进程间通信之管道、函数popen和pclose、协同进程以及FIFO
本文来自个人博客:https://dunkwan.cn
文章目录
-
- 管道
- 函数`popen`和`pclose`
- 协同进程
- FIFO(命名管道)
管道
管道是UNIX系统IPC的最古老形式,所有UNIX系统都支持该通信机制。
管道有以下两种局限性。
- 历史上,它们是半双工的(即数据只能在一个方向上流动)。
- 管道只能在具有公共祖先的两个进程间使用。
管道需要通过pipe函数来进行创建。
#include 下图显示了半双工管道的两种描绘方法。
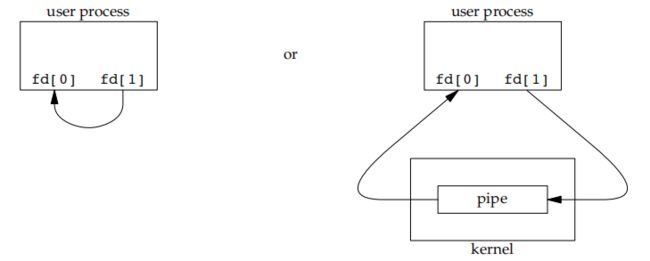
左图是管道两端在一个进程中相互连接,右图则强调数据需要通过内核在管道中流动。
由于单个进程中管道作用不大,通常,进程会先调用pipe,接着fork,从而创建从父进程到子进程的IPC通道,从子进程到父进程亦然。如下图所示。

对于从父进程到子进程的管道,父进程需要关闭管道的读端(fd[0]),子进程则要关闭管道写端(fd[1])。
对于从子进程到父进程的管道,父进程需要关闭管道写端(fd[1]),子进程则要关闭管道读端(fd[0])。

当管道的一端被关闭后,下列两条规则起作用。
- 当读(read)一个写端已关闭的管道时,在所有数据都被读取后,read返回0,表示文件结束。
- 如果写(write)一个读端已被关闭的管道,则产生信号
SIGPIPE。如果忽略该信号或者捕捉该信号并从其处理程序返回,则write返回-1,errno设置为EPIPE。
测试示例1:
父进程到子进程的管道与子进程到父进程的管道的例子。
/* parent to child */
#include "apue.h"
int
main(void)
{
int n;
int fd[2];
pid_t pid;
char line[MAXLINE];
if (pipe(fd) < 0)
err_sys("pipe error");
if ((pid = fork()) < 0) {
err_sys("fork error");
} else if (pid > 0) { /* parent */
close(fd[0]);
write(fd[1], "hello world\n", 12);
} else { /* child */
close(fd[1]);
n = read(fd[0], line, MAXLINE);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, line, n);
}
exit(0);
}
/* child to parent */
#include "apue.h"
int
main(void)
{
int n;
int fd[2];
pid_t pid;
char line[MAXLINE];
if (pipe(fd) < 0)
err_sys("pipe error");
if ((pid = fork()) < 0) {
err_sys("fork error");
} else if (pid > 0) { /* parent */
close(fd[1]);
n = read(fd[0], line, MAXLINE);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, line, n);
} else { /* child */
close(fd[0]);
write(fd[1], "pipe for child to parent",
strlen("pipe for child to parent"));
}
exit(0);
}
每次一页的显示已产生的输出。
#include "apue.h"
#include " );
if ((fp = fopen(argv[1], "r")) == NULL)
err_sys("can't open %s", argv[1]);
if (pipe(fd) < 0)
err_sys("pipe error");
if ((pid = fork()) < 0) {
err_sys("fork error");
} else if (pid > 0) { /* parent */
close(fd[0]); /* close read end */
/* parent copies argv[1] to pipe */
while (fgets(line, MAXLINE, fp) != NULL) {
n = strlen(line);
if (write(fd[1], line, n) != n)
err_sys("write error to pipe");
}
if (ferror(fp))
err_sys("fgets error");
close(fd[1]); /* close write end of pipe for reader */
if (waitpid(pid, NULL, 0) < 0)
err_sys("waitpid error");
exit(0);
} else { /* child */
close(fd[1]); /* close write end */
if (fd[0] != STDIN_FILENO) {
if (dup2(fd[0], STDIN_FILENO) != STDIN_FILENO)
err_sys("dup2 error to stdin");
close(fd[0]); /* don't need this after dup2 */
}
/* get arguments for execl() */
if ((pager = getenv("PAGER")) == NULL)
pager = DEF_PAGER;
if ((argv0 = strrchr(pager, '/')) != NULL)
argv0++; /* step past rightmost slash */
else
argv0 = pager; /* no slash in pager */
if (execl(pager, argv0, (char *)0) < 0)
err_sys("execl error for %s", pager);
}
exit(0);
}
函数popen和pclose
popen和pclose函数实现的操作是:创建一个管道,fork一个子进程,关闭未使用的管道端,执行一个shell运行命令,然后等待命令终止。
#include 测试示例1:
用popen重写分页输出程序。
#include "apue.h"
#include " );
if ((fpin = fopen(argv[1], "r")) == NULL)
err_sys("can't open %s", argv[1]);
if ((fpout = popen(PAGER, "w")) == NULL)
err_sys("popen error");
/* copy argv[1] to pager */
while (fgets(line, MAXLINE, fpin) != NULL) {
if (fputs(line, fpout) == EOF)
err_sys("fputs error to pipe");
}
if (ferror(fpin))
err_sys("fgets error");
if (pclose(fpout) == -1)
err_sys("pclose error");
exit(0);
}
测试示例2:
通过管道执行过滤程序进行大写字符串转小写。
/* myuclc.c */
#include "apue.h"
#include 协同进程
当一个过滤程序既产生某个过滤程序的输入,又读取该过滤程序的输出时,它就变成了协同进程。
测试示例1:
利用协同进程来进行两数和运算。
底层I/O版本
/* add.c */
#include "apue.h"
int main(void)
{
int n, int1, int2;
char line[MAXLINE];
while((n = read(STDIN_FILENO, line, MAXLINE)) > 0){
line[n] = 0;
if(sscanf(line, "%d%d", &int1, &int2) == 2){
sprintf(line, "%d\n", int1 + int2);
n = strlen(line);
if(write(STDOUT_FILENO, line, n) != n)
err_sys("write error");
}else{
if(write(STDOUT_FILENO, "invalid args\n", 13) != 13)
err_sys("write error");
}
}
return 0;
}
/* main.c */
#include "apue.h"
static void sig_pipe(int);
int main(void)
{
int n, fd1[2], fd2[2];
pid_t pid;
char line[MAXLINE];
if(signal(SIGPIPE, sig_pipe) == SIG_ERR)
err_sys("signal error");
if(pipe(fd1) < 0 || pipe(fd2) < 0)
err_sys("pipe error");
if((pid = fork()) < 0)
err_sys("pipe error");
if((pid = fork()) < 0){
err_sys("pipe error");
}else if(pid > 0)
{
close(fd1[0]);
close(fd2[1]);
while(fgets(line, MAXLINE, stdin) != NULL){
n = strlen(line);
if(write(fd1[1], line, n) != n)
err_sys("write error to pipe");
if((n = read(fd2[0], line, MAXLINE)) < 0)
err_sys("read error from pipe");
if(n == 0){
err_msg("child closed pipe");
break;
}
line[n] = 0;
if(fputs(line, stdout) == EOF)
err_sys("fputs error");
}
if(ferror(stdin))
err_sys("fgets error on stdin");
exit(0);
}else {
close(fd1[1]);
close(fd2[0]);
if(fd1[0] != STDIN_FILENO){
if(dup2(fd1[0], STDIN_FILENO) != STDIN_FILENO)
err_sys("dup2 error to stdin");
close(fd1[0]);
}
if(fd2[1] != STDOUT_FILENO){
if(dup2(fd2[1], STDOUT_FILENO) != STDOUT_FILENO)
err_sys("dup2 error to stdout");
close(fd2[1]);
}
if(execl("./add2", "add2", (char *)0) < 0)
err_sys("execl error");
}
return 0;
}
static void sig_pipe(int signo)
{
printf("SIGPIPE caught\n");
exit(1);
}
标准I/O版本
/* add2stdio.c */
#include "apue.h"
int main(void)
{
int int1, int2;
char line[MAXLINE];
if(setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IOLBF, 0) != 0)
err_sys("setvbuf error");
if(setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IOLBF, 0) != 0)
err_sys("setvbuf error");
while(fgets(line, MAXLINE, stdin) != NULL){
if(sscanf(line, "%d%d", &int1, &int2) == 2){
if(printf("%d\n", int1 + int2) == EOF)
err_sys("printf error");
}else{
if(printf("invalid args\n") == EOF)
err_sys("printf error");
}
}
return 0;
}
/* main.c */
/* same as above */
FIFO(命名管道)
创建
FIFO文件类似于创建文件。
#include 参数说明:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
path |
指定绝对路径时,fd参数忽略,此时mkfifo和mkfifoat行为类似。指定相对路径名时,fd参数为一个打开目录的有效文件描述符,路径名和目录有关;若此时fd参数为AT_FDCWD时,则路径名以当前目录开始,mkfifo和mkfifoat类似。 |
fd |
打开文件的有效描述符。 |
mode |
与open函数mode参数相同。 |
源代码


