76. 最小覆盖子串
题解:力扣
算法模版:
/* 滑动窗口算法框架 */
void slidingWindow(string s, string t) {
unordered_map need, window;
for (char c : t) need[c]++;
int left = 0, right = 0;
int valid = 0;
while (right < s.size()) {
// c 是将移入窗口的字符
char c = s[right];
// 右移窗口
right++;
// 进行窗口内数据的一系列更新
...
/*** debug 输出的位置 ***/
printf("window: [%d, %d)\n", left, right);
/********************/
// 判断左侧窗口是否要收缩
while (window needs shrink) {
// d 是将移出窗口的字符
char d = s[left];
// 左移窗口
left++;
// 进行窗口内数据的一系列更新
...
}
}
}
class Solution {
public:
string minWindow(string s, string t) {
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
// 判断是否可以开始窗口左边移动
int valid = 0;
std::unordered_map need, window;
// need表示的key:需要的字符,value:字符个数
// window:key:窗口内字符,value窗口内need中字符串个数
for(auto ite : t) {
++need[ite];
}
int start = 0;
int len = INT_MAX;
//[left, right)
while(right < s.size()) {
char c = s[right];
++right;
/*判断窗口字符增加*/
if(need.count(c) != 0) {
++window[c];
if(window[c] == need[c]) {
++valid;
}
}
// 移动窗口左边
while(valid == need.size()) {
// 判断是否小于len
if(right - left < len) {
start = left;
len = right - left;
}
// 窗口左边移动
char d = s[left];
++left;
if(need.count(d) != 0) {
if(window[d] == need[d]) {
--valid;
}
// 窗口内字符数量减少
--window[d];
}
}
}
return len == INT_MAX ? "":s.substr(start, len);
}
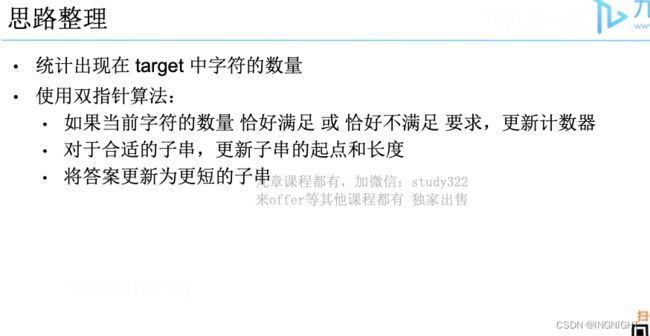
}; 滑动窗口算法的思路是这样:
1、我们在字符串 S 中使用双指针中的左右指针技巧,初始化 left = right = 0,把索引左闭右开区间 [left, right) 称为一个「窗口」。
2、我们先不断地增加 right 指针扩大窗口 [left, right),直到窗口中的字符串符合要求(包含了 T 中的所有字符)。
3、此时,我们停止增加 right,转而不断增加 left 指针缩小窗口 [left, right),直到窗口中的字符串不再符合要求(不包含 T 中的所有字符了)。同时,每次增加 left,我们都要更新一轮结果。
4、重复第 2 和第 3 步,直到 right 到达字符串 S 的尽头。
这个思路其实也不难,**第 2 步相当于在寻找一个「可行解」,然后第 3 步在优化这个「可行解」,最终找到最优解,**也就是最短的覆盖子串。左右指针轮流前进,窗口大小增增减减,窗口不断向右滑动,这就是「滑动窗口」这个名字的来历。
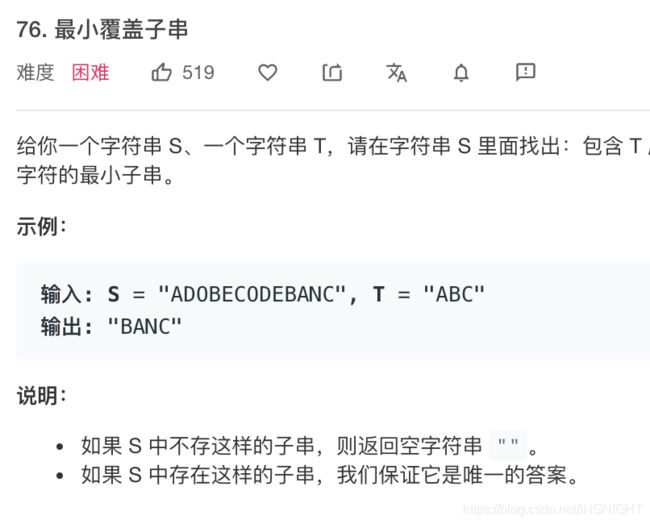
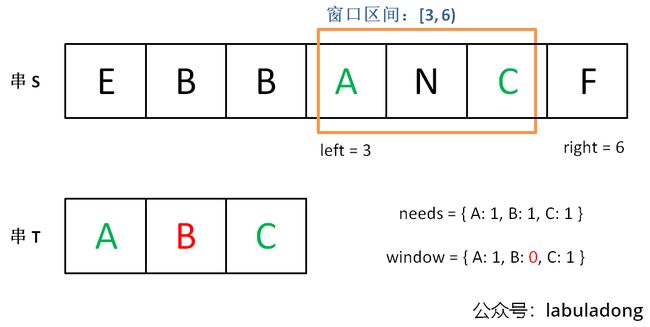
下面画图理解一下,needs 和 window 相当于计数器,分别记录 T 中字符出现次数和「窗口」中的相应字符的出现次数。
初始状态:
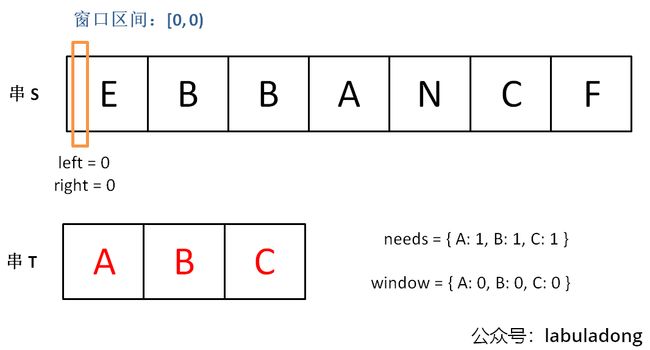
增加 right,直到窗口 [left, right] 包含了 T 中所有字符:
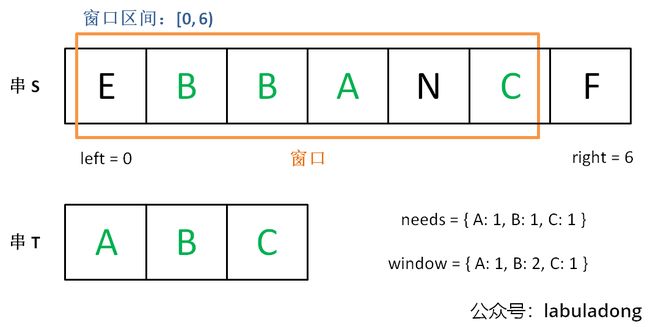
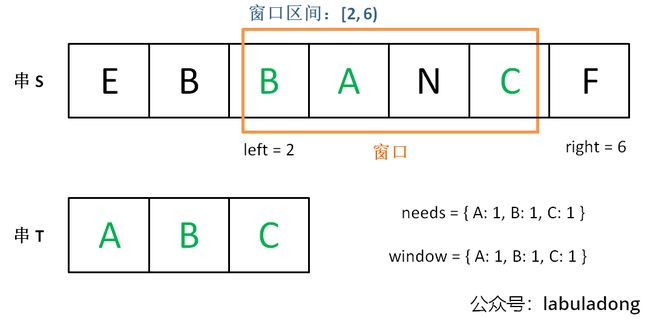
现在开始增加 left,缩小窗口 [left, right]。
直到窗口中的字符串不再符合要求,left 不再继续移动。
之后重复上述过程,先移动 right,再移动 left…… 直到 right 指针到达字符串 S 的末端,算法结束。
如果你能够理解上述过程,恭喜,你已经完全掌握了滑动窗口算法思想。现在我们来看看这个滑动窗口代码框架怎么用:
首先,初始化 window 和 need 两个哈希表,记录窗口中的字符和需要凑齐的字符:
unordered_map need, window;
for (char c : t) need[c]++;
然后,使用 left 和 right 变量初始化窗口的两端,不要忘了,区间 [left, right) 是左闭右开的,所以初始情况下窗口没有包含任何元素:
int left = 0, right = 0;
int valid = 0;
while (right < s.size()) {
// 开始滑动
}
其中 valid 变量表示窗口中满足 need 条件的字符个数,如果 valid 和 need.size 的大小相同,则说明窗口已满足条件,已经完全覆盖了串 T。
现在开始套模板,只需要思考以下四个问题:
1、当移动 right 扩大窗口,即加入字符时,应该更新哪些数据?
2、什么条件下,窗口应该暂停扩大,开始移动 left 缩小窗口?
3、当移动 left 缩小窗口,即移出字符时,应该更新哪些数据?
4、我们要的结果应该在扩大窗口时还是缩小窗口时进行更新?
如果一个字符进入窗口,应该增加 window 计数器;如果一个字符将移出窗口的时候,应该减少 window 计数器;当 valid 满足 need 时应该收缩窗口;应该在收缩窗口的时候更新最终结果。
需要注意的是,当我们发现某个字符在 window 的数量满足了 need 的需要,就要更新 valid,表示有一个字符已经满足要求。而且,你能发现,两次对窗口内数据的更新操作是完全对称的。
当 valid == need.size() 时,说明 T 中所有字符已经被覆盖,已经得到一个可行的覆盖子串,现在应该开始收缩窗口了,以便得到「最
class Solution {
public:
string minWindow(string s, string t) {
if (s.size() <= 0) {
return "";
}
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
// 统计目标字符串的信息
std::unordered_map t_table;
for_each(t.begin(), t.end(), [&t_table](auto ch) {
++t_table[ch];
});
std::unordered_map table;
std::string result;
// 判断窗口内字符是否满足答案
auto check = [&table, &t_table]() {
for (auto entry : t_table) {
if (table[entry.first] < entry.second) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
};
int result_l = 0;
int len = INT_MAX;
while (right < s.size()) {
// 非目标字符不需要存储
if (t_table.find(s[right]) != t_table.end()) {
++table[s[right]];
}
while (check() && left <= right) {
/*if (result.empty()
|| result.size() > right-left+1) {
result = s.substr(left, right-left+1);
}*/
// 更新结果
if (len > right-left+1) {
len = right-left+1;
result_l = left;
}
// 非目标字符串不需要删除
if (t_table.find(s[left]) != t_table.end()) {
--table[s[left]];
}
++left;
}
++right;
}
//cout << " left=" << left << " right=" << right << endl;
//return result;
return len == INT_MAX ? "" : s.substr(result_l, len);
}
}; 小覆盖子串」。
移动 left 收缩窗口时,窗口内的字符都是可行解,所以应该在收缩窗口的阶段进行最小覆盖子串的更新,以便从可行解中找到长度最短的最终结果。
class Solution {
public:
/**
* @param source: A string
* @param target: A string
* @return: A string denote the minimum window, return "" if there is no such a string
*/
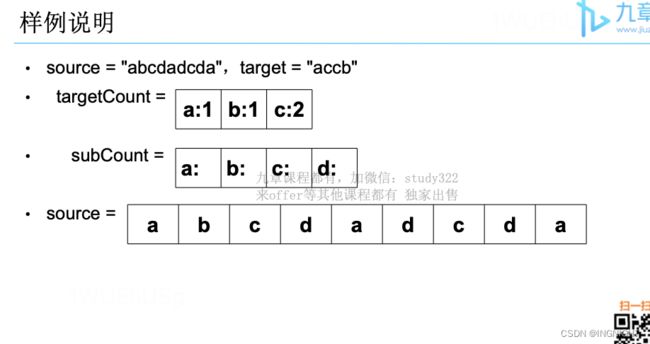
string minWindow(string &source, string &target) {
// write your code here
std::unordered_map original;
std::unordered_map table;
// 存储目标字符串字符数量
for_each(target.begin(), target.end(), [this, &original](char ch) {
this->incr_hash_value(original, ch);
});
int match_count = 0;
int len = source.size();
int result_len = INT_MAX;
int begin = 0;
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
// 判断是否能满足最小覆盖子串
while (j < len && match_count < original.size()) {
if (original.find(source[j]) != original.end()) {
incr_hash_value(table, source[j]);
// 记录满足字符的个数
if (table[source[j]] == original[source[j]]) {
++match_count;
}
}
// 右指针移动
++j;
}
// 满足匹配字符的数量达到
if (match_count == original.size()) {
// 打擂台
if (result_len > j-i) {
begin = i;
result_len = j-i;
}
}
// 坐窗口移动
if (table.find(source[i]) != table.end() && --table[source[i]] == original[source[i]] - 1) {
--match_count;
}
}
if (result_len == INT_MAX) {
return "";
}
return source.substr(begin, result_len);
}
private:
void incr_hash_value(std::unordered_map& hash_table, char ch) {
if (hash_table.find(ch) == hash_table.end()) {
hash_table[ch] = 0;
return;
}
++hash_table[ch];
}
}; class Solution {
public:
/**
* @param source: A string
* @param target: A string
* @return: A string denote the minimum window, return "" if there is no such a string
*/
string minWindow(string &source, string &target) {
// write your code here
if (source.size() <= 0) {
return "";
}
std::unordered_map table;
for (auto ch : target) {
++table[ch];
}
std::unordered_map count;
int start = -1;
int len = INT_MAX;
int j = 0;
int match_count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < source.size(); ++i) {
while (j < source.size() && match_count < table.size()) {
if (table.find(source[j]) != table.end()) {
++count[source[j]];
if (count[source[j]] == table[source[j]]) {
++match_count;
}
}
++j;
}
if (match_count == table.size()) {
if (start == -1 || len > j - i) {
start = i;
len = j - i;
}
}
--count[source[i]];
if (table.find(source[i]) != table.end()
&& count[source[i]] == table[source[i]]-1) {
--match_count;
}
if (count[source[i]] == 0) {
count.erase(source[i]);
}
}
if (start == -1) {
return "";
}
return source.substr(start, len);
}
}; class Solution {
public:
/**
* @param source: A string
* @param target: A string
* @return: A string denote the minimum window, return "" if there is no such a string
*/
string minWindow(string &source, string &target) {
// write your code here
if (source.size() <= 0) {
return "";
}
std::unordered_map ori;
for (auto ch : target) {
++ori[ch];
}
std::unordered_map table;
int j = 0;
int match_count = 0;
int result = INT_MAX;
int begin = 0;
int len = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < source.size(); ++i) {
while (j < source.size() && match_count < ori.size()) {
if (ori.find(source[j]) != ori.end()) {
auto ite = table.find(source[j]);
if (ite == table.end()) {
table[source[j]] = 1;
} else {
++table[source[j]];
}
if (table[source[j]] == ori[source[j]]) {
++match_count;
}
}
++j;
}
if (match_count == ori.size()) {
if (j-i < result) {
result = j-i;
begin = i;
len = j-i;
}
}
if (ori.find(source[i]) != ori.end()) {
if (table.find(source[i]) != table.end()) {
if (--table[source[i]] == ori[source[i]] - 1) {
--match_count;
}
if (table[source[i]] == 0) {
table.erase(source[i]);
}
}
}
}
return source.substr(begin, len);
}
};