spring MethodInvokingFactoryBean 的使用和了解,Spring 通过通过方法创建Bean的实例
spring MethodInvokingFactoryBean 的使用和了解
作用
- 让某个实例的某个方法的返回值注入为Bean的实例
- 让某个类的静态方法的返回值注入为Bean的实例
使用MethodInvokingFactoryBean
- 使用IDEA Maven项目非常方便的下载源码查看其类的说明信息,在这里非常方便的可以查看到这个方法的一些使用的说明
- 小测试一下子,简单的就跟着这个使用的作用的两个方法进行使用一下吧
资源不如下面创建一个:spring-methodInvoking.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="sysProps" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.MethodInvokingFactoryBean">
<property name="targetClass" value="java.lang.System"/>
<property name="targetMethod" value="getProperties"/>
bean>
<bean id="javaVersion" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.MethodInvokingFactoryBean">
<property name="targetObject" ref="sysProps"/>
<property name="targetMethod" value="getProperty"/>
<property name="arguments" value="java.version"/>
bean>
beans>下面是System中的静态方法的返回值Properties包含配置的属性的文件的信息,相当于调用静态方法
然后在调用生成的Properties这个Bean的实例的方法的某个属性
public static Properties getProperties() {
SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPropertiesAccess();
}
return props;
}
测试
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.AbstractJUnit4SpringContextTests;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* descrption:
* authohr: wangji
* date: 2017-08-24 13:35
*/
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations={
"classpath:spring-methodInvoking.xml"})
public class MethodTest extends AbstractJUnit4SpringContextTests{
@Resource(name = "sysProps")
public Properties properties;
@Resource(name ="javaVersion")
public String javaVersion;
@Test
public void test(){
log.info(properties.toString());
log.info(javaVersion.toString());
}
}
//2017-08-24 14:03:26,142 INFO [MethodTest.java:31] : {java.runtime.name=Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment,
// sun.boot.library.path=D:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_101\jre\bin, java.vm.version=25.101-b13,
//........
// java.library.path=D:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_101\bin;
// C:\Windows\Sun\Java\bin;C:\Windows\system32;
// C:\Windows;D:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_101\bin;
//2017-08-24 14:03:26,145 INFO [MethodTest.java:32] : 1.8.0_101测试总结
测试结果如同我们想象的一样,可以将某个方法或者某个具体的类的静态方法进行调用
因为我们总会调用这个方法,相当于初始化方法呗,对于返回值,你可以随便返回一个Boolean 这个就将这个Boolean的值注入到了
spring的容器中去了,不过这个不是最好的手段,你可以继承InitializingBean,或者使用注解@PostConstruct,在初始化Bean之前调用这个方法
但是有些时候不想初始化某个Bean你还是可以这么干的。
会使用开发中很重要,知其所以然也是很重要(了解这个背后实现的故事)
刚刚上面说了MethodInvokingFactoryBean将调用方法的返回值注入为Bean,我不注入可以?
可以的,其实就是调用刚刚那个类的父类MethodInvokingBean,调用某个静态的方法,调用某个类的实例的方法都可以
最后将MethodInvokingBean注入为Bean其实原理是差不多的。
id="testBean" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.MethodInvokingBean">
<property name="staticMethod" value="com.common.utils.test.MethodInvokingBeanTest.test">property>
package com.common.utils.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* descrption:测试调用静态方法不注入Bean
* authohr: wangji
* date: 2017-08-24 14:20
*/
@Slf4j
public class MethodInvokingBeanTest {
public static void test(){
log.info("调用了这个方法");
}
} @Resource(name = "testBean")
public MethodInvokingBean methodInvokingBean;
@Test
public void testMethod(){
log.info(methodInvokingBean.getTargetMethod());
}
// 2017-08-24 14:25:52,229 INFO [MethodInvokingBeanTest.java:15] : 调用了这个方法
// 2017-08-24 14:25:52,243 INFO [MethodTest.java:34] : test
继续看MethodInvokingBean的实现的原理
MethodInvokingBean实现了InitializingBean方法,Bean在初始化的时候会首先调用这个接口的实现,然后在初始化Bean
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
prepare();
invokeWithTargetException();
}调用父类MethodInvoker的prepare方法,进行校验传递的参数是否正确,因为有两种不同的搭配,静态和实例方法
- MethodInvoker的成员变量可以看出来
private Class targetClass;//目标Class
private Object targetObject;//目标Object
private String targetMethod;//实例的方法
private String staticMethod;//静态的方法
private Object[] arguments = new Object[0];
/** The method we will call */
private Method methodObject; //需要调用的方法- 准备函数(校验和设置调用的methObject,然后通过反射调用方法,无论是静态还是非静态的函数,静态的method.invoke(null, 参数),第一个传递为NULL
public void prepare() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
if (this.staticMethod != null) {
int lastDotIndex = this.staticMethod.lastIndexOf('.');
if (lastDotIndex == -1 || lastDotIndex == this.staticMethod.length()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(“必须使用全限定名")
}
String className = this.staticMethod.substring(0, lastDotIndex);
String methodName = this.staticMethod.substring(lastDotIndex + 1);
this.targetClass = resolveClassName(className);//反射找到类型
this.targetMethod = methodName;//要调用的方法的名称
}
Class targetClass = getTargetClass();
String targetMethod = getTargetMethod();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Either 'targetClass' or 'targetObject' is required");
}
if (targetMethod == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'targetMethod' is required");
}
Object[] arguments = getArguments();
Class[] argTypes = new Class[arguments.length];//根据传递的参数找到,参数的类型
for (int i = 0; i < arguments.length; ++i) {
argTypes[i] = (arguments[i] != null ? arguments[i].getClass() : Object.class);
}
// Try to get the exact method first.
try {
this.methodObject = targetClass.getMethod(targetMethod, argTypes);
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
// Just rethrow exception if we can't get any match.
this.methodObject = findMatchingMethod();//可能位置不对,没有找到方法
if (this.methodObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
}
- invokeWithTargetException();函数还是一样的,调用MethodInvoker的invoke函数,获取之前得到的需要反射的方法,这里会有静态和实例方法的区别,静态的targetObject为空
public Object invoke() throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
// In the static case, target will simply be {@code null}.
Object targetObject = getTargetObject();
Method preparedMethod = getPreparedMethod();
if (targetObject == null && !Modifier.isStatic(preparedMethod.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not be non-static without a target");
}
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(preparedMethod);
return preparedMethod.invoke(targetObject, getArguments());
}- 设置方法反射的可调用性,看类是不是私有的,方法是不是私有的,方法的访问性等等等!可以通过Modifier进行判断
/**
* Make the given method accessible, explicitly setting it accessible if
* necessary. The {@code setAccessible(true)} method is only called
* when actually necessary, to avoid unnecessary conflicts with a JVM
* SecurityManager (if active).
* @param method the method to make accessible
* @see java.lang.reflect.Method#setAccessible
*/
public static void makeAccessible(Method method) {
if ((!Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers()) ||
!Modifier.isPublic(method.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers()))
&& !method.isAccessible()) {
method.setAccessible(true);
}
}- 调用完了,没有对于返回的返回值进行处理,这样就完了!MethodInvokingBean,这个也是他的子类MethodInvokingFactoryBean的区别,MethodInvokingFactoryBean将会把返回的值注入为Bean的对象
- MethodInvokingBean将自己注册为Bean啦,他的子类MethodInvokingFactoryBean也将注册为Bean的实例,但是实际通过getBean调用的时候会将MethodInvokingFactoryBean.getObject作为结果返回给调用的对象,这个查看源码的时候会很清楚。
MethodInvokingFactoryBean的实现的原理
- 继承了之前的MethodInvokingBean,处理逻辑还是类似的,只是增加了一些判断,还有实现了一个接口FactoryBean(当前工厂是一个Bean的实例)FactoryBean这个接口很神奇,当实现了这个接口的时候,不会将当前的实例注册为Bean,而是注册getObject这个函数的返回值注册为SpringIO中的Bean具体的为什么稍后在说。
public interface FactoryBean<T> {
/**
* Return an instance (possibly shared or independent) of the object
* managed by this factory.
* As with a {@link BeanFactory}, this allows support for both the
* Singleton and Prototype design pattern.
*
If this FactoryBean is not fully initialized yet at the time of
* the call (for example because it is involved in a circular reference),
* throw a corresponding {@link FactoryBeanNotInitializedException}.
*
As of Spring 2.0, FactoryBeans are allowed to return {@code null}
* objects. The factory will consider this as normal value to be used; it
* will not throw a FactoryBeanNotInitializedException in this case anymore.
* FactoryBean implementations are encouraged to throw
* FactoryBeanNotInitializedException themselves now, as appropriate.
* @return an instance of the bean (can be {@code null})
* @throws Exception in case of creation errors
* @see FactoryBeanNotInitializedException
*/
T getObject() throws Exception;
Class getObjectType();
boolean isSingleton();
}- 覆盖了父类MethodInvokingBean的初始化方法afterPropertiesSet
- MethodInvokingFactoryBean 成员变量信息
private boolean singleton = true;
private boolean initialized = false;
/** Method call result in the singleton case */
private Object singletonObject;
- 覆盖后的afterPropertiesSet方法(创建Bean之前会调用)
添加了是不是单例的判断,将反射调用的返回值保存了下来
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
prepare();//MethodInvoker准备函数
if (this.singleton) {
this.initialized = true;
this.singletonObject = invokeWithTargetException();//函数调用方法的返回值保存下来
}
}- 完整的方法(现在的问题就是为啥继承了FactoryBean,我们通过getBean调用的时候会将getObject的返回值注入Spring Bean,而不是返回当前的FactoryBean的实例)
public class MethodInvokingFactoryBean extends MethodInvokingBean implements FactoryBean<Object> {
private boolean singleton = true;
private boolean initialized = false;
private Object singletonObject;
public void setSingleton(boolean singleton) {
this.singleton = singleton;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
prepare();
if (this.singleton) {
this.initialized = true;
this.singletonObject = invokeWithTargetException();
}
}
/**
* Returns the same value each time if the singleton property is set
* to "true", otherwise returns the value returned from invoking the
* specified method on the fly.
*/
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
//获取那个返回值,也就是当前由于继承了FactoryBean接口,获取到的Bean将是反射方法的返回的结果
if (this.singleton) {
if (!this.initialized) {
throw new FactoryBeanNotInitializedException();
}
// Singleton: return shared object.
return this.singletonObject;
}
else {
// Prototype: new object on each call.
return invokeWithTargetException();
}
}
/**
* Return the type of object that this FactoryBean creates,
* or {@code null} if not known in advance.
*/
@Override
public Class getObjectType() {//Bean实例的类型,就是反射调用返回值的类型
if (!isPrepared()) {
// Not fully initialized yet -> return null to indicate "not known yet".
return null;
}
return getPreparedMethod().getReturnType();
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return this.singleton;
}
}FactoryBean
简单的聊聊
- 由spring的bean容器管理的并且实现了FactoryBean接口的类实例本身也是一个Spring IOC中的一个Bean,通过spring的bean容器的getBean()方法获得bean实例时,实际上获得的是这个FactoryBean生产出来的实例对像(也就是getObject返回的对象),而非这个FactoryBean实例的本身。
- 但在getBean()指定的beanName前加上”&”符号就获得了这个FactoryBean的实例的本身,在spring框架中就有很多地方使用了FactoryBean。例如 org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean等.框架中有很多的类似的实现
- BeanFactory: 以Factory结尾,表示它是一个工厂类,是用于管理Bean的一个工厂
- FactoryBean:以Bean结尾,表示它是一个Bean,不同于普通Bean的是,它是实现了FactoryBean< T>接口的Bean,根据该Bean的Id从BeanFactory中获取的实际上是FactoryBean的getObject()返回的对象,而不是FactoryBean本身, 如果要获取FactoryBean对象,可以在id前面加一个&符号来获取。
- 一般情况下,Spring通过反射机制利用bean的class属性指定实现类来实例化bean 。在某些情况下,实例化bean过程比较复杂,如果按照传统的方式,则需要在bean中提供大量的配置信息,配置方式的灵活性是受限的,这时采用编码的方式可能会得到一个简单的方案。Spring为此提供了一个org.Springframework.bean.factory.FactoryBean的工厂类接口,用户可以通过实现该接口定制实例化bean的逻辑。
http://www.cnblogs.com/davidwang456/p/3688250.html/ FacroryBean的使用
看看怎么对于特殊的FacoryBean< T> 获取Bean呢?特殊的Bean哦!
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/u013185616/article/details/52335864/ FactoryBean的实现原理与作用
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}doGetBean中会调用bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
protected Object getObjectForBeanInstance(Object beanInstance, String name, String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
//如果是对FactoryBean的解引用(&继承FactoryBean,找真实的FactoryBean),
//但bean对象不是FactoryBean,抛出异常
if (BeanFactoryUtils.isFactoryDereference(name) && !(beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean)) {
throw new BeanIsNotAFactoryException(transformedBeanName(name), beanInstance.getClass());
}
//如果Bean实例不是FactoryBean,或者指定名称是FactoryBean的解引用,
//也就是普通的bean调用,则直接返回当前的Bean实例
if (!(beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean) || BeanFactoryUtils.isFactoryDereference(name)) {
return beanInstance;
}
//处理对FactoryBean的调用
Object object = null;
if (mbd == null) {
//从FactoryBean缓存中获取给定名称的实例对象
object = getCachedObjectForFactoryBean(beanName);
}
if (object == null) {
// Return bean instance from factory.
FactoryBean factory = (FactoryBean) beanInstance;
//如果从FacroryBean生产的Bean是单态模式的,则缓存
if (mbd == null && containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
boolean synthetic = (mbd != null && mbd.isSynthetic());
//调用FactoryBeanRegistrySupport(FactoryBean缓存仓库支持类)
//的getObjectFromFactoryBean方法,实现FactoryBean生产Bean对象实例的过程
object = getObjectFromFactoryBean(factory, beanName, !synthetic);
}
return object;
} - 获取Bean的逻辑
Object object = this.factoryBeanObjectCache.get(beanName);//缓存仓库中存在?
object = doGetObjectFromFactoryBean(factory, beanName);//不存在价值从FactoryBean的实例中加载- 全部代码
protected Object getObjectFromFactoryBean(FactoryBean factory, String beanName, boolean shouldPostProcess) {
if (factory.isSingleton() && containsSingleton(beanName)) {
synchronized (getSingletonMutex()) {
Object object = this.factoryBeanObjectCache.get(beanName);
if (object == null) {
object = doGetObjectFromFactoryBean(factory, beanName);
Object alreadyThere = this.factoryBeanObjectCache.get(beanName);
if (alreadyThere != null) {
object = alreadyThere;
}
else {
if (object != null && shouldPostProcess) {
try {
object = postProcessObjectFromFactoryBean(object, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
//...
}
}
this.factoryBeanObjectCache.put(beanName, (object != null ? object : NULL_OBJECT));
}
}
return (object != NULL_OBJECT ? object : null);
}
}
else {
Object object = doGetObjectFromFactoryBean(factory, beanName);
if (object != null && shouldPostProcess) {
try {
object = postProcessObjectFromFactoryBean(object, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
//.....
}
}
return object;
}
}- doGetObjectFromFactoryBean,从FactoryBean的实例中获取getObject
private Object doGetObjectFromFactoryBean(final FactoryBean factory, final String beanName)
throws BeanCreationException {
//......
object = factory.getObject();
return object;
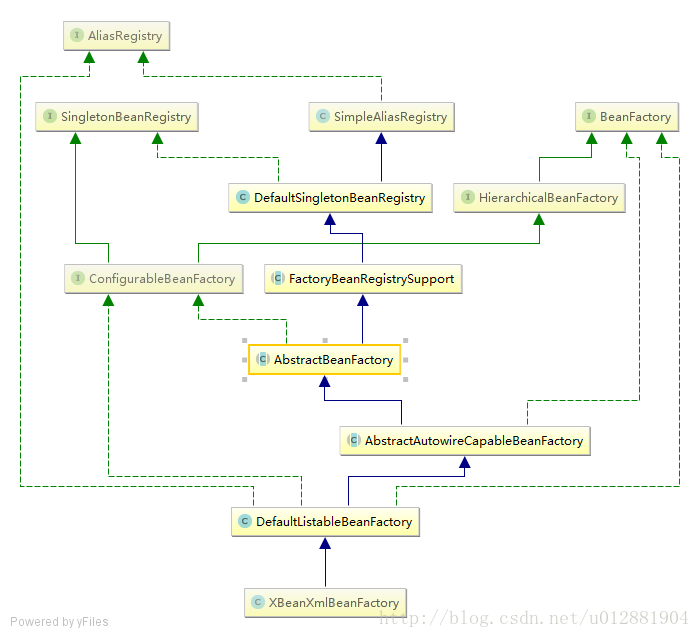
}- 这样的实现类很多,FactoryBean看图
总结
今天对于FactoryBean的原理进行了了解,也对于MethodInvokingFactoryBean的使用进行了了解,可以非常方便的将某个方法的返回值弄成Bean的实例
多看看,多总结,提升就在不经意之间, 或许还有很多不懂的地方,请多多指教,毕竟Spring的代码太大,我们只能慢慢的看,慢慢的了解。
类似这样MethodInvokingFactoryBean实例化类比较复杂的使用这个应该还是比较的简单吧!