【iOS高级资深工程师面试篇】①、2022年,金九银十我为你准备了《iOS高级资深工程师面试知识总结》 UI部分1/3 -UITableView-事件传递&视图响应
iOS高级资深工程师面试篇系列 - 已更新3篇
UI部分1/3 -UITableView-事件传递&视图响应
UI部分2/3 -图像显示原理-UI卡顿&掉帧
UI部分3/3 -UIView绘制原理-离屏渲染
技术:iOS底层原理、事件传递、视图响应、图像显示原理、UI卡顿&掉帧、UIView绘制原理、离屏渲染
①、《iOS高级资深工程师面试知识总结》 UI部分1/3 -UITableView-事件传递&视图响应
-
-
- 如何区分iOS的初级工程师、中级工程师、高级工程师、资深工程师
-
-
- 1. iOS初级工程师基本要求
- 2. iOS中级工程师基本要求
- 3. iOS高级工程师基本要求 - `一般作为公司的主力工程师`
- 4. iOS资深工程师基本要求
- 一、UITableView
-
- ❓面试考点: UITableview的重用机制是如何实现的/或者说底层原理是怎么样的、UITableview在多线程环境下如何实现数据源同步
- 1.1、UITableView - 重用机制
-
- `重用` `复用`机制的流程
- 例子1 - 通过一个自定义UI控件 - 字母索引条来实现一个重用机制
-
- 字母索引条来实现一个重用机制 -效果图
- 例子1 - Code
-
- ViewReusePool - 代表的是 一个重用池
- IndexedTableView - 代表的是 索引条的tableview
- ViewController - 代表的是 控制器实现一个重用机制的索引条
- 1.2、UITableView - 数据源同步
- ❓面试考点: 如果解决tableview多线程环境下去修改或者访问它的数据源同步问题
- 解决方案1 - 并发访问、数据拷贝
-
- 通过-时序图-查看 并发访问、数据拷贝
- 解决方案2 - 串行访问
-
- 通过-时序图-查看串行访问的流程
- 方案1`并发访问、数据拷贝` 和方案2`串行访问` 的利弊
- 二、事件传递&视图响应
-
- UIView和CALayer关系
- UIView和CALayer区别
- 例子2 - 事件传递与视图响应链
-
- 事件传递的主要跟两个方法有关
- ⭐️事件传递流程
- ⭐️hitTest系统内部实现
- 方形按钮指定区域接受事件响应 -效果图
- 例子2 - 代码实战 - Code
-
- ViewController - 代表的是 控制器实现一个方形按钮指定区域接受事件响应
- CustomButton - 代表的是 自定义按钮 - 重写了hitTest、pointInside来实现`方形按钮指定区域接受事件响应`
- 参考文献、[官方文档](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/technologies?language=objc)- 使用响应者和响应者链来处理事件([旧版本](https://developer.apple.com/library/archive/documentation/WindowsViews/Conceptual/ViewControllerPGforiOSLegacy/BasicViewControllers/BasicViewControllers.html#//apple_ref/doc/uid/TP40011381-CH101-SW45))([新版本](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/uikit/touches_presses_and_gestures/using_responders_and_the_responder_chain_to_handle_events?language=objc))
- 参考文献、[官方文档](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/technologies?language=objc)-[视图事件响应](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/uikit/uiresponder/1621142-touchesbegan?language=objc)
-
- 综合案例说明 - 传递机制
- ❓面试考点(易错题) - 假如此时传递到`UIApplicationDelegate`仍然没有响应处理,会发生什么场景
-
-
如何区分iOS的初级工程师、中级工程师、高级工程师、资深工程师
1. iOS初级工程师基本要求
1. 精通Objective-C语言基础
2. 精通UIkit等Cocoa Framework
3. 精通网络通讯机制以及常用数据传输协议
http和https的区别
算法:常见的加密算法 - 对称加密算法、以及非对称加密算法 有一定的认识
数据格式: Json和XML如何解析
4. 具备主流开源框架的使用经验
主要停留在会用的情况就行
主流开源框架有 : AFNetworking网络框架、SDWebImage异步下载图片网络框架。还有一些其他第三方框架。
加分项: 其他比较热门的第三方框架的使用心得
2. iOS中级工程师基本要求
公司对于中级工程师的要求
一般停留在为什么这样用的情况
1. 扎实的编程、数据结构、算法基础
2. 深入理解语言机制(Runtime)、内存管理、网络、多线程、GUI
3. 精通常用设计模式、框架、架构
针对现有的很多公司的产品都是一个成熟、稳重的。对于代码维护是耗费很多成本的。
所以设计模式、框架、架构是可以提高代码的可扩展性、灵活性。
4. 良好的分析、解决问题的能力
要学习别人如何解决问题的
这里最好的老师 就是研究Apple官方的源码 - 源码面前无密码
3. iOS高级工程师基本要求 - 一般作为公司的主力工程师
公司对于中级工程师的要求
一定能够创造性提出一些解决方案
1. 解决研发过程中的关键问题和技术难题
2. 调优设备流量、性能、电量等
比如你在美团 那么一定会针对外卖员送外卖的App进行电量的调优。因为使用到导航。我们如何减少控制电量。
比如你在今日头条 或者其他大厂的新闻类的App。那么就需要做Tableview的滚动的性能调优。因为用户看新闻是一直滚动的。
3. 较强的软件设计能力
对于一个复杂的页面上面。要求有一个架构性上的设计
4.对iOS内部原理有深刻理解
对于中级工程师其实也要求了。
对于高级需要有深刻的理解
4. iOS资深工程师基本要求
科普:什么是feed流
1. 精通高性能编程以及性能调优
在前期设计架构上面一定要做考虑
比如做一个feed流的这样一个实际应用的时候、一定要考虑性能上面的问题
性能方面:对象的创建、字符串的遍历(较优的算法)、
2. 灵活运用数据结构、算法解决复杂程序设计问题
什么样的情况用什么样的数据结构和算法
3. 提供性能优化、日志搜集、统计分析等方案 - 架构师必备
4. 架构、模块设计
往往对于一个App的掌控和设计
好了,废话不多说 直接进入正题 - 面试干货分析
一、UITableView
❓面试考点: UITableview的重用机制是如何实现的/或者说底层原理是怎么样的、UITableview在多线程环境下如何实现数据源同步
1.1、UITableView - 重用机制
写代码都会用到下面的重用机制
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:identifier];
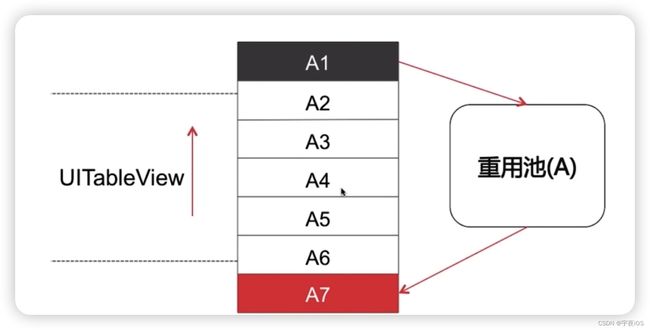
重用 复用机制的流程
- 当A1、A7都是使用同一个标识符的情况下
- 当Tableview向上滚动的时候 屏幕超出了A1部分 将A1存放到重用池里面
- 加载A7的情况 就会从重用池 那么A7就是重用A1的那一部分
例子1 - 通过一个自定义UI控件 - 字母索引条来实现一个重用机制
通过下面的demo 点击reloadTable 查看索引条是否使用了重用机制
字母索引条来实现一个重用机制 -效果图
例子1 - Code
ViewReusePool - 代表的是 一个重用池
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
// 实现重用机制的类
@interface ViewReusePool : NSObject
// 从重用池当中取出一个可重用的view
- (UIView *)dequeueReusableView;
// 向重用池当中添加一个视图
- (void)addUsingView:(UIView *)view;
// 重置方法,将当前使用中的视图移动到可重用队列当中
- (void)reset;
@end
// --- .m文件的实现
#import "ViewReusePool.h"
@interface ViewReusePool ()
// 等待使用的队列 - 使用集合实现
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableSet *waitUsedQueue;
// 使用中的队列
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableSet *usingQueue;
@end
@implementation ViewReusePool
- (id)init{
self = [super init];
if (self) {
_waitUsedQueue = [NSMutableSet set];
_usingQueue = [NSMutableSet set];
}
return self;
}
// 从重用池当中取出一个可重用的view
- (UIView *)dequeueReusableView{
// 从 等待使用的队列 取出一个对象 view
UIView *view = [_waitUsedQueue anyObject];
if (view == nil) {
// 没有可重用的view 就返回nil
return nil;
}
else{
// 进行队列移动
[_waitUsedQueue removeObject:view]; // 从等待重用中的移除可重用的view
[_usingQueue addObject:view];// 将可重用的view 添加到正在使用的队列里面
return view;
}
}
// 向重用池当中添加一个视图
- (void)addUsingView:(UIView *)view
{
// 如果view是空的 那么什么都不做
if (view == nil) {
return;
}
// 添加视图到使用中的队列
[_usingQueue addObject:view];
}
// 重置方法,将当前使用中的视图移动到可重用队列当中
- (void)reset{
UIView *view = nil;
// 进行一个循环 将使用中的队列 进行删除 添加到等待队列里面
while ((view = [_usingQueue anyObject])) {
// 从使用中队列移除
[_usingQueue removeObject:view];
// 加入等待使用的队列
[_waitUsedQueue addObject:view];
}
}
@end
IndexedTableView - 代表的是 索引条的tableview
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
// 定义了一个索引条tableview的数据源协议
@protocol IndexedTableViewDataSource <NSObject>
// 获取一个tableview的字母索引条数据的方法
- (NSArray <NSString *> *)indexTitlesForIndexTableView:(UITableView *)tableView;
@end
@interface IndexedTableView : UITableView
// 定义一个weak属性的数据源
@property (nonatomic, weak) id <IndexedTableViewDataSource> indexedDataSource;
@end
// --- .m文件的实现
#import "IndexedTableView.h"
#import "ViewReusePool.h"
@interface IndexedTableView ()
{
// 装载所有索引条的控件
UIView *containerView;
// 重用池机制的类
ViewReusePool *reusePool;
}
@end
@implementation IndexedTableView
// 重写reloaddata方法
- (void)reloadData{
[super reloadData];
// 懒加载
// 容器的view
if (containerView == nil) {
containerView = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectZero];
containerView.backgroundColor = [UIColor orangeColor];
//避免索引条随着table滚动
[self.superview insertSubview:containerView aboveSubview:self];
}
// 重用池 懒加载
if (reusePool == nil) {
reusePool = [[ViewReusePool alloc] init];
}
// 标记所有视图为可重用状态
[reusePool reset];
// reload字母索引条
[self reloadIndexedBar];
}
- (void)reloadIndexedBar
{
// 获取字母索引条的显示内容
NSArray <NSString *> *arrayTitles = nil;
if ([self.indexedDataSource respondsToSelector:@selector(indexTitlesForIndexTableView:)]) {
arrayTitles = [self.indexedDataSource indexTitlesForIndexTableView:self];
}
// 判断字母索引条是否为空
if (!arrayTitles || arrayTitles.count <= 0) {
[containerView setHidden:YES];
return;
}
NSUInteger count = arrayTitles.count;
CGFloat buttonWidth = 60;
// 当前tableview的高度 进行平分按钮的高度
CGFloat buttonHeight = self.frame.size.height / count;
for (int i = 0; i < [arrayTitles count]; i++) {
NSString *title = [arrayTitles objectAtIndex:i];
// 从重用池当中取一个Button出来
UIButton *button = (UIButton *)[reusePool dequeueReusableView];
// 如果没有可重用的Button重新创建一个
if (button == nil) {
button = [[UIButton alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectZero];
button.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
// 注册button到重用池当中
[reusePool addUsingView:button];
NSLog(@"新创建一个Button");
}
else{
NSLog(@"Button 重用了");
}
// 添加button到父视图控件
[containerView addSubview:button];
[button setTitle:title forState:UIControlStateNormal];
[button setTitleColor:[UIColor blackColor] forState:UIControlStateNormal];
// 设置button的坐标
[button setFrame:CGRectMake(0, i * buttonHeight, buttonWidth, buttonHeight)];
}
// 字母索引条的容器设置不隐藏 因为有可能上一次是没有Buttontitle的
// 防止重用所引起的问题
[containerView setHidden:NO];
containerView.frame = CGRectMake(self.frame.origin.x + self.frame.size.width - buttonWidth, self.frame.origin.y, buttonWidth, self.frame.size.height);
}
@end
ViewController - 代表的是 控制器实现一个重用机制的索引条
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
@interface ViewController : UIViewController
@end
// --- .m文件的实现
#import "ViewController.h"
#import "IndexedTableView.h"
@interface ViewController ()<UITableViewDataSource,UITableViewDelegate,IndexedTableViewDataSource>
{
IndexedTableView *tableView;//带有索引条的tableview
UIButton *button;
NSMutableArray *dataSource;
}
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
//创建一个Tableview
tableView = [[IndexedTableView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 60, self.view.frame.size.width, self.view.frame.size.height - 60) style:UITableViewStylePlain];
tableView.delegate = self;
tableView.dataSource = self;
// 设置table的索引数据源
tableView.indexedDataSource = self;
[self.view addSubview:tableView];
//创建一个按钮
button = [[UIButton alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 80, self.view.frame.size.width, 40)];
button.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
[button setTitle:@"reloadTable" forState:UIControlStateNormal];
[button addTarget:self action:@selector(doAction:) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside];
[self.view addSubview:button];
// 数据源
dataSource = [NSMutableArray array];
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
[dataSource addObject:@(i+1)];
}
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
}
#pragma mark IndexedTableViewDataSource
- (NSArray <NSString *> *)indexTitlesForIndexTableView:(UITableView *)tableView{
//奇数次调用返回6个字母,偶数次调用返回11个
static BOOL change = NO;
if (change) {
change = NO;
return @[@"A",@"B",@"C",@"D",@"E",@"F",@"G",@"H",@"I",@"J",@"K"];
}
else{
change = YES;
return @[@"A",@"B",@"C",@"D",@"E",@"F"];
}
}
#pragma mark UITableViewDataSource
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView
{
return 1;
}
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section
{
return [dataSource count];
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{
static NSString *identifier = @"reuseId";
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:identifier];
//如果重用池当中没有可重用的cell,那么创建一个cell
if (cell == nil) {
cell = [[UITableViewCell alloc] initWithStyle:UITableViewCellStyleDefault reuseIdentifier:identifier];
}
// 文案设置
cell.textLabel.text = [[dataSource objectAtIndex:indexPath.row] stringValue];
//返回一个cell
return cell;
}
#pragma mark - UITableViewDelegate
- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
return 40;
}
- (void)doAction:(id)sender{
NSLog(@"reloadData");
[tableView reloadData];
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
@end
1.2、UITableView - 数据源同步
常见的新闻、资讯类的App当中 比如今日头条、微博存在数据源同步
比如删除一条广告、然后进行刷新数据
- 删除广告是在
主线程执行的 - 数据源刷新是往往是在
子线程进行loadmore进行刷新的
❓面试考点: 如果解决tableview多线程环境下去修改或者访问它的数据源同步问题
解决方案1 - 并发访问、数据拷贝
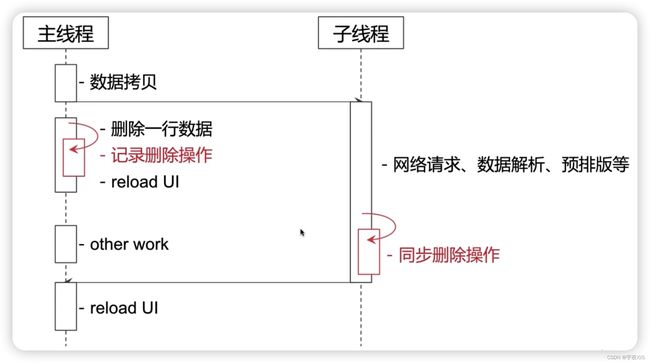
通过-时序图-查看 并发访问、数据拷贝
1、错误做法 -
1.1 - 删除过程中 拿到子线程的网络请求回来的数据 直接展示
1.2 - 上面存在的问题可能 子线程网络请求回来的数据 也可能包含删除那条数据 展示的时候 还是会展示出来删除的数据
2、正确做法
2.1 - 删除过程中 记录一下删除的数据
2.2 - 然后在子线程 进行网络请求回来的数据 如果发现数据还是存在删除的数据 也进行一次删除操作
解决方案2 - 串行访问
通过-时序图-查看串行访问的流程
- 通过子线程 网络请求、数据解析返回数据给到串行队列
- 串行队列进行一个新增数据预排版
- 主线程想删除某一行需要等待串行队列新增数据预排版之间进行删除一个数据即可
- 然后在回到主线程 进行一个刷新操作
方案1并发访问、数据拷贝 和方案2串行访问 的利弊
- 方案1 并发访问、数据拷贝的情况 可能会有数据同步操作,或者是记录同步删除的动作。还需要大量的数据源的拷贝,对内存的开销是有一定的问题
- 方案2 串行访问的时候 比如在串行队列访问比较耗时的情况 那么在某一个删除动作会有一定的延迟
- 在具体的场景根据业务需求 选择那种方案
二、事件传递&视图响应
UIView和CALayer关系
- UIView包含layer、backgroundColor
- layer包含 CALayer、contents-> bakcing store
位图- backgroundColor
我们在界面显示的对应的UI控件都是位图
UIView和CALayer区别
- UIView为其提供内容,以及负责处理触摸等事件,参与响应链
- CALayer 负责显示内容 contents
为什么UIView和CALayer只负责上面单独的内容呢
这就要从系统设计原则。单一原则
UIView只负责其提供内容,以及负责处理触摸等事件,参与响应链
CALayer 负责显示内容 contents
体现了职责的分工
例子2 - 事件传递与视图响应链
1.比如
ViewA 添加 ViewB1、ViewB2
ViewB2 添加 ViewC1、ViewC2
ViewC1 添加 ViewD
此时点击C2的空白处 系统怎样找到事件的响应是C2的呢
事件传递的主要跟两个方法有关
// 最终那个视图响应 就将那个视图返回
- (UIView *)hitTest:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
// 判断某一个点击的view是否在某个视图范围内
- (BOOL)pointInside:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
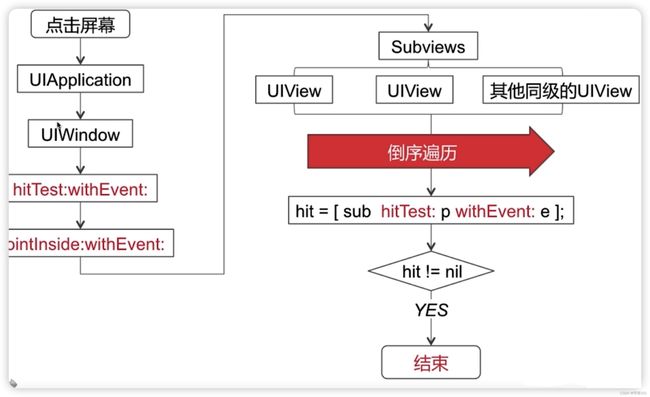
⭐️事件传递流程
pointInside:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
会进行一个遍历操作 遍历方式是以倒序的方式进行遍历 也就是说最后添加的视图 最优先会被遍历到
每个UIView 都会调用hitTest 。是属于递归调用
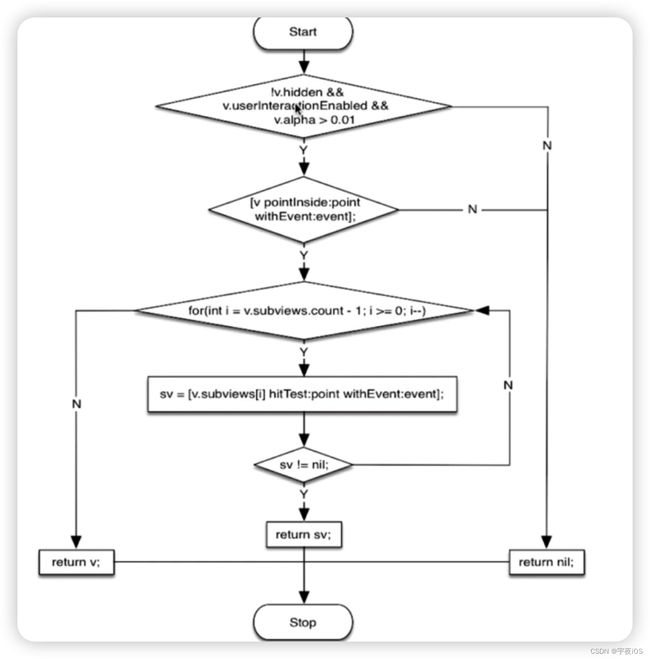
⭐️hitTest系统内部实现
检查视图是否满足下面的某一个条件 - 如果满足就继续往下走
- 判断视图是否可以交互、并且alpha是否大于0.01值
- 然后通过pointInside方法判断是否是在点击范围内
- 倒序方式遍历当前视图的子视图
- 然后调用 hitTest方法 如果返回最终事件的响应视图 那么就将视图 返回到hitTest方法里面
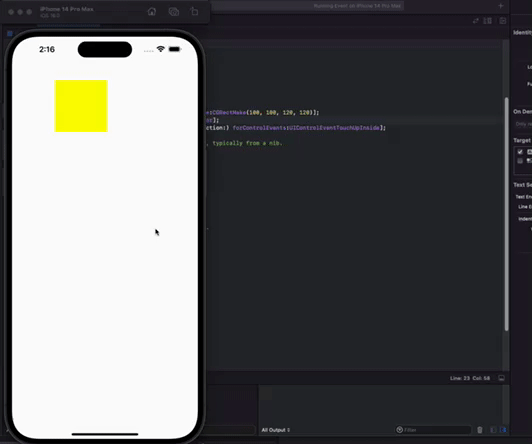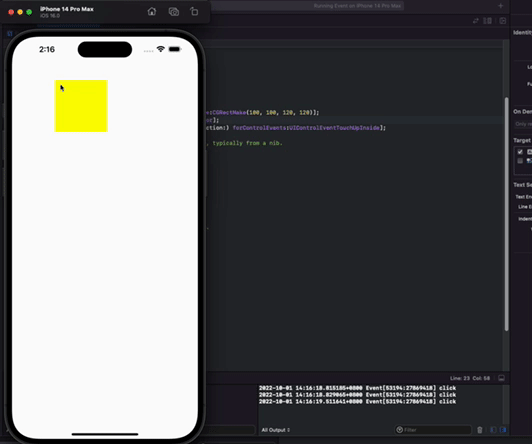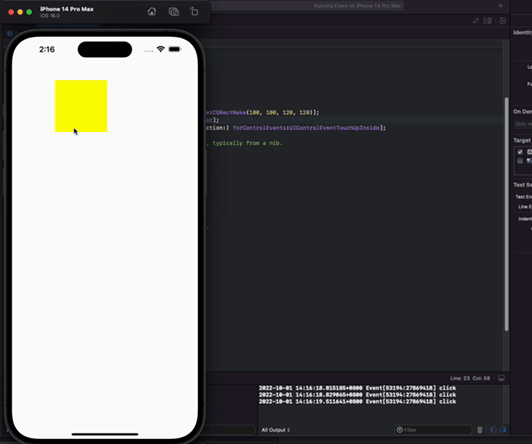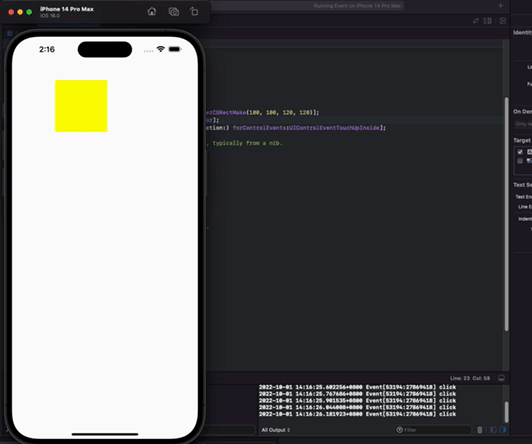
方形按钮指定区域接受事件响应 -效果图
例子2 - 代码实战 - Code
通过方形按钮指定区域接受事件响应
一个方形里面包含一个圆形。要求就是只想圆形有点击事件。不想四边多于的角有点击事件
- hitTest 先判断视图是否能交互、或者是否为透明
判断视图是否可以交互、并且alpha是否大于0.01值- 在hitTest里面进行倒序遍历检查然后再执行
(UIView *)hitTest:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event方法- 判断pointInside的点击范围
- 在pointInside内部 获取坐标
- 判断pointInside点击的点 是否在方向中心的距离就返回点击有效
ViewController - 代表的是 控制器实现一个方形按钮指定区域接受事件响应
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
@interface ViewController : UIViewController
@end
#import "ViewController.h"
#import "CustomButton.h"
@interface ViewController ()
{
CustomButton *cornerButton;
}
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
cornerButton = [[CustomButton alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(100, 100, 120, 120)];
cornerButton.backgroundColor = [UIColor blueColor];
[cornerButton addTarget:self action:@selector(doAction:) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside];
[self.view addSubview:cornerButton];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
self.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
}
- (void)doAction:(id)sender{
NSLog(@"click");
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
@end
CustomButton - 代表的是 自定义按钮 - 重写了hitTest、pointInside来实现方形按钮指定区域接受事件响应
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
@interface CustomButton : UIButton
@end
#import "CustomButton.h"
@implementation CustomButton
- (UIView *)hitTest:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
if (!self.userInteractionEnabled ||
[self isHidden] ||
self.alpha <= 0.01) {
return nil;
}
if ([self pointInside:point withEvent:event]) {
//遍历当前对象的子视图
__block UIView *hit = nil;
[self.subviews enumerateObjectsWithOptions:NSEnumerationReverse usingBlock:^(__kindof UIView * _Nonnull obj, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) {
// 坐标转换
CGPoint vonvertPoint = [self convertPoint:point toView:obj];
//调用子视图的hittest方法
hit = [obj hitTest:vonvertPoint withEvent:event];
// 如果找到了接受事件的对象,则停止遍历
if (hit) {
*stop = YES;
}
}];
if (hit) {
return hit;
}
else{
return self;
}
}
else{
return nil;
}
}
- (BOOL)pointInside:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
CGFloat x1 = point.x;
CGFloat y1 = point.y;
CGFloat x2 = self.frame.size.width / 2;
CGFloat y2 = self.frame.size.height / 2;
double dis = sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
// 67.923
if (dis <= self.frame.size.width / 2) {
return YES;
}
else{
return NO;
}
}
@end
参考文献、官方文档- 使用响应者和响应者链来处理事件(旧版本)(新版本)
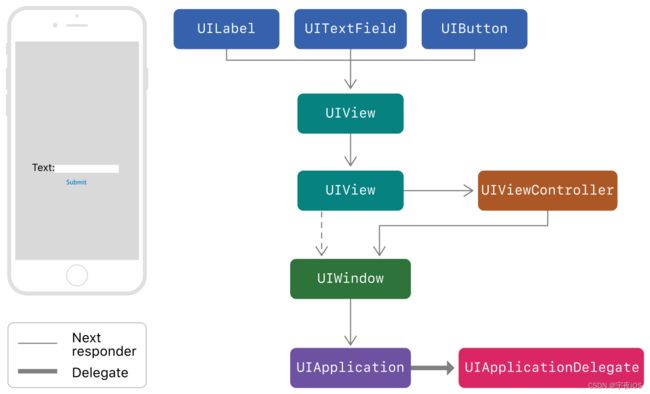
我们看一下官网文档的视图响应流程图
事件传递的流程
响应链、响应链机制的流程图
- 其中UITextField、UIButton、UILabel三个它们下一个响应者都是当前这个页面的self.view
- 如果它们是有一个容器View包裹起来。那么这个容器的View下一个响应者可能是当前这个页面的self.view. 那么self.view的下一个响应者就是UIViewController。
- UIViewController下一个响应者就是UIWindow
如果UIView里面中间没有UIViewController。那么UIView下一个响应者就是UIWindow
4.UIWindow下一个响应者就是UIApplication
5.UIApplication下一个响应者就是UIApplicationDelegate
这上面就是一个视图响应、或者说是一个传递链一个节点
参考文献、官方文档-视图事件响应
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
}
- (void)touchesMoved:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
}
- (void)touchesEnded:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
}
- (void)touchesCancelled:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
}
- (void)touchesEstimatedPropertiesUpdated:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches
{
}
综合案例说明 - 传递机制
这些方法都是UIResponder,
UIView继承于UIResponder,
所以UIView都包含以上的方法
- 点击到C2的小白点的时候
- 系统是如何找到这个事件的
- 最终这个事件是否由View C2 处理吗
那么这里就是涉及到视图响应链的流程机制
- 点击View C2事件,如果View C2
不处理的情况下 - 会
传递给View C2的父容器 View B2处理 。 如果 View B2不处理的情况下 - 会
传递给View B2的父容器 View A处理 。 如果 View A不处理的情况下 - 那么会继续传递给View A的下一个父容器。直到传递给UIApplicationDelegate
- 如果最终都不响应的话。最终就会产生一个面试题。
- 假如此时
❓面试考点(易错题) - 假如此时传递到UIApplicationDelegate仍然没有响应处理,会发生什么场景
答案: 会忽略当前这个事件。当做什么都没有发生。
错误答案: 会引起崩溃