OpenSSL之七:openssl.cnf
openssl.cnf
openssl.cnf是OpenSSL的主配置文件,用户可以在OpenSSL源代码apps目录下找到它。目前openssl.cnf用于req、ca和X509等指令中,当然所有使用openssl.cnf的指令,都可以通过-config来指定配置文件,否则默认使用openssl.cnf。
openssl.cnf的文件内容包括了三大部分: 默认的文件配置、 证书请求配置及 证书签发配置。除此之外还可以配置X.509证书的扩展项,在使用OpenSSL函数库时也可以使用配置机制。
#
# OpenSSL example configuration file.
# This is mostly being used for generation of certificate requests.
#
# Note that you can include other files from the main configuration
# file using the .include directive.
#.include filename
# This definition stops the following lines choking if HOME isn't
# defined.
HOME = .
# Extra OBJECT IDENTIFIER info:
#oid_file = $ENV::HOME/.oid
oid_section = new_oids
# To use this configuration file with the "-extfile" option of the
# "openssl x509" utility, name here the section containing the
# X.509v3 extensions to use:
# extensions =
# (Alternatively, use a configuration file that has only
# X.509v3 extensions in its main [= default] section.)
[ new_oids ]
# We can add new OIDs in here for use by 'ca', 'req' and 'ts'.
# Add a simple OID like this:
# testoid1=1.2.3.4
# Or use config file substitution like this:
# testoid2=${testoid1}.5.6
# Policies used by the TSA examples.
tsa_policy1 = 1.2.3.4.1
tsa_policy2 = 1.2.3.4.5.6
tsa_policy3 = 1.2.3.4.5.7
####################################################################
[ ca ]
default_ca = CA_default # The default ca section
####################################################################
[ CA_default ]
dir = ./demoCA # Where everything is kept
certs = $dir/certs # Where the issued certs are kept
crl_dir = $dir/crl # Where the issued crl are kept
database = $dir/index.txt # database index file.
#unique_subject = no # Set to 'no' to allow creation of
# several certs with same subject.
new_certs_dir = $dir/newcerts # default place for new certs.
certificate = $dir/cacert.pem # The CA certificate
serial = $dir/serial # The current serial number
crlnumber = $dir/crlnumber # the current crl number
# must be commented out to leave a V1 CRL
crl = $dir/crl.pem # The current CRL
private_key = $dir/private/cakey.pem# The private key
x509_extensions = usr_cert # The extensions to add to the cert
# Comment out the following two lines for the "traditional"
# (and highly broken) format.
name_opt = ca_default # Subject Name options
cert_opt = ca_default # Certificate field options
# Extension copying option: use with caution.
# copy_extensions = copy
# Extensions to add to a CRL. Note: Netscape communicator chokes on V2 CRLs
# so this is commented out by default to leave a V1 CRL.
# crlnumber must also be commented out to leave a V1 CRL.
# crl_extensions = crl_ext
default_days = 365 # how long to certify for
default_crl_days= 30 # how long before next CRL
default_md = default # use public key default MD
preserve = no # keep passed DN ordering
# A few difference way of specifying how similar the request should look
# For type CA, the listed attributes must be the same, and the optional
# and supplied fields are just that :-)
policy = policy_match
# For the CA policy
[ policy_match ]
countryName = match
stateOrProvinceName = match
organizationName = match
organizationalUnitName = optional
commonName = supplied
emailAddress = optional
# For the 'anything' policy
# At this point in time, you must list all acceptable 'object'
# types.
[ policy_anything ]
countryName = optional
stateOrProvinceName = optional
localityName = optional
organizationName = optional
organizationalUnitName = optional
commonName = supplied
emailAddress = optional
####################################################################
[ req ]
default_bits = 2048
default_keyfile = privkey.pem
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
attributes = req_attributes
x509_extensions = v3_ca # The extensions to add to the self signed cert
# Passwords for private keys if not present they will be prompted for
# input_password = secret
# output_password = secret
# This sets a mask for permitted string types. There are several options.
# default: PrintableString, T61String, BMPString.
# pkix : PrintableString, BMPString (PKIX recommendation before 2004)
# utf8only: only UTF8Strings (PKIX recommendation after 2004).
# nombstr : PrintableString, T61String (no BMPStrings or UTF8Strings).
# MASK:XXXX a literal mask value.
# WARNING: ancient versions of Netscape crash on BMPStrings or UTF8Strings.
string_mask = utf8only
# req_extensions = v3_req # The extensions to add to a certificate request
[ req_distinguished_name ]
countryName = Country Name (2 letter code)
countryName_default = AU
countryName_min = 2
countryName_max = 2
stateOrProvinceName = State or Province Name (full name)
stateOrProvinceName_default = Some-State
localityName = Locality Name (eg, city)
0.organizationName = Organization Name (eg, company)
0.organizationName_default = Internet Widgits Pty Ltd
# we can do this but it is not needed normally :-)
#1.organizationName = Second Organization Name (eg, company)
#1.organizationName_default = World Wide Web Pty Ltd
organizationalUnitName = Organizational Unit Name (eg, section)
#organizationalUnitName_default =
commonName = Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name)
commonName_max = 64
emailAddress = Email Address
emailAddress_max = 64
# SET-ex3 = SET extension number 3
[ req_attributes ]
challengePassword = A challenge password
challengePassword_min = 4
challengePassword_max = 20
unstructuredName = An optional company name
[ usr_cert ]
# These extensions are added when 'ca' signs a request.
# This goes against PKIX guidelines but some CAs do it and some software
# requires this to avoid interpreting an end user certificate as a CA.
basicConstraints=CA:FALSE
# Here are some examples of the usage of nsCertType. If it is omitted
# the certificate can be used for anything *except* object signing.
# This is OK for an SSL server.
# nsCertType = server
# For an object signing certificate this would be used.
# nsCertType = objsign
# For normal client use this is typical
# nsCertType = client, email
# and for everything including object signing:
# nsCertType = client, email, objsign
# This is typical in keyUsage for a client certificate.
# keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
# This will be displayed in Netscape's comment listbox.
nsComment = "OpenSSL Generated Certificate"
# PKIX recommendations harmless if included in all certificates.
subjectKeyIdentifier=hash
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer
# This stuff is for subjectAltName and issuerAltname.
# Import the email address.
# subjectAltName=email:copy
# An alternative to produce certificates that aren't
# deprecated according to PKIX.
# subjectAltName=email:move
# Copy subject details
# issuerAltName=issuer:copy
#nsCaRevocationUrl = http://www.domain.dom/ca-crl.pem
#nsBaseUrl
#nsRevocationUrl
#nsRenewalUrl
#nsCaPolicyUrl
#nsSslServerName
# This is required for TSA certificates.
# extendedKeyUsage = critical,timeStamping
[ v3_req ]
# Extensions to add to a certificate request
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
[ v3_ca ]
# Extensions for a typical CA
# PKIX recommendation.
subjectKeyIdentifier=hash
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid:always,issuer
basicConstraints = critical,CA:true
# Key usage: this is typical for a CA certificate. However since it will
# prevent it being used as an test self-signed certificate it is best
# left out by default.
# keyUsage = cRLSign, keyCertSign
# Some might want this also
# nsCertType = sslCA, emailCA
# Include email address in subject alt name: another PKIX recommendation
# subjectAltName=email:copy
# Copy issuer details
# issuerAltName=issuer:copy
# DER hex encoding of an extension: beware experts only!
# obj=DER:02:03
# Where 'obj' is a standard or added object
# You can even override a supported extension:
# basicConstraints= critical, DER:30:03:01:01:FF
[ crl_ext ]
# CRL extensions.
# Only issuerAltName and authorityKeyIdentifier make any sense in a CRL.
# issuerAltName=issuer:copy
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid:always
[ proxy_cert_ext ]
# These extensions should be added when creating a proxy certificate
# This goes against PKIX guidelines but some CAs do it and some software
# requires this to avoid interpreting an end user certificate as a CA.
basicConstraints=CA:FALSE
# Here are some examples of the usage of nsCertType. If it is omitted
# the certificate can be used for anything *except* object signing.
# This is OK for an SSL server.
# nsCertType = server
# For an object signing certificate this would be used.
# nsCertType = objsign
# For normal client use this is typical
# nsCertType = client, email
# and for everything including object signing:
# nsCertType = client, email, objsign
# This is typical in keyUsage for a client certificate.
# keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
# This will be displayed in Netscape's comment listbox.
nsComment = "OpenSSL Generated Certificate"
# PKIX recommendations harmless if included in all certificates.
subjectKeyIdentifier=hash
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer
# This stuff is for subjectAltName and issuerAltname.
# Import the email address.
# subjectAltName=email:copy
# An alternative to produce certificates that aren't
# deprecated according to PKIX.
# subjectAltName=email:move
# Copy subject details
# issuerAltName=issuer:copy
#nsCaRevocationUrl = http://www.domain.dom/ca-crl.pem
#nsBaseUrl
#nsRevocationUrl
#nsRenewalUrl
#nsCaPolicyUrl
#nsSslServerName
# This really needs to be in place for it to be a proxy certificate.
proxyCertInfo=critical,language:id-ppl-anyLanguage,pathlen:3,policy:foo
####################################################################
[ tsa ]
default_tsa = tsa_config1 # the default TSA section
[ tsa_config1 ]
# These are used by the TSA reply generation only.
dir = ./demoCA # TSA root directory
serial = $dir/tsaserial # The current serial number (mandatory)
crypto_device = builtin # OpenSSL engine to use for signing
signer_cert = $dir/tsacert.pem # The TSA signing certificate
# (optional)
certs = $dir/cacert.pem # Certificate chain to include in reply
# (optional)
signer_key = $dir/private/tsakey.pem # The TSA private key (optional)
signer_digest = sha256 # Signing digest to use. (Optional)
default_policy = tsa_policy1 # Policy if request did not specify it
# (optional)
other_policies = tsa_policy2, tsa_policy3 # acceptable policies (optional)
digests = sha1, sha256, sha384, sha512 # Acceptable message digests (mandatory)
accuracy = secs:1, millisecs:500, microsecs:100 # (optional)
clock_precision_digits = 0 # number of digits after dot. (optional)
ordering = yes # Is ordering defined for timestamps?
# (optional, default: no)
tsa_name = yes # Must the TSA name be included in the reply?
# (optional, default: no)
ess_cert_id_chain = no # Must the ESS cert id chain be included?
# (optional, default: no)
ess_cert_id_alg = sha1 # algorithm to compute certificate
# identifier (optional, default: sha1)
-
证书请求配置字段
(1)证书请求主配置字段[ req ]

主配置字段参数说明:

(2)特征名称字段[ req_distinguished_name ],由req字段中的distinguished_name指定,包含了用户主要信息,包括国家、省份、城市、组织及名字等信息,该字段所有信息总和称为“特征名称”。

(3)证书请求属性字段[ req_attributes ],由req字段中的attributes指定,定义了CA签发的时候可能用到的属性。

(4)证书请求扩展字段


-
证书签发配置
(1) 证书签发主配置[ ca ]

主配置字段参数说明:

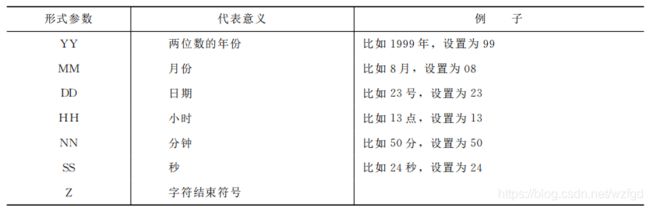
UTCTime格式:YYMMDDHHNNSSZ
(2)请求信息匹配策略字段[ policy_match ],由CA主配置字段policy参数指定,该字段包含了跟证书特征名称(DN)域相关的名称。变量值可能为match、optional、supplied。

(3)扩展字段项目

-
X.509 v3扩展项

(1)描述字符串型扩展项

(2)nsCertType,证书类型扩展项。Netscape定义证书用途扩展项目

(3)keyUsage,密钥用途扩展项。PKIX定制用于限制证书中密钥用途的扩展项

(4)basicConstraints,基本限制扩展项。PKIX定义的证书扩展项,值域包括CA参数和pathlen
#basicConstraints=CA:FALSE 表示签发的时用户证书
#basicConstraints=CA:FALSE 表示签发的时用户证书
#basicConstraints=critical,CA:TRUE 表示签发证书的证书,及CA证书
#pathlen只对CA有效(及CA:TRUE时),表示CA下可以出现多少级CA证书
#basicConstraints=CA:TRUE,pathlen:0 表示CA只能签发最终用户证书而不能签发更低级别的证书
(5)extendedKeyUsage,扩展密钥扩展项。允许用户添加额外的密钥应用信息,用户可将自己定义的对象和相应的信息添加到extendedKeyUsage列表中。下图展示了extendedKeyUsage的参数值:

(6)subjectKeyIdentifier,主体密钥标识扩展项。用于在证书主体拥有多个密钥集的时候指定密钥属于哪个密钥集。
subjectKeyIdentifier=hash
(7)authorityKeyIdentifier,验证机构密钥标识扩展项。用于构造证书链的时候标识签发机构的证书和密钥,证书中的验证机构密钥标识分为三个部分:密钥ID(keyID)、验证机构DN和CA证书序列号。
(8)subjectAltName,主体别名扩展项。为证书提供了形式更加灵活的命名方式,理论上可以包含IP地址、URL、email、DNS域名、RID(已注册对象标识)及IP地址等信息作为主体别名。
subjectAltName=email:copy,email:[email protected],URL:http://www.OpenSSL.cn/
(9)issuerAltName,颁发者别名扩展项。为颁发者提供了不同形式的命名方式,采用的形式与subjectAltName相似,它支持subjectAltName的所有参数,但是不支持email参数的copy值。
issuerAltName=issure:copy #证书颁发者主体别名中所有别名都会被复制到新签发证书的颁发者别名扩展项中
(10)authorityInfoAccess,验证机构信息处理扩展项。给出了如何处理跟CA相关的信息的详细细节。
(11)crlDistributionPoints,CRL分布点扩展项。用于指明用户为了验证证书吊销状态而需要查找CRL(证书吊销列表)信息的发布站点。
(12)certificatePolicies,证书策略扩展项。定义证书应用策略,比如证书验证策略。
关于一些缩写的描述
# MD : MD摘要算法
# DN : Distinguished Name(特征名称)
# CRL : Certificate Revocation List(证书吊销列表)
# RID : Registered object identification(已注册对象标识)