day20 二叉树part6
654. 最大二叉树
中等
给定一个不重复的整数数组 nums 。 最大二叉树 可以用下面的算法从 nums 递归地构建:
创建一个根节点,其值为 nums 中的最大值。
递归地在最大值 左边 的 子数组前缀上 构建左子树。
递归地在最大值 右边 的 子数组后缀上 构建右子树。
返回 nums 构建的 最大二叉树 。
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
return build(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode build(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
//if (start > end) return null;
// 找到当前数组里的最大值及其对应的索引
int maxNum = nums[start], maxIndex = start;
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++){
if (maxNum < nums[i]) {
maxNum = nums[i];
maxIndex = i;
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(maxNum);
// 像下面这样写总是让人担心边界问题,很不好理解
// root.left = build(nums, start, maxIndex - 1);
// root.right = build(nums, maxIndex + 1, end);
// 这样写就更好理解了
if (start <= maxIndex - 1){ // 如果边界没问题的话可以继续构造
root.left = build(nums, start, maxIndex - 1); //超出边界其实也就最多超出一格,因为无论如何,maxNum都是数组里的数,那么他的下标最多就是0到 length-1
}else {
root.left = null;
}
if (maxIndex + 1 <= end){
root.right = build(nums, maxIndex + 1, end);
}else {
root.right = null;
}
return root;
}
}
617. 合并二叉树
简单
给你两棵二叉树: root1 和 root2 。
想象一下,当你将其中一棵覆盖到另一棵之上时,两棵树上的一些节点将会重叠(而另一些不会)。你需要将这两棵树合并成一棵新二叉树。合并的规则是:如果两个节点重叠,那么将这两个节点的值相加作为合并后节点的新值;否则,不为 null 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
返回合并后的二叉树。
注意: 合并过程必须从两个树的根节点开始。
以下是错误示例:
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
TreeNode root = getTree(root1, root2);
return root;
}
public TreeNode getTree(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode();
if (root1 != null && root2 != null) {
root.val = root1.val + root2.val;
} else if (root1 != null && root2 == null) {
root.val = root1.val;
} else if (root1 == null && root2 != null) {
root.val = root2.val;
} else { // 都为空的情况
root = null;
}
root.left = getTree(root1.left, root2.left);
root.right = getTree(root1.right, root2.right); // null节点没有左右节点!!!
return root;
}
}
正确答案:
// 直接在root1上进行修改,不再开辟新的节点
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
// 如果root1是空的,那root1及以下的节点全都会被root2替换,如果root2也是null,也还是返回null,不必单独判断
if (root1 == null) return root2;
if (root2 == null) return root1;
// 经过上面两条判断后两个根节点都不可能是空了
root1.val += root2.val;
root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left, root2.left);
root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right, root2.right);
return root1;
}
}
700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
简单
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和一个整数值 val。
你需要在 BST 中找到节点值等于 val 的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回 null 。


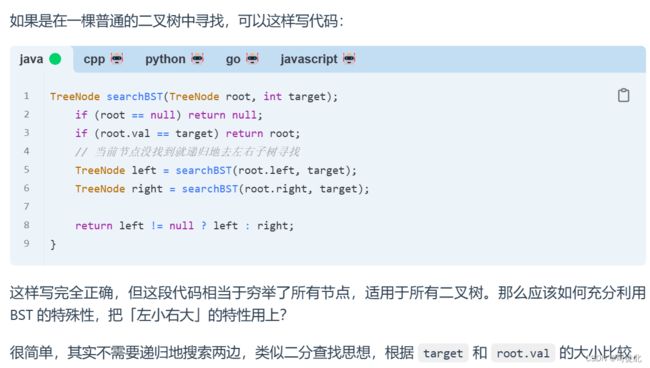
// 二叉树中的搜索,它只会找一条路径,沿着这条路径一直走,如果遇到等于val的值就返回这个节点,如果一直没遇到等于的,就会碰到最底下的null
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null) return null;
if (root.val == val) return root;
TreeNode res;
if (val < root.val) { //目标值比节点值小,找左树
res = searchBST(root.left, val);
} else { //否则就找右树
res = searchBST(root.right, val);
}
return res;
}
}
98. 验证二叉搜索树
中等
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
节点的左子树只包含 小于 当前节点的数。
节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树
难点:二叉搜索树的性质
自我总结:以下是一个二叉搜索树的图片,为什么中序遍历的结果是升序的呢?先看它升序遍历的结果:0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 发现没有,假如给每个节点一个坐标(x, y),那么中序遍历顺序是按照x坐标由小到大的顺序来的(越左边的越小)。然而二叉搜索树的性质也是,左边的永远比右边的要小。所以,这俩性质就对上了,即:中序遍历的结果是升序的!
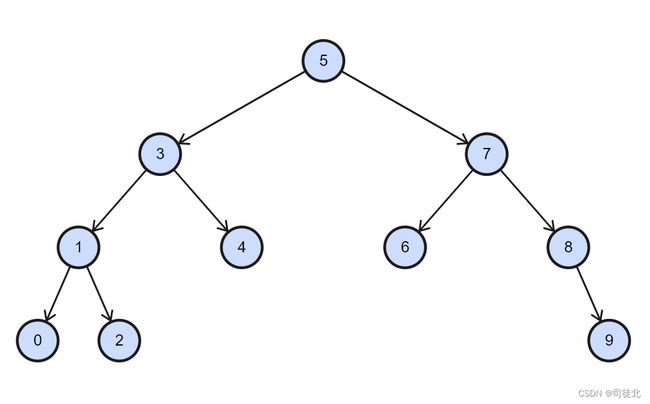
以下截图来自:https://labuladong.github.io/algo/

// 用中序遍历存数组里的方法
class Solution {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
inOrder(root);
int pre = res.get(0);
for (int i = 1; i < res.size(); i++) { // 这里要用int i = 1
if (pre >= res.get(i)) return false; // 是大于等于,不是大于
pre = res.get(i);
}
return true;
}
public void inOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
inOrder(node.left);
res.add(node.val);
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
关于初始值的优化:因为测试数据中有int类型的最小值,所以取long类型的最小值作为初始值。但是这样治标不治本,如果测试数据中存在long类型的最小值,不可能再初始化一个更小的值,所以建议取二叉树中序遍历序列的第一个值作为初始值。
下面这个解法我想了很久,有了更深的理解,没事可以看看
class Solution {
// 最小值初始化为中序序列的第一个节点值
Integer pre;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
// 结束条件:如果root为null,返回true,因为空节点不会占据中序遍历数组的任何一个位置,而返回false的条件是中序遍历数组相邻左右两数不满足升序
// 所以空节点也要返回true
// 因为空的二叉搜索树也是符合条件的
if (root == null) return true;
// 中序遍历:左根右
// 递归左子树,获取结果
boolean left = isValidBST(root.left);
// 如果当前节点的值大于等于中序序列中上一个值,证明不是二叉搜索树
// 如果pre为null,证明pre还没有初始化所以首先将pre初始化(证明这是第一个节点,不用和前面的比较,因为前面没有节点
if (pre != null && root.val <= pre){ // 先思考简化版,假设pre是一个无限小的数,捋清楚了再思考当跳过第一个节点的做法
return false;
}
// 如果当前节点小于中序序列上一个值,证明符合条件,更新pre为
// 当前值,继续判断下一个值,
pre = root.val;
// 递归右子树,获取结果
boolean right = isValidBST(root.right);
// 左右子树都是二叉搜索树,则返回true,否则返回false
return left && right;
}
}