Binder机制 在Android中的具体实现原理
Binder机制在 Android中的实现主要依靠 Binder类,其实现了IBinder 接口 下面会详细说明
实例说明:Client进程 需要调用 Server进程的函数 即:
Client进程 需要传两个整数给Server进程Server进程 需要把相加后的结果 返回给Client进程- 具体步骤 下面,我会根据
Binder跨进程通信机制 模型的步骤进行分析
步骤1:注册服务
- 过程描述
Server进程 通过Binder驱动 向Service Manager进程 注册服务 - 代码实现
Server进程 创建 一个Binder对象Binder实体是Server进程 在Binder驱动中的存在形式- 该对象保存
Server和ServiceManager的信息(保存在内核空间中) Binder驱动通过 内核空间的Binder实体 找到用户空间的Server对象
代码分析:
Binder binder = new Stub();
// 步骤1:创建Binder对象 ->>分析1
// 步骤2:创建 IInterface 接口类 的匿名类
// 创建前,需要预先定义 继承了IInterface 接口的接口 -->分析3
IInterface plus = new IPlus(){
// 确定Client进程需要调用的方法
public int add(int a,int b) {
return a+b;
}
// 实现IInterface接口中唯一的方法
public IBinder asBinder(){
return null ;
}
};
// 步骤3
binder.attachInterface(plus,"add two int");
// 1. 将(add two int,plus)作为(key,value)对存入到Binder对象中的一个Map对象中
// 2. 之后,Binder对象 可根据add two int通过queryLocalIInterface()获得对应IInterface对象(即plus)的引用,可依靠该引用完成对请求方法的调用
// 分析完毕,跳出
<-- 分析1:Stub类 -->
public class Stub extends Binder {
// 继承自Binder类 ->>分析2
// 复写onTransact()
@Override
boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags){
// 具体逻辑等到步骤3再具体讲解,此处先跳过
switch (code) {
case Stub.add: {
data.enforceInterface("add two int");
int arg0 = data.readInt();
int arg1 = data.readInt();
int result = this.queryLocalIInterface("add two int") .add( arg0, arg1);
reply.writeInt(result);
return true;
}
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
// 回到上面的步骤1,继续看步骤2
<-- 分析2:Binder 类 -->
public class Binder implement IBinder{
// Binder机制在Android中的实现主要依靠的是Binder类,其实现了IBinder接口
// IBinder接口:定义了远程操作对象的基本接口,代表了一种跨进程传输的能力
// 系统会为每个实现了IBinder接口的对象提供跨进程传输能力
// 即Binder类对象具备了跨进程传输的能力
void attachInterface(IInterface plus, String descriptor);
// 作用:
// 1. 将(descriptor,plus)作为(key,value)对存入到Binder对象中的一个Map对象中
// 2. 之后,Binder对象 可根据descriptor通过queryLocalIInterface()获得对应IInterface对象(即plus)的引用,可依靠该引用完成对请求方法的调用
IInterface queryLocalInterface(Stringdescriptor) ;
// 作用:根据 参数 descriptor 查找相应的IInterface对象(即plus引用)
boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags);
// 定义:继承自IBinder接口的
// 作用:执行Client进程所请求的目标方法(子类需要复写)
// 参数说明:
// code:Client进程请求方法标识符。即Server进程根据该标识确定所请求的目标方法
// data:目标方法的参数。(Client进程传进来的,此处就是整数a和b)
// reply:目标方法执行后的结果(返回给Client进程)
// 注:运行在Server进程的Binder线程池中;当Client进程发起远程请求时,远程请求会要求系统底层执行回调该方法
final class BinderProxy implements IBinder {
// 即Server进程创建的Binder对象的代理对象类
// 该类属于Binder的内部类
}
// 回到分析1原处
}
<-- 分析3:IInterface接口实现类 -->
public interface IPlus extends IInterface {
// 继承自IInterface接口->>分析4
// 定义需要实现的接口方法,即Client进程需要调用的方法
public int add(int a,int b);
// 返回步骤2
}
<-- 分析4:IInterface接口类 -->
// 进程间通信定义的通用接口
// 通过定义接口,然后再服务端实现接口、客户端调用接口,就可实现跨进程通信。
public interface IInterface
{
// 只有一个方法:返回当前接口关联的 Binder 对象。
public IBinder asBinder();
}
// 回到分析3原处 注册服务后,Binder驱动持有 Server进程创建的Binder实体
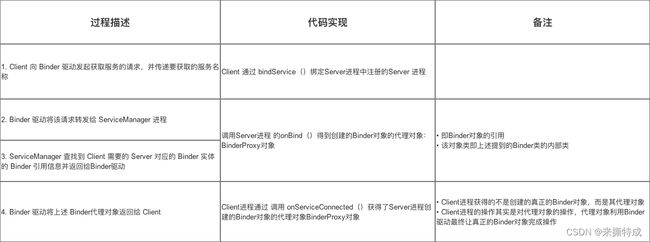
步骤2:获取服务
Client进程 使用 某个service前(此处是 相加函数),须 通过Binder驱动 向ServiceManager进程 获取相应的Service信息- 具体代码实现过程如下:
此时,Client进程与 Server进程已经建立了连接
步骤3:使用服务
Client进程 根据获取到的 Service信息(Binder代理对象),通过Binder驱动 建立与 该Service所在Server进程通信的链路,并开始使用服务
- 过程描述
Client进程 将参数(整数a和b)发送到Server进程Server进程 根据Client进程要求调用 目标方法(即加法函数)Server进程 将目标方法的结果(即加法后的结果)返回给Client进程
- 代码实现过程
步骤1: Client进程 将参数(整数a和b)发送到Server进程
// 1. Client进程 将需要传送的数据写入到Parcel对象中
// data = 数据 = 目标方法的参数(Client进程传进来的,此处就是整数a和b) + IInterface接口对象的标识符descriptor
android.os.Parcel data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInt(a);
data.writeInt(b);
data.writeInterfaceToken("add two int");;
// 方法对象标识符让Server进程在Binder对象中根据"add two int"通过queryLocalIInterface()查找相应的IInterface对象(即Server创建的plus),Client进程需要调用的相加方法就在该对象中
android.os.Parcel reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
// reply:目标方法执行后的结果(此处是相加后的结果)
// 2. 通过 调用代理对象的transact() 将 上述数据发送到Binder驱动
binderproxy.transact(Stub.add, data, reply, 0)
// 参数说明:
// 1. Stub.add:目标方法的标识符(Client进程 和 Server进程 自身约定,可为任意)
// 2. data :上述的Parcel对象
// 3. reply:返回结果
// 0:可不管
// 注:在发送数据后,Client进程的该线程会暂时被挂起
// 所以,若Server进程执行的耗时操作,请不要使用主线程,以防止ANR
// 3. Binder驱动根据 代理对象 找到对应的真身Binder对象所在的Server 进程(系统自动执行)
// 4. Binder驱动把 数据 发送到Server 进程中,并通知Server 进程执行解包(系统自动执行)步骤2:Server进程根据Client进要求 调用 目标方法(即加法函数)
// 1. 收到Binder驱动通知后,Server 进程通过回调Binder对象onTransact()进行数据解包 & 调用目标方法
public class Stub extends Binder {
// 复写onTransact()
@Override
boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags){
// code即在transact()中约定的目标方法的标识符
switch (code) {
case Stub.add: {
// a. 解包Parcel中的数据
data.enforceInterface("add two int");
// a1. 解析目标方法对象的标识符
int arg0 = data.readInt();
int arg1 = data.readInt();
// a2. 获得目标方法的参数
// b. 根据"add two int"通过queryLocalIInterface()获取相应的IInterface对象(即Server创建的plus)的引用,通过该对象引用调用方法
int result = this.queryLocalIInterface("add two int") .add( arg0, arg1);
// c. 将计算结果写入到reply
reply.writeInt(result);
return true;
}
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
// 2. 将结算结果返回 到Binder驱动步骤3:Server进程 将目标方法的结果(即加法后的结果)返回给Client进程
// 1. Binder驱动根据 代理对象 沿原路 将结果返回 并通知Client进程获取返回结果
// 2. 通过代理对象 接收结果(之前被挂起的线程被唤醒)
binderproxy.transact(Stub.ADD, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();;
result = reply.readInt();
}
}- 总结 下面,我用一个原理图 & 流程图来总结步骤3的内容
5. 优点
对比 Linux (Android基于Linux)上的其他进程通信方式(管道、消息队列、共享内存、 信号量、Socket),Binder 机制的优点有:
6. 总结
- 本文主要详细讲解 跨进程通信模型
Binder机制 ,总结如下:
特别地,对于从模型结构组成的Binder驱动来说: