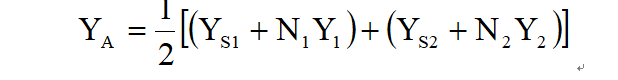c++摄影测量点投影系数法和共线方程法空间前方交会
立体像对空间前方交会程序设计
运用了eigen矩阵库
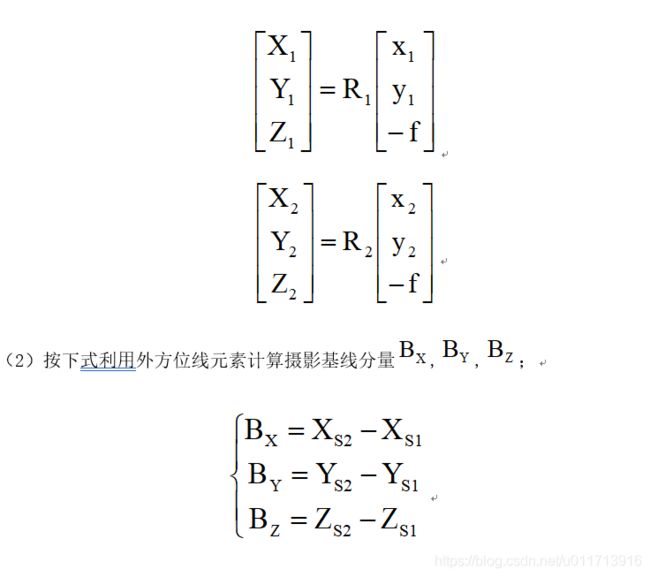
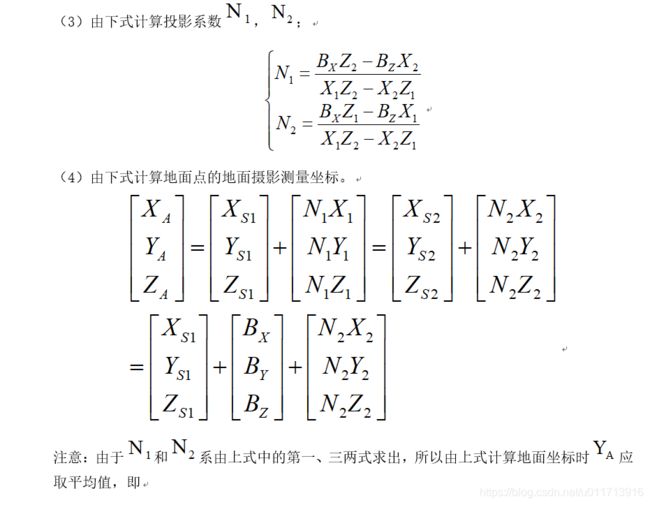
程序原理
【实验数据】:
左影像:x0=0; y0=0; f=152.91;
Xs=970302.448784;
Ys=-1138644.971216;
Zs=3154.584941;
phi=0.010425;
omega=-0.012437;
kapa=0.003380;
右影像:x0=0; y0=0; f=152.91;
Xs=971265.303768;
Ys=-1138634.245942;
Zs=3154.784258;
phi=0.008870;
omega=-0.005062;
kapa=-0.008703;
同名像点坐标:左:(0.153,91.798),右:(-78.672,89.122)
c++代码
写入头文件
#pragma once
#include 调用格式
#include "Function.h"
#include