鸿蒙常用容器组件介绍
鸿蒙常用容器组件介绍
- 前言
- 总结
- 1. Row/Column
- 2. flex
- 3. Stack
- 4. List
- 5. RelativeContainer
- 6. Grid
- 7. Scroll
- 8. Tabs
- 9. WaterFlow
- 参考资料
前言
-
本文不介绍Text,Image这种单独的视图控件,主要还是过一下在构成一个复杂页面时所需要的外层的容器组件。免得在实际开发的时候要构建外层组件时不知道要用什么比较好
-
本文虽然也会贴一些测试代码,但是参考还是以鸿蒙的API参考为主,最好在上手这些视图的同时,学习如何看API参考:
打开DevEco Studio -> View(视图) -> Tool Windows(工具窗口) -> API reference(API参考) -> ArkTs组件 -> 容器组件
如果你的DevEco没有该视图,更新一下版本。 -
代码测试方式:在DevEco中新建一个arkTs文件,将正文的代码丢进去,启动preview功能即可。
UI的点击事件和滚动功能不能直接通过@preview的测试标签来测试,必须要通过被@Entry标签标记过的页面才能生效,为了方便再贴上一个简单的页面代码。
在这里插入代码片
@Entry
@Component
export struct UIText {
build() {
Column() {
//把正文的某个组件贴进来即可
}.width('100%').height('100%')
}
}
总结
一图流总结(这里的Android对标只是方便刚上手的时候理解,实际上鸿蒙的声明式UI的逻辑和Android的命令式并不同):
| 容器名称 | 容器说明 | 对标的Android视图 |
| Row/Conlumn | 最常用的横向/纵向组件,里面的元素按照约定好的顺序排列 | LinearLayout |
| Flex | 柔性组件,自带换行功能的Row/Column | LinearLayout 部分对应GridLayout |
| List和ListItem | 列表组件,当需要重复的元素排列的时候使用这个 | 部分对应RecyclerView |
| Stack | 堆栈式组件,后加入的元素会覆盖前面的元素 但是实测别的布局也有这个特点,所以适用该布局的场景还有待探索 |
FrameLayout? |
| RelativeContainer | 相对组件,里面的控件都是根据和其他控件的相对位置来进行摆放 | RelativeLayout ConstaintLayout |
| Grid | 网格组件,里面的元素按照网格进行排列,可以横向也可以纵向 | GridLayout |
| Scroll | 滑动组件,需要让某个页面可以滚动的时候就用它 | ScrollView |
| Tab | 标签组件,通过点击不同的项目展示不同的页面 | TabLayout |
| WaterFlow | 瀑布流容器,用它可以很方便的实现 淘宝首页那种左右视图不一样高的列表视图 |
/ |
1. Row/Column
最常用的排列视图的容器组件,可以横向排列或者纵向排列。这个还真没有什么好说的,哪个UI语言都有
内部的控件设置position的时候,剩下其他的元素会对应的往前
而设置offset的时候则不会。
@Preview
@Component
export struct ColumnRowView {
build() {
Column({space:10}) {
Row() {
Text('文案A')
.fontColor('#FFFFFF')
.margin({top:'20vp', bottom:'20vp', left:'20vp', right:'20vp'})
Text('文案B')
.fontColor('#FFFFFF')
.margin({top:'20vp', bottom:'20vp', left:'20vp', right:'20vp'})
.position({x:'50%', y:'50%'}) //文案B设置了绝对位置
Text('文案C') // 文案C就顺位到第二个
.fontColor('#FFFFFF')
.margin({top:'20vp', bottom:'20vp', left:'20vp', right:'20vp'})
}.backgroundColor('#123456').width('90%').height('20%')
Row() {
Text('文案A')
.fontColor('#FFFFFF')
.margin({top:'20vp', bottom:'20vp', left:'20vp', right:'20vp'})
Text('文案B')
.fontColor('#FFFFFF')
.margin({top:'20vp', bottom:'20vp', left:'20vp', right:'20vp'})
.offset({x:'40%', y:'40%'}) //文案B设置了相对于自身原本位置的相对位置
Text('文案C') // 文案C没有顺位
.fontColor('#FFFFFF')
.margin({top:'20vp', bottom:'20vp', left:'20vp', right:'20vp'})
}.backgroundColor('#123456').width('90%').height('20%')
}.width('100%').height('100%')
}
}
2. flex
柔性组件,这个布局我们可以把他简单的理解成加强版的Column或者Row
- 这个布局就可以通过参数设置的方式将其设定成横向或者纵向,反向的排列也能做到
- 可以自带换行功能,当放不下的时候自动换到下一行或者下一列,该功能也可以不启用。
简单介绍一下主轴和交叉轴的概念:
当内部元素横向排列的时候,横轴(X轴)就是主轴,纵轴(Y轴)就是交叉轴
纵向排列的时候也是同理,Y轴是主轴,X轴就反过来变成交叉轴
@Preview
@Component
export struct MyFlexView {
build() {
Column({space:10}) {
//flex可以看成是自带换行功能的row或者Column
//主轴和交叉轴
Flex({direction:FlexDirection.Row, // 排列方式,行或者列或者反向的行列
wrap:FlexWrap.Wrap, // 单行还是多行排列
alignItems:ItemAlign.Start}) { // 所有子组件在交叉轴上的对齐方式
Text('文案1').fontColor(0xffffff)
.width('100').height('50')
.margin({top:'20vp', bottom:'20vp', left:'20vp', right:'20vp'})
.backgroundColor(0x123456)
Text('文案2').fontColor(0xffffff)
.width('100').height('100') // 没有办法通过flex实现瀑布流的那种左右自适应高度的效果
.margin({top:'20vp', bottom:'20vp', left:'20vp', right:'20vp'})
.backgroundColor(0x123456)
Text('文案3').fontColor(0xffffff)
.width('100').height('50')
.margin({top:'20vp', bottom:'20vp', left:'20vp', right:'20vp'})
.backgroundColor(0x123456)
}.width('90%').height('100%').backgroundColor(0xFFCC99).align(Alignment.Center)
}.height('100%').width('100%')
}
}
3. Stack
堆栈组件,里面的元素都是直接摆放,后面放上去的视图在视觉效果上会显示在前面。
@Preview
@Component
export struct MyStackView {
build() {
Column({space:10}) {
//后面一个视图会盖住前面视图的Stack
Stack() {
Text('我是第一加进来的视图').fontColor(0xffffff).backgroundColor(0x123456)
.height('100%').width('100%')
Text('我是第二个加进来的视图').width('100%').fontColor(0xffffff).backgroundColor(0xffcc99)
.height('40%').width('50%').align(Alignment.Center)
}.alignContent(Alignment.Bottom)
}.width('100%').height('50%')
}
}
4. List
列表组件,适用于摆放多个类型相同的视图
5. RelativeContainer
相对组件,里面的子组件的具体位置都是相对于其他的子组件来摆放的,需要做一个复杂UI的时候一般都把他丢在最外层。
@Preview
@Component
export struct MyRelativeView {
build() {
RelativeContainer() {
//RelativeContainer的子组件必须得是有id这个方法的的容器
Row()
.backgroundColor(0xffcc99)
.height('20%')
.width('20%')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Top },
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Center }
})
.id('row1')
// 和Stack一样,后面添加的View会覆盖前面的View
Row()
.backgroundColor(0x000000)
.height('10%')
.width('20%')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Top },
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Center }
})
.id('row2')
// 虽然限制了10%的宽度,但是在设置了left和right且比10%更长的情况下会被拉长
Row()
.backgroundColor(0xf12562)
.height('10%')
.width('10%')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom },
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
right: { anchor: "row1", align: HorizontalAlign.Center },
})
.id('row3')
// 在和第三个Row对齐的时候,仍然以其实际的宽高为准,而不是代码的10%
Row() {
Text('第4个Row')
}.backgroundColor(0x999999)
.height('10%')
.width('20%')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: "row3", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom },
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
right: { anchor: "row3", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
}).id('row4')
// 如果约定好上下左右,不需要宽高也能设置视图
Row() {
Text('第5个Row')
}.backgroundColor(0x777777)
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom },
left: { anchor: "row1", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
right: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
bottom: { anchor: "row3", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
}).id('row5')
}.height('100%').width('100%')
}
}
6. Grid
网格组件,当需要子组件以一定规则排列的时候就用它。
比较值得说的一个是rowsTemplate和columnsTemplate
以columnsTemplate来说明的话,你可以用这个方法,来指定grid存在多少列,每一行的比重是多少
比如columnsTemplate('1fr 2fr ')就是分为两列,第二列的宽度是三分二,第一列则是三分一
columnsTemplate('1fr 2fr 1fr ')就是分为三列,第二列的宽度是一半,第一列和第三列则是四分一
@Preview
@Component
export struct MyGridView {
build() {
Grid() {
GridItem() {
Text('1').fontColor(0xffffff)
}
.width('30%')
.height('20%')
.backgroundColor(0x111111)
GridItem() {
Text('2').fontColor(0xffffff)
}
.width('30%')
.height('10%')
.backgroundColor(0x111111)
// 当判断放不下的时候就会自动换行
GridItem() {
Text('3').fontColor(0xffffff)
}
.width('30%')
.height('20%')
.backgroundColor(0x111111)
GridItem() {
Text('4').fontColor(0xffffff)
}
.width('30%')
.height('20%')
.backgroundColor(0x111111)
}.width('100%').height('50%')
.rowsGap(10) // 不同行之间的间距
.columnsGap(25) // 不同列之间的间距
//.columnsTemplate('1fr 2fr ') // 将GridItem分为两列,第二列的高度分了2/3,第一列分了1/3
.rowsTemplate('1fr 2fr 1fr') // 将Grid分为两行,同时设置rowsTemplate和columnsTemplate时会出问题,所以分开调试
// 当用上rowsTemplate或columnsTemplate的时候,item自己的宽高功能的设置就会某种程度的失效,需要多用preview确认
}
}
7. Scroll
滑动组件,当内部子组件的高度或者宽度超出可以父组件可以显示的距离时,可以通过滑动的方式查看内容
- 原本它有个既可以横向又可以纵向滑动的free模式,但是API9开始就废弃了,所以目前单个的Scroll组件只能横向或纵向滑动。
@Preview
@Component
export struct MyScroll {
build() {
Column() {
Scroll() {
// 滑动组件只能有一个子组件,通过该子组件来摆放实际的UI
Row() {
Text('1').height('10%').width('50%').backgroundColor(0x999999)
Text('2').height('10%').width('50%').backgroundColor(0x999999)
Text('3').height('10%').width('50%').backgroundColor(0x999999)
}
}.height('50%').width('100%').scrollable(ScrollDirection.Horizontal)
Scroll() {
Column() {
Text('1').height('50%').width('50%').backgroundColor(0x999999)
Text('2').height('50%').width('50%').backgroundColor(0x999999)
Text('3').height('50%').width('50%').backgroundColor(0x999999)
}
}.height('50%').width('100%').scrollable(ScrollDirection.Vertical)
}
}
}
8. Tabs
标签组件,有不同的标签视图和内容视图,点击不同的标签就会切换到对应的内容视图。
Tabs由三个不同的部分组成
tabBar:标签,用于标明不同视图的标签,是一个自定义UI,案例代码写的就是普通的Button
tabContent:内容,用于展示不同的内容,也是一个自定义UI,案例代码写的是普通的Text
TabsController:tabs的控制类,用于处理不同tab之间的切换逻辑。
@Preview
@Component
export struct MyTabView {
private tabsController = new TabsController() // 用于控制tabs切换到不同的tab
@Builder
myTabBar(pos: number) {
// 修改这里的高度过高了会失效,需要在tabs里面修改
Button('tabBar' + pos).backgroundColor(0x888888).height(50)//.height(300)
.onClick(() => {
this.tabsController.changeIndex(pos-1) // 点击不同的tabBar就会切换到对应的tabContent
})
}
@Builder
myTabContent(pos: number) {
Text('tabContent' + pos).backgroundColor(0x999999).height(100)
.onClick(() => {
console.log(pos + "")
})
}
build() {
Tabs({
barPosition: BarPosition.Start, //
controller: this.tabsController }) {
TabContent() {
this.myTabContent(1)
}.tabBar(this.myTabBar(1))
TabContent() {
this.myTabContent(2)
}.tabBar(this.myTabBar(2))
TabContent() {
this.myTabContent(3)
}.tabBar(this.myTabBar(3))
}.height('100%').width('100%')
.barHeight(100).barBackgroundColor(0x777777) // tabBar的高度由tabs控制
}
}
9. WaterFlow
瀑布流组件,他在grid的基础上,支持每个视图大小都不一样的情况时,仍然可以正常排列
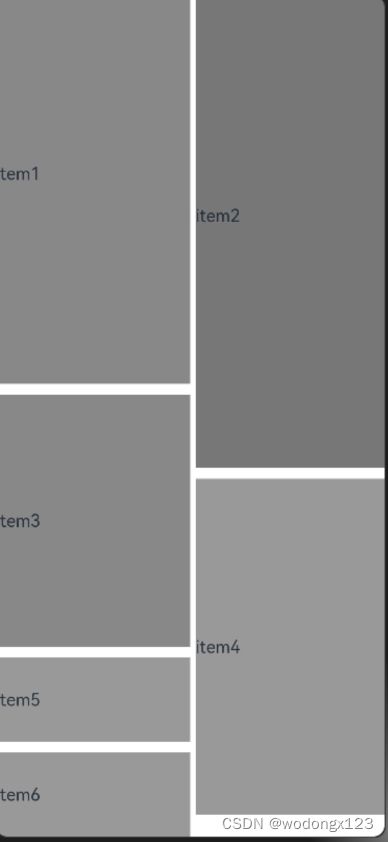
@Component
export struct MyFlowView {
build() {
WaterFlow() {
FlowItem() {
Text('item1').height('50%').width('50%').backgroundColor(0x888888)
}
FlowItem() {
Text('item2').height('60%').width('50%').backgroundColor(0x777777)
}
FlowItem() {
Text('item3').height('30%').width('50%').backgroundColor(0x888888)
}
FlowItem() {
Text('item4').height('40%').width('50%').backgroundColor(0x999999)
}
// 这两个加起来都没有超过右边的高度,所以一起在左边
FlowItem() {
Text('item5').height('10%').width('50%').backgroundColor(0x999999)
}
FlowItem() {
Text('item6').height('10%').width('50%').backgroundColor(0x999999)
}
}.height('100%').width('100%')
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr').columnsGap(10) // 通过columnsTemplate来限制有多少列,每列占多少比重
.rowsGap(10)
//.rowsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr')
}
}
参考资料
- 鸿蒙API参考
- harmony 鸿蒙弹性布局(Flex)
https://www.seaxiang.com/blog/022dc7507623403d8b5ee6af7f382dd8#menu_7