【LeetCode】112. 路径总和(简单)——代码随想录算法训练营Day18
题目链接:112. 路径总和
题目描述
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
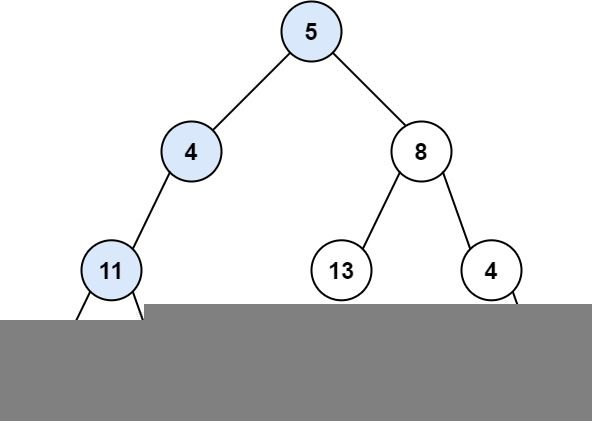
示例 1:
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22 输出:true 解释:等于目标和的根节点到叶节点路径如上图所示。
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 输出:false 解释:树中存在两条根节点到叶子节点的路径: (1 --> 2): 和为 3 (1 --> 3): 和为 4 不存在 sum = 5 的根节点到叶子节点的路径。
示例 3:
输入:root = [], targetSum = 0 输出:false 解释:由于树是空的,所以不存在根节点到叶子节点的路径。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[0, 5000]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
文章讲解:代码随想录
视频讲解:拿不准的遍历顺序,搞不清的回溯过程,我太难了! | LeetCode:112. 路径总和_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
题解1:递归法
思路:遍历左右子树,找出左右子树是否存在路径总和为目标值减根节点值的路径,递归函数需返回一个布尔值,为当前子树是否存在路径总和为目标值减根节点值的路径。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} targetSum
* @return {boolean}
*/
var hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
if (!root) {
return false;
}
if (!root.left && !root.right && targetSum === root.val) {
return true;
}
return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val); // 左 右
};分析:时间复杂度为 O(n),空间复杂度为 O(logn)。
题解2:迭代法
思路:使用前序遍历,记录每个节点的路径总和,判断所有叶子节点的路径总和是不是目标值。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} targetSum
* @return {boolean}
*/
var hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
const stack = [];
if (root) {
stack.push({ node: root, sum: 0 });
}
while (stack.length > 0) {
const item = stack.pop();
const node = item.node;
item.sum += node.val; // 中
if (!node.left && !node.right && item.sum === targetSum) {
return true;
}
node.right && stack.push({ node: node.right, sum: item.sum }); // 右
node.left && stack.push({ node: node.left, sum: item.sum }); // 左
}
return false;
};分析:时间复杂度为 O(n),空间复杂度为 O(logn)。
类似题 113. 路径总和 II(中等)
题目链接:113. 路径总和 II
思路:和上面题类似的方法,遍历中需要记录路径。
递归法
因为要列举出所有路径,需要遍历整棵树,递归函数不需要返回值。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} targetSum
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var pathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
const res = [];
if (!root) {
return [];
}
const order = function (node, sum, path) {
sum += node.val;
path.push(node.val); // 中
if (!node.left && !node.right && sum === targetSum) {
res.push([...path]);
}
if (node.left) {
order(node.left, sum, path); // 左
path.pop();
}
if (node.right) {
order(node.right, sum, path); // 右
path.pop();
}
}
order(root, 0, []);
return res;
};迭代法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} targetSum
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var pathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
const res = [];
const stack = [];
if (root) {
stack.push({ node: root, sum: 0, path: [] });
}
while (stack.length > 0) {
const item = stack.pop();
const node = item.node;
item.sum += node.val; // 中
item.path.push(node.val);
if (!node.left && !node.right && item.sum === targetSum) {
res.push(item.path);
}
node.right && stack.push({ node: node.right, sum: item.sum, path: [...item.path] }); // 右
node.left && stack.push({ node: node.left, sum: item.sum, path: [...item.path] }); // 左
}
return res;
};分析:时间复杂度为 O(n),空间复杂度为 O(logn)。
收获
当只需要处理左右子树,不需要处理中间节点时,使用前中后序都可以。