线程与线程池(一条龙详解)
一:前言
一个问题引出的学习笔记
并发类库提供的线程池实现有哪些?
其实Executors已经为我们封装好了 4 种常见的功能线程池,如下:
- 定长线程池(FixedThreadPool)
- 定时线程池(ScheduledThreadPool )
- 可缓存线程池(CachedThreadPool)
- 单线程化线程池(SingleThreadExecutor)
那么接下来就复习一波线程和线程池
二:线程
1:关于线程的理解
- 自我理解:(这是在javaweb中的文件上传部分 实际用到的线程 来帮助理解线程)
一个线程就是一条执行路径 ,实际例子当中 我们请求一个页面如果需要很长的时间的话,这时候我们需要设置线程来执行 请求消息中的代码,然后再写一个代码先显示出请求等待的信息 - 官方解读:
线程,程序执行流的最小执行单位,是行程中的实际运作单位,经常容易和进程这个概念混淆。那么,线程和进程究竟有什么区别呢?首先,进程是一个动态的过程,是一个活动的实体。简单来说,一个应用程序的运行就可以被看做是一个进程,而线程,是运行中的实际的任务执行者。可以说,进程中包含了多个可以同时运行的线程。
2:线程的声明周期
线程的生命周期,线程的生命周期可以利用以下的图解来更好的理解:

3:单线程和多线程
三:线程池
1:线程池从何处而来
- 在一个应用程序中,我们需要多次使用线程,也就意味着,我们需要多次创建并销毁线程。而创建并销毁线程的过程势必会消耗内存。而在Java中,内存资源是及其宝贵的,所以,我们就提出了线程池的概念
线程池:Java中开辟出了一种管理线程的概念,这个概念叫做线程池,从概念以及应用场景中,我们可以看出,线程池的好处,就是可以方便的管理线程,也可以减少内存的消耗。
2:线程池的好处
- (1) 降低资源消耗。 通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗。
- (2) 提高响应速度。当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等到线程创建就能立即执行。
- (3) 提高线程的可管理性。线程是稀缺资源,如果无限制的创建,不仅会消耗系统资源,还会降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池可以进行统一的分配,调优和监控。
3:如何实现线程池
那么,我们应该如何创建一个线程池那?Java中已经提供了创建线程池的一个类:Executor类,而我们创建时,一般使用它的子类:ThreadPoolExecutor.
线程池的真正实现类是 ThreadPoolExecutor,其构造方法有如下4种:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
threadFactory, defaultHandler);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
4:线程池的使用流程
// 创建线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(CORE_POOL_SIZE,
MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE,
KEEP_ALIVE,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
sPoolWorkQueue,
sThreadFactory);
// 向线程池提交任务
threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
... // 线程执行的任务
}
});
// 关闭线程池
threadPool.shutdown(); // 设置线程池的状态为SHUTDOWN,然后中断所有没有正在执行任务的线程
threadPool.shutdownNow(); // 设置线程池的状态为 STOP,然后尝试停止所有的正在执行或暂停任务的线程,并返回等待执行任务的列表
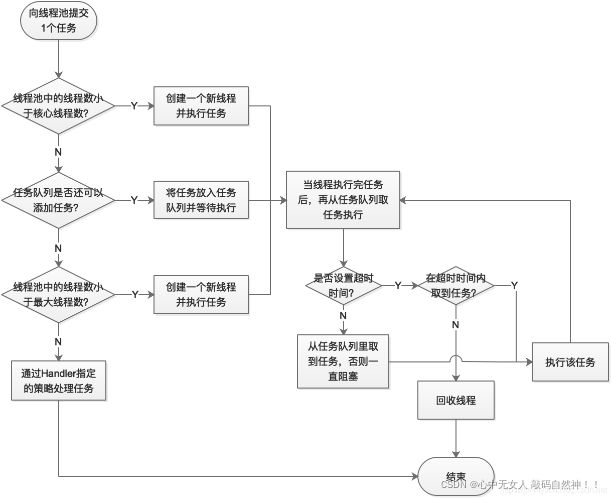
5:线程池的工作原理
6:线程池的重要参数解读
(1):任务队列
(2):线程工厂(threadFactory)
线程工厂指定创建线程的方式,需要实现 ThreadFactory 接口,并实现 newThread(Runnable r) 方法。该参数可以不用指定,Executors 框架已经为我们实现了一个默认的线程工厂:
(3):拒绝策略(handler)
7:功能性线程池
嫌上面使用线程池的方法太麻烦?其实Executors已经为我们封装好了 4 种常见的功能线程池,如下:
- 定长线程池(FixedThreadPool)
- 定时线程池(ScheduledThreadPool )
- 可缓存线程池(CachedThreadPool)
- 单线程化线程池(SingleThreadExecutor)
- newWorkStealingPool
(1): newFixedThreadPool (固定数量的线程池)
创建的源码:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory);
}
- 特点:只有核心线程,线程数量固定,执行完立即回收,任务队列为链表结构的有界队列。
- 应用场景:控制线程最大并发数。
- 使用实例:
// 1. 创建定长线程池对象 & 设置线程池线程数量固定为3
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// 2. 创建好Runnable类线程对象 & 需执行的任务
Runnable task =new Runnable(){
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行任务啦");
}
};
// 3. 向线程池提交任务
fixedThreadPool.execute(task);
(2): newWorkStealingPool

这个线程池的特性从名字就可以看出 Stealing,会窃取任务。
每个线程都有自己的双端队列,当自己队列的任务处理完毕之后,会去别的线程的任务队列尾部拿任务来执行,加快任务的执行速率。
至于 ForkJoin 的话,就是分而治之,把大任务分解成一个个小任务,然后分配执行之后再总和结果,
(3): newSingleThreadExecutor (单线程池)
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory));
}
特点:只有 1 个核心线程,无非核心线程,执行完立即回收,任务队列为链表结构的有界队列。
应用场景:不适合并发但可能引起 IO 阻塞性及影响 UI 线程响应的操作,如数据库操作、文件操作等。
使用实例:
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory));
}
(4):newCachedThreadPool (可缓存的线程池)
创建方法的源码:
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory);
}
特点:无核心线程,非核心线程数量无限,执行完闲置 60s 后回收,任务队列为不存储元素的阻塞队列。
应用场景:执行大量、耗时少的任务。
所以它适合用在短时间内有大量短任务的场景。如果暂无可用线程,那么来个任务就会新启一个线程去执行这个任务,快速响应任务。
但是如果任务的时间很长,那存在的线程就很多,上下文切换就很频繁,切换的消耗就很明显,并且存在太多线程在内存中,也有 OOM 的风险。
使用示例:
// 1. 创建可缓存线程池对象
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 2. 创建好Runnable类线程对象 & 需执行的任务
Runnable task =new Runnable(){
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行任务啦");
}
};
// 3. 向线程池提交任务
cachedThreadPool.execute(task);
(5): newScheduledThreadPool(定时线程池)
创建方法的源码:
private static final long DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS = 10L;
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(
int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, threadFactory);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory);
}
特点:核心线程数量固定,非核心线程数量无限,执行完闲置 10ms 后回收,任务队列为延时阻塞队列。
应用场景:执行定时或周期性的任务。
使用示例:
/ 1. 创建 定时线程池对象 & 设置线程池线程数量固定为5
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
// 2. 创建好Runnable类线程对象 & 需执行的任务
Runnable task =new Runnable(){
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行任务啦");
}
};
// 3. 向线程池提交任务
scheduledThreadPool.schedule(task, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 延迟1s后执行任务
scheduledThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(task,10,1000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);// 延迟10ms后、每隔1000ms执行任务
参考自这篇博客