yolov5模型Detection输出内容与源码详细解读
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、Detiction类源码说明
- 二、Detection类初始化参数解读
- 三、Detection的训练输出源码解读
- 四、Detection的预测输出源码解读
-
- 1、self.grid内容解读
- 2、xy/wh内容解读
- 3、推理输出解读
- 总结
前言
最近,需要修改yolov5推理结果,通过推理特征添加一些其它操作(如蒸馏)。显然,你需要对yolov5推理输出内容有详细了解,方可被你使用。为此,本文将记录个人对yolov5输出内容源码解读,这样对于你修改源码或蒸馏操作可提供理论参考。
一、Detiction类源码说明
yolov5的detection类输出包含2个部分,一个是训练的输出,一个是预测的输出。而我将在这里解释类参数与训练、预测输出内容。为什么我使用一篇文章来说明?显然是训练与预测输出内容与原始图像尺寸、模型尺寸、特征尺寸以及回归box含义与使用细节。
整体源码如下:
class Detect(nn.Module):
stride = None # strides computed during build
onnx_dynamic = False # ONNX export parameter
def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=(), inplace=True): # detection layer
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs per anchor
self.nl = len(anchors) # number of detection layers
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # number of anchors
self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init grid
self.anchor_grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init anchor grid
self.register_buffer('anchors', torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2)) # shape(nl,na,2)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.inplace = inplace # use in-place ops (e.g. slice assignment)
def forward(self, x):
z = [] # inference output
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
if not self.training: # inference
if self.onnx_dynamic or self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]:
self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i)
y = x[i].sigmoid()
if self.inplace:
y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
else: # for YOLOv5 on AWS Inferentia https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2953
xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, y[..., 4:]), -1)
z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))
return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), x)
二、Detection类初始化参数解读
我已voc数据为例说明,voc数据类别为20。我将其具体解释注释其代码中,如下:
def __init__(self, nc=20, anchors=(), ch=(), inplace=True): # detection layer
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc # =20 类别数量
self.no = nc + 5 # =25 每个类别需添加位置与置信度
self.nl = len(anchors) # =3 yolov5检测层为3,每层特征有一个anchor,可使用anchors替代
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # =3 获得每个grid的anchor数量
self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # =[tensor([0.]), tensor([0.]), tensor([0.])],初始化grid,后期会每个特征变成[1,3,feature_w,feature_h,2],共三个
self.anchor_grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # 初始化anchor grid,与上面self.grid类似,直白说就是占位初始化
self.register_buffer('anchors', torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2)) # 将anchors值变成shape(3,3,2)与对应格式
self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # 3个模型数据输出转换,每个特征图输出转换,
self.inplace = inplace # use in-place ops (e.g. slice assignment)
anchors值如下:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
self.m模块:
ModuleList(
(0): Conv2d(320, 75, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(1): Conv2d(640, 75, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(2): Conv2d(1280, 75, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
其中ch是输入,与模型图像大小关联。
三、Detection的训练输出源码解读
为便于快速理解模型训练输出内容,我直接去掉推理输出代码,这样一目了然知道模型输出内容。
def forward(self, x):
z = [] # inference output
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # 预测输出
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
return x
输出x值为三个特征层的值输出,都表示[batch,3,h,w,cls+5],含义为batch size图像的h*w个像素有3个预测,每个预测都是类别概率、置信度与box位置。其输出如下:
四、Detection的预测输出源码解读
为便于快速理解模型推理输出内容,我直去掉不必要判断,给出推理输出代码,这样一目了然知道模型输出内容。
def forward(self, x):
z = [] # inference output
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
# inference
if self.onnx_dynamic or self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]:
self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i)
y = x[i].sigmoid()
if self.inplace:
y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
else: # for YOLOv5 on AWS Inferentia https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2953
xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, y[..., 4:]), -1)
z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))
return (torch.cat(z, 1), x)
1、self.grid内容解读
grid为网格,可以理解是对应特征图的网格,以第一个特征宽高为80说明,grid[0]存的是像素位置坐标如下tensort示意。相当于,每个batch的高宽对应像素重复3次分别从0到79的x坐标和y坐标得到grid。而grid有三个特征,其它二个特征图也是同样原理,如下图。
tensor([[[[[ 0., 0.],
[ 1., 0.],
[ 2., 0.],
...,
[77., 0.],
[78., 0.],
[79., 0.]],
[[ 0., 1.],
[ 1., 1.],
[ 2., 1.],
...,
[77., 1.],
[78., 1.],
[79., 1.]],
[[ 0., 2.],
[ 1., 2.],
[ 2., 2.],
...,
[77., 2.],
[78., 2.],
[79., 2.]],
...,
2、xy/wh内容解读
yolov5在经历一次sigmoid为y = x[i].sigmoid(),获得dx、dy、dw、dh值(我暂时这么理解),在使用以下代码实现在该特征图对应xy值与wh值。特别注意,假设该特征图是8080尺寸,仅是获得在该特征8080层恢复到模型输入特征图像尺寸,还未到原始图像输入尺寸。源码如下:
y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
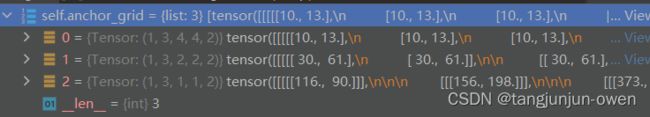
这里也说明一下,dw/dh转到对应尺寸是直接乘以self.anchor_grid,而self.anchor_grid保留是anchors值如下:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
注:这里知道dx/dy/dw/dh恢复到模型输入尺寸(如640)即可。dw/dh并没有*strid,而是直接*anchors值。
3、推理输出解读
最后将输出内容通过view转换为[batch,-1,25]形式。
z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))
即可获得(torch.cat(z, 1), x)这样的推理输出。我想说x实际还是训练输出内容,没有变化。
推理输出为2个列表,第一个列表就是上面说到的z值,其经历了sigmoid,包含类、置信度、box都使用了sigmoid,且box转为了模型输出对应尺寸位置。第二个列表为三个特征层的值输出,都表示[batch,3,h,w,cls+5],含义为batch size图像的h*w个像素有3个预测,每个预测都是类别概率、置信度与box位置,是没有经历过sigmoid,实际就是训练输出内容。其结果示意如下:
注:x没有经过sigmoid,而z经过sigmoid后转成模型输出尺寸box。
总结
掌握yolov5的Detection类训练与预测输出内容,有利于对源码更改提供理论依据。