VirtIO实现原理——virtblk设备初始化
文章目录
- 总线注册
- 驱动注册
- 设备探测
-
- specification
- match
- 驱动加载
-
- virtblk配置空间布局
- virtqueue初始化
- BLK-MQ初始化
-
- blk-mq框架简介
- blk-mq数据结构
-
- blk_mq_queue_map
- blk_mq_tag_set
- virtio_blk
- blk-mq初始化
-
- 设置硬件队列
- tagged IO初始化
- gendisk初始化
- virtio-blk设备状态
-
- VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_ACKNOWLEDGE
- VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_DRIVER
- virtio设备是指基于virtio-pci总线实现的磁盘、网络、console等设备。Qemu实现了如下virtio设备:
1af4:1041 network device (modern)
1af4:1042 block device (modern)
1af4:1043 console device (modern)
1af4:1044 entropy generator device (modern)
1af4:1045 balloon device (modern)
1af4:1048 SCSI host bus adapter device (modern)
1af4:1049 9p filesystem device (modern)
1af4:1050 virtio gpu device (modern)
1af4:1052 virtio input device (modern)
- 我们本章介绍其中的virtio-block设备初始化,下面简称virtblk。
总线注册
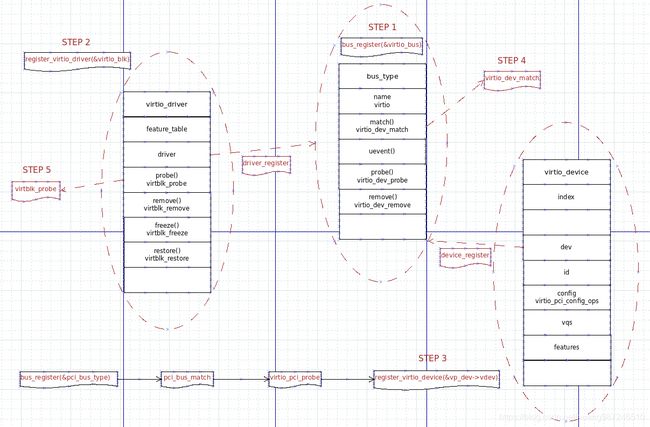
- virtio bus的注册是所有virtio设备注册的基础,所有virtio设备的探测都是在virtio bus注册完成后进行的。从virtio bus注册到最后的设备探测,整个步骤如下:
- 注册virtio bus
- 注册virtio设备驱动,比如virtio net driver或者virtio blk driver
- 注册virtio设备
- 触发驱动核心match操作virtio_dev_match
- match成功后驱动调用probe函数(virtnet_probe/virtblk_probe)探测virtio设备
static struct bus_type virtio_bus = {
.name = "virtio",
.match = virtio_dev_match,
.dev_groups = virtio_dev_groups,
.uevent = virtio_uevent,
.probe = virtio_dev_probe,
.remove = virtio_dev_remove,
};
virtio_init
bus_register(&virtio_bus)
驱动注册
- 驱动的注册流程如下:
static struct virtio_driver virtio_blk = {
.feature_table = features,
.feature_table_size = ARRAY_SIZE(features),
.feature_table_legacy = features_legacy,
.feature_table_size_legacy = ARRAY_SIZE(features_legacy),
.driver.name = KBUILD_MODNAME,
.driver.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.id_table = id_table, /* 1 */
.probe = virtblk_probe, /* 2 */
.remove = virtblk_remove,
.config_changed = virtblk_config_changed,
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP
.freeze = virtblk_freeze,
.restore = virtblk_restore,
#endif
};
register_virtio_driver(&virtio_blk)
driver->driver.bus = &virtio_bus // 将virtio_blk驱动的总线指向virtio
driver_register(&driver->driver) // 注册驱动
1. virtio_driver结构体中有一个id_table字段在驱动加载时起重要作用,virtio总线在match设备时会拿这里定义的id取比较设备的id,如果相等,认为匹配成功,然后将设备与驱动绑定,这里定义了一组ID,设置id.device为2,id.vendor为VIRTIO_DEV_ANY_ID。只要virtio设备的device能匹配驱动的device,就认为match成功。这里为什么device id是2?原因是 virtio-pci设备在探测过程中记录device id到virtio_device.id.device时对其做了处理,如果为modern(1.0)设备,要减去0x1040。
2. probe方法在驱动匹配后被调用,进一步地对virtio-blk驱动的加载,根据virtio-blk规范中的定义解析pci的bar空间。
- 仔细看virtio_blk驱动的id_table,后面
struct virtio_device_id {
__u32 device;
__u32 vendor;
};
#define VIRTIO_ID_BLOCK 2 /* virtio block */
static const struct virtio_device_id id_table[] = {
{ VIRTIO_ID_BLOCK, VIRTIO_DEV_ANY_ID },
{ 0 },
};
virtio_pci_modern_probe
vp_dev->vdev.id.device = pci_dev->device - 0x1040;
设备探测
specification
match
- 当virtio设备往virtio总线注册后,触发virtio_bus的match流程如下:
/* This looks through all the IDs a driver claims to support. If any of them
* match, we return 1 and the kernel will call virtio_dev_probe(). */
static int virtio_dev_match(struct device *_dv, struct device_driver *_dr)
{
unsigned int i;
struct virtio_device *dev = dev_to_virtio(_dv);
const struct virtio_device_id *ids;
ids = drv_to_virtio(_dr)->id_table; // 取出驱动定义的id
for (i = 0; ids[i].device; i++)
if (virtio_id_match(dev, &ids[i]))
return 1;
return 0;
}
static inline int virtio_id_match(const struct virtio_device *dev,
const struct virtio_device_id *id)
{
if (id->device != dev->id.device && id->device != VIRTIO_DEV_ANY_ID)
return 0;
return id->vendor == VIRTIO_DEV_ANY_ID || id->vendor == dev->id.vendor;
}
- match动作比较简单,只要驱动的device id和设备的device id相等,认为match成功,随后进行virtio-blk的设备探测
驱动加载
- virtio-blk设备的探测,主要是读取BAR空间中virtio-blk的配置结构virtio_blk_config,根据得到的信息进行virtqueue初始化,通用块设备初始化,virtio-blk设备初始化。
virtblk配置空间布局
- virio-pci的配置空间中,除了通用的common,isr和notify cap之外,还有一个device-specific config cap,它的结构不一,和具体的virtio设备有关,对于virtio-blk设备,其device-specific config结构为virtio_blk_config,如下图:

virtqueue初始化
- 设备探测的入口点是
virtblk_probe,virtqueue初始化在其后,函数调用如下:
virtblk_probe
init_vq
virtio_cread_feature(vdev, VIRTIO_BLK_F_MQ, /* 读取pci配置空间中的磁盘队列数 */
struct virtio_blk_config, num_queues,
&num_vqs);
num_vqs = min_t(unsigned int, nr_cpu_ids, num_vqs); /* 取配置队列数与CPU总数的最小值,作为队列数 */
virtio_find_vqs
vdev->config->find_vqs(vdev, nvqs, vqs, callbacks, names, NULL, desc)
virtio_pci_config_ops.find_vqs
vp_find_vqs
vp_find_vqs_msix
vp_setup_vq
vp_dev->setup_vq
- 在
drivers/virtio/virtio_pci_modern.c中有setup_vq的具体实现,这是virtqueue的初始化核心
static struct virtqueue *setup_vq(struct virtio_pci_device *vp_dev,
struct virtio_pci_vq_info *info,
unsigned index,
void (*callback)(struct virtqueue *vq),
const char *name,
u16 msix_vec)
{
......
if (index >= vp_ioread16(&cfg->num_queues)) /* 1 */
return ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
/* Select the queue we're interested in */ /* 2 */
vp_iowrite16(index, &cfg->queue_select);
/* Check if queue is either not available or already active. */
num = vp_ioread16(&cfg->queue_size);
if (!num || vp_ioread16(&cfg->queue_enable))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
/* get offset of notification word for this vq */ /* 3 */
off = vp_ioread16(&cfg->queue_notify_off);
vq = vring_create_virtqueue(index, num, /* 4 */
SMP_CACHE_BYTES, &vp_dev->vdev,
true, true, vp_notify, callback, name);
/* activate the queue */ /* 5 */
vp_iowrite16(virtqueue_get_vring_size(vq), &cfg->queue_size);
vp_iowrite64_twopart(virtqueue_get_desc_addr(vq),
&cfg->queue_desc_lo, &cfg->queue_desc_hi);
vp_iowrite64_twopart(virtqueue_get_avail_addr(vq),
&cfg->queue_avail_lo, &cfg->queue_avail_hi);
vp_iowrite64_twopart(virtqueue_get_used_addr(vq),
&cfg->queue_used_lo, &cfg->queue_used_hi);
vq->priv = (void __force *)vp_dev->notify_base + /* 6 */
off * vp_dev->notify_offset_multiplier;
1. 读取Host侧设置的队列数,如果要设置的队列位置超出了Host设置的队列数,返回
2. 选择要操作的队列,这时virtio规范定义的动作,一个virtio-blk设备可能有多个队列,当要操作其中某个队列时,首先通过queue_select字段告知
后端
3. virtqueue的队列深度由Host设置,读取队列深度,队列初始化时环的长度,descriptor表的长度都是这个
4. 创建一个vring
5. 创建成功,需要通知后端,前端创建的virtqueue的地址
6. 根据virtio规范计算notify字段的地址,当Guest想通知后端有数据到来时,需要向这个字段写入队列的idx
BLK-MQ初始化
blk-mq框架简介
- 传统磁盘因其工作原理随机访问比顺序访问性能低很多,内核块设备IO系统设计之初针对这种情况的主要优化手段是缓存用户态IO请求并尽可能合并,保证IO请求顺序访问磁盘。在实现时设计单队列存储用户态对块设备的IO请求,一把锁保护该队列上的IO请求数据结构。传统磁盘IO性能瓶颈在于硬件,跨分区访问,随机访问的速度远远没法和磁盘软件栈的处理速度匹配。使用单队列的传统Linux块设备架构图如下:

- 固态硬盘和NVME磁盘在并发访问上的性能较传统提升很多,硬件磁盘能够及时处理单队列的块设备IO请求,此时优化IO性能的手段是让多个CPU向磁盘驱动并发提交IO请求。单队列的锁转而成为多个CPU并发执行IO请求的软件瓶颈,为解决这个问题内核设计了Multi-Queue Block IO Queueing Mechanism(blk-mq)框架,使用多个队列缓存IO请求,每个socket或CPU独享一个队列。将对单队列拆成多队列,将原来的一把大锁拆成多个小锁,不同队列可独立处理IO请求并提交给硬件磁盘,没有了大锁的竞争和CPU跨NUMA访问性能开销。如下图所示:

- blk-mq的思想是设计两级队列来处理IO请求,一级队列作为传统队列的扩展,缓存IO并合并请求,基于一级队列可以实现Qos和IO调度器,二级队列用来缓存将要并发提交到磁盘的IO。前者称为软件暂存队列Software staging queues(下文称软件队列),后者称为硬件分发队列Hardware dispatch queues(硬件队列)。软件队列的个数由内核设备层驱动层基于用户程序(比如fio工具)的IO队列深度动态调整,用户程序IO队列越深软件队列数越多,但范围一定在系统socket数和CPU数之间。硬件队列数由厂商的磁盘驱动绝对,磁盘驱动会访问该磁盘最佳队列数和队列深度,块设备层驱动根据此信息分配相匹配的硬件队列数,下图是一个磁盘驱动队列数的配置:

- 在blk-mq框架设计中,设备驱动除了提供硬件队列数,还需要提供软件队列到硬件队列的映射函数,告诉块设备驱动如果实现软件队列到硬件队列的映射。
- blk-mq框架中还引入了tagged IO概念,一个IO的tag是个整数,范围在0到硬件队列深度([0, hw_queue_depth])之间,用来唯一标记块设备层驱动提交的IO在硬件队列的位置,当设备驱动完成该IO后,会根据IO的tag找到它在硬件队列的位置,将此IO标记为完成。通过引入tagged IO,原来通过块设备层驱动主动线性搜索才能标记IO完成的动作,现在只需要设备驱动根据IO的tagged来找到对应位置,标记IO完成,从而减少了IO延迟。
- 从上面的介绍我们可以得出,blk-mq框架需要设备驱动需要做3个事情,如下:
- 提供磁盘设备处理IO的最佳队列数和队列深度。
- 提供块设备层软件队列到硬件队列的映射函数。
- 增加tagged IO逻辑,当一个tagged IO完成后,设备驱动需要在硬件队列上标记其已完成。
- 在虚拟化场景下,因为磁盘不是真实物理磁盘,但仍然使用blk-mq的机制,所以以上工作都需要在virtblk驱动加载过程中完成,原来由设备驱动负责的工作现在需要virtblk驱动来完成。
blk-mq数据结构
blk_mq_queue_map
- blk_mq_queue_map用来存放软件队列到硬件队列的映射关系
struct blk_mq_queue_map {
unsigned int *mq_map; /* 1 */
unsigned int nr_queues; /* 2 */
unsigned int queue_offset; /* 3 */
};
- mq_map存放的是硬件队列的索引,由于软件队列个数最多为CPU个,因此mq_map数组长度为CPU的个数,mq_map[N]中存放的即CPU-N在硬件队列中的索引。
- 硬件队列的个数。
- 软件队列映射的硬件队列起始偏移,queue_offset和nr_queues一起,限定了CPU映射的队列范围在[queue_offset, queue_offset+nr_queues]
- 假设现在mq_map[5]为9,可以解析到映射关系为:CPU-5上软件队列会被映射到queue_offset+9这个队列上。
blk_mq_tag_set
- blk_mq_tag_set用来标志每一个IO请求在硬件队列的位置,这个数据结构硬件队列和设备驱动共享。
/**
* enum hctx_type - Type of hardware queue
* @HCTX_TYPE_DEFAULT: All I/O not otherwise accounted for.
* @HCTX_TYPE_READ: Just for READ I/O.
* @HCTX_TYPE_POLL: Polled I/O of any kind.
* @HCTX_MAX_TYPES: Number of types of hctx.
*/
enum hctx_type {
HCTX_TYPE_DEFAULT,
HCTX_TYPE_READ,
HCTX_TYPE_POLL,
HCTX_MAX_TYPES,
};
struct blk_mq_tag_set {
struct blk_mq_queue_map map[HCTX_MAX_TYPES]; /* 1 */
unsigned int nr_maps;
const struct blk_mq_ops *ops; /* 2 */
unsigned int nr_hw_queues; /* 3 */
unsigned int queue_depth; /* 4 */
......
void *driver_data; /* ? */
struct blk_mq_tags **tags; /* 5 */
struct blk_mq_tags *shared_tags;
......
};
- map,软件队列到硬件队列的映射关系,blk-mq设计了不同类型的硬件队列,每种队列都可以有自己的映射关系,因此map是一个数组。nr_maps表示map的元素个数。
- ops,设备驱动提供给块设备层的用于提交IO请求的方法。
- nr_hw_queues,硬件队列个数。
- queue_depth,硬件队列深度。
- tags,标记每个IO请求在硬件队列位置的数组。数组元素个数即为硬件队列的个数。
virtio_blk
- virtio_blk是virtblk磁盘的核心数据结构,它将内核的磁盘数据结构和blk-mq相关数据结构与virtblk的队列关联起来,让virtblk磁盘在内核层面看起来和普通块设备一样且兼容blk-mq框架,但后端却是通过virtblk的队列实现磁盘IO。
struct virtio_blk {
/*
* This mutex must be held by anything that may run after
* virtblk_remove() sets vblk->vdev to NULL.
*
* blk-mq, virtqueue processing, and sysfs attribute code paths are
* shut down before vblk->vdev is set to NULL and therefore do not need
* to hold this mutex.
*/
struct mutex vdev_mutex;
struct virtio_device *vdev; /* 关联的virtio设备 */
/* The disk structure for the kernel. */
struct gendisk *disk; /* 关联的内核磁盘设备 TODO */
/* Block layer tags. */
struct blk_mq_tag_set tag_set; /* 关联块设备层需要的tag */
......
/* num of vqs */
int num_vqs;
int io_queues[HCTX_MAX_TYPES]; /* 每类硬件队列的队列数 */
struct virtio_blk_vq *vqs; /* virtio队列 */
};
blk-mq初始化
设置硬件队列
- virtblk磁盘队列由驱动厂商来实现,块设备层依据这个信息初始化硬件队列。下图为virtio-blk内核模块设置的队列深度:

- virtblk驱动根据解析内核模块参数queue_depth,存放到全局变量virtblk_queue_depth中,在virtblk设备探测过程中,首先判断virtio-blk模块是否设置队列深度,如果没有设置,则取virtblk队列中当前空闲队列深度的二分之一,在设备探测阶段,通常就是整个virtblk队列深度的二分之一。如果virtio-blk模块设置了队列深度,则取设置的队列深度。
static unsigned int virtblk_queue_depth; /* 存放virtio-blk模块的队列深度参数 */
module_param_named(queue_depth, virtblk_queue_depth, uint, 0444); /* 定义virtio-blk queue_depth参数 */
virtblk_probe
unsigned int queue_depth;
/* Default queue sizing is to fill the ring. */
if (likely(!virtblk_queue_depth)) { /* virtio-blk模块参数未设置 */
queue_depth = vblk->vqs[0].vq->num_free; /* 取当前virtblk队列的空闲长度*/
/* ... but without indirect descs, we use 2 descs per req */
if (!virtio_has_feature(vdev, VIRTIO_RING_F_INDIRECT_DESC))
queue_depth /= 2;
} else {
queue_depth = virtblk_queue_depth; /* 取设置的virtio-blk参数 */
}
vblk->tag_set.queue_depth = queue_depth; /* 设置硬件队列深度 */
vblk->tag_set.nr_hw_queues = vblk->num_vqs; /* 设置硬件队列个数为virtblk队列个数 */
- virtio-blk磁盘在探测时,驱动把virtblk队列的数量设置成了块设备层的硬件队列数量,说明IO在经过块设备层后,往virtio-blk块设备提交时的硬件队列就是virtblk的队列。但virtblk的队列怎么和块设备层定义的硬件队列挂钩呢?内核提供了
struct blk_mq_ops中的map_queues方法,让块设备驱动可以指定自己的实现的队列作为硬件队列,virtblk驱动在virtio_mq_ops.map_queues中实现该逻辑,具体函数virtblk_map_queues:
static void virtblk_map_queues(struct blk_mq_tag_set *set)
{
struct virtio_blk *vblk = set->driver_data;
int i, qoff;
for (i = 0, qoff = 0; i < set->nr_maps; i++) {
/* 对每类硬件队列,逐一取出 */
struct blk_mq_queue_map *map = &set->map[i];
/* 获取每类硬件队列的个数 */
map->nr_queues = vblk->io_queues[i];
/* 设置队列偏移 */
map->queue_offset = qoff;
qoff += map->nr_queues;
/* 没有硬件队列可以映射 */
if (map->nr_queues == 0)
continue;
/*
* Regular queues have interrupts and hence CPU affinity is
* defined by the core virtio code, but polling queues have
* no interrupts so we let the block layer assign CPU affinity.
*/
if (i == HCTX_TYPE_POLL)
/* 如果是POLL类型的硬件队列,由于没有中断访问,因此参考硬件拓扑做映射 */
blk_mq_map_queues(&set->map[i]);
else
/* 将硬件队列映射到其中断亲和的CPU对应的软件队列上 */
blk_mq_virtio_map_queues(&set->map[i], vblk->vdev, 0);
}
}
blk_mq_virtio_map_queues函数是virtblk驱动提供的默认的块设备软件队列到硬件队列的映射函数,分析这个函数的本质工作,就是为每个硬件队列映射一个CPU上的软件队列,软件队列和硬件队列可以是一对一、一对多的关系,由于需要描述CPU上的软件队列,因此函数的输入是一个长度为CPU个数的数组,用于存放每个CPU软件队列对应的硬件队列的索引,函数的职责就是为每个硬件队列找到对应的软件队列,然后填充到这个数组,完成映射。为了性能考虑,函数默认获取硬件队列的中断亲和性,找到其中断亲和的CPU,然后将该CPU对应的软件队列映射到硬件队列上。
/**
* blk_mq_virtio_map_queues - provide a default queue mapping for virtio device
* @qmap: CPU to hardware queue map. /* 用来存放每个CPU上软件队列对应的硬件队列 */
* @vdev: virtio device to provide a mapping for.
* @first_vec: first interrupt vectors to use for queues (usually 0)
*
* This function assumes the virtio device @vdev has at least as many available
* interrupt vectors as @set has queues. It will then query the vector
* corresponding to each queue for it's affinity mask and built queue mapping
* that maps a queue to the CPUs that have irq affinity for the corresponding
* vector.
*/
void blk_mq_virtio_map_queues(struct blk_mq_queue_map *qmap,
struct virtio_device *vdev, int first_vec)
{
const struct cpumask *mask;
unsigned int queue, cpu;
/* virtio设备如果没有中断亲和性的设置,则使用平均分配,参考硬件拓扑将硬件队列平均分配到软件队列上 */
if (!vdev->config->get_vq_affinity)
goto fallback;
/* 逐一取出硬件队列,获取其中断亲和的cpu,映射 */
for (queue = 0; queue < qmap->nr_queues; queue++) {
mask = vdev->config->get_vq_affinity(vdev, first_vec + queue);
if (!mask)
goto fallback;
for_each_cpu(cpu, mask)
qmap->mq_map[cpu] = qmap->queue_offset + queue;
}
return;
fallback:
blk_mq_map_queues(qmap);
}
tagged IO初始化
- tagged IO初始化核心内容是初始化blk_mq_tag_set数据结构,如下:
virtblk_probe
memset(&vblk->tag_set, 0, sizeof(vblk->tag_set));
vblk->tag_set.ops = &virtio_mq_ops;
vblk->tag_set.queue_depth = queue_depth;
vblk->tag_set.numa_node = NUMA_NO_NODE;
vblk->tag_set.flags = BLK_MQ_F_SHOULD_MERGE;
vblk->tag_set.cmd_size =
sizeof(struct virtblk_req) +
sizeof(struct scatterlist) * sg_elems;
vblk->tag_set.driver_data = vblk;
vblk->tag_set.nr_hw_queues = vblk->num_vqs;
err = blk_mq_alloc_tag_set(&vblk->tag_set);
if (err)
goto out_put_disk;
q = blk_mq_init_queue(&vblk->tag_set);
vblk->disk->queue = q;
- TODO
gendisk初始化
- 完成
blk_mq_tag_set数据结构分配后,virtblk驱动基于该结构继续初始化gendisk(generic disk)数据结构,gendisk是块设备层中代表一个硬件块设备的核心数据结构,概念山该,一个gendisk可以包含多个硬件队列,可以包含多个磁盘分区,初始化gendisk同样在virtblk_probe流程中完成,blk_mq_alloc_disk函数实现该逻辑:
vblk->disk = blk_mq_alloc_disk(&vblk->tag_set, vblk);
blk_mq_alloc_disk
__blk_mq_alloc_disk
blk_mq_init_queue_data
blk_mq_init_allocated_queue
blk_mq_realloc_hw_ctxs
blk_mq_alloc_and_init_hctx
blk_mq_init_hctx
- TODO
virtio-blk设备状态
- virtio-blk初始化或者运行过程中,理论上是有可能失败的,因此需要有一个前后端都可以看到的字段,用来记录virtio-blk的状态,可以根据此状态做相应的处理。这个字段就是设备状态域。它存在于virtio-pci附加配置空间的common config中。
/* Fields in VIRTIO_PCI_CAP_COMMON_CFG: */
struct virtio_pci_common_cfg {
/* About the whole device. */
__le32 device_feature_select; /* read-write */
__le32 device_feature; /* read-only */
__le32 guest_feature_select; /* read-write */
__le32 guest_feature; /* read-write */
__le16 msix_config; /* read-write */
__le16 num_queues; /* read-only */
__u8 device_status; /* read-write */
__u8 config_generation; /* read-only */
/* About a specific virtqueue. */
__le16 queue_select; /* read-write */
__le16 queue_size; /* read-write, power of 2. */
__le16 queue_msix_vector; /* read-write */
__le16 queue_enable; /* read-write */
__le16 queue_notify_off; /* read-only */
__le32 queue_desc_lo; /* read-write */
__le32 queue_desc_hi; /* read-write */
__le32 queue_avail_lo; /* read-write */
__le32 queue_avail_hi; /* read-write */
__le32 queue_used_lo; /* read-write */
__le32 queue_used_hi; /* read-write */
};
- 设备状态的取值如下:
/* Status byte for guest to report progress, and synchronize features. */
/* We have seen device and processed generic fields (VIRTIO_CONFIG_F_VIRTIO) */
#define VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_ACKNOWLEDGE 1
/* We have found a driver for the device. */
#define VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_DRIVER 2
/* Driver has used its parts of the config, and is happy */
#define VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_DRIVER_OK 4
/* Driver has finished configuring features */
#define VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_FEATURES_OK 8
/* Device entered invalid state, driver must reset it */
#define VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_NEEDS_RESET 0x40
/* We've given up on this device. */
#define VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_FAILED 0x80
ACKNOWLEDGE:标记Guest已经发现了设备并识别到它是一个virtio设备
DRIVER:标记Guest知道这个virtio设备是什么驱动,知道用什么驱动让它工作
DRIVER_OK:标记Guest驱动加载这个设备成功
FEATURES_OK :标记Guest与Host完成特性协商
NEEDS_RESET:Host端标记该设备有问题,需要Guest复位
FAILED:Guest在初始化或者使用virtio设备过程中出了问题并且没法修复,Guest标记放弃这个设备,不使用
VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_ACKNOWLEDGE
- Guest侧
virtblk注册成virtio设备时,会写pci配置空间的device_status字段,设置设备状态为VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_ACKNOWLEDGE
register_virtio_device /* virtio设备注册 */
virtio_add_status(dev, VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_ACKNOWLEDGE) /* 通知后端已发现此virtio设备 */
dev->config->set_status(dev, dev->config->get_status(dev) | status)
vp_set_status
iowrite8(status, vp_dev->ioaddr + VIRTIO_PCI_STATUS) /* 传统实现:写pci配置空间的IO地址 */
- Host侧
qemu在模拟pci设备时,将pci设备的配置空间注册为IO空间,一旦Guest有对此空间的读写,会触发qemu注册的读写回调
virtio_pci_device_plugged
memory_region_init_io(&proxy->bar, OBJECT(proxy), &virtio_pci_config_ops, proxy, "virtio-pci", size)
virtio_pci_config_ops
static const MemoryRegionOps virtio_pci_config_ops = {
.read = virtio_pci_config_read,
.write = virtio_pci_config_write,
.....
}
/* Guest写pci配置空间的引发qemu侧注册的pci配置空间写回调 */
virtio_pci_config_write
virtio_ioport_write
switch (addr) { /* 判断客户机写的pci配置空间的字段 */
case VIRTIO_PCI_STATUS: /* 匹配到device_status字段 */
virtio_set_status(vdev, val & 0xFF);
/* Linux before 2.6.34 drives the device without enabling
the PCI device bus master bit. Enable it automatically
for the guest. This is a PCI spec violation but so is
initiating DMA with bus master bit clear. */
if (val == (VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_ACKNOWLEDGE | VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_DRIVER)) {
pci_default_write_config(&proxy->pci_dev, PCI_COMMAND,
proxy->pci_dev.config[PCI_COMMAND] |
PCI_COMMAND_MASTER, 1);
}
}
VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_DRIVER
- Guest侧
virtblk是一个virtio设备,因此Guest首先会将virtblk设备作为virtio设备进行注册,这是会触发virtio总线上的probe动作,为注册的virtio设备寻找匹配的驱动,VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_DRIVER状态就在probe的时候设置
virtio_dev_probe
virtio_add_status(dev, VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_DRIVER)
- Host侧
Host侧触发IO空间的回调,进入virtio_pci_config_write处理该状态,其核心动作除了将VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_DRIVER记录到qemu的数据结构以外,还会使能ioeventfd,也就是说,VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_DRIVER之后
virtio_pci_config_write
virtio_ioport_write
switch (addr) { /* 判断客户机写的pci配置空间的字段 */
case VIRTIO_PCI_STATUS: /* 匹配到device_status字段 */
virtio_set_status(vdev, val & 0xFF)
if (val & VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_DRIVER_OK) {
virtio_pci_start_ioeventfd(proxy)
if (!bus->ioeventfd_grabbed) {
vdc->start_ioeventfd(vdev) <=> virtio_device_start_ioeventfd_impl
}
}
virtio_device_start_ioeventfd_impl
/* 为每个virtio queue分配一个eventfd并注册对应的读fd的回调 */
for (n = 0; n < VIRTIO_QUEUE_MAX; n++) {
VirtQueue *vq = &vdev->vq[n];
if (!virtio_queue_get_num(vdev, n)) {
continue;
}
r = virtio_bus_set_host_notifier(qbus, n, true); /* 分配eventfd */
if (r < 0) {
err = r;
goto assign_error;
}
event_notifier_set_handler(&vq->host_notifier,
virtio_queue_host_notifier_read); /* 注册rfd读回调 */
}