<C++>STL->string
string类的由来
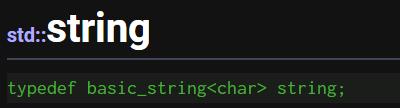
string类是模板实例化后的别名,basic_string是字符串类模板,常见的字符串类型有wchar_t char char16_t
char32_t ,basic_string类针对的是所有字符串类型设计出来的一个模板,而我们通常使用的字符串类型是char,模板实例化为char的类命名为string。
为什么要有string类?
- string更符合C++面向对象的设计,将对数据的处理和数据封装在一起
- 对字符串进行操作时使用string不需要考虑空间不够的问题,string类会自动扩容
- string类成员函数的可读性更强,操作更简便
string类的使用
string类文档
string的成员函数非常多,下面介绍常用的
构造函数

void test_string1()
{
string s1;
cout << s1 << endl;//空串
string s2("hello world");
cout << s2 << endl;//hello world
string s3(s2);
cout << s3 << endl;//hello world
string s4(s3, 6, 5);
cout << s4 << endl;//world
string s5("hello world", 6, 5);
cout << s5 << endl;//world
string s6(s2.begin(), s2.end());//使用迭代器初始化[h,/0)
cout << s6 << endl;//hello world
string s7(4, 'a');
cout << s7 << endl;//aaaa
}
复制重载
void test_string2()
{
string s1("abcdef");
string s2("123456");
cout << s2 << endl; //123456
s2 = s1;
cout << s2 << endl; //abcdef
s2 = "hello";
cout << s2 << endl; //hello
s2 = 'c';
cout << s2 << endl; //c
}
迭代器
迭代器STL六大组件之一,迭代器(iterator),是确使用户可在容器物件(container,例如链表或数组)上遍访的物件[1][2][3],设计人员使用此接口无需关心容器物件的内存分配的实现细节。
迭代器是一种方便使用者遍历所有容器通用的一个方法。使用者可以通过迭代器遍历所有的容器。
我们主要使用begin,end,rbegin,rend这四个迭代器,它们重载了const成员函数
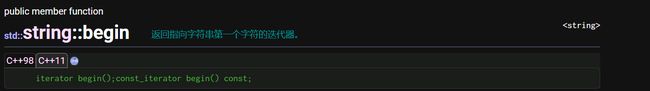
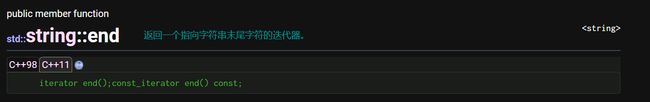
begin/end
begin/end是正向迭代器,每次结束begin()指向的是容器第一个元素,end指向容器最后一个元素后面一个位置。
string::iterator it++代表it指向容器的下一个数据
string s1("hello world");
const string s2("I am constant");
string::iterator it = s1.begin();//it是一个迭代器,是s1对象起始位置的迭代器
while (it != s1.end()) //当it为s1终止位置的迭代器时说明it已经将s1遍历完
{
cout << *it << " ";//迭代器的用法类似与指针
it++;//迭代器指向下一个数据
}
cout << endl;
string::const_iterator cit = s2.begin();//调用的是const成员函数begin()
while (cit != s2.end())
{
cout << *cit << " ";
cit++;
}
cout << endl;
rbegin/rend
string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();//rit是一个反向迭代器,指向容器最后一个数据
while (rit != s1.rend()) //rit为s1起始位置时说明已经将s1反向遍历完成
{
cout << *rit << " ";
rit++;//反向迭代器++是指向前一个数据
}
cout << endl;
string::const_reverse_iterator crit = s2.rbegin();
while (crit != s2.rend())
{
cout << *crit << " ";
crit++;
}
cout << endl;
}
**注意:**cbegin,cend,crbegin,crend是针对const string专门设计的迭代器,但是C++11已经重载了begin等函数的const成员函数,因此可以直接使用begin处理const string
容量相关函数
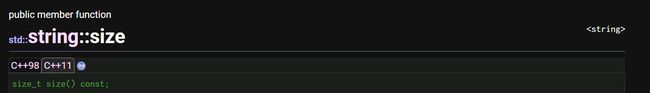
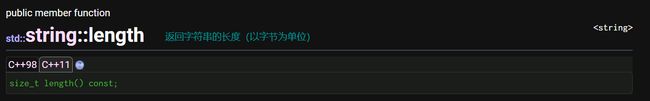
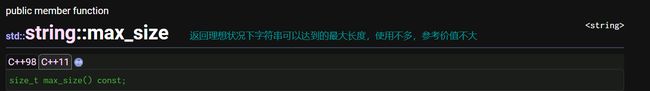
size:返回字符串长度
length:返回字符串长度
max_size:返回string对象最大长度
capacity:返回字符串容量
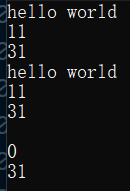
void test_string4()
{
string s("hello world");
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.length() << endl;
cout << s.max_size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
}

resize:调整字符串大小
- 如果n比当前对象有效元素长度小,则当前对象只保留前n个字符,删掉其余字符
- 如果n比当前对象有效元素长度大,则用指定的字符填充字符串直到字符串的长度等于n,若无指定字符则使用
\0填充。 - 如果n比当前容量大,则扩容到n个有效空间,并用指定字符填充空间
- resize影响容量,也影响内容
void test_string5()
{
string s("hello world");
s.resize(5);
cout << s << endl;//hello
cout << s.size() << endl;//5
cout << s.capacity() << endl//15;
s.resize(7, 'x');
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
cout << s << endl;
}
reserve:请求更改容量
-
求将字符串容量调整为计划的大小更改,长度最多为 n 个字符。
-
如果 n 大于当前字符串容量,该函数会使容器将其容量增加到 n 个字符(或更大)。
-
如果n小于等于当前字符串容量,会被视为不具有约束力的请求,容器可自由实现(VS下不会进行缩容,g++下会缩容,但是它们都不会删除数据)。
-
该函数不能改变字符串的长度和内容,只会影响容量.
-
reserve最大的价值是提前开好空间减少多次扩容的消耗.
clear:清理字符串
- clear不会改变字符串的容量
void test_string6()
{
string s("hello world");
s.reserve(20);
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.reserve(10);
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.clear();
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;//不改变capacity
}
VS下由于
内存对齐reserve函数实际申请的空间比需要的空间大
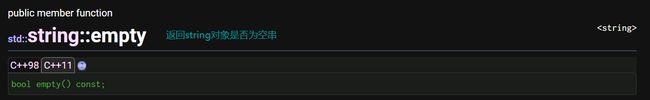
empty:测试字符串是否为空
访问元素类函数
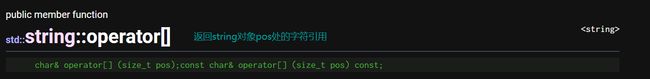
operator[]:获取pos处的字符
-
pos的值应该属于[0, size()]
-
若pos==size(),不应该更改pos处的值,因为此时pos处为
\0 -
当pos不合法时,operator[]会调用
assert终止程序
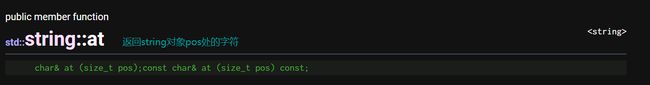
at:获取pos处的字符
- 和operator[]注意点一样,不同的是当pos不合法时,at会抛异常终止程序。
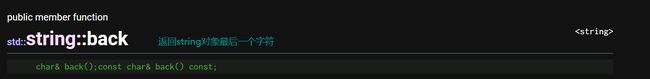
back:获取字符串最后一个字符
front:获取字符串第一个字符
void test_string7()
{
string s("hello world");
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
cout << s[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
cout << s.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
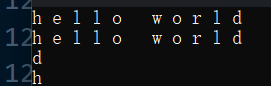
cout << s.back() << endl;
cout << s.front() << endl;
}
运行结果:
修改类函数
operator+=:追加字符串
append:追加字符串
push_back:尾插单个字符
assign:将内容分配给字符串
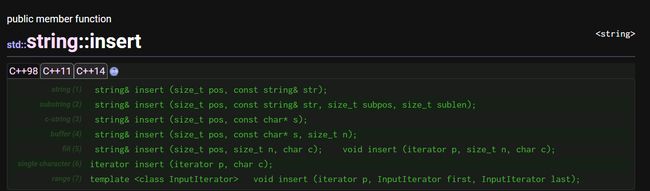
insert:pos位置前插入字符串
erase:从字符串中删除字符
若不指定删除字符个数,默认删除npos个字符
无符号的-1相当于
INT32_MAX,因此erase若不指定删除字符个数默认将pos后面所有字符全部删除。
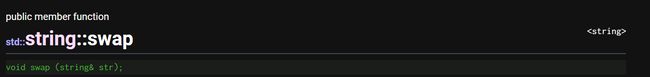
swap:交换字符串值
string中单独实现的swap算法效率比alogrithm里的swap效率高(不涉及深拷贝)
pop_back:删除最后一个字符
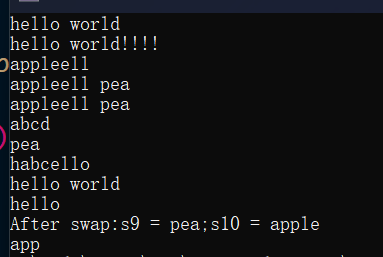
void test_string8()
{
string s1("hello ");
string s2("world");
s1 += s2;
cout << s1 << endl;
s1 += "!!!";
s1 += '!';
cout << s1 << endl;//hello world!!!!
string s3("apple");
s3.append(s1, 1, 3);
cout << s3 << endl;//appleell
const char* str = " pea";
s3.append(str, 4);
cout << s3 << endl;//appleell pea
string s4;
s4.append(s3.begin(), s3.end());
cout << s4 << endl;//apple pea
string s5;
s5.push_back('a');
s5.push_back('b');
s5.push_back('c');
s5.push_back('d');
cout << s5 << endl;//abcd
s5.assign(s3, 9, 3);//覆盖s5的内容
cout << s5 << endl;//pea
string s6("hello");
string s7(" world");
s6.insert(1, "abcde", 3);
cout << s6 << endl;//habcello
s6.assign("hello");
s6.insert(s6.size(), s7);
cout << s6 << endl; //hello world
string s8("hello world");
s8.erase(5);
cout << s8 << endl; //hello
string s9("apple");
string s10("pea");
s9.swap(s10);
cout << "After swap:s9 = " << s9 << ";s10 = " << s10 << endl;//s9=pea;s10=apple
string s11("apple");
s11.pop_back();
s11.pop_back();
cout << s11;
}
运行结果:
其他操作
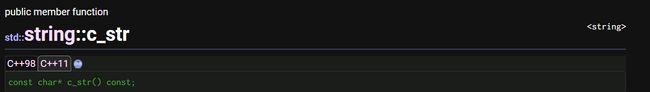
c_str:获取C风格字符串
find:在字符串中查找内容
-
字符串第一个字符被视为匹配的起始位置
-
pos若比len大 ,则不会查找
-
如果找到对应的字符串,返回第一个匹配的第一个字符的位置
-
如果没有找到对应的字符串,返回npos
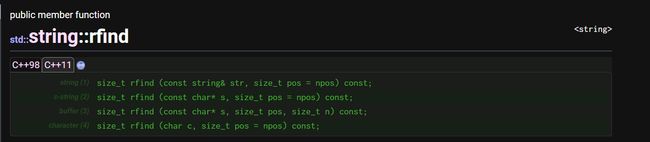
rfind:找到字符串中最后一次出现的内容
- 字符串最后一个字符将被视为匹配的起始位置
- 任何一个比length大的pos值意味着完整的字符串将被搜索
- 若查找到,则返回最后一次匹配的第一个字符的位置
- 若没有查找到,则返回npos.
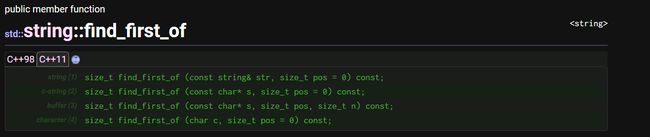
find_first_of:在string中查找字符
- 在字符串中搜索与其参数中指定的任何字符相匹配的第一个字符。
- string对象第一个字符被视为匹配的起始位置
- pos比length大则不会查找
- 在string中寻找匹配s或str任何字符
- 若搜索到则返回第一个匹配字符的位置
- 若没有搜索到返回npos
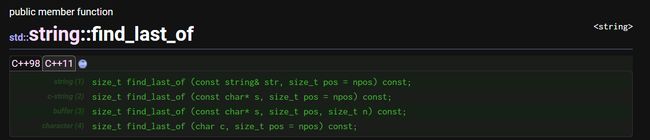
find_last_of:在string中从后往前查找字符
- 在字符串中搜索与其参数中指定的任何字符相匹配的最后一个字符。
- string中最后一个字符被视为匹配的起始位置
- 任何一个比length大的值意味着完整的string将被搜索
- 若搜索到返回最后一个匹配字符的位置
- 为搜索到返回npos
substr:获取子串
- 如果pos等于对象长度,返回一个空串
- 如果pos大于对象长度,抛异常
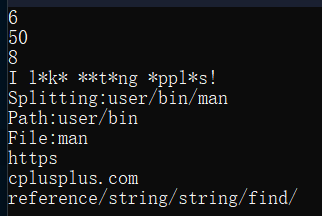
void test_string10()
{
string s("https://cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/find/");
size_t pos = s.find("/");//返回"cplus"第一次出现的位置
if (pos != string::npos)
{
cout << pos << endl;
}
size_t rpos = s.rfind("/");
if (rpos != string::npos)
{
cout << rpos << endl;//50
}
size_t apos = s.find_first_of("abcdef");
if (apos != string::npos)
{
cout << apos << endl;//8
}
string s1("I like eating apples!");
size_t find = s1.find_first_of("aeiou");
while (find != string::npos)
{
s1[find] = '*';
find = s1.find_first_of("aeiou", find + 1);
}
cout << s1 << endl;
string s2("user/bin/man");
cout << "Splitting:" << s2 << endl;
size_t found = s2.find_last_of("/\\");
if (found != string::npos)
{
cout << "Path:" << s2.substr(0, found) << endl;
cout << "File:" << s2.substr(found + 1) << endl;
}
s = "https://cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/find/";
size_t pos1 = s.find(":");
string protocols = s.substr(0, pos1);
cout << protocols << endl;
size_t pos2 = s.find("/", pos1 + 3);
string domain = s.substr(pos1 + 3, pos2 - pos1 - 3);
cout << domain << endl;
string source = s.substr(pos2 + 1);
cout << source << endl;
}
非成员函数
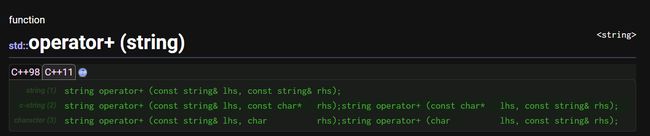
operator+:拼接字符串
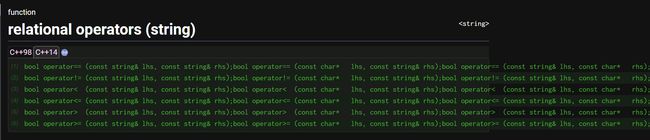
[ralational operators](https://cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/ralational operators/):对字符串的比较操作
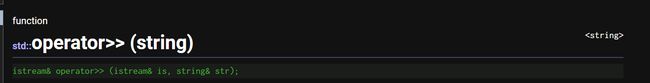
operaotr>>:从流中提取字符串
- 遇见空白符结束流提取
- 想要提取空白符需要使用
getline
operator<<:将字符串打印到流中
getline:从流中提取一行到string中
-
从 is 中提取字符并将其存储到 str 中,直到找到分隔符 delim(或换行符“\n”,对于 (2))
-
如果到达文件结尾或输入操作期间发生其他错误,提取也会停止。
-
如果找到分隔符,它将被提取并丢弃
不同编译器下的string结构
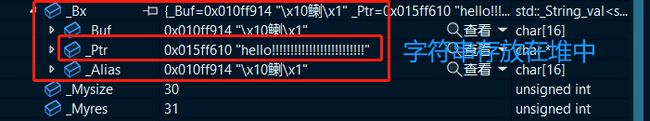
vs下string
下述结构是在32位平台下进行验证,32位平台下的指针为4字节
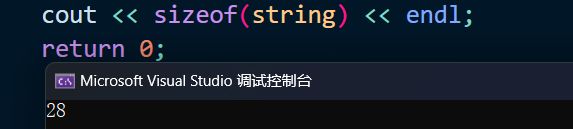
vs下string的结构总共占28字节,其中由以下几部分组成:
- 联合体_Bx
- 指针_Myproxy记录其他信息
- 记录字符串有效长度变量_Mysize
- 记录当前字符串容量变量_Myres
联合体_Bx中存放的是字符串的内容
故string的大小为 16 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 28 16+4+4+4=28 16+4+4+4=28
g++下string
g++下的string结构通过一个指针实现,指针指向一个结构,结构包含:
- 空间总大小
- 字符串有效长度
- 引用计数
- 指向堆空间的字符串,用来存放字符串内容
string的模拟实现
请移步string模拟实现