【数据结构】详细解读 Splay Tree(附完整代码)
详细解读 Splay Tree(伸展树)
昨天在研究决策树时遇到了一种特殊的搜索平衡二叉树Splay,很感兴趣,今天下午就深入了解了一下这种树。
前部分代码参考了书,后部分为原创,可能有误,敬请批评指正!
文章目录
- 详细解读 Splay Tree(伸展树)
- Splay树的介绍
- 旋转(Rotate)
-
- 旋转方式
-
-
- 名词介绍:
- 第一种:ZIG / ZAG
- 第二种:ZIG-ZIG / ZAG-ZAG
- 第三种:ZIG-ZAG / ZAG-ZIG
-
- Splay树的伸展特性
-
- 代码
- 前部分代码参考了书,后部分代码根据自己的理解编写,可能有误,谨慎使用,敬请批评指正!
- 完整代码
- 总结
Splay树的介绍
Splay树为BST(Binary Search Tree二叉搜索树)的一种,只要是Treap、AVL、红黑树能做的,Splay树都能做。其插入、查找、删除等等操作都是 O ( l o g 2 n ) O(log_2n) O(log2n)。
Splay树与其他BST不同的是,它具有把某个结点向上旋转至某位置的能力,包括旋转至根节点(这种方式我们称之为Splay)。
在查询系统中,如果经常查询某个结点,就可以通过Splay操作给它转到根结点上,这样一来下一次查这个结点就省事多了。
旋转(Rotate)
Splay树能在保持伸展树有序的情况下,把x移动到root(根节点)的位置。而这一操作依靠旋转(Rotate)进行,对应函数为Splay(x, root)。
针对不同位置的x,Splay树有不同的旋转方式。
旋转方式
名词介绍:
ZIG:右旋
ZAG:左旋
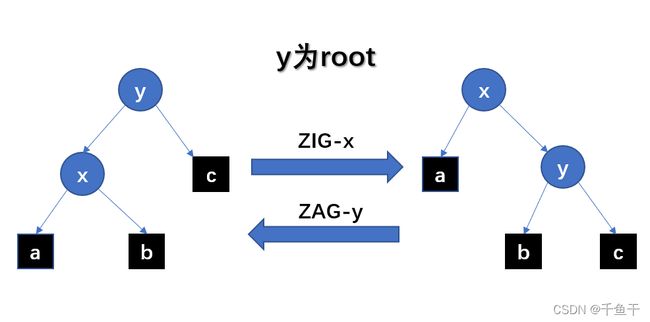
第一种:ZIG / ZAG
若结点x的父结点y是根节点。此时只需要将x右旋即可。同样的,若结点y的父结点x是根节点。此时只需要将y左旋即可。
以左图->右图的操作为例:
1.将x的右子树挂在y的左子树上;
2.将x右旋,时x变为根节点。
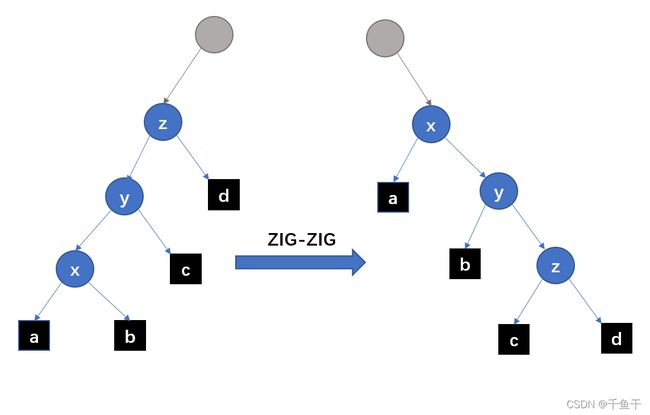
第二种:ZIG-ZIG / ZAG-ZAG
x的父结点y不是根节点,y的父结点为z,且x与y同时是各自父结点的左孩子或者同时是各自父结点的右孩子。此时进行一次ZIG-ZIG或ZAG-ZAG操作。
注意:此时z结点不一定是根结点。
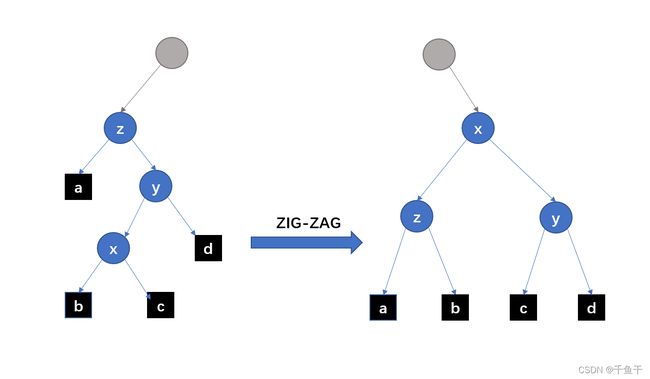
第三种:ZIG-ZAG / ZAG-ZIG
x的父结点y不是根节点,y的父结点为z,x与y中一个是其父结点的左孩子而另一个是其父结点的右孩子。此时进行一次Zig-Zag操作或者Zag-Zig操作。
以下图为例:
1.将z的右子树(以y为子树根结点)右旋,使x挂在原来y的位置上,此时y的左子树空缺,把x的右子树挂在y的左子树上;
2.将以z为根结点的子树左旋,使x挂在原来z的位置上,此时z的右子树空缺,把x的左子树挂在z的右子树即可。
注意:此时z结点不一定是根结点。
Splay树的伸展特性
Splay树的旋转能力会避免让BST成链表。
相对于Treap树的单旋,Splay树的双旋针对子结点、父结点、父结点的父结点在同一方向时会让树更加平衡。
比如在下图中,若结点通过两次单旋操作,把左图变成右图: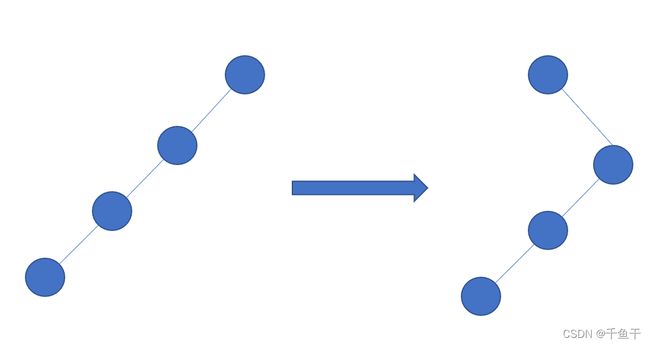
此时树的深度未改变,因此复杂度未变。
而通过双旋,此时左图变成右图的样子:
此时树的深度减小,树变得平衡,复杂度降低。
代码
了解了Splay树的基本原理后,我们将Splay树来实现进行各种操作,包括建树、插入、查找、删除等等,详细解释见我代码的注释。
注意:凡涉及查找结点操作的,都需要将被查找结点旋转至根结点。
前部分代码参考了书,后部分代码根据自己的理解编写,可能有误,谨慎使用,敬请批评指正!
完整代码
#include 总结
Splay树是一种结构简单、操作灵活的树(此处省略1000字)。。。
凌晨0点10分了,不能再说了,我要睡觉了,拜拜!