C语言:popen函数的使用
C语言:popen函数的使用
一、利用system函数调用shell命令,只能获取到shell命令的返回值,而不能获取shell命令的输出结果,那如果想获取输出结果怎么办呢?用popen函数可以实现。
二、定义函数:FILE * popen(const char * command, const char * type);
函数说明:popen()会调用fork()产生子进程,然后从子进程中调用/bin/sh -c 来执行参数command 的指令。
参数type 可使用 "r"代表读取,"w"代表写入。依照此type 值,popen()会建立管道连到子进程的标准输出设备或标准输入设备,然后返回一个文件指针。随后进程便可利用此文件指针来读取子进程的输出设备或是写入到子进程的标准输入设备中。
此外,所有使用文件指针(FILE*)操作的函数也都可以使用,除了fclose()以外。
返回值:若成功则返回文件指针, 否则返回NULL, 错误原因存于errno 中.
三、实例测试
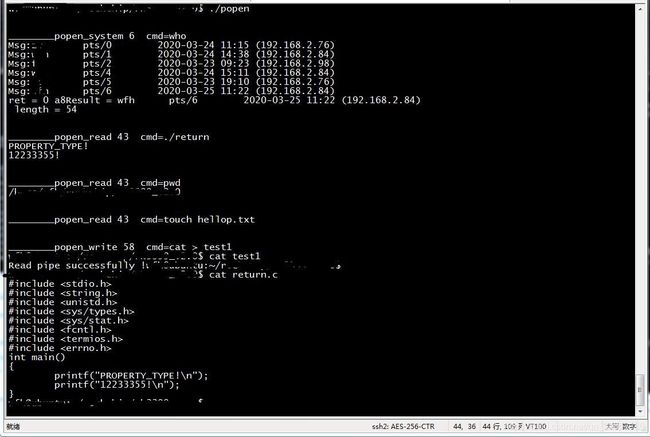
1、popen.c
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
int popen_system(const char * cmd, char *pRetMsg, int msg_len)
{
printf("\n\n________%s %d cmd=%s\n", __func__, __LINE__,cmd);
FILE * fp;
char * p = NULL;
int res = -1;
if (cmd == NULL || pRetMsg == NULL || msg_len < 0)
{
printf("Param Error!\n");
return -1;
}
if ((fp = popen(cmd, "r") ) == NULL)
{
printf("Popen Error!\n");
return -2;
}
else
{
memset(pRetMsg, 0, msg_len);
//get lastest result
while(fgets(pRetMsg, msg_len, fp) != NULL)
{
printf("Msg:%s",pRetMsg); //print all info
}
if ( (res = pclose(fp)) == -1)
{
printf("close popenerror!\n");
return -3;
}
//pRetMsg[strlen(pRetMsg)-1] = '\0';
pRetMsg[strlen(pRetMsg)] = '\0';
return 0;
}
}
void popen_read(const char*cmd)
{
printf("\n\n________%s %d cmd=%s\n", __func__, __LINE__,cmd);
FILE *fp;
char buf[200] = {0};
if((fp = popen(cmd, "r")) == NULL) {
perror("Fail to popen\n");
exit(1);
}
while(fgets(buf, 200, fp) != NULL) {
printf("%s", buf);
}
pclose(fp);
}
void popen_write(const char*cmd)
{
printf("\n\n________%s %d cmd=%s\n", __func__, __LINE__,cmd);
FILE *fp;
char buf[200] = {0};
if((fp = popen(cmd, "w")) == NULL) {
perror("Fail to popen\n");
exit(1);
}
fwrite("Read pipe successfully !", 1, sizeof("Read pipe successfully !"), fp);
pclose(fp);
}
int main()
{
char *cmd = "who ";
char a8Result[128] = {0};
int ret = 0;
int i=0;
memset(a8Result, 0, strlen(a8Result));
ret=popen_system(cmd, a8Result, sizeof(a8Result));
printf("ret = %d a8Result = %s length = %d \n", ret, a8Result, strlen(a8Result));
popen_read("./return");
popen_read("pwd");
popen_read("touch hellop.txt");
popen_write("cat > test1");//
return 0;
}2、编译&执行