indexedDB介绍
indexedDB介绍
原生介绍
indexedDB是一个前端数据持久化解决方案(即前端缓存),由浏览器实现。
0. 兼容性

1.特点
-
基于文件存储。意味着其容量可达到硬盘可用空间上限
-
非关系型数据库。意味着扩展或收缩字段一般无须修改数据库和表结构(除非新增字段用做索引)
-
键值对存储。意味着存取无须字符串转换过程
-
存储类型丰富。意味着浏览器缓存中不再是只能存字符串了
-
异步: 意味着所有操作都要在回调中进行
2. 数据库
一组相关业务数据的存储集合。
创建一个数据库
window.indexedDB.open(dbName, version)
示例:
const dbRequest = window.indexedDB.open('demo', 1);
onpen() 方法说明:
-
如果指定的数据库已经存在,直接连接数据库,返回
request实例。【因为indexedDB是异步的,所以它所有的操作都必须建立一个请求(request),请求的结果将被封装在request实例中返回】 -
如果不存在指定的数据库,则创建数据库,然后连接数据库,返回
request实例。 -
如果传入的数据库版本比浏览器实际最新的版本低,则会抛出一个错误。
3. 表-对象仓库
某项业务的数据集合,有三种类型
- 对象型仓库。
- 每次都存入一个对象
- 该对象有一个属性路径必须是
keyPath - 如果对象不存在对应的
keyPath,会报错
- 非对象型仓库
- 专门用来存储非对象数据
- 不需要传
keyPath
- 混合仓库
- 存放混合类型的数据
- 会发生对象污染——当你存入一个对象时,如果该对象中并没有对应的 keyPath,那么,它会在存入时被自动加上这个
keyPath
创建表
if (!db.objectStoreNames.contains(tableName)){
db.createObjectStore(tableName, options)
}
示例:
const dbRequest = window.indexedDB.open('demo', 2);
dbRequest.onupgradeneeded = (e) => {
const db = e.target.result;
if (!db.objectStoreNames.contains('objectStore')) {
db.createObjectStore('objectStore', { keyPath: 'id' });
}
if (!db.objectStoreNames.contains('objectStoreCopy')) {
db.createObjectStore('objectStoreCopy', { keyPath: 'id' });
}
if (!db.objectStoreNames.contains('notObjectStore')) {
db.createObjectStore('notObjectStore', { autoIncrement: true });
}
if (!db.objectStoreNames.contains('mixStore')) {
db.createObjectStore('mixStore', { autoIncrement: true, keyPath: 'id'});
}
}
createObjectStore 方法说明:
-
只能在
db-request的onupgradeneeded事件中进行,而onupgradeneeded事件只在数据库版本升级时触发,所以我们这里版本号升级了。对于库的版本说明,见下节。 -
options参数有两个可设置属性,见 5.记录 一节
4. 库版本
-
一个数据库同一时间只能存在一个最新的版本(该版本记录了当前使用的数据库和表结构)
-
只有在修改数据库结构和表结构时,版本才需要升级
-
修改数据库结构和表结构或升级数据库版本对数据库内的数据一般没有影响(除非删除表)
-
最小版本是:1
5. 记录
-
一条记录就是一个键值对
-
键
keyPath。在值对象中,获取一个节点值的属性链式方法的字符串表达- 自动生成。将没有
keyPath,只有自增的key
-
值
- 字符串
- 日期类型
- 对象
- 数组
- 文件
- Blob
- 图像数据
- ArrayBuffer
- 无法存储function等非结构化数据
6. 事务
- 所有记录的增删改查都要在事务中进行
- 之所以引入事务,是为了保证操作顺序和可靠性
- 顺序:事物中所有的操作必须排队进行
- 可靠性: 在【同一个事务】中,对于【同一张表】的一组操作有一个失败,之前的都回滚
- 事务的生命周期:事务会把你在它生命周期里规定的操作全部执行,执行完毕,事务就关闭了,无法利用事务实例进行下一步操作
创建事务
db.transaction(objectStoresArray, readWriteMode)
示例:
const request = window.indexedDB.open('demo', 2);
request.onsuccess = (e) => {
const db = e.target.result;
let transcation =
db.transaction(['objectStore', 'objectStoreCopy', 'notObjectStore', 'mixStore'], 'readwrite');
}
transaction()方法说明:
-
事务必须在
db-request的成功回调onsuccess方法中创建,另注意:数据库实例db需要从成功回调的结果的target.result中获取。 -
两个参数:
-
objectStoresArray, 一个数组,包含了当前事务中要操作的所有表的名称 -
readWriteMode: 本次操作是只读操作还是读写操作readonly: 只读readwrite:读写
-
读取表
transaction.objectStore(tableName)
示例:
// 省略连接数据库和读取数据库实例的过程,以下代码在dbRquest的回调中进行
let transcation =
db
.transaction(['objectStore', 'objectStoreCopy', 'notObjectStore'], 'readonly');
let os = transcation.objectStore('objectStore');
let osc = transcation.objectStore('objectStoreCopy');
let nos = transcation.objectStore('notObjectStore');
let ms = transcation.objectStore('mixStore');
objectStore()方法说明:
添加记录
objectStore.add(object)
示例:
const request = window.indexedDB.open('demo', 2);
request.onsuccess = (e) => {
const db = e.target.result;
let transcation =
db
.transaction(['objectStore', 'objectStoreCopy', 'notObjectStore','mixStore'], 'readwrite');
let os = transcation.objectStore('objectStore');
let osc = transcation.objectStore('objectStoreCopy');
let nos = transcation.objectStore('notObjectStore');
let ms = transcation.objectStore('mixStore');
// 对象型仓库,keyPath为对象的一个属性
os.add({
id: 1,
name: '张三',
sex: '男',
other:{
age: 18
}
});
// 非对象型仓库,存入几个非对象数据
// Date类型
const date = new Date();
// Blob类型
const s = "Hello World!!";
const blob = new Blob([s], {type: 'text/xml'});
// ArrayBuffer
const buffer = new ArrayBuffer(8);
// 数组
const arr = [1,2,3];
// 图像数据
const imageData = new ImageData(100, 100);
// 文件
const file = new File(["foo"], "foo.txt", {
type: "text/plain",
});
nos.add(date);
nos.add(blob);
nos.add(buffer);
nos.add(arr);
nos.add(imageData);
nos.add(file);
// 混合型仓库
ms.add({
id: 1,
name: '张三',
sex: '男',
other:{
age: 18
}
});
ms.add(blob);
ms.add(buffer);
ms.add(arr);
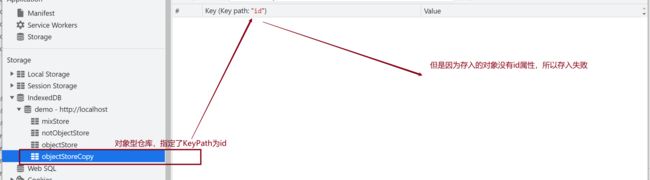
// 对象型仓库,keyPath 不是对象的属性,将添加失败
osc.add({
name: '张三',
sex: '男',
other:{
age: 18
}
});
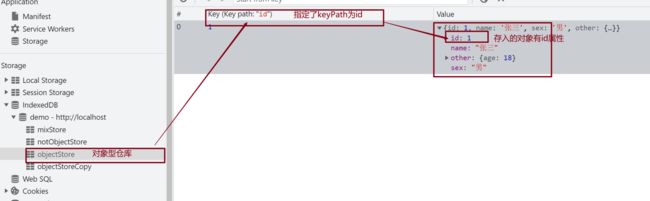
看一下添加结果:
添加失败与事务回滚
当我们试图插入一条keyPath与已有记录的keyPath相同的记录时,将会失败,如果同一张表还有其他操作,将随事务回滚也一起失败。
let transcation =
db
.transaction(['objectStore'], 'readwrite');
let os = transcation.objectStore('objectStore');
// 试图插入一个主键不同的数据
let rs3 = os.add({
id: 2,
name: '张四',
sex: '女',
other:{
age: 18
}
});
rs3.onsuccess = e => {
console.log('rs3成功');
};
rs3.onerror = e => {
console.log('rs3失败');
console.log(e.target.error.message);
};
// 视图插入一个主键相同的数据
let rs = os.add({
id: 1,
name: '张四',
sex: '女',
other:{
age: 18
}
});
rs.onsuccess = e => {
console.log('rs成功');
};
rs.onerror = e => {
console.log('rs失败');
console.log(e.target.error.message);
};
我们看到,这里试图插入一个与已有记录keyPath不同的记录,实际上显示成功了,而尝试插入一条与已有记录keyPath 相同的记录时,提示失败了,然后我们看数据库:
虽然id为2的数据提示插入成功了,但是数据里并没有,说明因为它之后进行的rs失败了,所以导致事务回滚了,它本来成功的操作也被回滚,最终数据没有插入进去。
更新记录
objectStore.put(object)
示例:
// 更新一个记录
let rs2 = os.put({
id: 1,
name: '张四',
sex: '女',
other:{
age: 18
}
});
rs2.onsuccess = e => {
console.log('rs2成功');
};
rs2.onerror = e => {
console.log('rs2失败');
console.log(e.target.error.message);
};
我们将之前添加到对象型仓库里id为1的记录的名字由张三改为张四,性别由男改为女,看看结果:
可以看到,更新成功了
更新一条keyPath不存在的数据:
let rs4 = os.put({
id: 2,
name: '张三三',
sex: '男',
other:{
age: 18
}
});
rs4.onsuccess = e => {
console.log('rs4成功');
};
rs4.onerror = e => {
console.log('rs4失败');
console.log(e.target.error.message);
};
可以看到,更新操作如果更新的是一条keyPath不存在的记录,它将按照新增add() 来处理。
所以:
我们强烈建议,添加数据都使用put()操作
读取记录
objectStore.get(KeyPathValue)
示例:
const db = e.target.result;
let transcation =
db
.transaction(['objectStore'], 'readwrite');
let os = transcation.objectStore('objectStore');
// 先插入几条数据
os.put({
id: 3,
name: '王五',
sex: '男',
other:{
age: 16
}
});
os.put({
id: 4,
name: '王六',
sex: '女',
other:{
age: 16
}
});
os.put({
id: 5,
name: '鬼脚七',
sex: '男',
other:{
age: 16
}
});
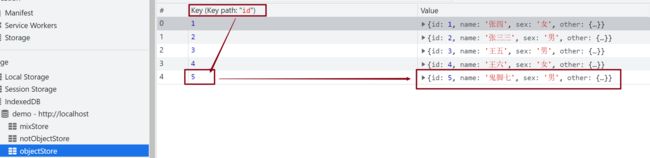
let rs = os.get(5);
rs.onsuccess = e => {
console.log('rs成功');
console.log(e.target.result);
};
rs.onerror = e => {
console.log('rs失败');
console.log(e.target.error.message);
};
看看结果
删除记录
objectStore.delete(keyPathValue)
示例
let transcation =
db
.transaction(['objectStore'], 'readwrite');
let os = transcation.objectStore('objectStore');
let rs = os.delete(3);
rs.onsuccess = e => {
console.log('rs成功');
console.log(e.target.result);
};
rs.onerror = e => {
console.log('rs失败');
console.log(e.target.error.message);
};
7. 索引
- 索引是一个特殊的表
- 索引是对查询条件的补充
- 这个表有两个键
- 一个是主键
- 一个是索引键
- 索引仓库是以索引键为键对表中记录的重新组织
- 一个表可以有多个索引
创建索引
objectStore.createIndex(indexName, Path, options)
参数说明
-
indexName: 索引名称 -
Path: 索引在对象中的路径 -
options: 可选参数对象unique。如果为true,索引将不允许单个键的值重复。multiEntry。如果为 true,则当 Path 解析为数组时,索引将为每个数组元素在索引中添加一个条目。 如果为 false,它将添加一个包含数组的条目。locale。目前只有Firefox(43+)支持,这允许您为索引指定区域设置
示例:
const request = window.indexedDB.open('demo', 3);
request.onupgradeneeded = (e) => {
const db = e.target.result
let os;
if (!db.objectStoreNames.contains('objectStore')) {
os = db.createObjectStore('objectStore', { keyPath: 'id' });
} else {
os = e.target.transaction.objectStore('objectStore');
}
os.createIndex('sex', 'sex', { unique: false });
os.createIndex('age', 'other.age', { unique: false });
os.createIndex('name', 'name', { unique: true });
}
- 创建(删除和修改)索引的操作必须在db的
onupgradeneeded中进行,这表示要对数据库升级,所以我们又升了版本号。
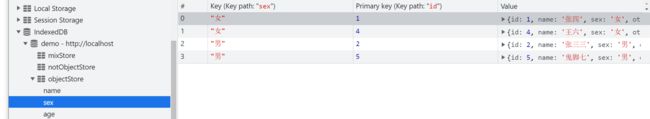
看看结果:
更具索引查询记录
objectStore.index(indexName)
示例:
const request = window.indexedDB.open('demo', 3);
request.onsuccess = (e) => {
const db = e.target.result;
let transcation =
db
.transaction(['objectStore'], 'readwrite');
let os = transcation.objectStore('objectStore');
let objIndexName = os.index('name');
let objIndexAge = os.index('age');
let objIndexSex = os.index('sex');
let rs1 = objIndexName.get('张三');
rs1.onsuccess = e => {
console.log('rs1查询成功');
console.log(e.target.result);
}
rs1.onerror = e => {
console.log('rs1查询失败');
console.log(e.target.error.message);
}
let rs2 = objIndexAge.get(16);
rs2.onsuccess = e => {
console.log('rs2查询成功');
console.log(e.target.result);
}
rs2.onerror = e => {
console.log('rs2查询失败');
console.log(e.target.error.message);
}
let rs3 = objIndexSex.get('男');
rs3.onsuccess = e => {
console.log('rs3查询成功');
console.log(e.target.result);
}
rs3.onerror = e => {
console.log('rs3查询失败');
console.log(e.target.error.message);
}
}
看看结果:
可以看到,上例中我们以索引名称查询,
- 第一个查询由于没有
name为张三的用户,所以返回为undefined - 第二个和第三个查询,分别以
age与sex来查询,都查到了相应的结果 - 但是,查询到的结果都只有一条,但是我们前面看到,
age为16和sex为男的记录都不止一条 - 这是因为
get()操作只返回符合条件的第一条记录,要获得所有符合条件的记录,就需要下面要将的游标。
8. 游标
一个可以遍历整个表的接口。
建立游标
index.openCursor()
移动游标
cursor.continue();
示例:
const request = window.indexedDB.open('demo', 3);
request.onsuccess = (e) => {
const db = e.target.result;
let transcation =
db
.transaction(['objectStore'], 'readwrite');
let os = transcation.objectStore('objectStore');
let objIndexSex = os.index('sex');
let rs1 = objIndexSex.openCursor();
let results = []; // 用来存放这个表中所有记录,它的声明必须放在 onsuccess 回调函数的外部,因为该回调函数会在遍历过程中反复执行
let resultsMan = []; // 用来存放男人
rs1.onsuccess = e => {
console.log('rs1查询成功');
let cursor = e.target.result;
if (cursor) {
results.push(cursor.value);
if (cursor.value.sex === '男') {
resultsMan.push(cursor.value);
}
cursor.continue();
} else {
console.log(results);
console.log(resultsMan);
}
}
rs1.onerror = e => {
console.log('rs1查询失败');
console.log(e.target.error.message);
}
}
看看结果:
删除索引
objectStore.deleteIndex(indexName)
示例:
const request = window.indexedDB.open('demo', 4);
request.onupgradeneeded = (e) => {
const db = e.target.result
let os;
if (!db.objectStoreNames.contains('objectStore')) {
os = db.createObjectStore('objectStore', { keyPath: 'id' });
} else {
os = e.target.transaction.objectStore('objectStore');
}
os.deleteIndex('sex');
}