Java常用API汇总
目录
API定义
常用API(一)
String
集合框架
常用API(二)
Object类中常见API
Objects类中常见API
包装类
StringBuilder & StringBuffer & StringJoiner
常用API(三)
Math、System、Runtime
BigDecimal
JDK8之前传统的日期、时间
JDK8开始新增的日期、时间
Arrays
JDK8新特性:Lambda表达式
JDK8新特性:方法引用
API定义
全称应用程序编程接口,就是Java自己写好的程序,给程序员调用的,方便完成一些功能的。
使用可查阅API文档
常用API(一)
String
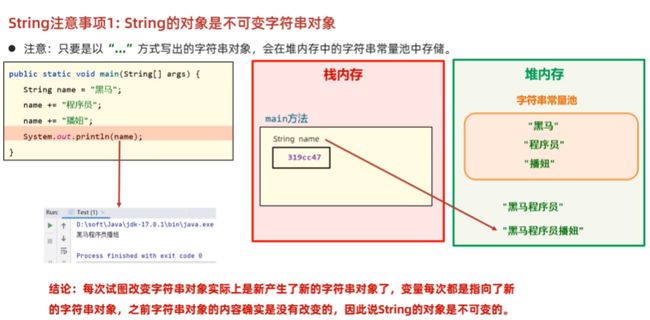
- String是字符串类型,它定义的变量可以指向一个字符串对象
- String是不可变字符串
String创建对象的方式:
- 直接使用
" "围起来
String name = "张三";2. new构造器得到字符串对象
public String(){ ... }
public String(String original){ ... }
public String(char[] chars){ ... }
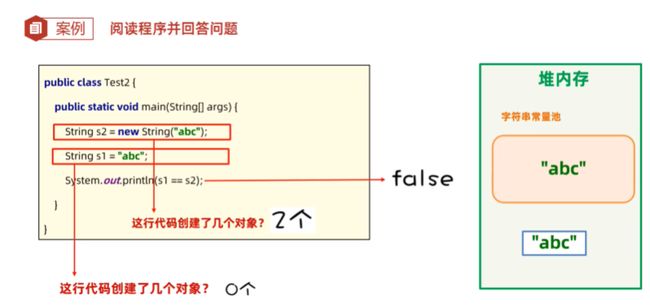
public String(byte[] bytes){ ... }3. 两种方式的区别:
a. 双引号给出的字符串对象,存在于堆内存的常量池中,且相同内容仅会存储一份
b. new 字符串对象,每new一次都会在堆内存中产生一个新的字符串对象
4. case:
- String的常用方法(API)
public class StringDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//TODO 目标:快速熟悉String提供的处理字符串的常用方法:
String s = "黑马Java";
//1.获取字符串长度[.length()]
int length = s.length();
System.out.println(length); //6
//2.提取字符串中某个索引位置处的字符[.charAt()]
char c = s.charAt(1);
System.out.println(c); //马
//结合上述方法[.length() + .charAt()],我们可以遍历字符串对象
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c1 = s.charAt(i);
System.out.print(i == s.length()-1 ? c1 : c1 + ",");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("---------------------");
//3.把字符串转换成字符数组[.toCharArray()],再进行遍历
char[] charArray = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++) {
char c1 = charArray[i];
System.out.print(i == charArray.length - 1 ? c1 : c1 + ",");
}
System.out.println();
//4.判断字符串内容[.equals()],内容一样就返回true
String s1 = "heima";
String s2 = "heima";
String s3 = new String("heima");
//其中 == 比较地址值,.equals()比较字符串内容
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
System.out.println(s1 == s3);//false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));//true
//5.忽略大小写的比较字符串内容[.equalsIgnoreCase()]
String c1 = "34dsAF";
String c2 = "34DSaF";
System.out.println(c1.equals(c2));//false
System.out.println(c1.equalsIgnoreCase(c2));//true
//6.截取字符串内容[ , ) [.substring( , )]
String s0 = "Java是最好的编程语言之一";
String rs = s0.substring(0, 12);
System.out.println(rs);
//7.从当前索引位置一直截取到字符串的末端[.substring()]
String rs2 = s0.substring(5);
System.out.println(rs2);
//8.把字符串中的某个内容转换成新内容,并返回新的字符串对象给我们[.replace()]
String info = "这电影简直是个垃圾,垃圾电影!!!";
String rs3 = info.replace("垃圾", "***");
System.out.println(rs3);
//9.判断字符串中是否包含某个关键字[.contains()]
String info2 = "Java是最好的编程语言之一,我爱Java,但Java不爱我!";
System.out.println(info2.contains("Java"));//true
System.out.println(info2.contains("java"));//false
//10.判断字符串是否以某个字符串开头[.startsWith()]
String rs4 = "张三丰";
System.out.println(rs4.startsWith("张"));//true
System.out.println(rs4.startsWith("张三"));//true
//11.把字符串按照某个指定内容分割成多个字符串,放到一个字符串数组中返回给我们[.split()]
String rs5 = "张无忌,周芷若,殷素素,赵敏";
String[] names = rs5.split(",");
String[] names1 = rs5.split("周芷若");
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
String name = names[i];
System.out.println(name);
}
for (int i = 0; i < names1.length; i++) {
String name = names1[i];
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}集合框架
- 集合:代表的是一种容器,类似于数组
- 集合的特点:大小可变,类型可以不固定,功能更加强大,适合做元素个数不确定,同时存在增删改查操作的业务场景
- 泛型:Java泛型是一种参数化类型的机制,它允许在程序中定义通用的类、接口和方法,以便在运行时根据具体的数据类型进行实例化。使用泛型可以提高Java程序的类型安全性和可重用性。集合都是支持泛型的。
- 注意:集合和泛型都不支持基本数据类型,只能支持引用数据类型
ps:这里只给出ArrayList的常见API,想要了解其他集合框架所用API,跳转至集合框架总结
ArrayList
- ArrayList是集合的一种,元素可以重复,元素存在索引。
- 如何构建ArrayList的对象代表一个集合容器,存储数据
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>(); - ArrayList常用方法
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//TODO 目标:掌握如何创建ArrayList集合对象,并熟悉ArrayList提供的常用方法
//0.创建一个ArrayList的集合对象
// //当未约束时,各种数据类型可以共存
// ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
//进行约束:
// 麻烦写法: ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
//1.增(从末尾依次添加数据) [.add()]
int[] is = {1, 2, 3, 4};
list.add("黑马");
list.add("黑马");
// list.add(567);
// list.add(1.23);
list.add("Java");
// list.add(is);
System.out.println(list);
//重载 往集合中的某个索引位置处添加一个数据
list.add(1, "MySQL");
System.out.println(list);
//2.删: 根据索引删除集合中的某个元素值,会返回被删除的元素值 [.remove]
String remove = list.remove(1);
System.out.println(remove);
System.out.println(list);
list.add(1, "MySQL");//偷偷加上,方便后边方法演示
//直接删除某个元素值(第一个),返回boolean
System.out.println(list.remove("黑马"));
System.out.println(list);
//3.改:修改某个索引位置处的数据,修改后会返回修改前的值给我们 [.set()]
System.out.println(list.set(1, "黑马程序员"));
System.out.println(list);
//4.查:根据索引获取集合中某个索引位置处的元素值[.get()]
String s = list.get(1);
System.out.println(s);
//5.获取集合的大小
System.out.println(list.size());
}
} 常用API(二)
- API:应用程序编程接口
Object类中常见API
- toString 返回对象的字符串表示形式
- equals 判断两个对象是否相等
- clone 对象克隆
其中toString、equals方法重写较多
Objects类中常见API
包装类
- 包装类就是把基本类型的数据包装成对象
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标:掌握包装类的使用
// Integer i1 = new Integer(1);//过时
Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf(2);
System.out.println(i2);
//自动装箱:可以自动把基本数据类型的数据转换成相应对象
Integer i3 = 3;
//自动拆箱:可以自动把包装类类型的对象转换成对应的基本数据类型
int i4 = i3 + 1;
//泛型和集合不支持基本数据类型,只能支持引用数据类型
// ArrayList lis t1 = new ArrayList();//
ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add(1);//自动装箱
list2.add(2);//自动装箱
int rs = list2.get(1);//自动拆箱
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
//包装类的其他常见操作
//1.toString()把基本类型的数据转换成字符串
Integer i = 12;
String s1 = Integer.toString(i);//"12"
System.out.println(s1 + 3);//"123"
String s2 = i.toString();//"12"
System.out.println(s2 + 3);//"123"
String s3 = i + "";//"12"
System.out.println(s3 + 3);//"123"
System.out.println("------------------------------");
//2.把字符串类型的数据转换成对应的基本类型
String ageStr = "29";
// int ageI = Integer.parseInt(ageStr);//29
int ageI = Integer.valueOf(ageStr);
System.out.println(ageI + 1);//30
String scoreStr = "99.5";
// double score = Double.parseDouble(scoreStr);//99.5
Double score = Double.valueOf(scoreStr);
System.out.println(score + 0.5);//100.0
}
} StringBuilder & StringBuffer & StringJoiner
- StringBuilder代表可变字符串对象,它里面装的字符串是可以改变的,就是用来操作字符串的
- 好处:StringBuilder比String更适合做字符串的修改操作,效率会更高。
StringBuilder & StringBuffer构造器 & 常用方法
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标:掌握StringBuilder & StringBuffer的用法和作用
//StringBuffer和StringBuilder使用几乎一样,但StringBuffer线程更加安全
// StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();//s ""
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder("ABC");//s "abc"
//1.拼接内容
s.append(12);
s.append(true);
s.append('c');
s.append(new int[]{1,2,3});
System.out.println(s);
//支持链式编程,append完后的返回值还是StringBuilder这个对象,故可以一直链式添加数据
System.out.println(s.append(new boolean[]{true, false}).append(012).append("wxy"));
System.out.println(s);
//2.reverse反转操作
System.out.println(s.reverse());
//3.length()返回字符串长度
System.out.println(s.length());
//4.把StringBuilder对象又转换成String类型
String rs = s.toString();
System.out.println(rs);
}
}StringJoiner构造器 & 常用方法
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//StringJoiner
// StringJoiner sj = new StringJoiner(",");//分隔符
StringJoiner sj = new StringJoiner(",","[","]");//分隔符,开始符,结束符
//add添加数据(只能是String),并返回对象本身
sj.add("java1");
sj.add("java2");
sj.add("java3");
System.out.println(sj);
//返回长度
System.out.println(sj.length());
//场景:将数组数据打印出来
System.out.println(getArrayData(new int[]{11, 22, 33}));
}
public static String getArrayData(int[] arr){
//1.判断是否为空
if(arr == null){
return null;
}
//2.arr数组对象存在
StringJoiner sj = new StringJoiner(",","[","]");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sj.add(arr[i] + "");//StringJoiner只能添加字符串
}
return sj.toString();//返回一个字符串
}
}String & StringBuilder比较
- 对于字符串的相关操作,如频繁的拼接、修改等,建议用StringBuilder,效率更高
- 注意:如果操作字符串较少,或者不需要操作,以及定义字符串变量,还是建议用String
StringBuffer & StringBuilder比较
- StringBuffer & StringBuilder用法是一模一样的
- 但StringBuilder是线程不安全的,StringBuffer是线程安全的
StringJoiner & StringBuilder比较
- 两者都是用来操作字符串的,都可以看成是一个容器,且内容可变
- StringJoiner好处:不仅能提高字符串的操作效率,并且有些场景下使用它操作字符串,代码会更简洁
常用API(三)
Math、System、Runtime
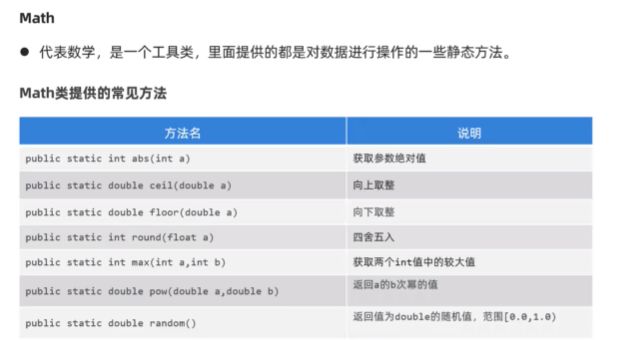
Math
- 数学工具类,里面提供的都是对数据进行操作的一些静态方法
public class MathTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标:了解Math类提供的常见方法
//1.public static int abs(int a)//取绝对值
// public static double abs(double a)//取绝对值
System.out.println(Math.abs(0));
System.out.println(Math.abs(-6.66));
System.out.println("---------------");
//2.public static double ceil(double a) //向上取整
System.out.println(Math.ceil(6.66));//7.0
System.out.println(Math.ceil(-6.66));//-6.0
System.out.println("----------------");
//3.public static double floor(double a) //向下取整
System.out.println(Math.floor(6.66));//6.0
System.out.println(Math.floor(-6.66));//-7.0
System.out.println("----------------");
//4.public static long round(double a) //四舍五入
System.out.println(Math.round(3.499999));//3
System.out.println(Math.round(-3.499999));//-3
System.out.println(Math.round(3.5));//4
System.out.println("----------------");
//5.public static int max(int a,int b) //取最大值
// public static int min(int a,int b) //取最小值
System.out.println(Math.max(1, 2));
System.out.println(Math.min(1, 2));
System.out.println("----------------");
//6.public static double pow(double a,double b) //取次方
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 3));//2的3次方 8.0
System.out.println(Math.pow(1.2, 2.3));
System.out.println("----------------");
//7.public static double random() //取随机数 [0.0,1.0)
System.out.println(Math.random());
}
}System
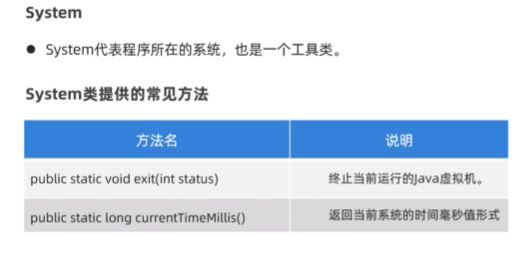
- System代表程序所在的系统,也是一个工具类
public class SystemTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标:了解下System类的常见方法
//1.public static void exit(int status);
// 终止当前运行的Java虚拟机
// int status 该参数用作状态代码;按照惯例,非零状态代码表示异常种植
// System.exit(0);//人为的终止虚拟机 (不要使用)
//2.public static long currenTimeMillis();
// 获取当前系统的时间
// 返回的是long类型的时间毫秒值,指的是从1970-1-1 0:0:0 开始走到此刻的总得毫秒值,1s = 1000ms
long time1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(time1);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
System.out.println("输出了" + i);
}
long time2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("共耗费" + (time2 - time1) / 1000.0 + "s");
}
}Runtime
- 代表程序所在的运行环境
- Runtime是一个单例类
import java.io.IOException;
public class RuntimeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//Runtime(单例类)
//1.public static Runtime getRuntime() //返回与当前Java应用程序关联的运行时对象
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
//2.public void exit(int status) //终结当前运行的虚拟机,该参数用作状态代码;按照惯例,非零状态表示异常终止
// r.exit(0);(不要使用)
//3.public int availableProcessors() //获取虚拟机能够使用的处理器数量
System.out.println(r.availableProcessors());
//4.public long totalMemory() //返回Java虚拟机中的内存总量
System.out.println(r.totalMemory()/1024.0/1024.0 + "MB");//1024B = 1KB ,1024KB = 1MB
//5.public long freeMemory() //返回Java虚拟机中的可用内存量
System.out.println(r.freeMemory()/1024.0/1024.0 + "MB");
//6.public Process exec(String command) //启动某个程序,并返回代表该程序的对象
Process p = r.exec("\"C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Tencent\\QQ\\Bin\\QQScLauncher.exe\"");
Thread.sleep(3000);//等待3秒钟再往下走
p.destroy();//销毁!关闭程序!
}
}BigDecimal
- 用于解决浮点型运算时出现结果失真的问题
- 把浮点型转换成BigDecimal的对象:
BigDecimal b = BigDecimal.valueOf(0.1);
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
public class BigDecimalDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标:掌握BigDecimal的使用,解决浮点数运算失真的问题
double a = 0.1;
double b = 0.2;
double c = a + b;
System.out.println(c);
System.out.println("--------------------");
//1.把浮点数转换成字符串进而来封装成BigDecimal对象来运算
// BigDecimal a1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(a));
// BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(b));
//推荐用以下方式,把小数转换成字符串再得到BigDecimal对象来使用(更简洁)
BigDecimal a1 = BigDecimal.valueOf(a);
BigDecimal b1 = BigDecimal.valueOf(b);
BigDecimal c1 = a1.add(b1);// +
BigDecimal c2 = a1.subtract(b1);// -
BigDecimal c3 = a1.multiply(b1);// *
BigDecimal c4 = a1.divide(b1);// /
System.out.println(c1);
BigDecimal i = BigDecimal.valueOf(0.1);
BigDecimal j = BigDecimal.valueOf(0.3);
// BigDecimal k = i.divide(j);
// System.out.println(k);//无法精确计算 报错
BigDecimal k = i.divide(j, 2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);//向上取整
System.out.println(k);
//把BigDecimal类型的数据转为Double类型的数据
double rs = k.doubleValue();
System.out.println(rs);
}
}JDK8之前传统的日期、时间
Date
- 代表的是日期和时间
- 日期对象的创建Data d = new Data();
- 获取日期对象的时间毫秒值long time = d.getTime();
- 时间毫秒转换成日期对象Date d1 = new Date(time + 1000 * 2);//2秒后的
Date d2 = new Date();
d2.setTime(time + 1000 * 2);方法综合运用:
import java.util.Date;
public class DateTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标:掌握Data日期类的使用
//1.创建一个Data的对象,代表系统当前的日期时间信息
Date d = new Date();
System.out.println(d);
//2.获取对象所对应的时间信息的时间毫秒值 距离 1970-01-01 00:00:00的毫秒值
long time = d.getTime();
System.out.println(time);
//时间毫秒值 -> 日期对象(对应的日期时间信息):
{
//3.把时间毫秒值转换成日期对象
time += 10 * 1000;//多了10s
Date d2 = new Date(time);
System.out.println(d2);
//4.直接把日期对象的时间通过setTime方法进行修改
// 设置日期对象的时间 为 当前时间毫秒值对应的时间
Date d3 = new Date();
d3.setTime(time);
System.out.println(d3);
}
}
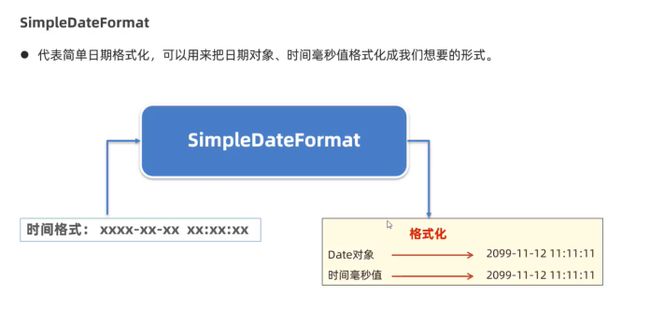
}SimpleDateFormat
- 代表简单日期格式化,用来把日期对象、时间毫秒值格式化成我们想要的形式
- SimpleDateFormat代表简单日期格式化,可以把日期对象、时间毫秒值格式化为我们想要的格式
- SimpleDateFormat创建对象SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("时间的格式");
- SimpleDateFormat格式化的方法
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss EEE a")//年-月-日 时-分-秒 周几 上/下午
//将日期对象格式化
Date d = new Date();
String rsByDate = sdf1.format(d);
//将时间毫秒值格式化
long time = d.getTime();
String rsByTime = sdf1.format(time);- SimpleDateFormat解析时间的方法(将字符串时间转换为Date)
String dateStr = "2023-7-22 21:33:05 周六 下午";
SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss EEE a")//年-月-日 时-分-秒 周几 上/下午
Date d = sdf2.parse(dateStr);方法概括:
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class SimpleDateFormatTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ParseException {
//目标:掌握SimpleDataFormat的使用
//1.准备一些时间(Data对象所指向的日期时间信息,以及调用Data方法得到的时间毫秒值)
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date);
long time = date.getTime();
System.out.println(time);
System.out.println("-----------------------");
//2.格式化日期对象,和时间毫秒值
//创建简单日期格式化对象,并封装想要得到的时间的格式
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss EEE a");
String rsByData = sdf.format(date);//将日期格式化成日期/时间字符串
System.out.println(rsByData);
// Thread.sleep(3000);
String rsByTime = sdf.format(time);//将时间毫秒值格式化成日期/时间字符串
System.out.println(rsByTime);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------");
//目标:掌握SimpleDataFormat解析字符串时间 成为 日期对象
String dataStr = "2022-12-12 12:12:12";
SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date d2 = sdf2.parse(dataStr);
System.out.println(d2);
}
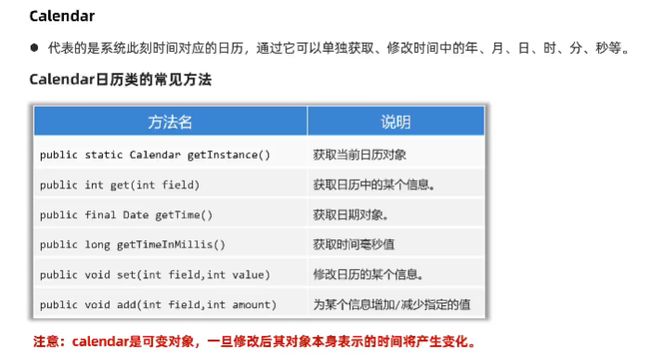
}Canlendar
- 代表的是系统此刻时间对应的日历
- 通过它可以单独获取、修改时间中的年、月、日、时、分、秒等
- 创建一个Calendar对象Calendar now = Calendar.getInstance();
常见方法汇总:
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class CalendarTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标:掌握Calendar的使用和特点
//1.得到系统此刻时间对应的日历对象
Calendar now = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println(now);
//2.获取日历的某个信息
int year = now.get(Calendar.YEAR);
System.out.println(year);
int month = now.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1;
System.out.println(month);
int days = now.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR);
System.out.println(days);
//3.拿到日历中记录的日期对象
Date d = now.getTime();
System.out.println(d);
//4.拿到日历所对应的时间毫秒值
long time = now.getTimeInMillis();
System.out.println(time);
//5.修改日历中的某个信息(只修改特定的常量值,其他常量值并不会随之该改变)
now.set(Calendar.MONTH,9);//修改月份成为10月份,月份从0开始
now.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR,1);//修改成一年中的第1天
System.out.println(now);
//6.为某个信息增加后减少多少
now.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR,100);
now.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR,-10);
now.add(Calendar.HOUR,12);
System.out.println(now);
}
}JDK8开始新增的日期、时间
为什么JDK8之后用这些API替换老的时间API
- 传统的实践类(Date、SimpleDateFormat、Calendar)存在如下问题:
-
- 1.设计不合理,使用不方便,很多都被淘汰了
- 2.老API都是可变对象,修改后会丢失最开始的时间信息
- 3.线程不安全
- 4.不能精确到纳秒,只能精确到毫秒
- Localxxx & Zonexxx
- LocalDate:代表本地日期(年、月、日、星期)
- LocalTime:代表本地时间(时、分、秒、纳秒)
- LocalDateTime:代表本地日期、时间(年、月、日、星期、时、分、秒、纳秒)
它们获取对象的方案
public static Localxxx now();//获取系统当前时间对应的该对象
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.now();
LocalTime lt = LocalTime.now();
LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.now();
public static Localxxx of(...);//获取指定时间的对象
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.of(2023,7,24);
LocalTime lt = LocalTime.of(16,17,12);
LocalDateTime ld = LocalDateTime.of(2023,7,24,16,17,12);Localxxx的常用API
| 获取Locaxxx对象特定信息 |
public int getxxx(); |
| 直接修改某个信息 |
public int withxxx(); |
| 把某个信息加多少 |
public int plusxxx(); |
| 把某个信息减多少 |
public int minusxxx(); |
| 获取指定日期(年月日时分秒)的Localxxx对象: |
public static Localxxx of(...);//获取指定时间的对象 |
| 判断2个日期对象,是否相等,在前还是在后 |
equals isBefore、isAfter |
| 可以把LocalDateTime对象转换成LocalDate和LocalTime对象 |
public LocalDate toLocalDate()//拆分 public LocalTime toLocalTime()//拆分 public static LocalDateTime of(LocalDate date,LocalTime time)//合并 |
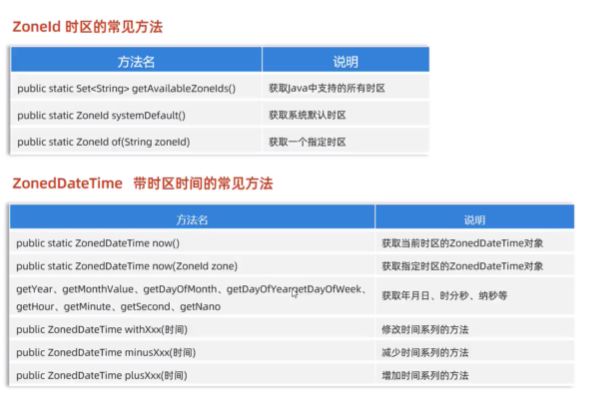
- ZoneId:代表时区ID(由于世界各个国家与地区的京都不同,各地区的时间也有所不同,因此会划分为不同的时区)
-
- 世界标准时间(UTC)
- 中国标准时间:UTC + 8小时
ZoneId & ZonedDateTime常用API
import java.time.Clock;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class Test4_ZoneId_ZonedDateTime {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标:了解时区和带时区的时间
//1.ZoneId的常见方法
//public static ZoneId systemDefault(); 获取当前系统默认的时区
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.systemDefault();
System.out.println(zoneId.getId());
System.out.println(zoneId);//jvm调用toString(toString重写,调用getId方法)
//public static Set getAvailableZoneIds 获取Java支持的全部时区Id
System.out.println(ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds());
//public static ZoneId of(String zoneId) : 把某个时区id封装成ZoneId对象
ZoneId zoneId1 = ZoneId.of("America/New_York");
System.out.println(zoneId1);
//2.ZonedDateTime 带时区的时间
//public static ZonedDateTime now(ZoneId zone) 获取某个时区的ZoneDateTime对象
ZonedDateTime nowInNew_York = ZonedDateTime.now(zoneId1);
System.out.println(nowInNew_York);
//世界标准时间
ZonedDateTime nowBasic = ZonedDateTime.now(Clock.systemUTC());
System.out.println(nowBasic);
//public static ZonedDateTime now() 获取当前系统默认时区的ZonedDateTime对象
ZonedDateTime now_moren = ZonedDateTime.now();
System.out.println(now_moren);
//ZonedDateTime还有一些与LocalDateTime相同的api,修改时间,增减某一特定信息
}
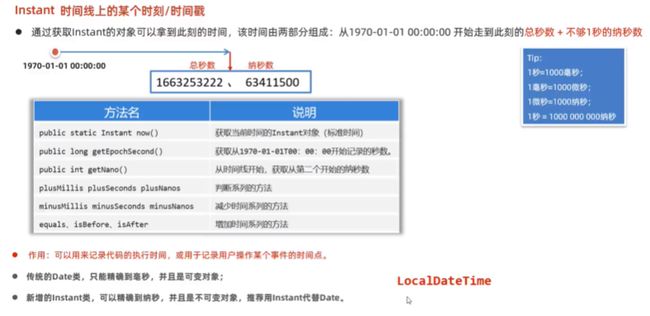
} - Instant
- 时间线上的某个时刻
- 通过获取Instant的对象可以拿到此刻的时间,该时间由两部分组成:从1970-01-01 00:00:00开始走到此刻的总秒数 + 不够1秒的纳秒数
import java.time.Instant;
public class Test5_instant {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建Instant对象,获取此刻时间信息
Instant now = Instant.now();//不可变对象
System.out.println(now);
//2.获取距1970-01-01 00:00:00的总秒数
long second = now.getEpochSecond();
System.out.println(second);
//3.不够1秒的纳秒数
int nano = now.getNano();
System.out.println(nano);
//经典的加plus、减时间minus、判断时间(equals、isBefore、isAfter)
Instant now1 = now.plusSeconds(100).minusSeconds(40);
System.out.println(now1);
System.out.println(now.isBefore(now1));//true
//Instant对象的作用:做代码的性能分析,或者记录用户的操作时间点
Instant now2 = Instant.now();
//代码执行
// for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
// System.out.println("输出" + i);
// }
Instant now3 = Instant.now();
System.out.println((now3.getEpochSecond() - now2.getEpochSecond() + "s ") + (now3.getNano() - now2.getNano() + "ns"));
}
}- 作用:可以用来记录代码的执行时间,或用于记录用户操作某个时间的时间点
- 传统的Date类,只能精确到毫秒,并且是可变对象
- 新增的Instant类,可以精确到纳秒,并且时不可变对象,推荐用Instant代替Date
- 为什么不用LocalDateTime代替Date?
-
- 相比于LocalDateTime类,Instant多出了转换成时间秒数、纳秒数的方法,使用起来更方便
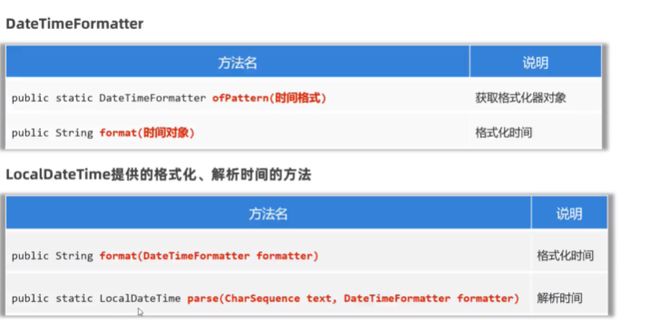
- DateTimeFormatter
- 日期时间格式化器,用于时间的格式化(时间对象 -> 字符串形式)、解析(字符串形式 -> 时间对象)
- 支持LocalDateTime类、ZoneDateTime类、Instant类
- 较SimpleDateFormatter类的优点:线程安全
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class Test6_DateTimeFormatter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建一个日期时间格式化器对象
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
//2.对时间对象进行格式化(LocalDateTime、ZoneDateTime、Instant...)
LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(ldt);
String rs = dtf.format(ldt);//正向格式化
System.out.println(rs);
//3.格式化时间,对于LocalDateTime类其实还有一种方案
String rs1 = ldt.format(dtf);//反向格式化
System.out.println(rs1);
//4.解析时间:解析时间一般使用LocalDateTime提供的解析方法parse来解析
String dtStr = "2012年12月12日 12:12:12";
LocalDateTime ldt1 = LocalDateTime.parse(dtStr, dtf);
System.out.println(ldt1);
}
}- Period & Duration
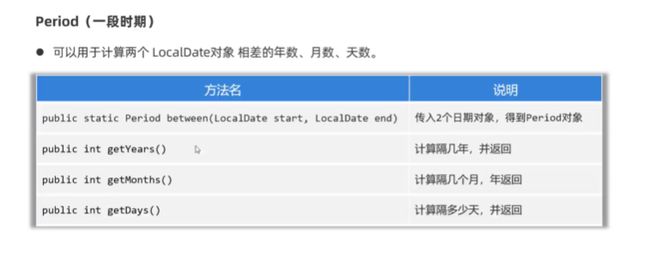
- Period:计算日期间隔(年、月、日)
-
- 支持LocalDate类的对象
- Duration:计算时间间隔(时、分、秒、纳秒)
-
- 支持LocalTime类、LocalDateTime类、Instant类的对象
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.Period;
public class Test7_Period {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//掌握Period的作用,计算两个日期对象(LocalDate)相差的年、月、日
LocalDate d1 = LocalDate.of(2049, 1, 31);
LocalDate d2 = LocalDate.of(2049, 3, 1);
//1.创建Period对象,需要封装两个想要判断的日期对象
Period period = Period.between(d1, d2);
//2.通过Period对象获取两个日期对象相差的信息
System.out.println(period.getYears());
System.out.println(period.getMonths());
System.out.println(period.getDays());
}
}import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class Test8_Duration {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Duration的使用
//计算两个日期对象(LocalDateTime、LocalTime、Instant)相差的天、小时、分钟、秒、毫秒、纳秒
LocalDateTime start = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 10, 5, 12, 12, 12);
LocalDateTime end = LocalDateTime.now();
//1.创建一个Duration对象
Duration duration = Duration.between(start, end);
//2.获取两个时间对象间隔信息
System.out.println(duration.toDays());
System.out.println(duration.toHours());
System.out.println(duration.toMinutes());
System.out.println(duration.toSeconds());
System.out.println(duration.toMillis());
System.out.println(duration.toNanos());
}
}Arrays
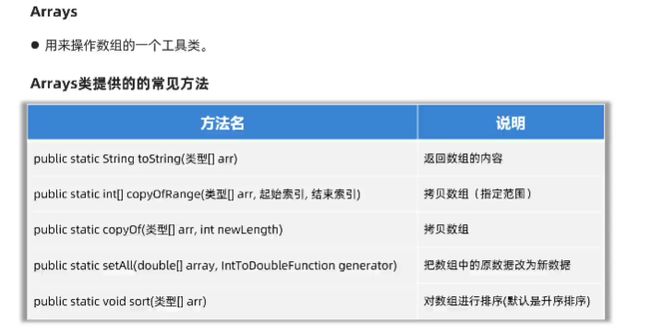
- 用来操作数组的一个工具类
Arrays类提供的常见API
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.function.IntToDoubleFunction;
public class ArraysTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.public static String toString(类型[] arr) 返回数组的内容
int[] arr = {10,20,30,40,50,60};
System.out.println(arr.toString());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
//2.public static 类型[] copyOfRange(类型[] arr ,起始索引,结束索引) 将该地址下的数组的指定范围元素拷贝一份到新数组(包前不包后)
int[] arr1 = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, 1, 4);//[20,30,40]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
//3.public static copyOf(类型[] arr,int newLength) 拷贝数据,可以指定新数组的长度
int[] arr2 = Arrays.copyOf(arr, 10);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
//4.public static setAll(double[] array,IntToDoubleFunction generator) 把数组中的每个值取出来改变为想要的值再放回去
double[] prices = {99.8,120,100};
//打八折
Arrays.setAll(prices, new IntToDoubleFunction() {
@Override
public double applyAsDouble(int value) {
BigDecimal b = BigDecimal.valueOf(prices[value]);
BigDecimal zheKou = BigDecimal.valueOf(0.8);
double rs = b.multiply(zheKou).doubleValue();
return rs;
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(prices));
//5.public static void sort(类型[] arr) 对数组进行排序(默认是升序排序)
Arrays.sort(prices);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(prices));
}
}如果数组中存储的是对象,该如何排序
- 让该对象的类实现Comparable(比较规则)接口,然后重写compareTo方法,自己来制定比较规则
推荐:
- 使用下面这个sort方法,创建Comparator比较器接口的匿名内部类对象,然后自己制定比较规则
public static void sort(T[] arr,Comparator c)
//对数组进行自定义排序规则 import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class ArrrayTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标:掌握如何对存储对象的数组中的对象进行排序
Student[] students = new Student[4];
students[0] = new Student("蜘蛛精",23,169.5);
students[1] = new Student("至尊宝",27,178);
students[2] = new Student("紫霞",26,170.5);
students[3] = new Student("紫霞",26,170.5);
//1.public static void sort(类型[] arr) 对数组进行排序
// Arrays.sort(students);
//2.public static void sort(T[] ,Comparator c)
//参数一:需要排序的数组
//参数二:Comparator比较器对象(用来制定对象的比较规则)
Arrays.sort(students, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
//制定比较规则:左边对象o1,右边对象o2
//约定1:认为左边对象大于右边对象 返回正整数
//约定2:认为左边对象小于右边对象 返回负整数
//约定3:认为左边对象等于右边对象 返回0
return Double.compare(o1.getHeight(),o2.getHeight());
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(students));
}
}
//a.Comparable 比较规则接口
class Student implements Comparable{
private String name;
private int age;
private double height;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, double height) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.height = height;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
@Override
//交给sort方法调用,所比较的数组中的元素调用 arr[?].compareTo(???)
public int compareTo(Student o) {
//约定1:认为左边对象大于右边对象 返回正整数
//约定2:认为左边对象小于右边对象 返回负整数
//约定3:认为左边对象等于右边对象 返回0
return this.age - o.age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", height=" + height +
'}';
}
} JDK8新特性:Lambda表达式
- Lambda表达式是JDK8开始新增的一种语法形式;作用:用于简化匿名内部类的代码写法
- 注意:Lambda表达式只能简化函数式接口的匿名内部类
-
- 函数式接口
-
-
- 有且仅有一个抽象方法的接口
- 注意:将来我们见到的大部分函数式接口,上面都可能会有@FunctionalInterface的注解,有该注解的接口必定是函数式接口
-
- 格式
(被重写的方法的形参列表) -> {
被重写方法的方法体代码;
}Lambda表达式的省略写法(进一步简化Lambda表达式的写法)
- 参数类型可省略不写
- 如果只有一个形参,()也可以省略
- 如果Lambda表达式的方法体只有一行代码,可以省略大括号不谢,同时要省略分号!此时,若这行代码是return语句,也必须去掉return不写。
Arrays.sort(students, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
}
});
//使用Lambda简化后的形式
Arrays.sort(students, ( o1, o2) -> o1.getAge() - o2.getAge()); JDK8新特性:方法引用
用来更进一步简化Lambda表达式
- 注意:正常编码时发现能简化则简化,不要刻意使用
静态方法的引用
- 类名::静态方法
- 使用场景:如果某个Lambda表达式里只是调用了一个静态方法,并且前后参数的形式一致,就可以使用静态方法引用
//使用Lambda简化后的形式
Arrays.sort(students, ( o1, o2) -> o1.getAge() - o2.getAge());
Arrays.sort(students, (Student o1, Student o2) -> CompareByData.compareByAge(o1,o2));
//静态方法引用
Arrays.sort(students, CompareByData::compareByAge);实例方法的引用
- 对象名::静态方法
- 使用场景:如果某个Lambda表达式里只是调用了一个实例方法,并且前后参数的形式一致,就可以使用实例方法引用
//实例方法引用
CompareByData cp = new CompareByData();
Arrays.sort(students,(o1, o2) -> cp.compareByAgeDesc(o1,o2));
Arrays.sort(students,cp::compareByAgeDesc);特定类型的方法的引用
- 类型::静态方法
- 使用场景:如果某个Lambda表达式里只是调用了一个实例方法,并且前后参数的形式一致,就可以使用特定类型的方法引用
//忽略大小写排序
// Arrays.sort(names, new Comparator() {
// @Override
// public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
// return o1.compareToIgnoreCase(o2);
// }
// });
//Lambda表达式简化
// Arrays.sort(names, (o1, o2) -> o1.compareToIgnoreCase(o2));
//类型简化
Arrays.sort(names, String::compareToIgnoreCase);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(names)); 构造器的引用
- 类名::静态方法
- 使用场景:如果某个Lambda表达式里只是创建对象,并且前后参数的形式一致,就可以使用构造器引用
//1.创建这个接口的匿名内部类对象
// CreateCar cc = new CreateCar() {
// @Override
// public Car create(String name, double price) {
// return new Car(name, price);
// }
// };
//Lambda表达式简化
// CreateCar cc = (name, price) -> new Car(name, price);
//构造器引用
CreateCar cc = Car::new;
cc.create("奔驰",49.9);
System.out.println(cc);