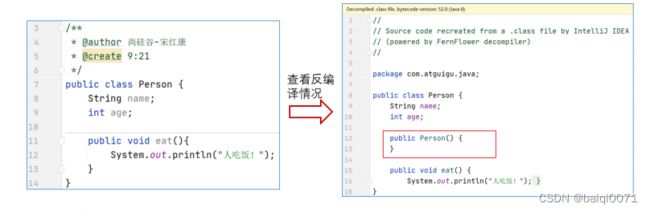
面向对象编程(基础)(下)
上篇链接见:面向对象编程(基础)(上)
文章目录
- 六. 对象数组
- 七. 再谈方法
-
- 7.1 方法的重载(overload)
-
- 7.1.1 概念及特点
- 7.1.2 示例
- 7.1.3 练习
- 7.2 可变个数的形参
- 7.3 方法的参数传递机制
-
- 7.3.1 形参和实参
- 7.3.2 参数传递机制:值传递
- 7.3.3 举例
- 7.3.4 练习
- 7.4 递归(recursion)方法
- 八. 关键字:package、import
-
- 8.1 package(包)
-
- 8.1.1 语法格式
- 8.1.2 包的作用
- 8.1.3 应用举例
- 8.1.4 JDK中主要的包介绍
- 8.2 import(导入)
-
- 8.2.1 **语法格式**
- 8.2.2 **应用举例**
- 8.2.3 **注意事项**
- 九. 面向对象特征一:封装性(encapsulation)
-
- 9.1 为什么需要封装?
- 9.2 何为封装性?
- 9.3 Java如何实现数据封装
- 9.4 封装性的体现
-
- 9.4.1 成员变量/属性私有化
- 9.4.2 私有化方法
- 9.5 练习
- 十. 类的成员之三:构造器(Constructor)
-
- 10.1 构造器的作用
- 10.2 构造器的语法格式
- 10.3 使用说明
- 10.4 练习
- 十一. 阶段性知识补充
-
- 11.1 类中属性赋值过程
- 11.2 JavaBean
- 11.3 UML类图
六. 对象数组
数组的元素可以是基本数据类型,也可以是引用数据类型。当元素是引用类型中的类时,我们称为对象数组。
1、案例
定义类Student,包含三个属性:学号number(int),年级state(int),成绩score(int)。 创建20个学生对象,学号为1到20,年级和成绩都由随机数确定。
问题一:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。
问题二:使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息
提示:
- 生成随机数:Math.random(),返回值类型double;
- 四舍五入取整:Math.round(double d),返回值类型long。
/*
* 定义类Student,包含三个属性:学号number(int),年级state(int),成绩score(int)。
*/
public class Student {
int number;//学号
int state;//年级
int score;//成绩
public void info() {
System.out.println("number : " + number
+ ",state : " + state + ",score : " + score);
}
}
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Student s1 = new Student();
// s1.number = 1;
// s1.state = (int)(Math.random() * 6 + 1);//[1,6]
// s1.score = (int)(Math.random() * 101);//[0,100]
//
// Student s2 = new Student();
// s2.number = 2;
// s2.state = (int)(Math.random() * 6 + 1);//[1,6]
// s2.score = (int)(Math.random() * 101);//[0,100]
//
// //....
// 对象数组
// String[] arr = new String[10];
// 数组的创建
Student[] students = new Student[20];
// 通过循环结构给数组的属性赋值
for (int i = 0; i < students.length; i++) {
// 数组元素的赋值
students[i] = new Student();
// 数组元素是一个对象,给对象的各个属性赋值
students[i].number = (i + 1);
students[i].state = (int) (Math.random() * 6 + 1);// [1,6]
students[i].score = (int) (Math.random() * 101);// [0,100]
}
// 问题一:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。
for (int i = 0; i < students.length; i++) {
if (students[i].state == 3) {
// System.out.println(
// "number:" + students[i].number + ",state:" + students[i].state + ",score:" + students[i].score);
students[i].info();
}
}
System.out.println("******************************");
// 问题二:使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息
// 排序前
for (int i = 0; i < students.length; i++) {
// System.out.println(
// "number:" + students[i].number + ",state:" +
// students[i].state + ",score:" + students[i].score);
students[i].info();
}
System.out.println();
// 排序:
for (int i = 0; i < students.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < students.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (students[j].score > students[j + 1].score) {
Student temp = students[j];
students[j] = students[j + 1];
students[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
// 排序后:
for (int i = 0; i < students.length; i++) {
// System.out.println(
// "number:" + students[i].number + ",state:" +
// students[i].state + ",score:" + students[i].score);
students[i].info();
}
}
}
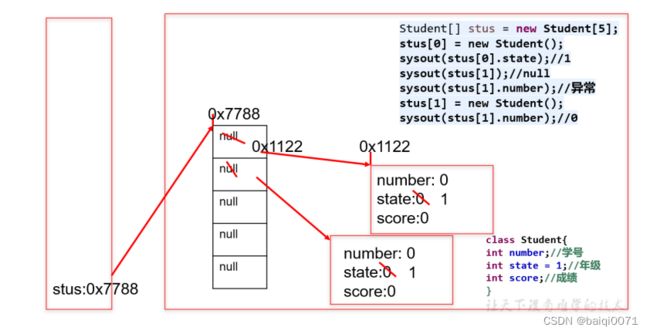
内存解析:
2、注意点
对象数组,首先要创建数组对象本身,即确定数组的长度,然后再创建每一个元素对象,如果不创建,数组的元素的默认值就是 null ,所以很容易出现 空指针异常NullPointerException 。
3、练习
- 定义矩形类Rectangle,包含长、宽属性,area()返回矩形面积的方法,perimeter()返回矩形周长的方法,String getInfo()返回圆对象的详细信息(如:长、宽、面积、周长等数据)的方法
- 在测试类中创建长度为3的Rectangle[]数组,用来装3个矩形对象,并给3个矩形对象的长分别赋值为10,20,30,宽分别赋值为5,15,25,遍历输出
package com.atguigu.test08.array;
public class Rectangle {
double length;
double width;
public double area() {//面积
return length * width;
}
public double perimeter() {//周长
return 2 * (length + width);
}
public String getInfo() {
return "长:" + length +
",宽:" + width +
",面积:" + area() +
",周长:" + perimeter();
}
}
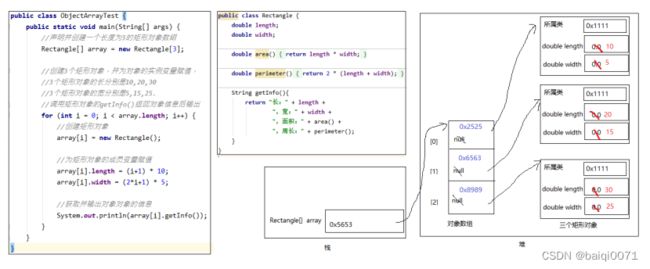
package com.atguigu.test08.array;
public class ObjectArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//声明并创建一个长度为3的矩形对象数组
Rectangle[] array = new Rectangle[3];
//创建3个矩形对象,并为对象的实例变量赋值,
//3个矩形对象的长分别是10,20,30
//3个矩形对象的宽分别是5,15,25
//调用矩形对象的getInfo()返回对象信息后输出
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
//创建矩形对象
array[i] = new Rectangle();
//为矩形对象的成员变量赋值
array[i].length = (i + 1) * 10;
array[i].width = (2 * i + 1) * 5;
//获取并输出对象对象的信息
System.out.println(array[i].getInfo());
}
}
}
内存解析:
七. 再谈方法
7.1 方法的重载(overload)
7.1.1 概念及特点
- 方法重载:在同一个类中,允许存在一个以上的同名方法,只要它们的参数列表不同即可。
- 参数列表不同,意味着参数个数或参数类型的不同
- 重载的特点:与修饰符、返回值类型无关,只看参数列表,且参数列表必须不同。(参数个数或参数类型)。调用时,根据方法参数列表的不同来区别。
- 重载方法调用:JVM通过方法的参数列表,调用匹配的方法。
- 先找个数、类型最匹配的
- 再找个数和类型可以兼容的,如果同时多个方法可以兼容将会报错
7.1.2 示例
举例1:
//System.out.println()方法就是典型的重载方法,其内部的声明形式如下:
public class PrintStream {
public void println(byte x)
public void println(short x)
public void println(int x)
public void println(long x)
public void println(float x)
public void println(double x)
public void println(char x)
public void println(double x)
public void println()
}
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(3);
System.out.println(1.2f);
System.out.println("hello!");
}
}
举例2:
//返回两个整数的和
public int add(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
//返回三个整数的和
public int add(int x, int y, int z) {
return x + y + z;
}
//返回两个小数的和
public double add(double x, double y) {
return x + y;
}
举例3:方法的重载和返回值类型无关
public class MathTools {
//以下方法不是重载,会报错
public int getOneToHundred() {
return (int) (Math.random() * 100);
}
public double getOneToHundred() {
return Math.random() * 100;
}
}
7.1.3 练习
练习1:判 断与 void show(int a,char b,double c){} 构成重载的有:
a)void show(int x,char y,double z){} // no
b)int show(int a,double c,char b){} // yes
c)void show(int a,double c,char b){} // yes
d)boolean show(int c,char b){} // yes
e)void show(double c){} // yes
f)double show(int x,char y,double z){} // no
g)void shows(){double c} // no
练习2:编写程序,定义三个重载方法并调用。
- 方法名为mOL。
- 三个方法分别接收一个int参数、两个int参数、一个字符串参数。分别执行平方运算并输出结果,相乘并输出结果,输出字符串信息。
- 在主类的main ()方法中分别用参数区别调用三个方法。
练习3:定义三个重载方法max(),第一个方法求两个int值中的最大值,第二个方法求两个double值中的最大值,第三个方法求三个double值中的最大值,并分别调用三个方法。
7.2 可变个数的形参
在JDK 5.0 中提供了Varargs(variable number of arguments)机制。即当定义一个方法时,形参的类型可以确定,但是形参的个数不确定,那么可以考虑使用可变个数的形参。
格式:
方法名(参数的类型名 ...参数名)
举例:
//JDK 5.0以前:采用数组形参来定义方法,传入多个同一类型变量
public static void test(int a ,String[] books);
//JDK5.0:采用可变个数形参来定义方法,传入多个同一类型变量
public static void test(int a ,String...books);
特点:
- 可变参数:方法参数部分指定类型的参数个数是可变多个:0个,1个或多个
- 可变个数形参的方法与同名的方法之间,彼此构成重载
- 可变参数方法的使用与方法参数部分使用数组是一致的,二者不能同时声明,否则报错。
- 方法的参数部分有可变形参,需要放在形参声明的最后
- 在一个方法的形参中,最多只能声明一个可变个数的形参
案例分析:
案例1:n个字符串进行拼接,每一个字符串之间使用某字符进行分割,如果没有传入字符串,那么返回空字符串""
public class StringTools {
String concat(char seperator, String... args) {
String str = "";
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
str += args[i];
} else {
str += seperator + args[i];
}
}
return str;
}
}
package com.atguigu.test05.param;
public class StringToolsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringTools tools = new StringTools();
System.out.println(tools.concat('-'));
System.out.println(tools.concat('-', "hello"));
System.out.println(tools.concat('-', "hello", "world"));
System.out.println(tools.concat('-', "hello", "world", "java"));
}
}
案例2:求n个整数的和
public class NumberTools {
public int total(int[] nums) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
sum += nums[i];
}
return sum;
}
public int sum(int... nums) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
sum += nums[i];
}
return sum;
}
}
public class TestVarParam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NumberTools tools = new NumberTools();
System.out.println(tools.sum());//0个实参
System.out.println(tools.sum(5));//1个实参
System.out.println(tools.sum(5, 6, 2, 4));//4个实参
System.out.println(tools.sum(new int[]{5, 6, 2, 4}));//传入数组实参
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
System.out.println(tools.total(new int[]{}));//0个元素的数组
System.out.println(tools.total(new int[]{5}));//1个元素的数组
System.out.println(tools.total(new int[]{5, 6, 2, 4}));//传入数组实参
}
}
案例3:如下的方法彼此构成重载
public class MathTools {
//求两个整数的最大值
public int max(int a, int b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
//求两个小数的最大值
public double max(double a, double b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
//求三个整数的最大值
public int max(int a, int b, int c) {
return max(max(a, b), c);
}
//求n个整数的最大值
public int max(int... nums) {
int max = nums[0];//如果没有传入整数,或者传入null,这句代码会报异常
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > max) {
max = nums[i];
}
}
return max;
}
/* //求n整数的最大值
public int max(int[] nums) { //编译就报错,与(int... nums)无法区分
int max = nums[0];//如果没有传入整数,或者传入null,这句代码会报异常
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > max) {
max = nums[i];
}
}
return max;
}*/
/* //求n整数的最大值
public int max(int first, int... nums) { //当前类不报错,但是调用时会引起多个方法同时匹配
int max = first;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > max) {
max = nums[i];
}
}
return max;
}*/
}
7.3 方法的参数传递机制
7.3.1 形参和实参
- 形参(formal parameter):在定义方法时,方法名后面括号()中声明的变量称为形式参数,简称形参。
- 实参(actual parameter):在调用方法时,方法名后面括号()中的使用的值/变量/表达式称为实际参数,简称实参。
7.3.2 参数传递机制:值传递
Java里方法的参数传递方式只有一种: 值传递 。 即将实际参数值的副本(复制品)传入方法内,而参数本身不受影响。
- 形参是基本数据类型:将实参基本数据类型变量的“数据值”传递给形参
- 形参是引用数据类型:将实参引用数据类型变量的“地址值”传递给形参
7.3.3 举例
1、形参是基本数据类型
案例:编写方法,交换两个整型变量的值
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int m = 10;
int n = 20;
System.out.println("m = " + m + ", n = " + n);
// 交换m和n的值
// int temp = m;
// m = n;
// n = temp;
ValueTransferTest1 test = new ValueTransferTest1();
test.swap(m, n);
System.out.println("m = " + m + ", n = " + n);
}
public void swap(int m, int n) {
int temp = m;
m = n;
n = temp;
}
}
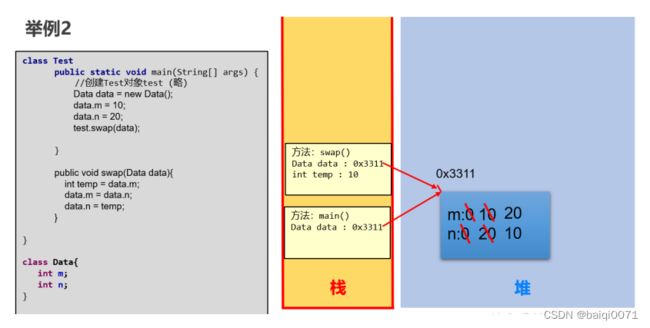
2、形参是引用数据类型
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data d1 = new Data();
d1.m = 10;
d1.n = 20;
System.out.println("m = " + d1.m + ", n = " + d1.n);
//实现 换序
ValueTransferTest2 test = new ValueTransferTest2();
test.swap(d1);
System.out.println("m = " + d1.m + ", n = " + d1.n);
}
public void swap(Data data) {
int temp = data.m;
data.m = data.n;
data.n = temp;
}
}
class Data {
int m;
int n;
}
7.3.4 练习
练习1:判断如下程序输出的结果
public class AssignNewObject {
public void swap(MyData my) {
my = new MyData(); //考虑堆空间此新创建的对象,和main中的data对象是否有关
int temp = my.x;
my.x = my.y;
my.y = temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AssignNewObject tools = new AssignNewObject();
MyData data = new MyData();
data.x = 1;
data.y = 2;
System.out.println("交换之前:x = " + data.x + ",y = " + data.y);//
tools.swap(data);//调用完之后,x与y的值交换?
System.out.println("交换之后:x = " + data.x + ",y = " + data.y);//
}
}
class MyData {
int x;
int y;
}
练习2:如下操作是否可以实现数组排序
public class ArrayTypeParam {
//冒泡排序,实现数组从小到大排序
public void sort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
//打印数组的元素
public void print(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayTypeParam tools = new ArrayTypeParam();
int[] nums = {4, 3, 1, 6, 7};
System.out.println("排序之前:");
tools.print(nums);
tools.sort(nums);//对nums数组进行排序
System.out.println("排序之后:");
tools.print(nums);//输出nums数组的元素
}
}
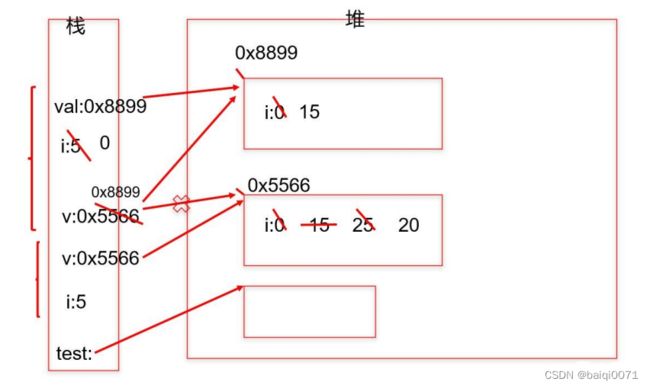
练习3:通过内存结构图,写出如下程序的输出结果
//栈:每个方法在调用时,都会有以栈帧的方法压入栈中。栈帧中保存了当前方法中声明的变量:方法内声明的,形参
//堆:存放new出来的"东西":对象(成员变量在对象中)、数组实体(数组元素)。
//注意:变量前如果声明有类型,那么这就是一个新的刚要定义的变量。如果变量前没有声明类型,那就说明此变量在之前已经声明过。
public class TransferTest3 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
TransferTest3 test = new TransferTest3();
test.first();
}
public void first() {
int i = 5;
Value v = new Value();
v.i = 25;
second(v, i);
System.out.println(v.i);
}
public void second(Value v, int i) {
i = 0;
v.i = 20;
Value val = new Value();
v = val;
System.out.println(v.i + " " + i);
}
}
class Value {
int i = 15;
}
练习4: 貌似是 考查方法的参数传递
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
method(a,b);//需要在method方法被调用之后,仅打印出a=100,b=200,请写出method方法的代码
System.out.println("a=" + a);
System.out.println("b=" + b);
}
}
//法一:
public static void method(int a, int b) {
// 在不改变原本题目的前提下,如何写这个函数才能在main函数中输出a=100,b=200?
a = a * 10;
b = b * 20;
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.exit(0);
}
//法二:
public static void method(int a, int b) {
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(System.out) {
@Override
public void println(String x) {
if ("a=10".equals(x)) {
x = "a=100";
} else if ("b=10".equals(x)) {
x = "b=200";
}
super.println(x);
}
};
System.setOut(ps);
}
练习5:将对象作为参数传递给方法
(1)定义一个Circle类,包含一个double型的radius属性代表圆的半径,一个findArea()方法返回圆的面 积。
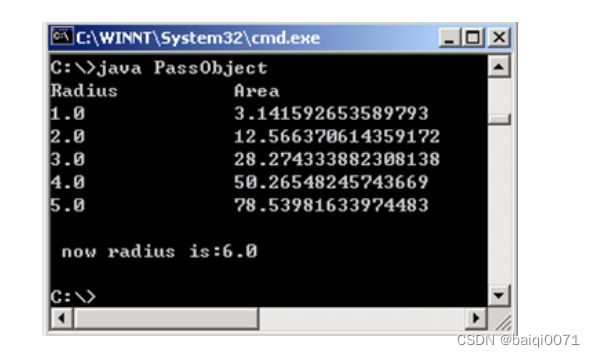
(2)定义一个类PassObject,在类中定义一个方法printAreas(),该方法的定义如下:public void printAreas(Circle c, int time),在printAreas方法中打印输出1到time之间的每个整数半径值,以及对应的面积。例如,times为5,则输出半径1,2,3,4,5,以及对应的圆面积。
(3)在main方法中调用 printAreas()方法,调用完毕后输出当前半径值。程序运行结果如图所示。
7.4 递归(recursion)方法
举例1:
举例2:
从前有座山,山上有座庙,庙里有个老和尚,老和尚在给小和尚讲故事,讲的啥?
从前有座山,山上有座庙,庙里有个老和尚,老和尚在给小和尚讲故事,讲的啥?
从前有座山,山上有座庙,庙里有个老和尚,老和尚在给小和尚讲故事,讲的啥?
从前有座山,山上有座庙,庙里有个老和尚,老和尚在给小和尚讲故事,讲的啥?...
...
老和尚没了,庙塌了,小和尚还俗结婚了。
递归方法调用:方法自己调用自己的现象就称为递归。
递归的分类:直接递归、间接递归。
- 直接递归:方法自身调用自己。
public void methodA(){
methodA();
}
- 间接递归:可以理解为A()方法调用B()方法,B()方法调用C()方法,C()方法调用A()方法。
public static void A(){
B();
}
public static void B(){
C();
}
public static void C(){
A();
}
说明:
- 递归方法包含了一种
隐式的循环。 - 递归方法会
重复执行某段代码,但这种重复执行无须循环控制。 - 递归一定要向
已知方向递归,否则这种递归就变成了无穷递归,停不下来,类似于死循环。最终发生栈内存溢出。
举例:
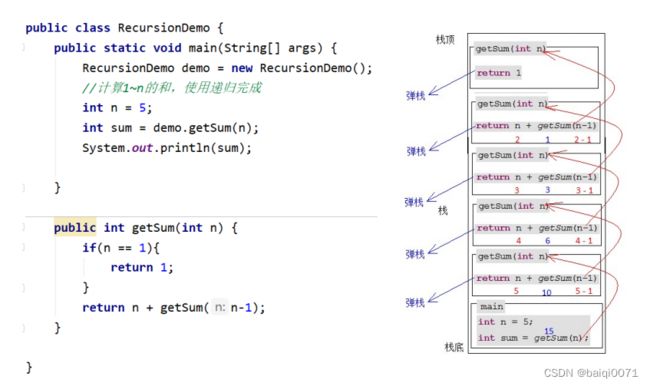
举例1:计算1 ~ n的和
public class RecursionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RecursionDemo demo = new RecursionDemo();
//计算1~num的和,使用递归完成
int num = 5;
// 调用求和的方法
int sum = demo.getSum(num);
// 输出结果
System.out.println(sum);
}
/*
通过递归算法实现.
参数列表:int
返回值类型: int
*/
public int getSum(int num) {
/*
num为1时,方法返回1,
相当于是方法的出口,num总有是1的情况
*/
if (num == 1) {
return 1;
}
/*
num不为1时,方法返回 num +(num-1)的累和
递归调用getSum方法
*/
return num + getSum(num - 1);
}
}
代码执行图解:
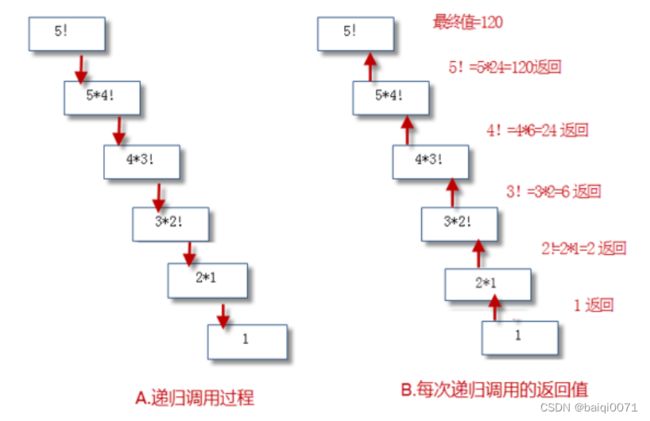
举例2:递归方法计算n!
public int multiply(int num){
if(num == 1){
return 1;
}else{
return num * multiply(num - 1);
}
}
举例3:已知有一个数列:f(0) = 1,f(1) = 4,f(n+2)=2*f(n+1) + f(n),其中n是大于0的整数,求f(10)的值。
public int f(int num){
if(num == 0){
return 1;
}else if(num == 1){
return 4;
}else{
return 2 * f(num - 1) + f(num - 2);
}
}
举例4:已知一个数列:f(20) = 1,f(21) = 4,f(n+2) = 2*f(n+1)+f(n),其中n是大于0的整数,求f(10)的值。
public int func(int num){
if(num == 20){
return 1;
}else if(num == 21){
return 4;
}else{
return func(num + 2) - 2 * func(num + 1);
}
}
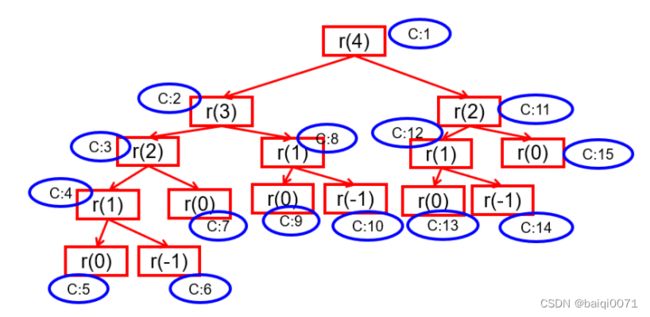
举例5:计算斐波那契数列(Fibonacci)的第n个值,斐波那契数列满足如下规律,
1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,....
即从第三个数开始,一个数等于前两个数之和。假设f(n)代表斐波那契数列的第n个值,那么f(n)满足:
f(n) = f(n-2) + f(n-1);
//使用递归的写法
int f(int n) {//计算斐波那契数列第n个值是多少
if (n < 1) {//负数是返回特殊值1,表示不计算负数情况
return 1;
}
if (n == 1 || n == 2) {
return 1;
}
return f(n - 2) + f(n - 1);
}
//不用递归
int fValue(int n) {//计算斐波那契数列第n个值是多少
if (n < 1) {//负数是返回特殊值1,表示不计算负数情况
return 1;
}
if (n == 1 || n == 2) {
return 1;
}
//从第三个数开始, 等于 前两个整数相加
int beforeBefore = 1; //相当于n=1时的值
int before = 1;//相当于n=2时的值
int current = beforeBefore + before; //相当于n=3的值
//再完后
for (int i = 4; i <= n; i++) {
beforeBefore = before;
before = current;
current = beforeBefore + before;
/* 假设i = 4
beforeBefore = before; //相当于n=2时的值
before = current; //相当于n=3的值
current = beforeBefore + before; //相当于n = 4的值
假设i = 5
beforeBefore = before; //相当于n=3的值
before = current; //相当于n = 4的值
current = beforeBefore + before; //相当于n = 5的值
....*/
}
return current;
}
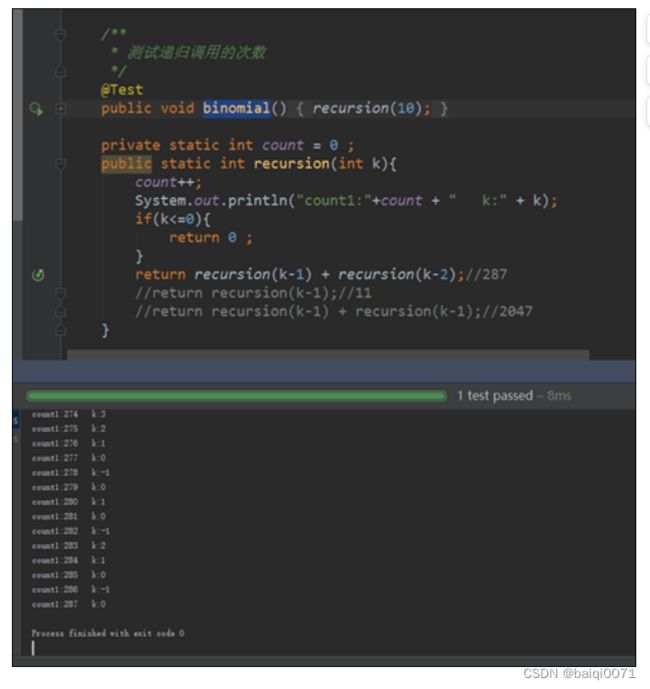
举例6:面试题
private int count = 0;
public int recursion(int k) {
count++;
System.out.println("count1:" + count + " k:" + k);
if (k <= 0) {
return 0;
}
return recursion(k - 1) + recursion(k - 2);//287
//return recursion(k - 1);//11
//return recursion(k - 1) + recursion(k - 1);//2047
}
剖析:
- 递归调用会占用大量的系统堆栈,内存耗用多,在递归调用层次多时速度要比循环
慢的多,所以在使用递归时要慎重。- 在要求高性能的情况下尽量避免使用递归,递归调用既花时间又
耗内存。考虑使用循环迭
代
八. 关键字:package、import
8.1 package(包)
package,称为包,用于指明该文件中定义的类、接口等结构所在的包。
8.1.1 语法格式
package 顶层包名.子包名 ;
举例:pack1\pack2\PackageTest.java
package pack1.pack2; //指定类PackageTest属于包pack1.pack2
public class PackageTest {
public void display() {
System.out.println("in method display()");
}
}
说明:
- 一个源文件只能有一个声明包的package语
- package语句作为Java源文件的第一条语句出现。若缺省该语句,则指定为无名包。
- 包名,属于标识符,满足标识符命名的规则和规范(全部小写)、见名知意
- 包通常使用所在公司域名的倒置:com.atguigu.xxx。
- 大家取包名时不要使用" java.xx "包
- 包对应于文件系统的目录,package语句中用 “.” 来指明包(目录)的层次,每一次就表示一层文件目录。
- 同一个包下可以声明多个结构(类、接口),但是不能定义同名的结构(类、接口)。不同的包下可以定义同名的结构(类、接口)
8.1.2 包的作用
- 包可以包含类和子包,划分
项目层次,便于管理 - 帮助
管理大型软件系统:将功能相近的类划分到同一个包中。比如:MVC的设计模式 - 解决
类命名冲突的问题 - 控制
访问权限
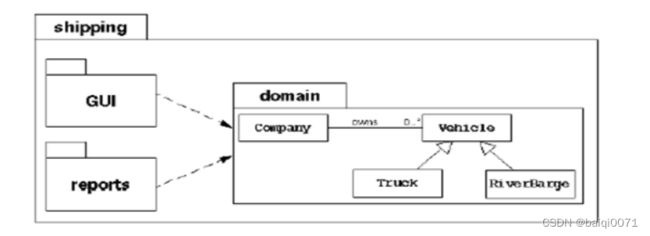
8.1.3 应用举例
举例1:某航运软件系统包括:一组域对象、GUI和reports子系统
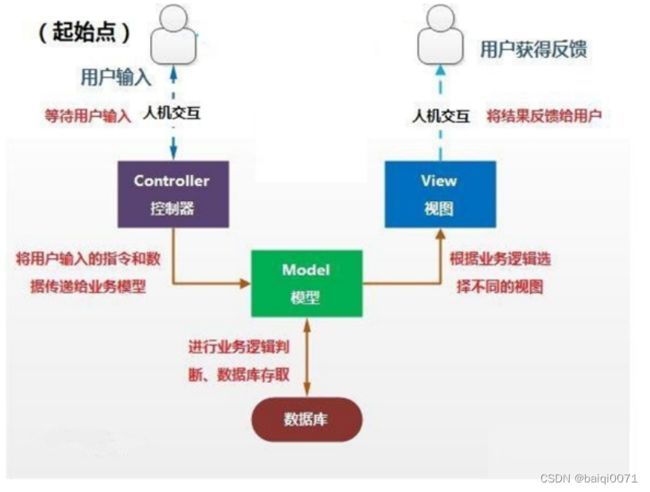
举例2:MVC设计模式
MVC是一种软件构件模式,目的是为了降低程序开发中代码业务的耦合度。
MVC设计模式将整个程序分为三个层次: 视图模型(Viewer)层 , 控制器(Controller)层 ,与 (Model)层 。这种将程序输入输出、数据处理,以及数据的展示分离开来的设计模式使程序结构变的灵活而且清晰,同时也描述了程序各个对象间的通信方式,降低了程序的耦合性。
视图层viewer:显示数据,为用户提供使用界面,与用户直接进行交互。
>相关工具类 view.utils
>自定义view view.ui
控制层controller:解析用户请求,处理业务逻辑,给予用户响应
>应用界面相关 controller.activity
>存放fragment controller.fragment
>显示列表的适配器 controller.adapter
>服务相关的 controller.service
>抽取的基类 controller.base
模型层model:主要承载数据、处理数据
>数据对象封装 model.bean/domain
>数据库操作类 model.dao
>数据库 model.db
8.1.4 JDK中主要的包介绍
java.lang ----包含一些Java语言的核心类,如String、Math、Integer、 System和Thread,提供常用功能
java.net ----包含执行与网络相关的操作的类和接口。
javs.io ----包含能提供多种输入/输出功能的类。
java.util ----包含一些实用工具类,如定义系统特性、接口的集合框架类、使用与日期日历相关的函数。
java.text ----包含了一些java格式化相关的类
java.sql ----包含了java进行JDBC数据库编程的相关类/接口
java.awt ----包含了构成抽象窗口工具集(abstract window toolkits)的多个类,这些类被用来构建和管理应用程序的图形用户界面(GUI)。
8.2 import(导入)
为了使用定义在其它包中的Java类,需用import语句来显式引入指定包下所需要的类。相当于 import语句告诉编译器到哪里去寻找这个类
8.2.1 语法格式
import 包名.类名;
8.2.2 应用举例
import pack1.pack2.Test; //import pack1.pack2.*;表示引入pack1.pack2包中的所有结构
public class PackTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
Test t = new Test(); //Test类在pack1.pack2包中定义
t.display();
}
}
8.2.3 注意事项
- import语句,声明在包的声明和类的声明之间。
- 如果需要导入多个类或接口,那么就并列显式多个import语句即可
- 如果使用
a.*导入结构,表示可以导入a包下的所有的结构。举例:可以使用java.util.*的方式,一
次性导入util包下所有的类或接口。 - 如果导入的类或接口是java.lang包下的,或者是当前包下的,则可以省略此import语句。
- 如果已经导入java.a包下的类,那么如果需要使用a包的子包下的类的话,仍然需要导入。
- 如果在代码中使用不同包下的同名的类,那么就需要使用类的全类名的方式指明调用的是哪个类。
- (了解)
import static组合的使用:调用指定类或接口下的静态的属性或方法
九. 面向对象特征一:封装性(encapsulation)
9.1 为什么需要封装?
- 我要用洗衣机,只需要按一下开关和洗涤模式就可以了。有必要了解洗衣机内部的结构吗?有必要碰电动机吗?
- 我要开车,我不需要懂离合、油门、制动等原理和维修也可以驾驶。
- 客观世界里每一个事物的内部信息都隐藏在其内部,外界无法直接操作和修改,只能通过指定的方式进行访问和修改。
随着我们系统越来越复杂,类会越来越多,那么类之间的访问边界必须把握好,面向对象的开发原则要遵循“ 高内聚、低耦合 ”。
高内聚、低耦合是软件工程中的概念,也是UNIX 操作系统设计的经典原则。
内聚,指一个模块内各个元素彼此结合的紧密程度;耦合指一个软件结构内不同模块之间互连程度的度量。内聚意味着重用和独立,耦合意味着多米诺效应牵一发动全身。
而“高内聚,低耦合”的体现之一:
高内聚:类的内部数据操作细节自己完成,不允许外部干涉;低耦合:仅暴露少量的方法给外部使用,尽量方便外部调用。
9.2 何为封装性?
所谓封装,就是把客观事物封装成抽象概念的类,并且类可以把自己的数据和方法只向可信的类或者对象开放,向没必要开放的类或者对象隐藏信息。
通俗的讲,把该隐藏的隐藏起来,该暴露的暴露出来。这就是封装性的设计思想。
9.3 Java如何实现数据封装
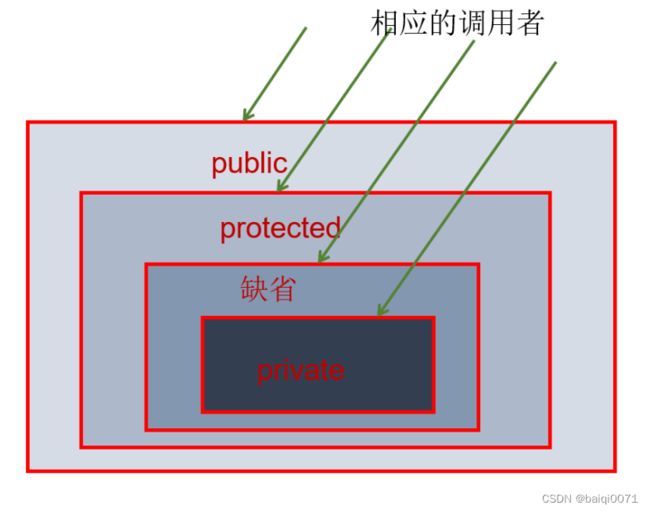
- 实现封装就是控制类或成员的可见性范围。这就需要依赖访问控制修饰符,也称为权限修饰符来控制。
- 权限修饰符:
public、protected、缺省、private。具体访问范围如下:
| 修饰符 | 本类内部 | 本包内 | 其他包的子类 | 其他包非子类 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| private | √ | × | × | × |
| 缺省 | √ | √ | × | × |
| protected | √ | √ | √ | × |
| public | √ | √ | √ | √ |
- 具体修饰的结构:
- 外部类:public、缺省
- 成员变量、成员方法、构造器、成员内部类:public、protected、缺省、private
9.4 封装性的体现
9.4.1 成员变量/属性私有化
概述:私有化类的成员变量,提供公共的get和set方法,对外暴露获取和修改属性的功能。
实现步骤:
① 使用private修饰成员变量
private 数据类型 变量名 ;
代码如下:
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private boolean marry;
}
② 提供 getXxx 方法 / setXxx 方法,可以访问成员变量,代码如下:
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private boolean marry;
public void setName(String n) {
name = n;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setAge(int a) {
age = a;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setMarry(boolean m) {
marry = m;
}
public boolean isMarry() {
return marry;
}
}
③ 测试:
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person();
//实例变量私有化,跨类是无法直接使用的
/* p.name = "张三";
p.age = 23;
p.marry = true;*/
p.setName("张三");
System.out.println("p.name = " + p.getName());
p.setAge(23);
System.out.println("p.age = " + p.getAge());
p.setMarry(true);
System.out.println("p.marry = " + p.isMarry());
}
}
成员变量封装的好处:
- 让使用者只能通过事先预定的方法来
访问数据,从而可以在该方法里面加入控制逻辑,限制对成员变量的不合理访问。还可以进行数据检查,从而有利于保证对象信息的完整性。 便于修改,提高代码的可维护性。主要说的是隐藏的部分,在内部修改了,如果其对外可以的访问方式不变的话,外部根本感觉不到它的修改。例如:Java8->Java9,String从char[]转为byte[]内部实现,而对外的方法不变,我们使用者根本感觉不到它内部的修改。
9.4.2 私有化方法
/**
* @Description 自定义的操作数组的工具类
*/
public class ArrayUtil {
/**
* @param arr
* @return
* @Description 求int型数组的最大值
*/
public int max(int[] arr) {
int maxValue = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (maxValue < arr[i]) {
maxValue = arr[i];
}
}
return maxValue;
}
/**
* @param arr
* @return
* @Description 求int型数组的最小值
*/
public int min(int[] arr) {
int minValue = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (minValue > arr[i]) {
minValue = arr[i];
}
}
return minValue;
}
/**
* @param arr
* @return
* @Description 求int型数组的总和
*/
public int sum(int[] arr) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
/**
* @param arr
* @return
* @Description 求int型数组的元素的平均值
*/
public int avg(int[] arr) {
int sumValue = sum(arr);
return sumValue / arr.length;
}
// 创建一系列重载的上述方法
// public double max(double[] arr){}
// public float max(float[] arr){}
// public byte max(byte[] arr){}
/**
* @param arr
* @Description 遍历数组
*/
public void print(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* @param arr
* @return
* @Description 复制数组arr
*/
public int[] copy(int[] arr) {
int[] arr1 = new int[arr.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr1[i] = arr[i];
}
return arr1;
}
/**
* @param arr
* @Description 反转数组
*/
public void reverse(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0, j = arr.length - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
/**
* @param arr
* @param desc 指明排序的方式。 ascend:升序 descend:降序
* @Description 数组的排序
*/
public void sort(int[] arr, String desc) {
if ("ascend".equals(desc)) {//if(desc.equals("ascend")){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
// int temp = arr[j];
// arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
// arr[j + 1] = temp;
swap(arr, j, j + 1);
}
}
}
} else if ("descend".equals(desc)) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[j + 1]) {
// int temp = arr[j];
// arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
// arr[j + 1] = temp;
swap(arr, j, j + 1);
}
}
}
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的排序方式有误!");
}
}
private void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
/**
* @param arr
* @param value
* @return 返回value值出现的位置 或 -1:未找到
* @Description 查找指定的value值在arr数组中出现的位置
*/
public int getValue(int[] arr, int value) {
//方法:线性查找
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (value == arr[i]) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
注意:
开发中,一般成员实例变量都习惯使用private修饰,再提供相应的public权限的get/set方法访问。
对于final的实例变量,不提供set()方法。(后面final关键字的时候讲)
对于static final的成员变量,习惯上使用public修饰。
9.5 练习
练习1:
创建程序:在其中定义两个类:Person和PersonTest类。定义如下:
用setAge()设置人的合法年龄(0~130),用getAge()返回人的年龄。在PersonTest类中实例化Person类的对象b,调用setAge()和getAge()方法,体会Java的封装性。
练习2:
自定义图书类。设定属性包括:书名bookName,作者author,出版社名publisher,价格price;方法包括:相应属性的get/set方法,图书信息介绍等。
十. 类的成员之三:构造器(Constructor)
我们new完对象时,所有成员变量都是默认值,如果我们需要赋别的值,需要挨个为它们再赋值,太麻烦了。我们能不能在new对象时,直接为当前对象的某个或所有成员变量直接赋值呢?
可以,Java给我们提供了 构造器(Constructor) ,也称为 构造方法 。
10.1 构造器的作用
new对象,并在new对象的时候为实例变量赋值。
举例:Person p = new Person(“Peter”,15);
解释:如同我们规定每个“人”一出生就必须先洗澡,我们就可以在“人”的构造器中加入完成“洗澡”的程序代码,于是每个“人”一出生就会自动完成“洗澡”,程序就不必再在每个人刚出生时一个一个地告诉他们要“洗澡”了。
10.2 构造器的语法格式
[修饰符] class 类名{
[修饰符] 构造器名(){
// 实例初始化代码
}
[修饰符] 构造器名(参数列表){
// 实例初始化代码
}
}
说明:
- 构造器名必须与它所在的类名必须相同。
- 它没有返回值,所以不需要返回值类型,也不需要void。
- 构造器的修饰符只能是权限修饰符,不能被其他任何修饰。比如,不能被static、final、synchronized、abstract、native修饰,不能有return语句返回值。
代码如下:
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
// 无参构造
public Student() {
}
// 有参构造
public Student(String n, int a) {
name = n;
age = a;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String n) {
name = n;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int a) {
age = a;
}
public String getInfo() {
return "姓名:" + name + ",年龄:" + age;
}
}
public class TestStudent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//调用无参构造创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student();
//调用有参构造创建学生对象
Student s2 = new Student("张三", 23);
System.out.println(s1.getInfo());
System.out.println(s2.getInfo());
}
}
10.3 使用说明
- 当我们没有显式的声明类中的构造器时,系统会默认提供一个无参的构造器并且该构造器的修饰符默认与类的修饰符相同
- 当我们显式的定义类的构造器以后,系统就不再提供默认的无参的构造器了。
- 在类中,至少会存在一个构造器。
- 构造器是可以重载的。
10.4 练习
练习1:编写两个类,TriAngle和TriAngleTest,其中TriAngle类中声明私有的底边长base和高height,同时声明公共方法访问私有变量。此外,提供类必要的构造器。另一个类中使用这些公共方法,计算三角形的面积。
练习2:
(1)定义Student类,有4个属性: String name; int age; String school; String major;
(2)定义Student类的3个构造器:
- 第一个构造器Student(String n, int a)设置类的name和age属性;
- 第二个构造器Student(String n, int a, String s)设置类的name, age 和school属性;
- 第三个构造器Student(String n, int a, String s, String m)设置类的name, age ,school和major属性;
(3)在main方法中分别调用不同的构造器创建的对象,并输出其属性值。
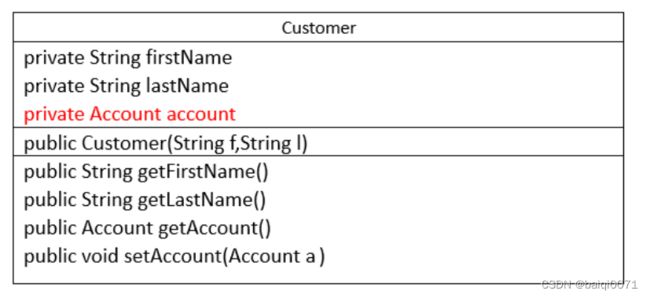
练习3:
- 写一个名为Account的类模拟账户。该类的属性和方法如下图所示。
该类包括的属性:账号id,余额balance,年利率annualInterestRate;
包含的方法:访问器方法(getter和setter方法),取款方法withdraw(),存款方法deposit()。
提示:在提款方法withdraw中,需要判断用户余额是否能够满足提款数额的要求,如果不能,应给出提示。
- 创建Customer类。
a. 声明三个私有对象属性:firstName、lastName和account。 b. 声明一个公有构造器,这个构造器带有两个代表对象属性的参数(f和l) c. 声明两个公有存取器来访问该对象属性,方法getFirstName和 getLastName返回相应的属性。 d. 声明setAccount 方法来对account属性赋值。 e. 声明getAccount 方法以获取account属性。
- 写一个测试程序。
(1)创建一个Customer ,名字叫 Jane Smith, 他有一个账号为1000,余额为2000元,年利率为 1.23% 的账户。
(2)对Jane Smith操作。 存入 100 元,再取出960元。再取出2000元。 打印出Jane Smith 的基本信息
成功存入 :100.0
成功取出:960.0
余额不足,取款失败
Customer [Smith, Jane] has a account: id is 1000, annualInterestRate is 1.23%, balance is 1140.0
十一. 阶段性知识补充
11.1 类中属性赋值过程
- 在类的属性中,可以有哪些位置给属性赋值?
① 默认初始化
② 显式初始化
③ 构造器中初始化
④ 通过"对象.属性"或"对象.方法"的方式,给属性赋值
- 这些位置执行的先后顺序是怎样?
顺序:① - ② - ③ - ④
- 说明:
- 上述中的①、②、③在对象创建过程中,只执行一次。
- ④ 是在对象创建后执行的,可以根据需求多次执行。
11.2 JavaBean
-
JavaBean是一种Java语言写成的可重用组件。
- 好比你做了一个扳手,这个扳手会在很多地方被拿去用。这个扳手也提供多种功能(你可以拿这个扳手扳、锤、撬等等),而这个扳手就是一个组件。
-
所谓JavaBean,是指符合如下标准的Java类:
- 类是公共的
- 有一个无参的公共的构造器
- 有属性,且有对应的get、set方法
-
用户可以使用JavaBean将功能、处理、值、数据库访问和其他任何可以用Java代码创造的对象进行打包,并且其他的开发者可以通过内部的JSP页面、Servlet、其他JavaBean、applet程序或者应用来使用这些对象。用户可以认为JavaBean提供了一种随时随地的复制和粘贴的功能,而不用关心任何改变。
-
《Think in Java》中提到,JavaBean最初是为Java GUI的可视化编程实现的。你拖动IDE构建工具创建一个GUI 组件(如多选框),其实是工具给你创建Java类,并提供将类的属性暴露出来给你修改调整,将事件监听器暴露出来。
-
示例
public class JavaBean {
private String name; // 属性一般定义为private
private int age;
public JavaBean() {
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int a) {
age = a;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String n) {
name = n;
}
}
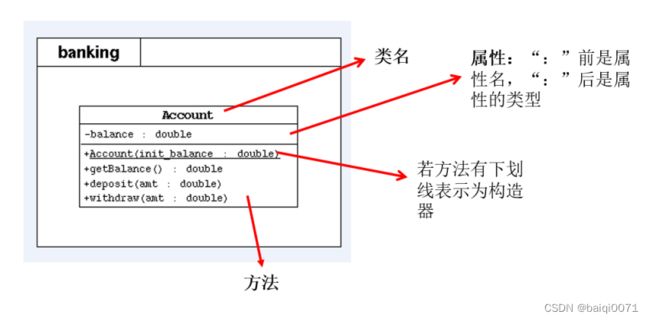
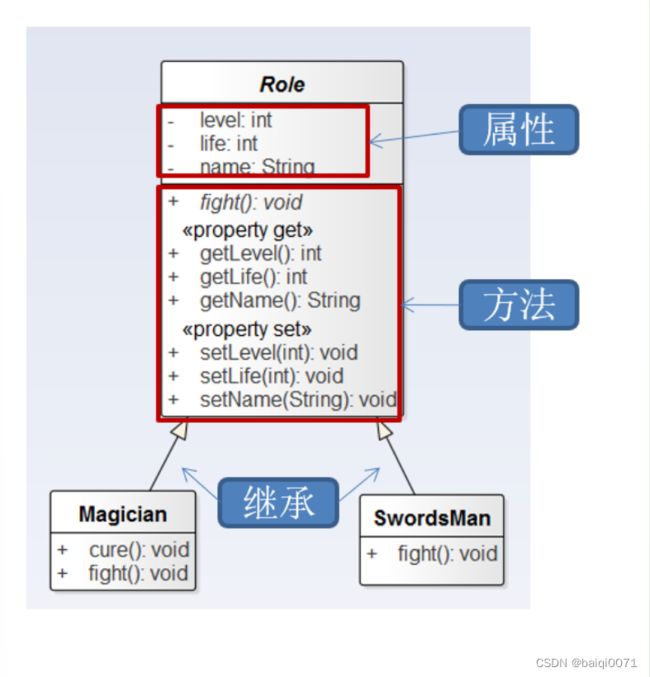
11.3 UML类图
- UML(Unified Modeling Language,统一建模语言),用来描述
软件模型和架构的图形化语言。 - 常用的UML工具软件有
PowerDesinger、Rose和Enterprise Architect。 - UML工具软件不仅可以绘制软件开发中所需的各种图表,还可以生成对应的源代码。
- 在软件开发中,使用
UML类图可以更加直观地描述类内部结构(类的属性和操作)以及类之间的关系(如关联、依赖、聚合等)。- +表示 public 类型, - 表示 private 类型,#表示protected类型
- 方法的写法: 方法的类型(+、-) 方法名(参数名: 参数类型):返回值类型
- 斜体表示抽象方法或类。
(来源:尚硅谷-宋红康)