一、为什么封装数据库?
其实封装数据库的原因和封装网络连接的原因是相同的。在这我们就简单的说一下原因:类似于网络连接,数据库创建和操作的方式也是很多了:不同数据库有不同的API,像MySQL,SQLite等,在Xutils框架中也给我们封装了数据库的操作方法。假设在开发应用时,我们使用的是SQLite数据库及其API,但是在接下来的升级和维护中,我们要将数据库的操作修改为xUtils框架提供的方法,这时,如果我们没有封装数据库就会需要大量的修改代码,这样会给我们的应用打来很大的威胁。如果我们应用的数据库操作封装为一个类,当替换数据库操作方法时,只替换封装的部分即可,简单方便又安全。
二、封装数据库
在本次的开发实践中我们使用的是SQLite数据库,整理就封装SQLite数据库了。
1. 创建SQLiteOpenHelper
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2015/10/8.
*/
public class MySQLiteOpenHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private static MySQLiteOpenHelper helper;
private MySQLiteOpenHelper(Context context, String name, SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory, int version) {
super(context, name, factory, version);
}
private MySQLiteOpenHelper(Context context, String name) {
this(context, name, null, 1);
}
public static synchronized MySQLiteOpenHelper getInstance(Context context) {
if(helper==null){
helper = new MySQLiteOpenHelper(context, "DayDayUpDb");
}
return helper;
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase) {
sqLiteDatabase.execSQL("create table if not exists "+TableConfig.TABLE_CUSTOMER+"("
+TableConfig.Customer.CUSTOMER_ID+" integer not null primary key autoincrement,"
+TableConfig.Customer.CUSTOMER_NAME+ " verchar(20),"
+TableConfig.Customer.DELIVERY_PHONE+ " verchar(20),"
+TableConfig.Customer.ADDR+ " verchar(20) ,"
+TableConfig.Customer.ACCESS_TYPE+ " verchar(20),"
+TableConfig.Customer.CUSTOMER_RATING+ " verchar(20), "
+TableConfig.Customer.LAYERS+ " verchar(20),"
+TableConfig.Customer.CONTACTS+ " verchar(20),"
+TableConfig.Customer.REMARK+ " verchar(20))");
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase, int i, int i1) {
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
Point: 创建一个数据库,初始化数据库时创建数据库中包含的数据表。可能大家会注意到,创建数据表如下:
sqLiteDatabase.execSQL("create table if not exists "+TableConfig.TABLE_CUSTOMER+"("
+TableConfig.Customer.CUSTOMER_ID+" integer not null primary key autoincrement,"
+TableConfig.Customer.CUSTOMER_NAME+ " verchar(20),"
+TableConfig.Customer.DELIVERY_PHONE+ " verchar(20),"
+TableConfig.Customer.ADDR+ " verchar(20) ,"
+TableConfig.Customer.ACCESS_TYPE+ " verchar(20),"
+TableConfig.Customer.CUSTOMER_RATING+ " verchar(20), "
+TableConfig.Customer.LAYERS+ " verchar(20),"
+TableConfig.Customer.CONTACTS+ " verchar(20),"
+TableConfig.Customer.REMARK+ " verchar(20))");
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
在创建时,使用到了TableConfig这个类,这个类也是我们自己定义的,用来存储一些数据库中数据表的表名,字段名等常量。可以看一下TableConfig类:
public class TableConfig {
public static final String TABLE_CUSTOMER = "customer";
/**
* Customer数据表的字段
*/
public static class Customer{
public static final String CUSTOMER_ID="id";
public static final String CUSTOMER_NAME="customerName";
public static final String DELIVERY_PHONE="deliveryPhone";
public static final String ADDR="addr";
public static final String ACCESS_TYPE="accessType";
public static final String CUSTOMER_RATING="customerRating";
public static final String LAYERS="layers";
public static final String REMARK="remark";
public static final String CONTACTS="contacts";
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
2. 创建数据库
咦,为什么第二部还是创建数据库来?
因为在第一步中我们指创建了一个数据库的创建类,并没有调用它创建数据库,在这一布中我们就要创建数据库啦!
public class DbManager {
private static DbManager manager;
private MySQLiteOpenHelper mySQLiteOpenHelper;
private SQLiteDatabase db;
/**
* 私有化构造器
*/
private DbManager() {
mySQLiteOpenHelper = MySQLiteOpenHelper.getInstance(BaseApplication.getContext());
if (db == null) {
db = mySQLiteOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
}
}
/**
* 单例DbManager类
*
* @return 返回DbManager对象
*/
public static DbManager newInstances() {
if (manager == null) {
manager = new DbManager();
}
return manager;
}
/**
* 获取数据库的对象
*
* @return 返回SQLiteDatabase数据库的对象
*/
public SQLiteDatabase getDataBase() {
return db;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
PointOne: 这里我们创建了一个数据库的创建类,这样当我们要创建数据库只需要调用如下简单的异步就可以了:
DbManager manager = DbManager.newInstances();
SQLiteDatabase db = manager.getDataBase();
PointTwo: 细心的同志们一定会发现在我们构造器中创建数据库时还是用到了另一个类:
/**
* 私有化构造器
*/
private DbManager() {
mySQLiteOpenHelper = MySQLiteOpenHelper.getInstance(BaseApplication.getContext());
if (db == null) {
db = mySQLiteOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
}
}
这里使用到了BaseApplication,先看BaseApplication的定义:
public class BaseApplication extends Application {
private static BaseApplication mApplication;
/**
* 获取Context
* @return 返回Context的对象
*/
public static Context getContext(){
return mApplication.getApplicationContext();
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
this.mApplication = this;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
在这个类中我们定义一个静态获得Context上下文的方法,以后我们在也不用为获得不了Context二发愁啦!
BaseApplication类继承Application ,我们定义当应用启动时调用这个BaseApplication启动。然后我们在BaseApplication类中做一些初始化等的操作,这个了诶的定义会在接下来的博客中详细讲解。这里不多说。
3. 操作数据库
数据库,数据表都创建好了,我们就该哦操作数据库了,我们定义有一个数据表达额操作类,将数据库的操作封装在这里:
public class TableOperate {
private DbManager manager;
private SQLiteDatabase db;
public TableOperate() {
manager = DbManager.newInstances();
db = manager.getDataBase();
}
/**
* 查询数据库的名,数据库的添加
*
* @param tableName 查询的数据库的名字
* @param entityType 查询的数据库所对应的module
* @param fieldName 查询的字段名
* @param value 查询的字段值
* @param 泛型代表AttendInformation,Customer,Order,User,WorkDaily类
* @return 返回查询结果,结果为AttendInformation,Customer,Order,User,WorkDaily对象
*/
public ArrayList query(String tableName, Class entityType, String fieldName, String value) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
Cursor cursor = db.query(tableName, null, fieldName + " like ?", new String[]{value}, null, null, " id desc", null);
cursor.moveToFirst();
while (!cursor.isAfterLast()) {
try {
T t = entityType.newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < cursor.getColumnCount(); i++) {
String content = cursor.getString(i);
String columnName = cursor.getColumnName(i);
Field field = entityType.getDeclaredField(columnName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, content);
field.setAccessible(false);
}
list.add(t);
cursor.moveToNext();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return list;
}
/**
* 向数据库插入数据
*
* @param tableName 数据库插入数据的数据表
* @param object 数据库插入的对象
*/
public void insert(String tableName, Object object) {
Class clazz = object.getClass();
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
ContentValues value = new ContentValues();
for (Field field : fields) {
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
String content = (String) field.get(object);
value.put(field.getName(), content);
field.setAccessible(false);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
db.insert(tableName, null, value);
}
/**
* 删除数据
*
* @param tableName 删除数据库的表名
* @param fieldName 删除的字段名
* @param value 删除的字段的值
*/
public void delete(String tableName, String fieldName, String value) {
db.delete(tableName, fieldName + "=?", new String[]{value});
}
/**
* 更改数据库内容
*
* @param tableName 更改数据的数据表
* @param columnName 更改的数据的字段名
* @param columnValue 更改的数据的字段值
* @param object 更改的数据
*/
public void uptate(String tableName, String columnName, String columnValue, Object object) {
try {
Class clazz = object.getClass();
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
ContentValues value = new ContentValues();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
String content = (String) field.get(object);
value.put(field.getName(), content);
field.setAccessible(false);
}
db.update(tableName, value, columnName+ "=?", new String[]{columnValue});
} catch (IllegalAccessException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
这里定义了数据库“增删改查”四种操作。在讲解四种方法之前,首先要说明一下,每一个数据表都一个他自己对应的module类,一般我们都会将这个module类存放在dao文件夹下(dao文件夹是新建的,用于存放module类的),就像我们的”客户“数据表,就有一个它对应的Customer类:
public class Customer {
private String customerName;
private String deliveryPhone;
private String addr;
private String accessType;
private String customerRating;
private String layers;
private String remark;
private String contacts;
public String getCustomerName() {
return customerName;
}
public void setCustomerName(String customerName) {
this.customerName = customerName;
}
public String getDeliveryPhone() {
return deliveryPhone;
}
public void setDeliveryPhone(String deliveryPhone) {
this.deliveryPhone = deliveryPhone;
}
public String getAddr() {
return addr;
}
public void setAddr(String addr) {
this.addr = addr;
}
public String getAccessType() {
return accessType;
}
public void setAccessType(String accessType) {
this.accessType = accessType;
}
public String getCustomerRating() {
return customerRating;
}
public void setCustomerRating(String customerRating) {
this.customerRating = customerRating;
}
public String getLayers() {
return layers;
}
public void setLayers(String layers) {
this.layers = layers;
}
public String getRemark() {
return remark;
}
public void setRemark(String remark) {
this.remark = remark;
}
public String getContacts() {
return contacts;
}
public void setContacts(String contacts) {
this.contacts = contacts;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
PointOne: ”增“:
/**
* 向数据库插入数据
*
* @param tableName 数据库插入数据的数据表
* @param object 数据库插入的对象
*/
public void insert(String tableName, Object object) {
Class clazz = object.getClass();
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
ContentValues value = new ContentValues();
for (Field field : fields) {
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
String content = (String) field.get(object);
value.put(field.getName(), content);
field.setAccessible(false);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
db.insert(tableName, null, value);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
因为我们针对的是不同的数据表,所有我们这里使用到了反射,将传入的modulel类通过返回或的它所有的属性,然后将属性中的内容添加到ContentValues 对象中,进而添加到数据表中。
PointTwo: ”删“:
/**
* 删除数据
* @param tableName 删除数据库的表名
* @param fieldName 删除的字段名
* @param value 删除的字段的值
*/
public void delete(String tableName, String fieldName, String value) {
db.delete(tableName, fieldName + "=?", new String[]{value});
}
删除比较简单,不用多讲吧。
PointThree: ”改“:
/**
* 更改数据库内容
* @param tableName 更改数据的数据表
* @param columnName 更改的数据的字段名
* @param columnValue 更改的数据的字段值
* @param object 更改的数据
*/
public void uptate(String tableName, String columnName, String columnValue, Object object) {
try {
Class clazz = object.getClass();
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
ContentValues value = new ContentValues();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
String content = (String) field.get(object);
value.put(field.getName(), content);
field.setAccessible(false);
}
db.update(tableName, value, columnName+ "=?", new String[]{columnValue});
} catch (IllegalAccessException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
同样是利用反射的原理,将object中的内容添加到ContentValues 对象中,然后调用update()方法修改。
PointFour: ”查“:
/**
* 查询数据库的名,数据库的添加
*
* @param tableName 查询的数据库的名字
* @param entityType 查询的数据库所对应的module
* @param fieldName 查询的字段名
* @param value 查询的字段值
* @param 泛型代表AttendInformation,Customer,Order,User,WorkDaily类
* @return 返回查询结果,结果为AttendInformation,Customer,Order,User,WorkDaily对象
*/
public ArrayList query(String tableName, Class entityType, String fieldName, String value) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
Cursor cursor = db.query(tableName, null, fieldName + " like ?", new String[]{value}, null, null, " id desc", null);
cursor.moveToFirst();
while (!cursor.isAfterLast()) {
try {
T t = entityType.newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < cursor.getColumnCount(); i++) {
String content = cursor.getString(i);
String columnName = cursor.getColumnName(i);
Field field = entityType.getDeclaredField(columnName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, content);
field.setAccessible(false);
}
list.add(t);
cursor.moveToNext();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return list;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
查询数据库传入了四个参数,其中Class entityType是传入的数据库中数据表的module。通过反射机制查询。
4. 数据库初始化
创建好数据库,在每次加载应用时,我么需要对数据库进行初始化。这里我们定义一个类:
public class DataBaseInit {
/**
* 初始化客户数据表
*/
public static void initCustomerTable() {
Customer customer1 = new Customer();
customer1.setCustomerName("华庆丰");
customer1.setDeliveryPhone("15345675673");
customer1.setAddr("前进");
customer1.setAccessType("农贸批发");
customer1.setCustomerRating("A");
customer1.setLayers("默认图层");
customer1.setRemark("");
customer1.setContacts("");
Customer customer2 = new Customer();
customer2.setCustomerName("物美草桥");
customer2.setDeliveryPhone("");
customer2.setAddr("");
customer2.setAccessType("");
customer2.setCustomerRating("");
customer2.setLayers("");
customer2.setRemark("");
customer2.setContacts("");
Customer customer3 = new Customer();
customer3.setCustomerName("京客隆");
customer3.setDeliveryPhone("15937542659");
customer3.setAddr("前进华润五金机电附近");
customer3.setAccessType("农贸批发");
customer3.setCustomerRating("A");
customer3.setLayers("默认图层");
customer3.setRemark("");
customer3.setContacts("");
TableOperate operate = new TableOperate();
operate.insert(TableConfig.TABLE_CUSTOMER,customer1);
operate.insert(TableConfig.TABLE_CUSTOMER,customer2);
operate.insert(TableConfig.TABLE_CUSTOMER, customer3);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
这里我们就只向数据表中添加了几条数据。
然后下面注释掉的部分是数据库其他操作的使用范例。
目录结构
这样我们的数据库就基本封装完成了,我们来通过一个目录结构来理一下封装的思路:
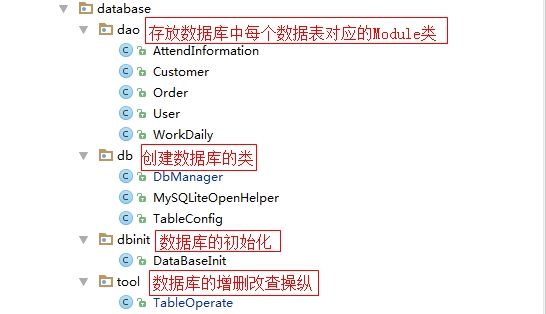
我们通过下面这张图来加深印象:
![]()