Linux 文件管理
一、创建文件 touch
语法
touch [文件名称]
示例
#在 /opt 目录下创建一个 test.txt 文件
~]# touch /opt/test.txt
~]# ls /opt/test.txt
/opt/test.txt
#批量创建文件
~]# touch /opt/test_{1..10}.txt
~]# ls /opt/
test_10.txt test_1.txt test_2.txt test_3.txt test_4.txt test_5.txt test_6.txt test_7.txt test_8.txt test_9.txt二、复制文件 cp
语法
cp [参数] [源文件] [目标位置]
常用参数
-p:保留文件原有属性
-r:递归复制,常用于复制目录
示例
#将 /etc/passwd 复制到 /root 下
~]# cp /etc/passwd /root/
~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg passwd
#将 /etc/hosts 复制到 /root 下并保持原有属性
~]# cp -p /etc/hosts /root/
~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg hosts passwd
#将 /etc 复制到 /root 下并保持原有属性
~]# cp -rp /etc/ /root/
~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg etc hosts passwd其他用法
#复制文件或目录并修改文件名称:
~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg etc hosts passwd
~]# cp /etc/hosts /root/test_hosts
~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg etc hosts passwd test_hosts
#免交互式确认覆盖重复文件:
~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg etc hosts passwd test_hosts
~]# cp -rp /etc/ /root/
#会提示是否要覆盖某某文件
cp: overwrite ‘/root/etc/fstab’?
#免交互方式
~]# \cp -rp /etc/ /root/
~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg etc hosts passwd test_hosts三、查看文件内容
cat
语法
cat [文件名称]
常用参数
-n:显示文件行数
-A:显示文件中的所有内容,包括特殊符号
EOF:插入内容到文件中
示例
#使用 cat 命令查看刚刚复制到 /root/hosts 文件
~]# cat /root/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
#使用 cat 命令查看 /root/hosts 文件并显示行数
~]# cat -n /root/hosts
1 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
2 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
3 bin
4 usr
5 var
#使用 cat 命令查看 /root/hosts 文件中的特殊字符
~]# cat -A /root/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4$
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6$
bin$
usr$
var$
其他用法
cat 命令配合重定向符 “>” 或 追加符 “>>” ,可以做到创建文件、插入内容到文件中、清空文件内容。
#在 /root/hosts 文件中追加插入以下内容
bin
usr
var
~]# cat >> /root/hosts < bin
> usr
> var
> EOF
~]# cat hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
bin
usr
var
#创建一个名为 cat.txt 的文件,这个文件中需要有 test 这几个字符
~]# cat > cat.txt < test
> EOF
~]# cat cat.txt
test
#清空 cat.txt 文件
~]# >cat.txt
~]# cat cat.txt PS:cat > [文件] <
less / more
语法
less [文件名称]
用法:使用光标上下翻动,f 下翻,b 上翻,q 退出。
more [文件名称]
用法:用法同上,唯一区别是 more 会显示百分比。
示例
#less
~]# less /etc/services
#more
~]# more /etc/serviceshead
语法
head [参数] [文件名称]
常用参数
-n:指定数量(不指定默认显示前10行,-n 参数可以忽略可以直接用 -5 的方式指定数量)
示例
#打印 /etc/services 文件的前 5 行
~]# head -n 5 /etc/services
# /etc/services:
# $Id: services,v 1.55 2013/04/14 ovasik Exp $
#
# Network services, Internet style
# IANA services version: last updated 2013-04-10其他用法
配合 | (管道符),将前一条命令的结果作为条件进行数据过滤
#打印 ps -ef 命令的前 5 行数据。(ps 命令会在进程管理中详细讲解)
~]# ps -ef | head -5
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 1 0 0 10:00 ? 00:00:04 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --switched-root --system --deserialize 22
root 2 0 0 10:00 ? 00:00:00 [kthreadd]
root 4 2 0 10:00 ? 00:00:00 [kworker/0:0H]
root 6 2 0 10:00 ? 00:00:00 [ksoftirqd/0]tail
语法
tail [参数] [文件名称]
常用参数
-n:指定数量(不指定默认显示后10行,-n 参数可以忽略可以直接用 -5 的方式指定数量)
-f:随着文件的增减输出附加的数据,简单来说就是流动式显示数据,通常用来看实时日志
示例
~]# tail -n 5 /etc/services
com-bardac-dw 48556/tcp # com-bardac-dw
com-bardac-dw 48556/udp # com-bardac-dw
iqobject 48619/tcp # iqobject
iqobject 48619/udp # iqobject
matahari 49000/tcp # Matahari Broker
~]# tail -f /var/log/messages
Jan 11 10:15:34 localhost systemd: Starting Cleanup of Temporary Directories...
Jan 11 10:15:34 localhost systemd: Started Cleanup of Temporary Directories.
Jan 11 11:01:01 localhost systemd: Started Session 3 of user root.
Jan 11 12:01:01 localhost systemd: Started Session 4 of user root.
Jan 11 13:01:01 localhost systemd: Started Session 5 of user root.
Jan 11 14:01:01 localhost systemd: Started Session 6 of user root.
其他用法
#流动式查看日志,每次更新 200 条
~]# tail -fn 200 /var/log/messages
四、过滤文件内容 grep
语法
grep [内容] 文件
常用参数
-n:显示过滤到的数据在文件中的第几行
-v:排除某些内容
-i:Linux中严格区分大小写,-i 参数可以在过滤数据时无视大小写
-E:支持正则表达式(正则会在Shell编程中详细讲解)
-A:显示匹配到的行以及下面的行,通常配合数字使用例如 -A5
-B:显示匹配到的行以及上面的行,通常配合数字使用例如 -B5
-C:显示匹配到的行已经上下的行,通常配合数字使用例如 -C5
示例
#过滤 /etc/passwd 文件中带 root 的行
~]# grep "root" /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
#过滤 /etc/passwd 文件中带 root 的行,并显示行号
~]# grep -n "root" /etc/passwd
1:root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
10:operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
#排除 /etc/passwd 文件中带 nologin 的行
~]# grep -v "nologin" /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
#过滤 /etc/passwd 文件中无论大小写 root 的行。
##先插入插入一条数据:
~]# echo "ROOT:x:0:0:ROOT:/ROOT:/bin/bash" >> /etc/passwd
##开始过滤
~]# grep -i "root" /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
ROOT:x:0:0:ROOT:/ROOT:/bin/bash
#过滤 /etc/passwd 文件中带 root 的行和下一行
~]# grep -A1 "root" /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
--
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin
#过滤 /etc/passwd 文件中带 root 的行和上一行
~]# grep -B1 "root" /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
--
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
#过滤 /etc/passwd 文件中带 root 的行和上下一行
~]# grep -C1 "root" /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
--
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin
其他使用方法
与 head 方法一样。通过管道符配合其他命令一起使用
~]# ps -ef | grep sshd
root 844 1 0 10:00 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D
root 1318 844 0 10:00 ? 00:00:02 sshd: root@pts/0
root 3835 1322 0 15:24 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto sshd
~]# ps -ef | grep "sshd" | grep -v "grep"
root 844 1 0 10:00 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D
root 1318 844 0 10:00 ? 00:00:03 sshd: root@pts/0
五、文件下载
wegt
语法
wget [文件链接]
常用参数
-O:指定下载文件的目标路径
示例
#首先使用 yum 安装 wget 命令(yum会在软件管理中详细讲解)
~]# yum -y install wget现在我们去下载一个阿里云的 CentOS 7 yum 源文件
~]# wget https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
--2024-01-11 15:35:55-- https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
Resolving mirrors.aliyun.com (mirrors.aliyun.com)... 116.171.176.213, 116.171.176.217, 116.171.176.215, ...
Connecting to mirrors.aliyun.com (mirrors.aliyun.com)|116.171.176.213|:443... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 2523 (2.5K) [application/octet-stream]
Saving to: ‘Centos-7.repo’
100%[==========================================================================================================================================>] 2,523 --.-K/s in 0s
2024-01-11 15:35:56 (18.7 MB/s) - ‘Centos-7.repo’ saved [2523/2523]
[root@localhost ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg cat.txt Centos-7.repo etc file.txt hosts passwd但是 Centos-7.repo 这个文件放在 /root 目录下是不能用的,需要放在 /etc/yum.repos.d 目录下,所以可以通过 -O 参数直接将这个文件下载在我们指定的目录,并将 Centos-7.repo 名称修改为 CentOS-Base.repo。
~]# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
--2024-01-11 15:40:01-- https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
Resolving mirrors.aliyun.com (mirrors.aliyun.com)... 116.171.176.212, 116.171.176.216, 116.171.176.213, ...
Connecting to mirrors.aliyun.com (mirrors.aliyun.com)|116.171.176.212|:443... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 2523 (2.5K) [application/octet-stream]
Saving to: ‘/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo’
100%[==========================================================================================================================================>] 2,523 --.-K/s in 0s
2024-01-11 15:40:02 (17.9 MB/s) - ‘/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo’ saved [2523/2523]curl
curl 与 wget 的语法是一样的,文件下载只是 curl 的一种功能,curl 是一个非常强大的工具,可以发送请求、请求接口、探测接口是否可用等等功能。我们这里主要讲解 -o 参数用来下载文件,如想了解详细用法可以参考一位大佬的博客 Linux curl命令最全详解_linux curl命令详解-CSDN博客
示例
#参数说明
-o:将请求到的页面保存到文件中
#使用 curl 命令将 epel 源的 repo 文件保存至 /etc/yum.repo.d/
~]# curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 664 100 664 0 0 1005 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 1007
~]# ls /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo
/etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo六、本地与虚拟机上传或下载文件
这里会用到一个工具 lrzsz ,初始化系统需要下载该工具
~]# yum install lrzsz -y上传 rz
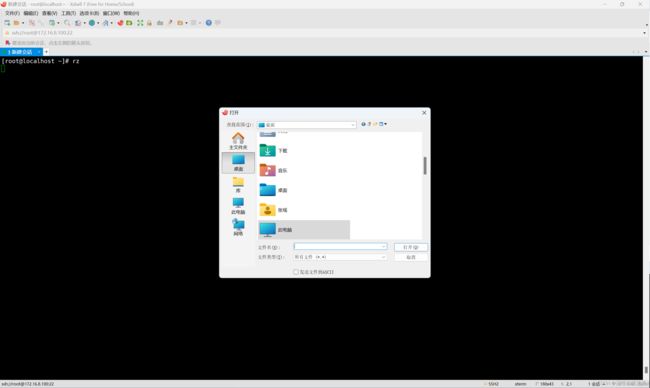
在命令行输入 rz 命令后回车会弹出来一个与本地通讯的窗口(也可以将文件直接拖拽至Xshell窗口)
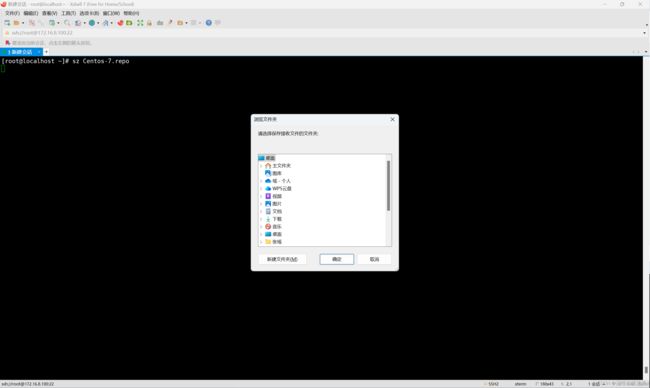
下载 sz
使用 sz 时直接使用 sz [文件名称] 即可,之后也会有一个与本地通讯的窗口弹出来
~]# sz Centos-7.repo七、文件查找 find
语法
find [路径] [参数] [表达式]
常用参数
-name:通过文件名称查找
-iname:通过文件名称查找但不区分文件名称大小写
-size:通过文件大小查找,文件单位包括 M、k、G
-type:通过文件类型查找,文件类型包括以下类型:
f:普通文件
d:目录
s:socket套接字文件
l:链接文件
c:字符设备
b:块设备
-mtime:通过文件修改时间查找
示例
#通过文件名称查找
~]# find /etc -name "passwd"
/etc/passwd
/etc/pam.d/passwd
#通过文件大小查找
##大于 20M
~]# find /root -size +5M
/root/etc/udev/hwdb.bin
##小于 20M
~]# find /root -size -1k
/root/etc/crypttab
#通过文件类型查找
##目录
~]# find /root -maxdepth 1 -type d
/root
/root/etc
/root/.pki
##文件
~]# find /root -maxdepth 1 -type f
/root/.bash_logout
##套接字文件
~]# find / -type s
/dev/log
##链接文件
~]# find /usr/bin/ -type l
/usr/bin/bashbug
##字符设备
~]# find / -type c
/dev/vsock
##块设备
~]# find / -type b
/dev/sda3
#通过文件修改时间进行查找
##查找 1 天前的文件
~]# find /var/log/ -mtime +1
##查找最近 1 天的文件
~]# find /var/log/ -mtime -1查找到文件后的动作
-print 打印查找到的内容(print 是 查找到的默认动作)
-ls 以长格式显示的方式打印查找到的内容
-delete 删除查找到的文件 (删除目录,仅能删除空目录)
-ok 后面跟自定义命令(会提示是否操作)
-exec 后面跟自定义命令(标准写法 -exec \;
示例
最常用的是 exec ,还可以配合管道符使用,但是 find 使用管道符时需要加 xargs
#查找当前目录下以find_开头的目录然后删除
~]# find ./ -type d -name "find_*" -exec rm -rf {} \;
#查找当前目录下以find_开头的目录然后删除,删除大量文件时用 xargs
~]# find ./ -type d -name "find_*" | xargs rm -f
#删除七天之前日志文件
~]# find /var/log/ -type f -name "*.log" -mtime +7 -exec rm -f {} \'
~]# find /var/log/ -type f -name "*log" -mtime +7 | xargs rm -f