常见Java层反调试技术之root检测方式总结—之用Shamiko能过绕过多少
常见Java层反调试技术之root检测方式总结—之用Shamiko能过绕过多少
测试设备:红米Note7
安卓版本:9
环境:Magisk+Shamiko模块
1、检测which su----------可绕过
-
java层代码实现
-
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); if(checkSuExists()){ Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "检测到su命令", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); }else { Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "没有检测到su命令", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } } public boolean checkSuExists(){ Process process = null; try { process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String[] {"which","su"}); BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream())); return in.readLine() != null; } catch (Throwable t) { return false; }finally { if (process != null) process.destroy(); } } } -
未使用Shamiko
-
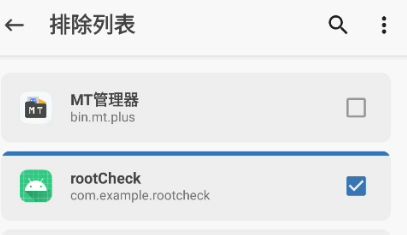
使用Shamiko进行排除
2、检测在常用目录下是否存在非法的二进制文件—可绕过
- root过红米Note7存在的root目录
1|lavender:/ $ which magisk
/sbin/magisk
lavender:/ $ which su
/sbin/su
lavender:/ $
-
检测方法—遍历系统文件 存在sbin/的就是非法的
-
lavender:/ $ echo $PATH | grep /system/bin /sbin:/system/sbin:/system/bin:/system/xbin:/odm/bin:/vendor/bin:/vendor/xbin lavender:/ $ -
// checkForBinary("magisk"); // checkForBinary("su"); // checkForBinary("busybox"); public void checkForBinary(String filename){ String[] pathsArray = this.getPaths(); boolean flag = false; for (String path : pathsArray) { String fullPath = path + filename; Log.e("fullPath",fullPath); File f = new File(path, filename); boolean fileExists = f.exists(); if (fileExists){ Log.e("fullPath","检测到非法二进制文件"); Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "检测到非法二进制文件", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } } } private String[] getPaths() { ArrayListpaths = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(suPaths)); String sysPaths = System.getenv("PATH"); //如果获取不到这个系统路径变量 返回静态路径 if (sysPaths == null || "".equals(sysPaths)){ //创建一个类型为String的空数组,长度为0。这可能会用作占位符或初始化一个变量,稍后会用字符串值填充该变量。 return paths.toArray(new String[0]); } for (String path : sysPaths.split(":")) { if (!path.endsWith("/")){ path = path + '/'; } if (!paths.contains(path)){ paths.add(path); } } return paths.toArray(new String[0]); } -
Shamiko隐藏后
3、判断SELinux是否开启(过时)
-
用java反射获取ro.build.selinux值判断
-
private boolean isSelinuxFlagInEnabled() { try { Class<?> c = Class.forName("android.os.SystemProperties"); Method get = c.getMethod("get", String.class); String selinux = (String) get.invoke(c,"ro.build.selinux"); return "1".equals(selinux); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return false; } -
没开Shamiko
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-FRrNfbfY-1679632197642)(C:\Users\李世林\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230324094117527.png)]
4、检测ro.debuggable和ro.secure值----未知
-
ro.debuggable-------------是否开启Android Debug Bridge功能
-
在生产环境中,该属性通常应该被设置为 “0” 以增加设备的安全性。如果该属性设置为 “1”,则任何人都可以使用 ADB 命令访问设备,从而可能会导致设备受到攻击或其他安全问题
-
lavender:/ $ getprop ro.debuggable 0
-
-
ro.secure---------Android中的系统属性 是否开启安全性强化措施 1开启 0 未开启
-
不可信 我的红米note7 root过
-
lavender:/ $ getprop ro.secure 1
-
-
private void checkForDangerousProps(){ final Map<String,String> dangerousProps = new HashMap<>(); dangerousProps.put("ro.debuggable","1"); boolean result = false; String[] lines = propsReader(); if (lines == null){ return; } for (String line : lines) { for (String key : dangerousProps.keySet()){ if (line.contains(key)){ String badValue = dangerousProps.get(key); badValue = "["+ badValue + "]"; if (line.contains(badValue)){ Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "检测到危险值 "+key+": "+badValue, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); }else { Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "未检测到危险值 "+line, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } } } } } private String[] propsReader() { try { InputStream inputStream = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("getprop").getInputStream(); if (inputStream == null) return null; /* 这行代码的意思是从输入流(InputStream)中获取文本内容并将其以字符串(String)的形式存储在propVal变量中。具体来说,代码使用Scanner类的构造函数将InputStream对象inputstream作为参数,创建了一个Scanner对象。 然后,代码使用useDelimiter("\A")方法来设置Scanner对象的分隔符,该分隔符表示使用"\A"正则表达式,即匹配输入的开始处,即输入流的开头。这样设置分隔符的目的是让Scanner将整个输入流作为一个标记读取。 紧接着,代码使用Scanner的next()方法来读取Scanner对象的下一个标记,即整个输入流。将读取到的标记以字符串形式存储在propVal变量中。 可以使用这行代码读取文件或网络流中的文本内容,也可以读取控制台输入的文本内容。 */ String propVal = new Scanner(inputStream).useDelimiter("\\A").next(); return propVal.split("\n"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; }很奇怪 我开不开这个Shamiko这个值都是0 估计是把面具隐藏了?
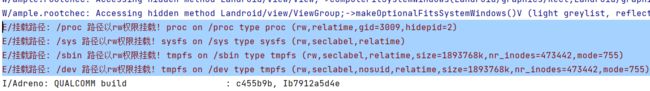
5、检查特定路径是否有写权限-----绕过失败
-
Java代码将使用mount命令检查这些路径的读写权限,如果可读写,说明设备可能被root了
-
/system /system/bin /system/sbin /system/xbin /vendor/bin /sbin /etc /sys /proc /dev -
以空格隔开了
-
private String[] pathsThatShouldNotBeWritable = { "/system", "/system/bin", "/system/sbin", "/system/xbin", "/vendor/bin", "/sbin", "/etc", "/sys", "/proc", "/dev" }; public String[] mountReader(){ /* 在安卓中,mount命令用于挂载文件系统或卸载文件系统,具体功能包括但不限于以下几种: 挂载存储设备:使用mount命令可以挂载已经插入的SD卡、U盘等存储设备,以便在系统中访问其内容。 系统分区读写:挂载系统分区后,可以访问和修改Linux系统下的各种配置文件、启动文件以及用户数据等。 安装软件包:在安卓系统中,软件包安装文件通常安装在系统分区中,如果要正常安装软件包,就需要先挂载系统分区。 卸载文件系统:展开程序运行时不同的功能模块时,可能需要动态地加载或卸载文件系统。卸载文件系统时,可以利用mount命令将文件系统卸载,以免占用过多的系统资源。 总之,mount命令在安卓中是一个非常重要的命令,对于维护安卓系统的稳定性和正常运行有非常重要的作用。 */ try { InputStream inputStream = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("mount").getInputStream(); if(inputStream == null) return null; String propVal = new Scanner(inputStream).useDelimiter("\\A").next(); return propVal.split("\n"); } catch (IOException e) { Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), e.getMessage(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); return null; } } public void checkForRWPaths(){ //Run the command "mount" to retrieve all mounted directories String[] lines = mountReader(); if (lines == null){ return; } int sdkVersion = Build.VERSION.SDK_INT; for (String line : lines) { String[] args = line.split(" "); if ((sdkVersion <= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.M && args.length < 4) || (sdkVersion > android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.M && args.length < 6)) { // If we don't have enough options per line, skip this and log an error Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Error formatting mount line: "+line+line, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); continue; } String mountPoint; String mountOptions; /** * To check if the device is running Android version higher than Marshmallow or not */ if (sdkVersion > android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.M) { mountPoint = args[2];//就是挂载路径 mountOptions = args[5]; } else { mountPoint = args[1]; mountOptions = args[3]; } for (String pathToCheck: this.pathsThatShouldNotBeWritable){ if (mountPoint.equalsIgnoreCase(pathToCheck)){ /** * If the device is running an Android version above Marshmallow, * need to remove parentheses from options parameter; */ if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT > android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.M) { mountOptions = mountOptions.replace("(", ""); mountOptions = mountOptions.replace(")", ""); } // Split options out and compare against "rw" to avoid false positives for (String option : mountOptions.split(",")){ if (option.equalsIgnoreCase("rw")){ Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), pathToCheck+" 路径以rw权限挂载! "+line, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } } } } } } -
开启Shamiko
6、检测test-keys
-
ro.build.tags 参数值为"test-key" 说明是测试版的数字签名构造的 有root的风险
-
ro.build.tags 参数值为"release-keys" 正式发布的版本 这种密钥是由厂家发布的数字签名,更难被攻击,因此是相对安全的。
-
lavender:/ $ getprop ro.build.tags release-keys -
我的红米Note7 root过但是还是release-keys
-
换模拟器试试 也一样
-
getprop ro.build.tags release-keys这个可能是编译了源码 变成的test-key
-
public boolean detectTestKeys() { String buildTags = android.os.Build.TAGS; return buildTags != null && buildTags.contains("test-keys"); }
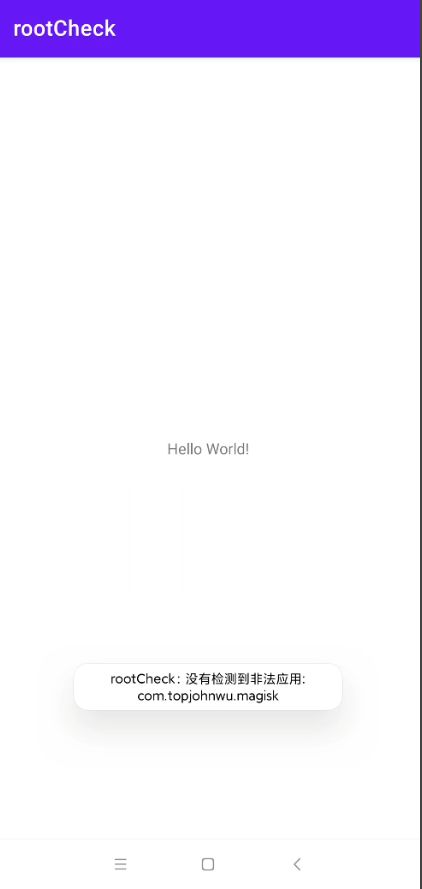
7、检测非法应用----可绕过
-
lavender:/ $ pm list packages | findstr magisk /system/bin/sh: findstr: not found 127|lavender:/ $ -
我的migisk被我隐藏了 应该是这样 检测不出来
-
static final String[] knownRootAppsPackages = { "com.topjohnwu.magisk" //add.... }; public void detectPotentiallyDangerousApps(){ ArrayList<String> packages = new ArrayList<>(); packages.addAll(Arrays.asList(this.knownRootAppsPackages)); sAnyPackageFromListInstalled(packages); } private void sAnyPackageFromListInstalled(List<String> packages) { PackageManager pm = getApplicationContext().getPackageManager(); for (String packageName : packages) { try { pm.getPackageInfo(packageName,0); Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "检测到非法应用: "+packageName, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) { Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "没有检测到非法应用: "+packageName, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } } } -
先取消隐藏
-
Shamiko隐藏一下 重启.
总结
- Magisk + Shamiko 基本上除了挂载文件的rw权限搞不定 其他的都OK的
- java层上的ROOT检测 以这篇帖子为参考来测试
- https://www.52pojie.cn/thread-1763111-1-1.html
- 以后有其他的检测点 在做测试
附录代码
package com.example.rootcheck;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.os.Build;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Toast;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// if(checkSuExists()){
// Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "检测到su命令", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// }else {
// Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "没有检测到su命令", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// }
// checkForBinary("magisk");
// checkForBinary("su");
// checkForBinary("busybox");
//
// if(isSelinuxFlagInEnabled())
// {
// Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "SELinux开启",
// Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// }
// else
// {
// Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "SELinux没有开启",
// Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// }
// checkForDangerousProps();
// checkForRWPaths();
// if(detectTestKeys())
// Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Test Keys",
// Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// else
// Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Relese Keys",
// Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
detectPotentiallyDangerousApps();
}
public boolean detectTestKeys() {
String buildTags = android.os.Build.TAGS;
return buildTags != null && buildTags.contains("test-keys");
}
private static final String[] suPaths = {
"/data/local/",
"/data/local/bin/",
"/data/local/xbin/",
"/sbin/",
"/su/bin/",
"/system/bin/",
"/system/bin/.ext/",
"/system/bin/failsafe/",
"/system/sd/xbin/",
"/system/usr/we-need-root/",
"/system/xbin/",
"/cache/",
"/data/",
"/dev/"
};
private String[] pathsThatShouldNotBeWritable = {
"/system",
"/system/bin",
"/system/sbin",
"/system/xbin",
"/vendor/bin",
"/sbin",
"/etc",
"/sys",
"/proc",
"/dev"
};
static final String[] knownRootAppsPackages = {
"com.topjohnwu.magisk"
//add....
};
public void detectPotentiallyDangerousApps(){
ArrayList<String> packages = new ArrayList<>();
packages.addAll(Arrays.asList(this.knownRootAppsPackages));
sAnyPackageFromListInstalled(packages);
}
private void sAnyPackageFromListInstalled(List<String> packages) {
PackageManager pm = getApplicationContext().getPackageManager();
for (String packageName : packages) {
try {
pm.getPackageInfo(packageName,0);
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "检测到非法应用: "+packageName,
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "没有检测到非法应用: "+packageName,
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
}
public String[] mountReader(){
/*
在安卓中,mount命令用于挂载文件系统或卸载文件系统,具体功能包括但不限于以下几种:
挂载存储设备:使用mount命令可以挂载已经插入的SD卡、U盘等存储设备,以便在系统中访问其内容。
系统分区读写:挂载系统分区后,可以访问和修改Linux系统下的各种配置文件、启动文件以及用户数据等。
安装软件包:在安卓系统中,软件包安装文件通常安装在系统分区中,如果要正常安装软件包,就需要先挂载系统分区。
卸载文件系统:展开程序运行时不同的功能模块时,可能需要动态地加载或卸载文件系统。卸载文件系统时,可以利用mount命令将文件系统卸载,以免占用过多的系统资源。
总之,mount命令在安卓中是一个非常重要的命令,对于维护安卓系统的稳定性和正常运行有非常重要的作用。
*/
try {
InputStream inputStream = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("mount").getInputStream();
if(inputStream == null) return null;
String propVal = new Scanner(inputStream).useDelimiter("\\A").next();
return propVal.split("\n");
} catch (IOException e) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), e.getMessage(),
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return null;
}
}
public void checkForRWPaths(){
//Run the command "mount" to retrieve all mounted directories
String[] lines = mountReader();
if (lines == null){
return;
}
int sdkVersion = Build.VERSION.SDK_INT;
for (String line : lines) {
String[] args = line.split(" ");
if ((sdkVersion <= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.M && args.length < 4)
|| (sdkVersion > android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.M && args.length < 6)) {
// If we don't have enough options per line, skip this and log an error
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Error formatting mount line: "+line+line,
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
continue;
}
String mountPoint;
String mountOptions;
/**
* To check if the device is running Android version higher than Marshmallow or not
*/
if (sdkVersion > android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.M) {
mountPoint = args[2];//就是挂载路径
mountOptions = args[5];
} else {
mountPoint = args[1];
mountOptions = args[3];
}
for (String pathToCheck: this.pathsThatShouldNotBeWritable){
if (mountPoint.equalsIgnoreCase(pathToCheck)){
/**
* If the device is running an Android version above Marshmallow,
* need to remove parentheses from options parameter;
*/
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT > android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.M) {
mountOptions = mountOptions.replace("(", "");
mountOptions = mountOptions.replace(")", "");
}
// Split options out and compare against "rw" to avoid false positives
for (String option : mountOptions.split(",")){
if (option.equalsIgnoreCase("rw")){
Log.e("挂载路径",pathToCheck+" 路径以rw权限挂载! "+line);
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), pathToCheck+" 路径以rw权限挂载! "+line,
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
}
}
}
}
public void checkForBinary(String filename) {
String[] pathsArray = this.getPaths();
boolean flag = false;
for (String path : pathsArray) {
String fullPath = path + filename;
Log.e("fullPath", fullPath);
File f = new File(path, filename);
boolean fileExists = f.exists();
if (fileExists) {
Log.e("fullPath", "检测到非法二进制文件");
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "检测到非法二进制文件", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
private String[] getPaths() {
ArrayList<String> paths = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(suPaths));
String sysPaths = System.getenv("PATH");
//如果获取不到这个系统路径变量 返回静态路径
if (sysPaths == null || "".equals(sysPaths)) {
//创建一个类型为String的空数组,长度为0。这可能会用作占位符或初始化一个变量,稍后会用字符串值填充该变量。
return paths.toArray(new String[0]);
}
for (String path : sysPaths.split(":")) {
if (!path.endsWith("/")) {
path = path + '/';
}
if (!paths.contains(path)) {
paths.add(path);
}
}
return paths.toArray(new String[0]);
}
public boolean checkSuExists() {
Process process = null;
try {
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String[]{"which", "su"});
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));
return in.readLine() != null;
} catch (Throwable t) {
return false;
} finally {
if (process != null) process.destroy();
}
}
private boolean isSelinuxFlagInEnabled() {
try {
Class<?> c = Class.forName("android.os.SystemProperties");
Method get = c.getMethod("get", String.class);
String selinux = (String) get.invoke(c, "ro.build.selinux");
return "1".equals(selinux);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}
private void checkForDangerousProps() {
final Map<String, String> dangerousProps = new HashMap<>();
dangerousProps.put("ro.debuggable", "1");
boolean result = false;
String[] lines = propsReader();
if (lines == null){
// Could not read, assume false;
return;
}
for (String line : lines) {
Log.e("line",line);
for (String key : dangerousProps.keySet()) {
//Log.e("key",key);
if (line.contains(key)) {
String badValue = dangerousProps.get(key);
badValue = "[" + badValue + "]";
//Log.e("badValue",badValue);
if (line.contains(badValue)) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "检测到危险值 "+key+": "+badValue,
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}else {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "未检测到危险值 "+line,
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
}
}
}
private String[] propsReader() {
try {
InputStream inputStream = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("getprop").getInputStream();
if (inputStream == null) return null;
/*
这行代码的意思是从输入流(InputStream)中获取文本内容并将其以字符串(String)的形式存储在propVal变量中。具体来说,代码使用Scanner类的构造函数将InputStream对象inputstream作为参数,创建了一个Scanner对象。
然后,代码使用useDelimiter("\A")方法来设置Scanner对象的分隔符,该分隔符表示使用"\A"正则表达式,即匹配输入的开始处,即输入流的开头。这样设置分隔符的目的是让Scanner将整个输入流作为一个标记读取。
紧接着,代码使用Scanner的next()方法来读取Scanner对象的下一个标记,即整个输入流。将读取到的标记以字符串形式存储在propVal变量中。
可以使用这行代码读取文件或网络流中的文本内容,也可以读取控制台输入的文本内容。
*/
String propVal = new Scanner(inputStream).useDelimiter("\\A").next();
return propVal.split("\n");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}