
*/
Subject createSubject(SubjectContext context);
}1.1 Authenticator
登录认证器,定义了用户登录认证方法,交由子类具体实现,如下:
public interface Authenticator {
/**
* Authenticates a user based on the submitted {@code AuthenticationToken}.
*/
public AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken)
throws AuthenticationException;
}1.2 Authorizer
用户鉴权器,引入了鉴权方法对登录用户执行鉴权操作,交由子类具体实现;
Authorizer定义如下:
public interface Authorizer {
/**
* Returns true if the corresponding subject/user is permitted to perform an action or access a resource
*/
boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, String permission);
/**
* Ensures the corresponding Subject/user implies the specified permission String.
*/
void checkPermission(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, String permission) throws AuthorizationException;
/**
* Returns true if the corresponding Subject/user has the specified role, false otherwise.
*/
boolean hasRole(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, String roleIdentifier);
/**
* Asserts the corresponding Subject/user has the specified role by returning quietly if they do or throwing an
* {@link AuthorizationException} if they do not.
*/
void checkRole(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, String roleIdentifier) throws AuthorizationException;
//其它鉴权方法
}1.3 SessionManager
Session管理器,提供了创建Session以及获取Session操作方法:
public interface SessionManager {
/**
* Starts a new session based on the specified contextual initialization data, which can be used by the underlying
* implementation to determine how exactly to create the internal Session instance.
*
* This method is mainly used in framework development, as the implementation will often relay the argument
* to an underlying {@link SessionFactory} which could use the context to construct the internal Session
* instance in a specific manner. This allows pluggable {@link org.apache.shiro.session.Session Session} creation
* logic by simply injecting a {@code SessionFactory} into the {@code SessionManager} instance.
*/
Session start(SessionContext context);
/**
* Retrieves the session corresponding to the specified contextual data (such as a session ID if applicable), or
* {@code null} if no Session could be found. If a session is found but invalid (stopped or expired), a
* {@link SessionException} will be thrown.
*/
Session getSession(SessionKey key) throws SessionException;
}2. DefaultWebSecurityManager解析
在Web服务中,Shiro中应用的SecurityManager具体为子类DefaultWebSecurityManager,为了对其有足够的理解,下面对DefaultWebSecurityManager类继承层次中相关类进行解析说明,其类继承结构如下:
2.1 Destroyable
Shiro框架自定义了Destroyable接口,引入了destroy方法,支持销毁操作:
public interface Destroyable {
void destroy() throws Exception;
}2.2 CacheManagerAware
子类实现支持注入缓存管理器,进而获取构造缓存实例,执行缓存操作;
public interface CacheManagerAware {
/**
* Sets the available CacheManager instance on this component.
*
* @param cacheManager the CacheManager instance to set on this component.
*/
void setCacheManager(CacheManager cacheManager);
}2.3 EventBusAware
子类对象支持注入EventBus对象,类似Guava EventBus,引入事件机制,可以发布事件(publish),进而调用已注册(register)的事件监听器;
public interface EventBusAware {
/**
* Sets the available {@code EventBus} that may be used for publishing and subscribing to/from events.
*
* @param bus the available {@code EventBus}.
*/
void setEventBus(EventBus bus);
}public interface EventBus {
void publish(Object event);
void register(Object subscriber);
void unregister(Object subscriber);
}2.4 CachingSecurityManager(聚合缓存管理和事件监听管理功能)
同时实现了Destroyable, CacheManagerAware, EventBusAware,支持注入成员变量cacheManager和eventBus,并定义了销毁操作,主要实现如下:
public abstract class CachingSecurityManager implements SecurityManager, Destroyable, CacheManagerAware, EventBusAware {
/**
* The CacheManager to use to perform caching operations to enhance performance. Can be null.
*/
private CacheManager cacheManager;
/**
* The EventBus to use to use to publish and receive events of interest during Shiro's lifecycle.
* @since 1.3
*/
private EventBus eventBus;
/**
* Default no-arg constructor that will automatically attempt to initialize a default cacheManager
*/
public CachingSecurityManager() {
//use a default event bus:
setEventBus(new DefaultEventBus());
}
/**
* Destroys the {@link #getCacheManager() cacheManager} via {@link LifecycleUtils#destroy LifecycleUtils.destroy}.
*/
public void destroy() {
LifecycleUtils.destroy(getCacheManager());
this.cacheManager = null;
LifecycleUtils.destroy(getEventBus());
this.eventBus = new DefaultEventBus();
}
}2.5 RealmSecurityManager(聚合Realm管理功能)
RealmSecurityManager引入成员变量Realm,支持Realm的管理,包括:注册、销毁等操作;
Realm:Shiro引入的安全组件,支持获取App本地的用户安全相关数据,包括:用户信息、角色、权限等,用于执行用户认证和用户鉴权;
官方释义:
A Realm is a security component that can access application-specific security entities
such as users, roles, and permissions to determine authentication and authorization operations.
RealmSecurityManager主要实现如下:
public abstract class RealmSecurityManager extends CachingSecurityManager {
/**
* Internal collection of Realms used for all authentication and authorization operations.
*/
private Collection realms;
public void setRealms(Collection realms) {
if (realms == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Realms collection argument cannot be null.");
}
if (realms.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Realms collection argument cannot be empty.");
}
this.realms = realms;
afterRealmsSet();
}
protected void afterRealmsSet() {
applyCacheManagerToRealms();
applyEventBusToRealms();
}
public void destroy() {
LifecycleUtils.destroy(getRealms());
this.realms = null;
super.destroy();
}
} 2.6 AuthenticatingSecurityManager(聚合登录认证功能)
AuthenticatingSecurityManager注入成员变量authenticator(默认初始化的实例是ModularRealmAuthenticator)并进行初始化设置(注入认证组件Realm),同时实现了接口Authenticator定义的authenticate方法,内部委托给成员变量authenticator,如下:
private Authenticator authenticator;
/**
* Default no-arg constructor that initializes its internal
* authenticator instance to a
* {@link org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.ModularRealmAuthenticator ModularRealmAuthenticator}.
*/
public AuthenticatingSecurityManager() {
super();
this.authenticator = new ModularRealmAuthenticator();
}
/**
* Passes on the {@link #getRealms() realms} to the internal delegate Authenticator instance so
* that it may use them during authentication attempts.
*/
protected void afterRealmsSet() {
super.afterRealmsSet();
if (this.authenticator instanceof ModularRealmAuthenticator) {
((ModularRealmAuthenticator) this.authenticator).setRealms(getRealms());
}
}
public AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
return this.authenticator.authenticate(token);
}2.7 AuthorizingSecurityManager(聚合访问控制功能)
和AuthenticatingSecurityManager类似,这里注入了成员变量authorizer来实现访问控制的鉴权功能,authorizer的默认实现是ModularRealmAuthorizer,同样也对authorizer进行了初始化设置,注入Reaml,并具体实现了接口Authorizer引入的访问控制方法,如下:
/**
* The wrapped instance to which all of this SecurityManager authorization calls are delegated.
*/
private Authorizer authorizer;
/**
* Default no-arg constructor that initializes an internal default
* {@link org.apache.shiro.authz.ModularRealmAuthorizer ModularRealmAuthorizer}.
*/
public AuthorizingSecurityManager() {
super();
this.authorizer = new ModularRealmAuthorizer();
}
protected void afterRealmsSet() {
super.afterRealmsSet();
if (this.authorizer instanceof ModularRealmAuthorizer) {
((ModularRealmAuthorizer) this.authorizer).setRealms(getRealms());
}
}
public boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, String permissionString) {
return this.authorizer.isPermitted(principals, permissionString);
}2.8 SessionsSecurityManager(聚合Session管理功能)
内部注入了成员变量sessionManagerSession管理器,实现了session创建、session获取的方法:
/**
* The internal delegate SessionManager used by this security manager that manages all the
* application's {@link Session Session}s.
*/
private SessionManager sessionManager;
/**
* Default no-arg constructor, internally creates a suitable default {@link SessionManager SessionManager} delegate
* instance.
*/
public SessionsSecurityManager() {
super();
this.sessionManager = new DefaultSessionManager();
applyCacheManagerToSessionManager();
}
public Session start(SessionContext context) throws AuthorizationException {
return this.sessionManager.start(context);
}
public Session getSession(SessionKey key) throws SessionException {
return this.sessionManager.getSession(key);
}2.9 DefaultSecurityManager
DefaultSecurityManager主要聚合了3部分功能,这点可以从其包含的成员变量看出,下面进行分别说明:
protected RememberMeManager rememberMeManager;
protected SubjectDAO subjectDAO;
protected SubjectFactory subjectFactory;
/**
* Default no-arg constructor.
*/
public DefaultSecurityManager() {
super();
this.subjectFactory = new DefaultSubjectFactory();
this.subjectDAO = new DefaultSubjectDAO();
}2.9.1 创建用户(Subject)功能
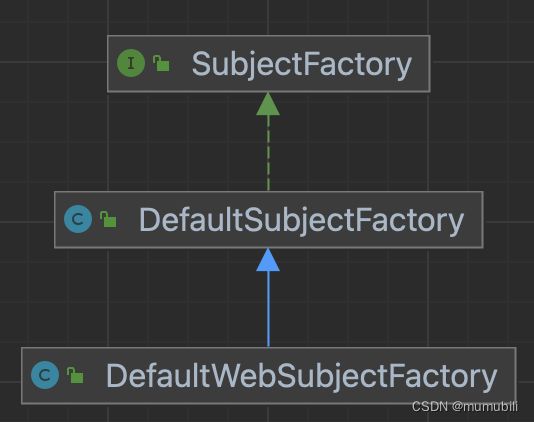
Subject创建过程是通过工厂方法模式实现了,其工厂类为SubjectFactory,Web服务中具体的工厂类为DefaultWebSubjectFactory,工厂类的继承结构如下:
DefaultSecurityManager的方法doCreateSubject委托给了SubjectFactory来完成:
protected Subject doCreateSubject(SubjectContext context) {
return getSubjectFactory().createSubject(context);
}具体创建过程这里不做展开,后续在用户登录流程中再进行深入分析;
2.9.2 存储用户(Subject)功能
Subject的CRUD操作是通过SubjectDAO完成的,具体实现类为DefaultSubjectDAO,在DefaultSubjectDAO中,Subject的内部状态是通过存放到Session中完成的;
DefaultSecurityManager的save和delete方法实现内部委托给了成员变量subjectDAO来完成;
/**
* Saves the subject's state to a persistent location for future reference if necessary.
*
* This implementation merely delegates to the internal {@link #setSubjectDAO(SubjectDAO) subjectDAO} and calls
* {@link SubjectDAO#save(org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject) subjectDAO.save(subject)}.
*
* @param subject the subject for which state will potentially be persisted
* @see SubjectDAO#save(org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject)
* @since 1.2
*/
protected void save(Subject subject) {
this.subjectDAO.save(subject);
}
/**
* Removes (or 'unbinds') the Subject's state from the application, typically called during {@link #logout}..
*
* This implementation merely delegates to the internal {@link #setSubjectDAO(SubjectDAO) subjectDAO} and calls
* {@link SubjectDAO#delete(org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject) delete(subject)}.
*
* @param subject the subject for which state will be removed
* @see SubjectDAO#delete(org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject)
* @since 1.2
*/
protected void delete(Subject subject) {
this.subjectDAO.delete(subject);
}2.9.3 用户RememberMe管理功能
在用户登录成功之后,可以通过RememberMeManager记录用户登录信息,比如登录用户名称,内部是通过记录Cookie的方法实现的,具体过程后续分析用户登录认证过程时再展开分析;
RememberMeManager通过如下的方法对用户登录成功、登录失败、退出时进行拦截,并进行相应后处理操作;
protected void rememberMeSuccessfulLogin(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info, Subject subject) {
RememberMeManager rmm = getRememberMeManager();
if (rmm != null) {
try {
rmm.onSuccessfulLogin(subject, token, info);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
String msg = "Delegate RememberMeManager instance of type [" + rmm.getClass().getName() +
"] threw an exception during onSuccessfulLogin. RememberMe services will not be " +
"performed for account [" + info + "].";
log.warn(msg, e);
}
}
} else {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("This " + getClass().getName() + " instance does not have a " +
"[" + RememberMeManager.class.getName() + "] instance configured. RememberMe services " +
"will not be performed for account [" + info + "].");
}
}
}
protected void rememberMeFailedLogin(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationException ex, Subject subject) {
RememberMeManager rmm = getRememberMeManager();
if (rmm != null) {
try {
rmm.onFailedLogin(subject, token, ex);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
String msg = "Delegate RememberMeManager instance of type [" + rmm.getClass().getName() +
"] threw an exception during onFailedLogin for AuthenticationToken [" +
token + "].";
log.warn(msg, e);
}
}
}
}
protected void rememberMeLogout(Subject subject) {
RememberMeManager rmm = getRememberMeManager();
if (rmm != null) {
try {
rmm.onLogout(subject);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
String msg = "Delegate RememberMeManager instance of type [" + rmm.getClass().getName() +
"] threw an exception during onLogout for subject with principals [" +
(subject != null ? subject.getPrincipals() : null) + "]";
log.warn(msg, e);
}
}
}
}2.10 DefaultWebSecurityManager
DefaultWebSecurityManager继承自DefaultSecurityManager,同时实现了WebSecurityManager接口,标识session模式是http模式(Servlet管理sessiion),非native模式(Shiro管理session),
同时初始化了成员变量的具体实现类,包括DefaultWebSubjectFactory、CookieRememberMeManager、ServletContainerSessionManager,如下:
public DefaultWebSecurityManager() {
super();
((DefaultSubjectDAO) this.subjectDAO).setSessionStorageEvaluator(new DefaultWebSessionStorageEvaluator());
this.sessionMode = HTTP_SESSION_MODE;
setSubjectFactory(new DefaultWebSubjectFactory());
setRememberMeManager(new CookieRememberMeManager());
setSessionManager(new ServletContainerSessionManager());
}至此,SecurityManager的内容解析完毕,可以看到在不同的继承层次上为SecurityManager聚合了不同的功能,层次清楚、职责分明,通过关注点分离的方式满足了“单一职责”的设计原则,是个很好的借鉴。