0127-2-Vue深入学习5—Vue-Router路由模式
1、Vue-Router三种路由模式:
hash:#️⃣使用URL hash 值来做路由,支持所有路由器;history:依赖HTML5 History API和服务器配置;abstract:⛓支持所有JS运行环境,Node.js服务端;
1.1、路由作用:根据不同的路径,来映射到不同的视图;
1.2、路由基本使用:
<div id="app">
<h1>Hello kuishou!h1>
<p>
<router-link to="/foo"> 睡觉 Foorouter-link>
<router-link to="/bar"> 敲代码 barrouter-link>
p>
<router-view>router-view>
div>
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
// 注册路由
Vue.use(VuerRouter)
// 1.定义组件
const Foo = { template: 'foo' }
const Bar = { template: 'bar' }
// 2.定义路由
const routes = [
{ path: '/foo', components: Foo },
{ path: '/bar', components: Bar },
]
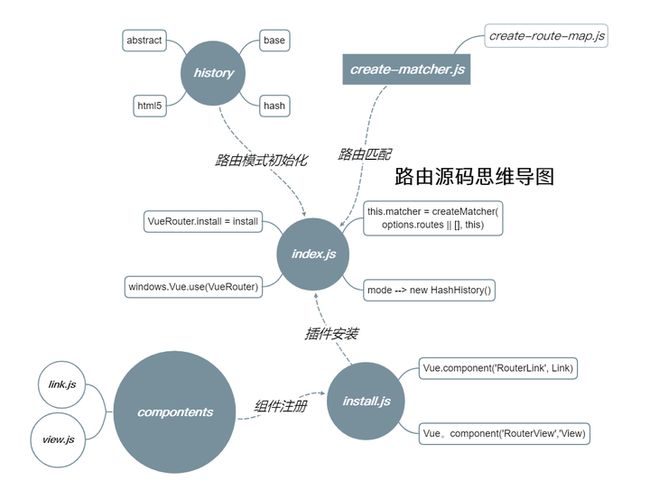
2、路由注册:
2.1、Vue插件的注册原理: 每个插件都需要实现一个静态的
install方法,当我们执行Vue.use的时候,就会执行这个install方法,并且在这个install方法中第一个参数拿到Vue对象。
3、路由安装:
Vue-Router 安装最重要的一步就是利用
Vue.mixin去把beforeCreate和destroyed两个钩子函数注入到每一个组件中,在beforeCreateed 中定义 私有属性和初始化 路由。
// install.js
// 把 _Vue export 出去,在源码的任何地方都可以访问 Vue
export let _Vue
export function install (Vue) {
// 判断是否有注册指令,如果多次执行install方法,则会return
if (install.installed && _Vue === Vue) return
install.installed = true
// 使用下划线 _Vue 保留 传过来的Vue
_Vue = Vue
const isDef = v => v !== undefined
const registerInstance = (vm, callVal) => {
let i = vm.$options._parentVnode
if (isDef(i) && isDef(i = i.data) && isDef(i = i.registerRouteInstance)) {
i(vm, callVal)
}
}
// mixin 作用:把mergeOptions 扩展到全局的 options
Vue.mixin({
// 这样的话,每一个组件都有beforeCreate、destroyed这两个钩子函数
beforeCreate () {
if (isDef(this.$options.router)) {
this._routerRoot = this
this._router = this.$options.router
this._router.init(this)
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current)
} else {
this._routerRoot = (this.$parent && this.$parent._routerRoot) || this
}
registerInstance(this, this)
},
destroyed () {
registerInstance(this)
}
})
3、VueRouter对象:
当我们执行
new VueRouter时,beforeCreated钩子函数会执行router.init方法,
constructor (options: RouterOptions = {}) {
this.app = null // 根 Vue 实例
this.apps = [] // 保存所有子组件的 Vue 实例
this.options = options // 保存传入的路由配置
this.beforeHooks = [] // 钩子函数
this.resolveHooks = [] // 钩子函数
this.afterHooks = [] // 钩子函数
// 路由匹配器
this.matcher = createMatcher(options.routes || [], this)
// 路由创建的三种模式: hash、history、abstract
let mode = options.mode || 'hash'
// 路由创建失败的回调函数,检测浏览器中有没有历史记录(history)
this.fallback =
mode === 'history' && !supportsPushState && options.fallback !== false
// 路由历史的具体的实现实例, 如果没有则会使用hsah访问
if (this.fallback) {
mode = 'hash'
}
if (!inBrowser) {
mode = 'abstract'
}
this.mode = mode
switch (mode) {
case 'history':
this.history = new HTML5History(this, options.base)
break
case 'hash':
this.history = new HashHistory(this, options.base, this.fallback)
break
case 'abstract':
this.history = new AbstractHistory(this, options.base)
break
default:
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(false, `invalid mode: ${mode}`)
}
}
}
4、Matcher
路由匹配器,主要通过
matcher和match方法 ,匹配路径Router的.
- 4.1、
createRouteMap函数是把用户的 路由配置 转换成一张 路由映射表,
export function createRouteMap (
routes: Array<RouteConfig>,
oldPathList?: Array<string>, // 可选参数
oldPathMap?: Dictionary<RouteRecord>, // 可选参数
oldNameMap?: Dictionary<RouteRecord>, // 可选参数
parentRoute?: RouteRecord
): {
pathList: Array<string>,
pathMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord>,
nameMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord>
} {
// 路径列表用于控制路径匹配优先级
const pathList: Array<string> = oldPathList || []
// $flow-disable-line
const pathMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord> = oldPathMap || Object.create(null)
// $flow-disable-line
const nameMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord> = oldNameMap || Object.create(null)
// 对路由数组进行遍历
routes.forEach(route => {
// 遍历成功·拿到每个路由对象
addRouteRecord(pathList, pathMap, nameMap, route, parentRoute)
})
- 4.1、createMatcher的初始化逻辑
createMatcher首先执行的逻辑是 ````const { pathList, pathMap, nameMap } = createRouteMap(routes) ```用来创建一个映射表。
// 对路由数组进行遍历
routes.forEach(route => {
// 遍历成功·拿到每个路由对象
addRouteRecord(pathList, pathMap, nameMap, route, parentRoute)
})
- 4.3、match 的匹配过程
**
match方法作用:**根据传入的raw和当前的路径currentRoute计算一个新的路径并返回。
match方法接收3个参数:raw(Location 对象)、currentRoute(当前的路径)、redirectedFrom(与重定向相关)
function match (
raw: RawLocation, // url 字符串,也可以是⼀个 Location 对象
currentRoute?: Route, // Router 类型,表示当前的路径
redirectedFrom?: Location // 与重定向相关
): Route {
// 根据 raw , current 计算出新的 location
const location = normalizeLocation(raw, currentRoute, false, router)
const { name } = location
// 如果current传入属性有name
if (name) {
// 根据nameMap 匹配到 record
const record = nameMap[name]
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(record, `Route with name '${name}' does not exist`)
}
// 如果 record 不存在,则匹配失败!
if (!record) return _createRoute(null, location)
const paramNames = record.regex.keys
.filter(key => !key.optional)
.map(key => key.name)
if (typeof location.params !== 'object') {
location.params = {}
}
if (currentRoute && typeof currentRoute.params === 'object') {
for (const key in currentRoute.params) {
if (!(key in location.params) && paramNames.indexOf(key) > -1) {
location.params[key] = currentRoute.params[key]
}
}
}
location.path = fillParams(record.path, location.params, `named route "${name}"`)
return _createRoute(record, location, redirectedFrom)
} else if (location.path) {
location.params = {}
for (let i = 0; i < pathList.length; i++) {
const path = pathList[i]
const record = pathMap[path]
if (matchRoute(record.regex, location.path, location.params)) {
return _createRoute(record, location, redirectedFrom)
}
}
}
// no match
return _createRoute(null, location)
}
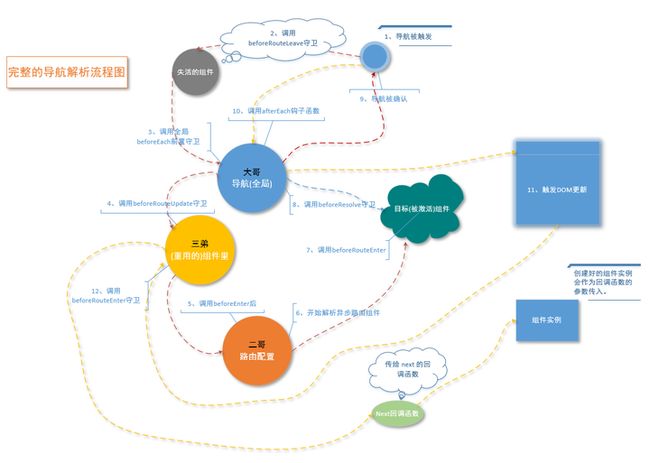
5、路径切换
发生路径切换的时候,执行的一系列钩子函数。
-
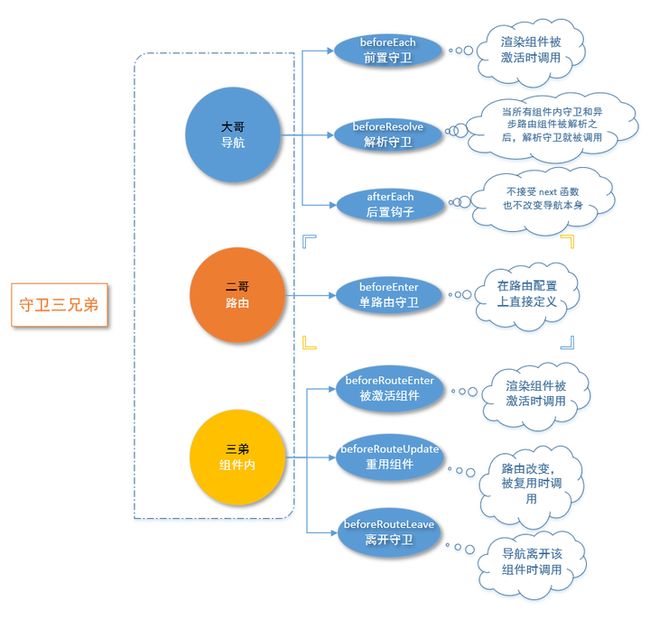
5.1、导航守卫的执行流程:
Vue项目中,导航被触发后,失活的组件(叛变的人)开始调用
beforeRouteLeave,全局守卫(大哥)beforeEach、组件内的守卫(三弟)重用组件beforeRouterUpdate被逐步触发;路由守卫(二哥)在路由配置里调用beforeEnter后开始解析异步路由组件;在被激活的目标组件(敌人)里调用beforeRouteEnter;全局守卫(大哥)beforeResolve检测到目标组件(敌人)被激活(打败),在router.js中查找到需要跳转的导航并被确认,afterEach钩子被调用,最终触发DOM更新;路由守卫(二哥)调用beforeRouteEnter传给next的回调函数。
// 全局守卫
router.beforeEach((to, from, next)=>{
// 进入路由前首先检查是否登录,如果没有则跳转到登录的视图组件
if(to.name != 'Login' && !isAuthenticated) next({
name: 'Login'
// 否则继续下一个脚本
}) else {
next()
}
})
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/60da87d4ec92
官方文档:Vue-Router
守卫识别路由的三把钥匙:
to : 即将进入的路由
from : 即将离开的路由
next : 进行管道中的下一个钩子
面试题:给路由组件传递数据有哪几种方式?
1、通过
params传递
// params 不能与 path 一起使用
router.push({ path: './details', parmas: { id: '001'} }) // ->跳转到details
2、通过
query传递
this.$router.push({ path: '/details/001', query: { kind: "car" }})
3、通过
hash传递
this.$touter.push({ path: './details001', hash: '#car'})
…
-
5.2、URL变化的逻辑
-
5.3、组件渲染的逻辑