linux内存管理(十三)-内存规整过程分析
现在看看内存规整迁移再分配函数,__alloc_pages_direct_compact,函数在mm/page_alloc.c文件中:
/* Try memory compaction for high-order allocations before reclaim */
static struct page *
__alloc_pages_direct_compact(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order,
unsigned int alloc_flags, const struct alloc_context *ac,
enum compact_priority prio, enum compact_result *compact_result)
{
struct page *page;
unsigned int noreclaim_flag;
if (!order)//order为0情况,不用进行内存规整
return NULL;
noreclaim_flag = memalloc_noreclaim_save();
//直接内存规整来满足高阶分配需求
*compact_result = try_to_compact_pages(gfp_mask, order, alloc_flags, ac,
prio);
memalloc_noreclaim_restore(noreclaim_flag);
if (*compact_result <= COMPACT_INACTIVE)
return NULL;
/*
* At least in one zone compaction wasn't deferred or skipped, so let's
* count a compaction stall
*/
count_vm_event(COMPACTSTALL);
//在规整完成后进行页面分配操作
page = get_page_from_freelist(gfp_mask, order, alloc_flags, ac);
if (page) {
struct zone *zone = page_zone(page);
zone->compact_blockskip_flush = false;
compaction_defer_reset(zone, order, true);
count_vm_event(COMPACTSUCCESS);
return page;
}
/*
* It's bad if compaction run occurs and fails. The most likely reason
* is that pages exist, but not enough to satisfy watermarks.
*/
count_vm_event(COMPACTFAIL);
cond_resched();
return NULL;
}
__alloc_pages_direct_compact首先执行规整操作,然后进行页面分配。页面分配就好说了,就是我们很熟悉的get_page_from_freelist函数,规整操作是调用try_to_compact_pages完成的。linux系统进行页面回收只有两种方式,一种是上面没有详细讲解的异步回收,通过唤醒一个线程回收页面,另一种就是try_to_compact_pages函数实现的同步页面回收。try_to_compact_pages函数位于mm/compaction.c文件中:
/**
* try_to_compact_pages - Direct compact to satisfy a high-order allocation
* @gfp_mask: The GFP mask of the current allocation
* @order: The order of the current allocation
* @alloc_flags: The allocation flags of the current allocation
* @ac: The context of current allocation
* @prio: Determines how hard direct compaction should try to succeed
*
* This is the main entry point for direct page compaction.
*/
enum compact_result try_to_compact_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order,
unsigned int alloc_flags, const struct alloc_context *ac,
enum compact_priority prio)
{
int may_perform_io = gfp_mask & __GFP_IO;
struct zoneref *z;
struct zone *zone;
enum compact_result rc = COMPACT_SKIPPED;
/*
* Check if the GFP flags allow compaction - GFP_NOIO is really
* tricky context because the migration might require IO
*/
//检查GFP标志是否允许规整
if (!may_perform_io)
return COMPACT_SKIPPED;
trace_mm_compaction_try_to_compact_pages(order, gfp_mask, prio);
/* Compact each zone in the list */
//根据掩码遍历zonelist每个zone
for_each_zone_zonelist_nodemask(zone, z, ac->zonelist, ac->high_zoneidx,
ac->nodemask) {
enum compact_result status;
//如果优先级低并且判断为可能overflow就跳过这个zone
if (prio > MIN_COMPACT_PRIORITY
&& compaction_deferred(zone, order)) {
rc = max_t(enum compact_result, COMPACT_DEFERRED, rc);
continue;
}
//针对特定zone进行规整
status = compact_zone_order(zone, order, gfp_mask, prio,
alloc_flags, ac_classzone_idx(ac));
rc = max(status, rc);
/* The allocation should succeed, stop compacting */
if (status == COMPACT_SUCCESS) {
/*
* We think the allocation will succeed in this zone,
* but it is not certain, hence the false. The caller
* will repeat this with true if allocation indeed
* succeeds in this zone.
*/
compaction_defer_reset(zone, order, false);
break;
}
if (prio != COMPACT_PRIO_ASYNC && (status == COMPACT_COMPLETE ||
status == COMPACT_PARTIAL_SKIPPED))
/*
* We think that allocation won't succeed in this zone
* so we defer compaction there. If it ends up
* succeeding after all, it will be reset.
*/
defer_compaction(zone, order);
/*
* We might have stopped compacting due to need_resched() in
* async compaction, or due to a fatal signal detected. In that
* case do not try further zones
*/
//检测到致命信号,停止规整,不要尝试进一步的区域
if ((prio == COMPACT_PRIO_ASYNC && need_resched())
|| fatal_signal_pending(current))
break;
}
return rc;
}
try_to_compact_pages会遍历每一个zone,然后针对每一个zone调用compact_zone_order进行内存规整,compact_zone_order:
static enum compact_result compact_zone_order(struct zone *zone, int order,
gfp_t gfp_mask, enum compact_priority prio,
unsigned int alloc_flags, int classzone_idx)
{
enum compact_result ret;
struct compact_control cc = {
.nr_freepages = 0,
.nr_migratepages = 0,
.total_migrate_scanned = 0,
.total_free_scanned = 0,
.order = order,//需要规整的页面阶数
.gfp_mask = gfp_mask,//页面规整的页面掩码
.zone = zone,
.mode = (prio == COMPACT_PRIO_ASYNC) ?
MIGRATE_ASYNC : MIGRATE_SYNC_LIGHT,//页面规整模式(同步、异步)
.alloc_flags = alloc_flags,
.classzone_idx = classzone_idx,
.direct_compaction = true,
.whole_zone = (prio == MIN_COMPACT_PRIORITY),
.ignore_skip_hint = (prio == MIN_COMPACT_PRIORITY),
.ignore_block_suitable = (prio == MIN_COMPACT_PRIORITY)
};
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cc.freepages);//初始化迁移目的地的链表
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cc.migratepages);//初始化将要迁移页面链表
ret = compact_zone(zone, &cc);//对zone进行规整
VM_BUG_ON(!list_empty(&cc.freepages));
VM_BUG_ON(!list_empty(&cc.migratepages));
return ret;
}
struct compact_control数据结构记录了被迁移的页面,以及规整过程中迁移到的页面列表,compact_zone_order主要将参数填入struct compact_control结构体,然后和zone一起作为参数传递给compact_zone,compact_zone:
static enum compact_result compact_zone(struct zone *zone, struct compact_control *cc)
{
enum compact_result ret;
unsigned long start_pfn = zone->zone_start_pfn;
unsigned long end_pfn = zone_end_pfn(zone);
const bool sync = cc->mode != MIGRATE_ASYNC;
cc->migratetype = gfpflags_to_migratetype(cc->gfp_mask);
//根据当前zone水位来判断是否需要进行内存规整,COMPACT_CONTINUE表示可以做内存规整
ret = compaction_suitable(zone, cc->order, cc->alloc_flags,
cc->classzone_idx);
/* Compaction is likely to fail */
if (ret == COMPACT_SUCCESS || ret == COMPACT_SKIPPED)
return ret;
/* huh, compaction_suitable is returning something unexpected */
VM_BUG_ON(ret != COMPACT_CONTINUE);
/*
* Clear pageblock skip if there were failures recently and compaction
* is about to be retried after being deferred.
*/
if (compaction_restarting(zone, cc->order))
__reset_isolation_suitable(zone);
/*
* Setup to move all movable pages to the end of the zone. Used cached
* information on where the scanners should start (unless we explicitly
* want to compact the whole zone), but check that it is initialised
* by ensuring the values are within zone boundaries.
*/
if (cc->whole_zone) {
cc->migrate_pfn = start_pfn;
cc->free_pfn = pageblock_start_pfn(end_pfn - 1);
} else {
//表示从zone的开始页面开始扫描和查找哪些页面可以被迁移
cc->migrate_pfn = zone->compact_cached_migrate_pfn[sync];
//从zone末端开始扫描和查找哪些空闲的页面可以用作迁移页面的目的地
cc->free_pfn = zone->compact_cached_free_pfn;
if (cc->free_pfn < start_pfn || cc->free_pfn >= end_pfn) {
cc->free_pfn = pageblock_start_pfn(end_pfn - 1);
zone->compact_cached_free_pfn = cc->free_pfn;
}
//下面对free_pfn和migrate_pfn进行范围限制
if (cc->migrate_pfn < start_pfn || cc->migrate_pfn >= end_pfn) {
cc->migrate_pfn = start_pfn;
zone->compact_cached_migrate_pfn[0] = cc->migrate_pfn;
zone->compact_cached_migrate_pfn[1] = cc->migrate_pfn;
}
if (cc->migrate_pfn == start_pfn)
cc->whole_zone = true;
}
cc->last_migrated_pfn = 0;
trace_mm_compaction_begin(start_pfn, cc->migrate_pfn,
cc->free_pfn, end_pfn, sync);
migrate_prep_local();
//while中从zone开头扫描查找合适的迁移页面,然后尝试迁移到zone末端空闲页面中,直到zone处于低水位WMARK_LOW之上
while ((ret = compact_finished(zone, cc)) == COMPACT_CONTINUE) {
int err;
//用于扫描和查找合适迁移的页,查找到后进行页面隔离
switch (isolate_migratepages(zone, cc)) {
case ISOLATE_ABORT://迁移失败
ret = COMPACT_CONTENDED;
putback_movable_pages(&cc->migratepages);//需要迁移回去
cc->nr_migratepages = 0;
goto out;
case ISOLATE_NONE://找不到
/*
* We haven't isolated and migrated anything, but
* there might still be unflushed migrations from
* previous cc->order aligned block.
*/
goto check_drain;
case ISOLATE_SUCCESS://成功
;
}
//migrate_pages是页面迁移核心函数,从cc->migratepages中摘取页,然后尝试去迁移
err = migrate_pages(&cc->migratepages, compaction_alloc,
compaction_free, (unsigned long)cc, cc->mode,
MR_COMPACTION);
trace_mm_compaction_migratepages(cc->nr_migratepages, err,
&cc->migratepages);
/* All pages were either migrated or will be released */
cc->nr_migratepages = 0;
//没处理成功的页面会放回到合适的LRU链表中
if (err) {
putback_movable_pages(&cc->migratepages);
/*
* migrate_pages() may return -ENOMEM when scanners meet
* and we want compact_finished() to detect it
*/
if (err == -ENOMEM && !compact_scanners_met(cc)) {
ret = COMPACT_CONTENDED;
goto out;
}
/*
* We failed to migrate at least one page in the current
* order-aligned block, so skip the rest of it.
*/
if (cc->direct_compaction &&
(cc->mode == MIGRATE_ASYNC)) {
cc->migrate_pfn = block_end_pfn(
cc->migrate_pfn - 1, cc->order);
/* Draining pcplists is useless in this case */
cc->last_migrated_pfn = 0;
}
}
check_drain:
/*
* Has the migration scanner moved away from the previous
* cc->order aligned block where we migrated from? If yes,
* flush the pages that were freed, so that they can merge and
* compact_finished() can detect immediately if allocation
* would succeed.
*/
if (cc->order > 0 && cc->last_migrated_pfn) {
int cpu;
unsigned long current_block_start =
block_start_pfn(cc->migrate_pfn, cc->order);
if (cc->last_migrated_pfn < current_block_start) {
cpu = get_cpu();
lru_add_drain_cpu(cpu);
drain_local_pages(zone);
put_cpu();
/* No more flushing until we migrate again */
cc->last_migrated_pfn = 0;
}
}
}
out:
/*
* Release free pages and update where the free scanner should restart,
* so we don't leave any returned pages behind in the next attempt.
*/
if (cc->nr_freepages > 0) {
unsigned long free_pfn = release_freepages(&cc->freepages);
cc->nr_freepages = 0;
VM_BUG_ON(free_pfn == 0);
/* The cached pfn is always the first in a pageblock */
free_pfn = pageblock_start_pfn(free_pfn);
/*
* Only go back, not forward. The cached pfn might have been
* already reset to zone end in compact_finished()
*/
if (free_pfn > zone->compact_cached_free_pfn)
zone->compact_cached_free_pfn = free_pfn;
}
count_compact_events(COMPACTMIGRATE_SCANNED, cc->total_migrate_scanned);
count_compact_events(COMPACTFREE_SCANNED, cc->total_free_scanned);
trace_mm_compaction_end(start_pfn, cc->migrate_pfn,
cc->free_pfn, end_pfn, sync, ret);
return ret;
}
compact_zone主要流程如下图:
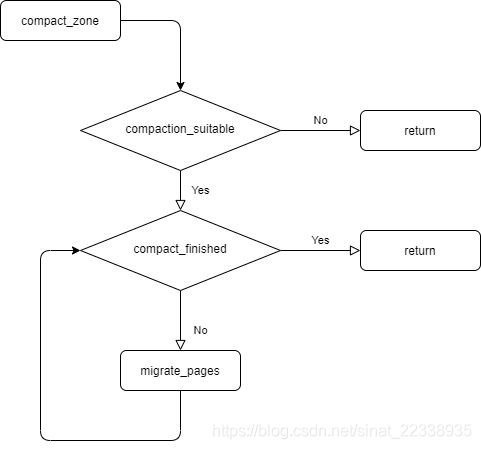
这里要分析3个函数:
- compaction_suitable 判断是否需要进行内存规整
- compact_finished 判断是否可以停止内存规整
- migrate_pages 页面迁移核心函数
先看compaction_suitable 函数如何判断是否需要进行内存规整:
enum compact_result compaction_suitable(struct zone *zone, int order,
unsigned int alloc_flags,
int classzone_idx)
{
enum compact_result ret;
int fragindex;
//检查是否继续规整主要函数
ret = __compaction_suitable(zone, order, alloc_flags, classzone_idx,
zone_page_state(zone, NR_FREE_PAGES));
/*
* fragmentation index determines if allocation failures are due to
* low memory or external fragmentation
*
* index of -1000 would imply allocations might succeed depending on
* watermarks, but we already failed the high-order watermark check
* index towards 0 implies failure is due to lack of memory
* index towards 1000 implies failure is due to fragmentation
*
* Only compact if a failure would be due to fragmentation. Also
* ignore fragindex for non-costly orders where the alternative to
* a successful reclaim/compaction is OOM. Fragindex and the
* vm.extfrag_threshold sysctl is meant as a heuristic to prevent
* excessive compaction for costly orders, but it should not be at the
* expense of system stability.
*/
if (ret == COMPACT_CONTINUE && (order > PAGE_ALLOC_COSTLY_ORDER)) {
fragindex = fragmentation_index(zone, order);
if (fragindex >= 0 && fragindex <= sysctl_extfrag_threshold)
ret = COMPACT_NOT_SUITABLE_ZONE;
}
trace_mm_compaction_suitable(zone, order, ret);
if (ret == COMPACT_NOT_SUITABLE_ZONE)
ret = COMPACT_SKIPPED;
return ret;
}
/*
* compaction_suitable: Is this suitable to run compaction on this zone now?
* Returns
* COMPACT_SKIPPED - If there are too few free pages for compaction
* COMPACT_SUCCESS - If the allocation would succeed without compaction
* COMPACT_CONTINUE - If compaction should run now
*/
static enum compact_result __compaction_suitable(struct zone *zone, int order,
unsigned int alloc_flags,
int classzone_idx,
unsigned long wmark_target)
{
unsigned long watermark;
if (is_via_compact_memory(order))
return COMPACT_CONTINUE;
watermark = zone->watermark[alloc_flags & ALLOC_WMARK_MASK];
/*
* If watermarks for high-order allocation are already met, there
* should be no need for compaction at all.
*/
//如果满足低水位,则不需要进行内存规整。
if (zone_watermark_ok(zone, order, watermark, classzone_idx,
alloc_flags))
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
/*
* Watermarks for order-0 must be met for compaction to be able to
* isolate free pages for migration targets. This means that the
* watermark and alloc_flags have to match, or be more pessimistic than
* the check in __isolate_free_page(). We don't use the direct
* compactor's alloc_flags, as they are not relevant for freepage
* isolation. We however do use the direct compactor's classzone_idx to
* skip over zones where lowmem reserves would prevent allocation even
* if compaction succeeds.
* For costly orders, we require low watermark instead of min for
* compaction to proceed to increase its chances.
* ALLOC_CMA is used, as pages in CMA pageblocks are considered
* suitable migration targets
*/
watermark = (order > PAGE_ALLOC_COSTLY_ORDER) ?
low_wmark_pages(zone) : min_wmark_pages(zone);
watermark += compact_gap(order);//增加水位高度为watermark+2<
//如果达不到新水位,说明当前zone中空闲页面很少,不适合作内存规整,跳过此zone
if (!__zone_watermark_ok(zone, 0, watermark, classzone_idx,
ALLOC_CMA, wmark_target))
return COMPACT_SKIPPED;
return COMPACT_CONTINUE;
}
compaction_suitable 主要通过__compaction_suitable来判断是否需要进行内存规整,__compaction_suitable则通过zone的水位来判断书否应该进行内存规整,只有低于低水位线和高于最低水位线才能进行内存规整,因为高于低水位线不需要进行内存规整,低于最低水位线则没办法进行内存规整。
然后看看compact_finished 如何判断是否可以停止内存规整:
static enum compact_result compact_finished(struct zone *zone,
struct compact_control *cc)
{
int ret;
ret = __compact_finished(zone, cc);//真正的规整结果检查
trace_mm_compaction_finished(zone, cc->order, ret);//追踪规整结果
if (ret == COMPACT_NO_SUITABLE_PAGE)
ret = COMPACT_CONTINUE;
return ret;
}
static enum compact_result __compact_finished(struct zone *zone,
struct compact_control *cc)
{
unsigned int order;
const int migratetype = cc->migratetype;
if (cc->contended || fatal_signal_pending(current))
return COMPACT_CONTENDED;
/* Compaction run completes if the migrate and free scanner meet */
//扫描可迁移页面和空闲页面,从zone的头尾向中间运行。当两者相遇,可以停止规整
if (compact_scanners_met(cc)) {
/* Let the next compaction start anew. */
reset_cached_positions(zone);
/*
* Mark that the PG_migrate_skip information should be cleared
* by kswapd when it goes to sleep. kcompactd does not set the
* flag itself as the decision to be clear should be directly
* based on an allocation request.
*/
if (cc->direct_compaction)
zone->compact_blockskip_flush = true;
if (cc->whole_zone)
return COMPACT_COMPLETE;
else
return COMPACT_PARTIAL_SKIPPED;
}
//如果order为-1表示强制执行内存规整,继续内存规整
if (is_via_compact_memory(cc->order))
return COMPACT_CONTINUE;
if (cc->finishing_block) {
/*
* We have finished the pageblock, but better check again that
* we really succeeded.
*/
if (IS_ALIGNED(cc->migrate_pfn, pageblock_nr_pages))
cc->finishing_block = false;
else
return COMPACT_CONTINUE;
}
/* Direct compactor: Is a suitable page free? */
//直接内存规整,在这里判断规整结果
for (order = cc->order; order < MAX_ORDER; order++) {
struct free_area *area = &zone->free_area[order];
bool can_steal;
/* Job done if page is free of the right migratetype */
if (!list_empty(&area->free_list[migratetype]))
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
#ifdef CONFIG_CMA
/* MIGRATE_MOVABLE can fallback on MIGRATE_CMA */
if (migratetype == MIGRATE_MOVABLE &&
!list_empty(&area->free_list[MIGRATE_CMA]))
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
#endif
/*
* Job done if allocation would steal freepages from
* other migratetype buddy lists.
*/
if (find_suitable_fallback(area, order, migratetype,
true, &can_steal) != -1) {
/* movable pages are OK in any pageblock */
if (migratetype == MIGRATE_MOVABLE)
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
/*
* We are stealing for a non-movable allocation. Make
* sure we finish compacting the current pageblock
* first so it is as free as possible and we won't
* have to steal another one soon. This only applies
* to sync compaction, as async compaction operates
* on pageblocks of the same migratetype.
*/
if (cc->mode == MIGRATE_ASYNC ||
IS_ALIGNED(cc->migrate_pfn,
pageblock_nr_pages)) {
return COMPACT_SUCCESS;
}
cc->finishing_block = true;
return COMPACT_CONTINUE;
}
}
return COMPACT_NO_SUITABLE_PAGE;
}
compact_finished主要通过__compact_finished来判断内存规整是否完成,__compact_finished判断内存规整流程是否可以结束,结束的条件有两个:一是cc->migrate_pfn和cc->free_pfn两个指针相遇;二是以order为条件判断当前zone的水位在低水位之上。
最后要看看migrate_pages 这个页面迁移核心函数如何进行页面迁移,首先知道migrate_pages 调用参数,
migrate_pages(&cc->migratepages, compaction_alloc,compaction_free, (unsigned long)cc, cc->mode,MR_COMPACTION);
migrate_pages 要从cc->migratepages中摘取页,然后尝试去迁移。然后通过第二参数compaction_alloc函数和第三参数compaction_free调整cc->migratepages。
所以,先看看compaction_alloc和compaction_free函数,函数位于mm/compaction.c文件:
static struct page *compaction_alloc(struct page *migratepage,
unsigned long data)
{
struct compact_control *cc = (struct compact_control *)data;
struct page *freepage;
/*
* Isolate free pages if necessary, and if we are not aborting due to
* contention.
*/
if (list_empty(&cc->freepages)) {
if (!cc->contended)
isolate_freepages(cc);//查找可以用来作为迁移目的页面
if (list_empty(&cc->freepages))//如果没有页面可被用来作为迁移目的页面,返回NULL
return NULL;
}
freepage = list_entry(cc->freepages.next, struct page, lru);//找到可以被用作迁移目的的页面
list_del(&freepage->lru);//将空闲页面从cc->freepages中摘除
cc->nr_freepages--;
return freepage;
}
static void compaction_free(struct page *page, unsigned long data)
{
struct compact_control *cc = (struct compact_control *)data;
list_add(&page->lru, &cc->freepages);//失败情况下,将页面放回cc->freepages
cc->nr_freepages++;
}
compaction_alloc从zone的末尾开始查找空闲页面,并把空闲页面添加到cc->freepages链表中,然后从cc->freepages中摘除页面,返回给migrate_pages作为迁移使用。compaction_free是规整失败的处理函数,将空闲页面返回给cc->freepages。
最后看看migrate_pages做了什么:
int migrate_pages(struct list_head *from, new_page_t get_new_page,
free_page_t put_new_page, unsigned long private,
enum migrate_mode mode, int reason)
{
int retry = 1;
int nr_failed = 0;
int nr_succeeded = 0;
int pass = 0;
struct page *page;
struct page *page2;
int swapwrite = current->flags & PF_SWAPWRITE;
int rc;
if (!swapwrite)
current->flags |= PF_SWAPWRITE;
//尝试10次,从from摘取一个页面,调用unmap_and_move()函数进行页迁移,返回MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS表示页迁移成功。
for(pass = 0; pass < 10 && retry; pass++) {
retry = 0;
list_for_each_entry_safe(page, page2, from, lru) {
retry:
cond_resched();
if (PageHuge(page))
rc = unmap_and_move_huge_page(get_new_page,
put_new_page, private, page,
pass > 2, mode, reason);
else
//尝试迁移页面page到新分配的页面newpage
rc = unmap_and_move(get_new_page, put_new_page,
private, page, pass > 2, mode,
reason);
switch(rc) {
case -ENOMEM:
/*
* THP migration might be unsupported or the
* allocation could've failed so we should
* retry on the same page with the THP split
* to base pages.
*
* Head page is retried immediately and tail
* pages are added to the tail of the list so
* we encounter them after the rest of the list
* is processed.
*/
if (PageTransHuge(page) && !PageHuge(page)) {
lock_page(page);
rc = split_huge_page_to_list(page, from);
unlock_page(page);
if (!rc) {
list_safe_reset_next(page, page2, lru);
goto retry;
}
}
nr_failed++;
goto out;
case -EAGAIN:
retry++;
break;
case MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS:
nr_succeeded++;
break;
default:
/*
* Permanent failure (-EBUSY, -ENOSYS, etc.):
* unlike -EAGAIN case, the failed page is
* removed from migration page list and not
* retried in the next outer loop.
*/
nr_failed++;
break;
}
}
}
nr_failed += retry;
rc = nr_failed;
out:
if (nr_succeeded)
count_vm_events(PGMIGRATE_SUCCESS, nr_succeeded);
if (nr_failed)
count_vm_events(PGMIGRATE_FAIL, nr_failed);
trace_mm_migrate_pages(nr_succeeded, nr_failed, mode, reason);
if (!swapwrite)
current->flags &= ~PF_SWAPWRITE;
return rc;
}
migrate_pages主要调用unmap_and_mov来尝试迁移页面page到新分配的页面newpage,下面看看unmap_and_mov函数:
static ICE_noinline int unmap_and_move(new_page_t get_new_page,
free_page_t put_new_page,
unsigned long private, struct page *page,
int force, enum migrate_mode mode,
enum migrate_reason reason)
{
int rc = MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS;
struct page *newpage;
if (!thp_migration_supported() && PageTransHuge(page))
return -ENOMEM;
//调用get_new_page参数,也就是上面的compaction_alloc函数
newpage = get_new_page(page, private);
if (!newpage)
return -ENOMEM;
if (page_count(page) == 1) {
/* page was freed from under us. So we are done. */
ClearPageActive(page);
ClearPageUnevictable(page);
if (unlikely(__PageMovable(page))) {
lock_page(page);
if (!PageMovable(page))
__ClearPageIsolated(page);
unlock_page(page);
}
if (put_new_page)
put_new_page(newpage, private);
else
put_page(newpage);
goto out;
}
//真正尝试迁移页面page到新分配的页面newpage的函数
rc = __unmap_and_move(page, newpage, force, mode);
if (rc == MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS)
set_page_owner_migrate_reason(newpage, reason);
out:
if (rc != -EAGAIN) {
/*
* A page that has been migrated has all references
* removed and will be freed. A page that has not been
* migrated will have kepts its references and be
* restored.
*/
list_del(&page->lru);
/*
* Compaction can migrate also non-LRU pages which are
* not accounted to NR_ISOLATED_*. They can be recognized
* as __PageMovable
*/
if (likely(!__PageMovable(page)))
mod_node_page_state(page_pgdat(page), NR_ISOLATED_ANON +
page_is_file_cache(page), -hpage_nr_pages(page));
}
/*
* If migration is successful, releases reference grabbed during
* isolation. Otherwise, restore the page to right list unless
* we want to retry.
*/
if (rc == MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS) {
put_page(page);
if (reason == MR_MEMORY_FAILURE) {
/*
* Set PG_HWPoison on just freed page
* intentionally. Although it's rather weird,
* it's how HWPoison flag works at the moment.
*/
if (set_hwpoison_free_buddy_page(page))
num_poisoned_pages_inc();
}
} else {
if (rc != -EAGAIN) {
if (likely(!__PageMovable(page))) {
putback_lru_page(page);
goto put_new;
}
lock_page(page);
if (PageMovable(page))
putback_movable_page(page);
else
__ClearPageIsolated(page);
unlock_page(page);
put_page(page);
}
put_new:
if (put_new_page)
put_new_page(newpage, private);
else
put_page(newpage);
}
return rc;
}
static int __unmap_and_move(struct page *page, struct page *newpage,
int force, enum migrate_mode mode)
{
int rc = -EAGAIN;
int page_was_mapped = 0;
struct anon_vma *anon_vma = NULL;
bool is_lru = !__PageMovable(page);
if (!trylock_page(page)) {//尝试给页面枷锁
if (!force || mode == MIGRATE_ASYNC)//加锁失败,且强制迁移或异步模式,则忽略这个页面
goto out;
/*
* It's not safe for direct compaction to call lock_page.
* For example, during page readahead pages are added locked
* to the LRU. Later, when the IO completes the pages are
* marked uptodate and unlocked. However, the queueing
* could be merging multiple pages for one bio (e.g.
* mpage_readpages). If an allocation happens for the
* second or third page, the process can end up locking
* the same page twice and deadlocking. Rather than
* trying to be clever about what pages can be locked,
* avoid the use of lock_page for direct compaction
* altogether.
*/
if (current->flags & PF_MEMALLOC)
goto out;
lock_page(page);
}
if (PageWriteback(page)) {
/*
* Only in the case of a full synchronous migration is it
* necessary to wait for PageWriteback. In the async case,
* the retry loop is too short and in the sync-light case,
* the overhead of stalling is too much
*/
switch (mode) {
case MIGRATE_SYNC:
case MIGRATE_SYNC_NO_COPY:
break;
default:
rc = -EBUSY;
goto out_unlock;
}
if (!force)
goto out_unlock;
wait_on_page_writeback(page);
}
/*
* By try_to_unmap(), page->mapcount goes down to 0 here. In this case,
* we cannot notice that anon_vma is freed while we migrates a page.
* This get_anon_vma() delays freeing anon_vma pointer until the end
* of migration. File cache pages are no problem because of page_lock()
* File Caches may use write_page() or lock_page() in migration, then,
* just care Anon page here.
*
* Only page_get_anon_vma() understands the subtleties of
* getting a hold on an anon_vma from outside one of its mms.
* But if we cannot get anon_vma, then we won't need it anyway,
* because that implies that the anon page is no longer mapped
* (and cannot be remapped so long as we hold the page lock).
*/
if (PageAnon(page) && !PageKsm(page))
anon_vma = page_get_anon_vma(page);
/*
* Block others from accessing the new page when we get around to
* establishing additional references. We are usually the only one
* holding a reference to newpage at this point. We used to have a BUG
* here if trylock_page(newpage) fails, but would like to allow for
* cases where there might be a race with the previous use of newpage.
* This is much like races on refcount of oldpage: just don't BUG().
*/
if (unlikely(!trylock_page(newpage)))
goto out_unlock;
if (unlikely(!is_lru)) {
rc = move_to_new_page(newpage, page, mode);
goto out_unlock_both;
}
/*
* Corner case handling:
* 1. When a new swap-cache page is read into, it is added to the LRU
* and treated as swapcache but it has no rmap yet.
* Calling try_to_unmap() against a page->mapping==NULL page will
* trigger a BUG. So handle it here.
* 2. An orphaned page (see truncate_complete_page) might have
* fs-private metadata. The page can be picked up due to memory
* offlining. Everywhere else except page reclaim, the page is
* invisible to the vm, so the page can not be migrated. So try to
* free the metadata, so the page can be freed.
*/
if (!page->mapping) {
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(PageAnon(page), page);
if (page_has_private(page)) {
try_to_free_buffers(page);
goto out_unlock_both;
}
} else if (page_mapped(page)) {//有pte映射的页面,调用try_to_unmap()解除页面所有映射
/* Establish migration ptes */
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(PageAnon(page) && !PageKsm(page) && !anon_vma,
page);
try_to_unmap(page,
TTU_MIGRATION|TTU_IGNORE_MLOCK|TTU_IGNORE_ACCESS);
page_was_mapped = 1;
}
if (!page_mapped(page))//已经解除完所有映射的页面,将页面迁移到新分配的页面newpage
rc = move_to_new_page(newpage, page, mode);
if (page_was_mapped)
remove_migration_ptes(page,
rc == MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS ? newpage : page, false);
out_unlock_both:
unlock_page(newpage);
out_unlock:
/* Drop an anon_vma reference if we took one */
if (anon_vma)
put_anon_vma(anon_vma);
unlock_page(page);
out:
/*
* If migration is successful, decrease refcount of the newpage
* which will not free the page because new page owner increased
* refcounter. As well, if it is LRU page, add the page to LRU
* list in here. Use the old state of the isolated source page to
* determine if we migrated a LRU page. newpage was already unlocked
* and possibly modified by its owner - don't rely on the page
* state.
*/
if (rc == MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS) {
if (unlikely(!is_lru))
put_page(newpage);
else
putback_lru_page(newpage);
}
return rc;
}
unmap_and_move主要调用了__unmap_and_move,__unmap_and_move工作如下图:

其中move_to_new_page是主要将page内容迁移到newpage的函数,move_to_new_page:
static int move_to_new_page(struct page *newpage, struct page *page,
enum migrate_mode mode)
{
struct address_space *mapping;
int rc = -EAGAIN;
bool is_lru = !__PageMovable(page);
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(!PageLocked(page), page);
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(!PageLocked(newpage), newpage);
//检查当前页面你是否被映射。如果page属于slab或是匿名页面,返回为空。SWAP则返回swap_address_space空间;其余page cache直接返回page->mapping
mapping = page_mapping(page);
if (likely(is_lru)) {
if (!mapping)
//slab或者匿名页面调用migrate_page()将旧页面相关信息迁移到新页面
rc = migrate_page(mapping, newpage, page, mode);
else if (mapping->a_ops->migratepage)
/*
* Most pages have a mapping and most filesystems
* provide a migratepage callback. Anonymous pages
* are part of swap space which also has its own
* migratepage callback. This is the most common path
* for page migration.
*/
//有mapping的情况,调用migratepage函数进行迁移
rc = mapping->a_ops->migratepage(mapping, newpage,
page, mode);
else
//没有映射则回退页面迁移操作
rc = fallback_migrate_page(mapping, newpage,
page, mode);
} else {
/*
* In case of non-lru page, it could be released after
* isolation step. In that case, we shouldn't try migration.
*/
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(!PageIsolated(page), page);
if (!PageMovable(page)) {
rc = MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS;
__ClearPageIsolated(page);
goto out;
}
rc = mapping->a_ops->migratepage(mapping, newpage,
page, mode);
WARN_ON_ONCE(rc == MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS &&
!PageIsolated(page));
}
/*
* When successful, old pagecache page->mapping must be cleared before
* page is freed; but stats require that PageAnon be left as PageAnon.
*/
if (rc == MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS) {
if (__PageMovable(page)) {
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(!PageIsolated(page), page);
/*
* We clear PG_movable under page_lock so any compactor
* cannot try to migrate this page.
*/
__ClearPageIsolated(page);
}
/*
* Anonymous and movable page->mapping will be cleard by
* free_pages_prepare so don't reset it here for keeping
* the type to work PageAnon, for example.
*/
if (!PageMappingFlags(page))
page->mapping = NULL;
if (unlikely(is_zone_device_page(newpage))) {
if (is_device_public_page(newpage))
flush_dcache_page(newpage);
} else
flush_dcache_page(newpage);
}
out:
return rc;
}
move_to_new_page函数首先会检查是否已经映射,如果是匿名页面映射就调用migrate_page进行迁移,如果是文件映射就回调migratepage函数进行迁移,没有映射则调用fallback_migrate_page回退页面迁移操作。现在看看migrate_page函数:
int migrate_page(struct address_space *mapping,
struct page *newpage, struct page *page,
enum migrate_mode mode)
{
int rc;
BUG_ON(PageWriteback(page)); /* Writeback must be complete */
//对于匿名页面来说,什么也不做直接返回
rc = migrate_page_move_mapping(mapping, newpage, page, NULL, mode, 0);
if (rc != MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS)
return rc;
if (mode != MIGRATE_SYNC_NO_COPY)
migrate_page_copy(newpage, page);//把页面page复制到新页面newpage中
else
migrate_page_states(newpage, page);
return MIGRATEPAGE_SUCCESS;
}
void migrate_page_copy(struct page *newpage, struct page *page)
{
if (PageHuge(page) || PageTransHuge(page))
copy_huge_page(newpage, page);
else
copy_highpage(newpage, page);
migrate_page_states(newpage, page);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(migrate_page_copy);
回调migratepage函数目前无法确定,后期补上,而fallback_migrate_page现在看看:
static int fallback_migrate_page(struct address_space *mapping,
struct page *newpage, struct page *page, enum migrate_mode mode)
{
if (PageDirty(page)) {//如果是脏页
/* Only writeback pages in full synchronous migration */
switch (mode) {
case MIGRATE_SYNC:
case MIGRATE_SYNC_NO_COPY:
break;
default:
return -EBUSY;
}
return writeout(mapping, page);//回写
}
/*
* Buffers may be managed in a filesystem specific way.
* We must have no buffers or drop them.
*/
//如果是私有文件并且没有办法释放返回错误
if (page_has_private(page) &&
!try_to_release_page(page, GFP_KERNEL))
return -EAGAIN;
return migrate_page(mapping, newpage, page, mode);
}
fallback_migrate_page主要做了三件事:1.如果文件页是脏页则回写后返回,2.如果文件页是私有文件且没办法释放则返回错误,3.嘴都调用migrate_page进行迁移。